Nearly Half of Businesses Leave Their IoT Unprotected
Nearly half of businesses do not protect their full IoT suite, leaving them vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches. This alarming statistic highlights a significant gap in cybersecurity awareness and implementation, putting businesses at risk of financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
The increasing interconnectedness of our world through the Internet of Things (IoT) has created a vast landscape of potential vulnerabilities, making it imperative for businesses to prioritize comprehensive security measures.
Imagine a scenario where a hacker gains access to a company’s network through a compromised smart thermostat, leading to the theft of sensitive customer data or the disruption of critical operations. This is not a far-fetched scenario, as real-world examples of IoT security breaches have demonstrated the devastating consequences of neglecting proper security practices.
The rise of sophisticated attacks targeting IoT devices, coupled with the lack of awareness and resources among businesses, has created a perfect storm for cybercriminals. Understanding the vulnerabilities and implementing robust security measures is crucial for safeguarding businesses in the age of the interconnected world.
The Scope of the Problem
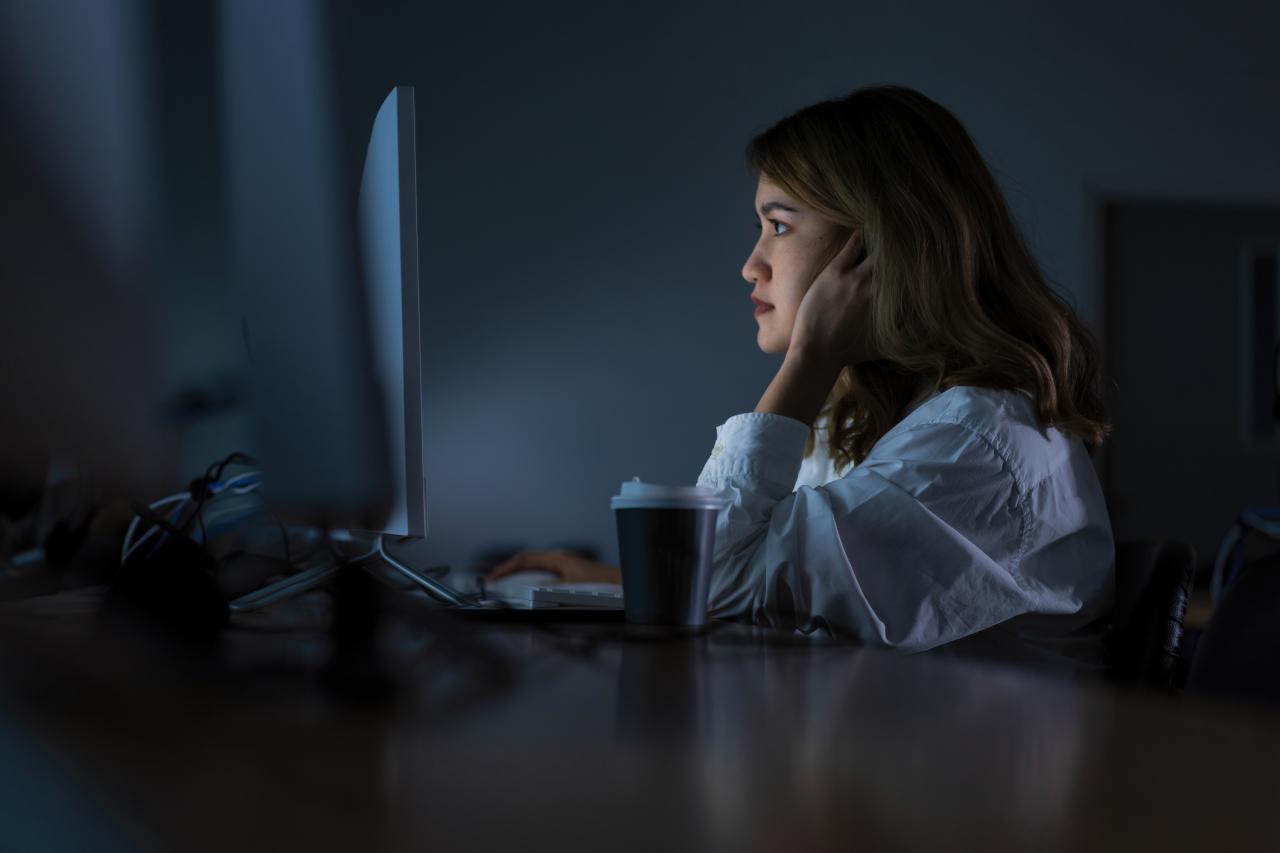

The statistic that nearly half of businesses do not protect their full IoT suite is a stark reminder of the widespread vulnerability within the connected world. This lack of comprehensive security poses a significant threat to businesses, potentially leading to data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
It’s a scary thought, but nearly half of businesses don’t protect their full IoT suite. This lack of security opens the door to all sorts of vulnerabilities, and it’s a major reason why machine learning strategies fail. A poorly secured IoT environment can lead to data breaches and inaccurate model training, as discussed in this insightful article on why machine learning strategies fail.
If businesses want to leverage the power of AI, they need to prioritize security and ensure their IoT devices are properly protected.
The Potential Consequences of Unprotected IoT Devices
The consequences of neglecting IoT security can be far-reaching and severe. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in IoT devices to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt business operations, and even cause physical harm. For example, a compromised industrial control system could lead to production shutdowns, while a hacked smart home system could allow attackers to control appliances and even monitor residents.
Examples of Real-World Security Breaches, Nearly half of businesses do not protect their full iot suite
Several high-profile security breaches involving vulnerable IoT devices highlight the real-world risks associated with inadequate protection.
Mirai Botnet
The Mirai botnet, which launched a massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack in 2016, exploited vulnerabilities in poorly secured IoT devices like cameras and routers. This attack caused widespread internet outages, affecting major websites and services.
Kaspersky’s Research on IoT Security
Kaspersky, a leading cybersecurity firm, conducted research that revealed that nearly 70% of IoT devices are vulnerable to attack. This research highlights the widespread nature of the problem and the urgent need for improved security measures.
The 2017 Equifax Data Breach
While not directly related to IoT devices, the 2017 Equifax data breach exposed the vulnerabilities of interconnected systems. The breach, which affected over 147 million individuals, highlighted the potential for cascading security failures when systems are not adequately secured.
“The Equifax data breach demonstrates the interconnected nature of modern systems and the importance of a holistic approach to security.”
It’s mind-boggling to think that nearly half of businesses don’t protect their entire IoT suite. It’s like leaving your front door unlocked while you’re on vacation! Maybe a bit of a tangent, but if you’re into crafts, you’ll want to check out these tips for sewing leather , as it’s surprisingly similar to securing your IoT – you need the right tools and techniques to get the job done right.
Anyway, back to IoT security, it’s crucial to be proactive and protect every device in your network, from your smart thermostat to your industrial machinery. Otherwise, you’re leaving yourself open to vulnerabilities and potential breaches.
Understanding the Vulnerabilities: Nearly Half Of Businesses Do Not Protect Their Full Iot Suite
IoT devices and systems are inherently vulnerable due to their interconnected nature and the diversity of manufacturers involved. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive data, or disrupt operations.
It’s alarming to think that nearly half of businesses aren’t fully protecting their IoT suites, leaving them vulnerable to cyberattacks. While I’m busy brainstorming ways to secure my network, I’m also dreaming of a delicious autumn bliss salad with stuffing croutons – the perfect fall comfort food.
Perhaps after I’ve tackled the IoT security issue, I can finally indulge in this culinary masterpiece!
Common IoT Vulnerabilities
Understanding the vulnerabilities in IoT devices and systems is crucial for implementing effective security measures. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to compromise devices, steal data, or disrupt operations.
- Insecure Default Configurations:Many IoT devices ship with default passwords or weak security settings, making them easy targets for attackers.
- Lack of Encryption:Sensitive data transmitted between IoT devices and the cloud is often unencrypted, making it vulnerable to eavesdropping and interception.
- Outdated Software:Many IoT devices lack automatic updates, leaving them vulnerable to known security flaws.
- Poor Authentication:Weak authentication mechanisms, such as simple usernames and passwords, make it easy for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Insufficient Device Management:Lack of centralized device management tools makes it difficult to monitor and control security risks across the entire IoT ecosystem.
Exploiting IoT Vulnerabilities
Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities using various methods, including:
- Brute-Force Attacks:Attackers use automated tools to guess default passwords or try various combinations until they gain access.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:Attackers intercept communication between IoT devices and the cloud to steal sensitive data or inject malicious code.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks:Attackers overload IoT devices with traffic, rendering them unresponsive and disrupting operations.
- Malware Infections:Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities to install malware on IoT devices, enabling them to control the device or steal data.
IoT Device Vulnerabilities
The following table showcases different types of IoT devices and their associated vulnerabilities:
| Device Type | Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|
| Smart Home Devices | Insecure default configurations, lack of encryption, outdated software, poor authentication |
| Industrial Control Systems | Lack of security awareness, outdated software, vulnerabilities in communication protocols |
| Wearable Devices | Data privacy concerns, weak authentication, lack of encryption |
| Medical Devices | Security flaws in software and firmware, vulnerabilities in communication protocols |
The Importance of Comprehensive Security
The sheer number of connected devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) creates a vast attack surface, making comprehensive security a critical necessity. A holistic approach ensures that every aspect of an IoT deployment, from devices to networks and data, is protected against potential threats.
Securing IoT Devices
Device security is the foundation of a robust IoT security strategy. Manufacturers should prioritize secure hardware and software design, incorporating strong encryption and secure boot processes. Regular firmware updates are essential to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security. Furthermore, manufacturers should consider implementing secure lifecycle management processes, including secure disposal and decommissioning procedures.
Addressing the Challenges

Securing an IoT infrastructure presents a unique set of challenges, often stemming from the inherent nature of these interconnected devices. From managing diverse device types to ensuring data privacy, businesses face a complex landscape in safeguarding their IoT investments.
Analyzing the Challenges Businesses Face in Securing Their IoT Infrastructure
The sheer scale and heterogeneity of IoT devices contribute significantly to security complexities. Businesses often struggle to manage the diverse range of devices, operating systems, and communication protocols involved in their IoT deployments. This diversity makes it challenging to implement consistent security policies across the entire ecosystem.
Additionally, the distributed nature of IoT devices, often operating in remote and potentially insecure environments, further complicates security management.
Comparing and Contrasting Different Security Solutions Available for IoT Environments
Several security solutions cater specifically to the unique needs of IoT environments. These solutions address various aspects of IoT security, including device authentication, data encryption, and intrusion detection.
- Network Security Solutions:Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) are commonly used to protect the network infrastructure that connects IoT devices. These solutions help prevent unauthorized access and malicious activity by monitoring network traffic and blocking suspicious connections.
- Device Security Solutions:Device-level security measures, such as secure boot mechanisms, firmware updates, and secure communication protocols, are essential to protect individual IoT devices from vulnerabilities. These solutions ensure that devices are only running trusted software and that data transmitted between devices is secure.
- Data Security Solutions:Data encryption, access control mechanisms, and data loss prevention technologies are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data collected by IoT devices. These solutions ensure that data is protected during transmission and storage, limiting unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Security Management Platforms:Centralized security management platforms provide a comprehensive approach to managing and monitoring IoT security. These platforms offer features like device inventory management, vulnerability scanning, security policy enforcement, and incident response capabilities. They simplify the management of security across diverse IoT deployments.
Detailing the Benefits and Drawbacks of Various Security Approaches
Each security approach offers specific benefits and drawbacks, and the optimal choice depends on the specific requirements of the IoT deployment.
- Network Security Solutions:
- Benefits:Provide a strong first line of defense against external threats by controlling network access and monitoring traffic for malicious activity.
- Drawbacks:May not effectively address device-level vulnerabilities and can be less effective against attacks that exploit internal network weaknesses.
- Device Security Solutions:
- Benefits:Enhance the security of individual devices, making them more resilient against attacks. They can also help prevent the spread of malware and other malicious software.
- Drawbacks:Implementing device-level security can be complex, especially when dealing with diverse device types. It can also require frequent updates to keep pace with evolving threats.
- Data Security Solutions:
- Benefits:Ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data collected by IoT devices. They help protect against data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Drawbacks:Data security solutions can add overhead to data processing and transmission, potentially impacting performance. They also require careful configuration and ongoing maintenance to ensure effectiveness.
- Security Management Platforms:
- Benefits:Offer a centralized and comprehensive approach to managing IoT security, simplifying security tasks and providing a single point of control. They also enable automation and proactive threat detection.
- Drawbacks:Can be complex to implement and manage, requiring specialized skills and expertise. They can also be costly, particularly for large-scale IoT deployments.
The Future of IoT Security
The world of IoT is rapidly evolving, and with it, the landscape of security threats and countermeasures is constantly changing. As more devices become interconnected, the potential attack surface expands, demanding innovative solutions to safeguard these increasingly vulnerable systems.
This section delves into emerging trends and technologies that will shape the future of IoT security, examining both potential challenges and opportunities.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in IoT Security
The future of IoT security will be driven by advancements in various technologies and approaches. Here are some key trends:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML are becoming increasingly vital in detecting and responding to IoT security threats. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from connected devices, identifying anomalies and patterns that indicate malicious activity. For example, AI-powered security systems can learn the normal behavior of a device and flag any deviations, such as unusual communication patterns or data access requests.
- Blockchain Technology:Blockchain’s inherent security features, including immutability and transparency, can be leveraged to enhance IoT security. Blockchain can provide a secure and auditable record of device interactions and data transactions, making it difficult for attackers to tamper with data or compromise device integrity.
For example, a blockchain-based system could track the provenance of data collected by IoT sensors, ensuring its authenticity and preventing unauthorized modifications.
- Zero-Trust Security:The zero-trust model assumes that no device or user can be trusted by default. This approach emphasizes strict authentication and authorization protocols, verifying every access request and limiting privileges to the bare minimum required. For example, in a zero-trust IoT environment, a smart home device would need to be authenticated and authorized before being allowed to access the home network or control other devices.
- Secure Hardware and Software:Building security into the very foundation of IoT devices is crucial. This involves incorporating secure hardware components, such as tamper-resistant chips and secure boot mechanisms, and developing secure software that is resistant to vulnerabilities and exploits. For instance, manufacturers can integrate secure hardware modules that encrypt data at the source, making it difficult for attackers to access sensitive information even if they compromise the device.
Potential Future Challenges and Opportunities
The future of IoT security presents both challenges and opportunities. Here are some key considerations:
- The Growing Complexity of IoT Systems:As IoT ecosystems become increasingly complex, with more interconnected devices and diverse applications, security management becomes more challenging. This complexity makes it difficult to identify and address vulnerabilities across the entire ecosystem, increasing the risk of security breaches.
- The Rise of 5G and Edge Computing:The widespread adoption of 5G and edge computing will create new security challenges. 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency will enable faster and more data-intensive IoT applications, but also increase the potential for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure.
Edge computing, which processes data closer to the source, will require robust security measures to protect sensitive information at the edge of the network.
- The Need for Interoperability and Standardization:The lack of standardized security protocols and interoperability between different IoT devices and platforms creates fragmentation and security risks. Developing common security standards and promoting interoperability will be essential for creating a more secure and robust IoT ecosystem.
- The Importance of User Education and Awareness:End-users play a crucial role in IoT security. Raising awareness about security best practices, such as strong passwords, regular updates, and avoiding suspicious links, is essential for mitigating risks. For example, educating users about the importance of updating their IoT devices’ firmware can help prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited by attackers.
Recommendations for Businesses to Improve Their IoT Security Posture
Businesses need to adopt a proactive approach to secure their IoT deployments. Here are some key recommendations:
- Implement a Comprehensive Security Strategy:A comprehensive security strategy should address all aspects of the IoT ecosystem, from device selection and configuration to data security and incident response. This strategy should be tailored to the specific needs and risks of the business and regularly reviewed and updated.
- Invest in Secure Hardware and Software:Businesses should prioritize the use of secure hardware components and software solutions that are resistant to vulnerabilities and exploits. This includes selecting devices with strong encryption capabilities, secure boot mechanisms, and tamper-resistant hardware.
- Adopt a Zero-Trust Security Model:A zero-trust approach should be implemented, assuming that no device or user can be trusted by default. This involves strict authentication and authorization protocols, verifying every access request and limiting privileges to the bare minimum required.
- Embrace AI and ML for Threat Detection and Response:Leveraging AI and ML technologies can significantly enhance threat detection and response capabilities. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from connected devices, identifying anomalies and patterns that indicate malicious activity.
- Prioritize Data Security and Privacy:Businesses should implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive information collected by IoT devices. This includes encrypting data at rest and in transit, using access controls to limit data access, and adhering to privacy regulations.
- Establish a Strong Incident Response Plan:A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for mitigating the impact of security breaches. This plan should Artikel steps for detecting, containing, and recovering from incidents, as well as for communicating with stakeholders.
- Foster Collaboration and Information Sharing:Collaboration and information sharing between businesses, security researchers, and government agencies are essential for addressing the evolving threat landscape. Sharing insights about vulnerabilities, attack methods, and best practices can help improve the overall security posture of the IoT ecosystem.