Use Windows Admin Center to Manage Azure Servers
Use windows admin center manage azure server – Use Windows Admin Center to manage Azure servers, and unlock a world of streamlined server management. Windows Admin Center offers a centralized interface to oversee your Azure infrastructure, simplifying complex tasks and boosting efficiency. It’s a powerful tool for IT professionals who want to manage their Azure servers with ease and confidence.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of connecting Windows Admin Center to your Azure servers, exploring the wide range of management capabilities it provides. From monitoring server performance and health to managing updates, security settings, and integrating with other Azure services, Windows Admin Center empowers you to control your Azure environment with precision.
Introduction to Windows Admin Center and Azure Servers
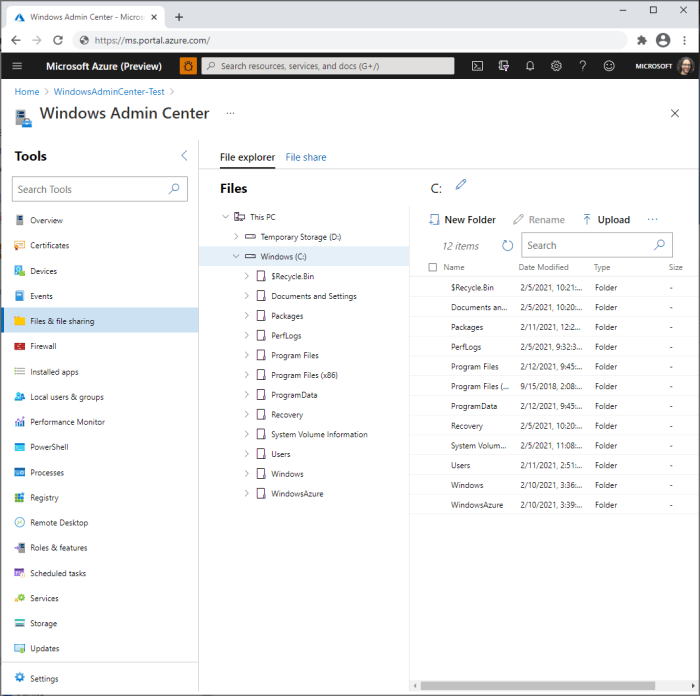
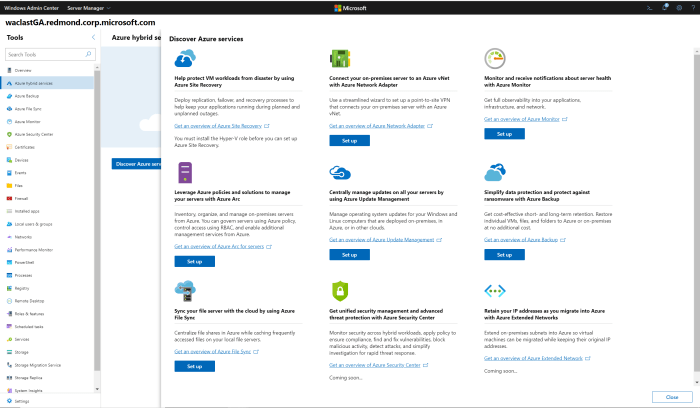
Windows Admin Center is a powerful, locally installed, web-based tool designed to manage Windows servers, both on-premises and in Azure. It provides a unified interface for managing various aspects of your server infrastructure, simplifying tasks and streamlining workflows. This tool offers significant advantages for managing Azure servers, offering a centralized platform for monitoring, configuring, and troubleshooting your virtual machines (VMs).
Managing Azure servers from your Windows Admin Center can be a powerful way to streamline your infrastructure. It’s all about centralized control, right? And speaking of leadership, check out this news about Titan’s appointment of a new president, focused on advancing the U.S.
domestic supply of critical materials. It’s a great example of how strategic leadership can make a real difference, just like using the right tools to manage your Azure servers.
Benefits of Managing Azure Servers with Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center offers a range of benefits for managing Azure servers, making it an attractive alternative to the Azure portal.
Managing Azure servers with Windows Admin Center is a breeze, especially when you’re used to the familiar Windows interface. It’s like taking a look at a Mandis dining room before-and-after – the transformation is remarkable! With Windows Admin Center, you can easily monitor, manage, and troubleshoot your Azure servers from a single console, making your life as an IT administrator much simpler.
- Simplified Management:Windows Admin Center consolidates server management tasks into a single, intuitive interface, simplifying complex operations and reducing the learning curve for administrators.
- Enhanced Efficiency:With its streamlined workflows and direct access to server resources, Windows Admin Center significantly improves operational efficiency, reducing the time required to perform common management tasks.
- Centralized Control:Windows Admin Center provides a centralized platform for managing both on-premises and Azure servers, offering a unified view of your entire infrastructure and simplifying cross-environment management.
- Enhanced Security:Windows Admin Center incorporates security features like role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication, ensuring secure access to your Azure servers and minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Improved Performance:Windows Admin Center utilizes a lightweight architecture and optimized communication protocols, ensuring efficient communication with your Azure servers and minimizing performance impact on your infrastructure.
Key Features and Capabilities of Windows Admin Center for Azure Server Management
Windows Admin Center offers a comprehensive set of features and capabilities specifically designed for managing Azure servers, enabling administrators to perform various tasks effectively.
- Server Management:Windows Admin Center provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing your Azure servers, including tasks like restarting, stopping, and starting VMs, managing disks and storage, configuring networking, and managing updates.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics:Windows Admin Center offers real-time monitoring capabilities, providing insights into server performance, resource utilization, and system health. It also includes diagnostic tools for identifying and resolving issues.
- Security Management:Windows Admin Center allows you to manage security settings on your Azure servers, including configuring firewalls, managing user accounts, and implementing security policies. You can also monitor security events and receive alerts for potential threats.
- Deployment and Configuration:Windows Admin Center simplifies the deployment and configuration of Azure servers. It provides tools for creating and configuring new VMs, deploying applications, and managing software updates.
- Integration with Azure Services:Windows Admin Center seamlessly integrates with various Azure services, including Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), Azure Storage, and Azure Key Vault. This integration allows you to leverage the capabilities of these services within the Windows Admin Center interface, simplifying management tasks.
Managing Azure servers from your Windows Admin Center can be a breeze, especially with the right tools and knowledge. It’s like having a digital control panel for your cloud infrastructure, allowing you to monitor, configure, and troubleshoot your servers with ease.
Speaking of control panels, I recently got a really cool light up photo frame for my desk, which adds a touch of personality to my workspace. Back to the topic at hand, Windows Admin Center can also help you manage your Azure VMs, including their performance, security, and updates, giving you complete control over your cloud resources.
Connecting to Azure Servers
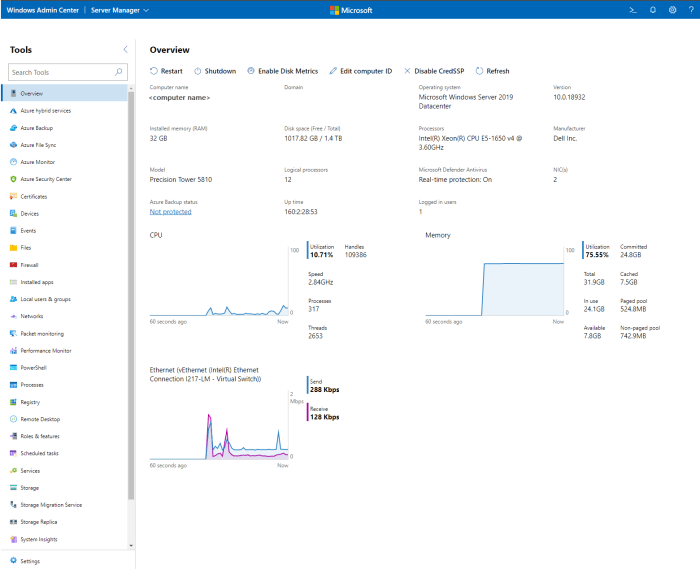
Connecting Windows Admin Center to Azure servers allows you to manage your virtual machines and other Azure resources directly from your local machine. This provides a convenient and efficient way to perform administrative tasks, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues.
Connecting to Azure Servers
To connect Windows Admin Center to Azure servers, you’ll need to configure the connection settings. This involves specifying the server’s details, such as its IP address or hostname, and selecting the appropriate authentication method.
Authentication Methods
Windows Admin Center supports several authentication methods for connecting to Azure servers. The most common methods are:
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): This method uses your Azure AD credentials to authenticate to the Azure server. This is the recommended method for enhanced security and central management.
- Local Administrator Credentials: This method allows you to connect to the Azure server using local administrator credentials.
This method is suitable for situations where Azure AD integration is not available or required.
- Certificate-Based Authentication: This method uses a digital certificate to authenticate to the Azure server. This is a secure method that is often used for automated deployments and scripts.
Steps to Connect to Azure Servers
Here are the steps to connect Windows Admin Center to Azure servers:
- Launch Windows Admin Center: Open the Windows Admin Center application on your local machine.
- Add a Connection: Click the “Add Connection” button on the left-hand side of the application.
- Select Connection Type: Choose “Azure Server” from the list of connection types.
- Enter Server Details: Provide the server’s details, such as its IP address or hostname.
- Select Authentication Method: Choose the authentication method that you want to use.
- Enter Credentials: Enter the required credentials for the chosen authentication method.
- Connect: Click the “Connect” button to establish the connection.
Example: Connecting to an Azure Server Using Azure AD Authentication
To connect to an Azure server using Azure AD authentication, you’ll need to ensure that the server is joined to an Azure AD domain and that you have the necessary permissions to access it.
- Join the Server to Azure AD: Join the Azure server to an Azure AD domain. This will allow the server to authenticate with Azure AD.
- Grant Permissions: Ensure that your Azure AD account has the necessary permissions to access the Azure server. This may involve assigning the appropriate roles or groups to your account.
- Connect Using Azure AD Credentials: When connecting to the Azure server in Windows Admin Center, select “Azure Active Directory” as the authentication method and enter your Azure AD credentials.
Note:You may need to configure firewall rules to allow communication between Windows Admin Center and the Azure server.
Managing Azure Servers with Windows Admin Center: Use Windows Admin Center Manage Azure Server
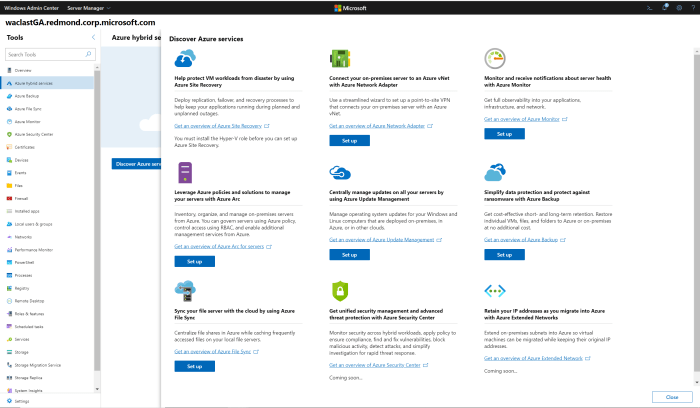
Windows Admin Center is a powerful tool that allows you to manage your Azure servers from a single console. It provides a unified interface for managing various tasks, including monitoring, updating, and troubleshooting. This eliminates the need for multiple tools and simplifies your management process.
Common Management Tasks
Windows Admin Center offers a comprehensive set of features for managing Azure servers. These include:
- Server Overview:View essential information about your Azure servers, including their name, IP address, operating system, and status.
- Performance Monitoring:Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. Identify potential bottlenecks and proactively address performance issues.
- Event Viewer:Access the event logs of your Azure servers to diagnose problems and troubleshoot issues.
- Remote Desktop:Connect to your Azure servers remotely to perform tasks or troubleshoot issues directly.
- File Explorer:Access files and folders on your Azure servers remotely.
- Task Scheduler:Schedule tasks to automate routine server maintenance, such as backups and updates.
- Services:Manage and configure services running on your Azure servers.
- Networking:Configure network settings, such as IP addresses and network adapters.
- Storage:Manage disks, volumes, and storage spaces on your Azure servers.
- Security:Configure security settings, such as user accounts and permissions.
Monitoring Azure Server Performance and Health
Monitoring your Azure servers’ performance and health is crucial for ensuring their stability and availability. Windows Admin Center provides various tools to monitor your servers effectively:
- Performance Charts:View real-time performance metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk I/O, in graphical format. Identify trends and potential issues early on.
- Performance Counters:Access a wide range of performance counters to gain detailed insights into your servers’ performance. Use these counters to identify specific areas requiring attention and to troubleshoot performance problems.
- Alerts:Configure alerts to be notified when performance metrics exceed predefined thresholds. This allows you to proactively address issues before they impact your server’s availability.
- Health Status:View the overall health status of your Azure servers, including any warnings or errors. Quickly identify potential problems and take corrective actions.
Managing Azure Server Updates and Patches, Use windows admin center manage azure server
Keeping your Azure servers up-to-date with the latest patches and updates is essential for security and stability. Windows Admin Center simplifies the process of managing updates:
- Update History:View the history of updates applied to your Azure servers, including the date and time of each update.
- Update Management:Manage updates for your Azure servers from a centralized location. This includes scheduling updates, approving updates, and installing updates.
- Update Deployment:Deploy updates to your Azure servers in a controlled manner. This allows you to test updates on a small group of servers before rolling them out to your entire environment.
- Patching Automation:Automate the process of patching your Azure servers. This helps you ensure that your servers are always up-to-date and secure.