Multicloud: The Smart Persons Guide
Multicloud the smart persons guide – Multicloud: The Smart Person’s Guide is your roadmap to navigating the exciting and complex world of distributed cloud computing. Forget about being locked into a single provider – multicloud empowers you with the flexibility to choose the best tools and services for your specific needs.
Imagine harnessing the power of multiple cloud giants like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, all working together to optimize your business operations. This approach offers a level of control and adaptability that’s simply unmatched, allowing you to scale effortlessly, manage costs effectively, and unlock a universe of innovation.
In this guide, we’ll explore the core concepts, benefits, and challenges of multicloud. We’ll dive deep into practical considerations for implementation, dissect the best management tools, and delve into security best practices. Get ready to unlock the potential of multicloud and discover how it can transform your organization.
What is Multicloud?
The world of cloud computing is constantly evolving, and one of the most talked-about trends is multicloud. It’s not just a buzzword; it’s a powerful strategy that can help businesses of all sizes achieve greater flexibility, resilience, and innovation.Multicloud simply means using multiple cloud providers, like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), within a single organization.
Imagine having a diverse portfolio of cloud services at your disposal, allowing you to pick and choose the best tools for each specific task.
Real-World Examples of Multicloud Implementations
The beauty of multicloud lies in its adaptability. It allows businesses to tailor their cloud strategy to their unique needs. Here are some real-world examples:
- A financial institution might use AWS for their core banking applications, Azure for their data analytics, and GCP for their AI and machine learning initiatives. This way, they can leverage the strengths of each provider.
- An e-commerce company might use AWS for their front-end website, Azure for their backend order processing, and GCP for their content delivery network (CDN). This distributed approach helps them handle peak traffic and ensure a smooth user experience.
Comparing Multicloud with Single-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
To understand the value of multicloud, it’s helpful to compare it with other cloud strategies:
- Single-Cloud:This approach involves relying on a single cloud provider for all your needs. While it can be simpler to manage, it creates vendor lock-in and limits your flexibility.
- Hybrid Cloud:This strategy combines on-premises infrastructure with one or more public clouds. It allows you to leverage the best of both worlds but can be complex to manage.
- Multicloud:This approach offers the most flexibility and resilience by distributing your workload across multiple cloud providers. It allows you to avoid vendor lock-in, take advantage of best-of-breed services, and ensure business continuity in case of outages.
“Multicloud is not just a technical decision, it’s a strategic one. It’s about maximizing your options and minimizing your risks.”
Navigating the multicloud landscape can feel like choosing the right shade of paint for your home. You want a color that complements your overall vision and creates a cohesive atmosphere, just like you want your cloud services to work seamlessly together.
For a comprehensive guide to choosing the perfect interior paint colors, check out elsies interior paint colors a complete guide , and then apply those same principles to your multicloud strategy for a winning combination.
Industry Expert
Benefits of Multicloud
The multicloud approach, with its ability to distribute workloads across multiple cloud providers, unlocks a wealth of advantages that can significantly enhance business agility, efficiency, and innovation.
Flexibility and Scalability
Adopting a multicloud strategy empowers organizations to tailor their infrastructure to specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. This flexibility extends to both computing resources and data storage, allowing for dynamic adjustments based on changing demands.
- Resource Optimization:Multicloud enables organizations to leverage the strengths of different cloud providers, allocating resources based on specific workloads. For example, a company might use one cloud provider for data analytics due to its powerful compute capabilities, while another cloud provider might be preferred for its expertise in AI and machine learning.
This targeted allocation optimizes resource utilization and minimizes unnecessary expenses.
- Scalability and Elasticity:Multicloud offers unmatched scalability, allowing businesses to seamlessly adjust their resources to meet fluctuating demands. Whether it’s a seasonal surge in traffic or a sudden spike in data processing requirements, multicloud infrastructure can scale up or down automatically, ensuring continuous service availability without manual intervention.
Cost Optimization
Multicloud strategies can significantly reduce IT costs by leveraging competitive pricing models and avoiding vendor lock-in.
- Competitive Pricing:By utilizing multiple cloud providers, organizations can benefit from competitive pricing models, negotiating favorable terms and potentially achieving significant cost savings.
- Avoid Vendor Lock-in:Multicloud eliminates dependence on a single provider, reducing the risk of vendor lock-in and allowing for greater flexibility in choosing the most cost-effective solutions. This freedom to switch providers or negotiate better deals ensures that organizations are not constrained by restrictive contracts or exorbitant pricing.
Enhanced Security
Multicloud offers a robust security posture by distributing sensitive data and applications across multiple cloud environments, making it more challenging for attackers to compromise the entire system.
- Data Security:Multicloud allows organizations to distribute data across different cloud providers, reducing the risk of data breaches. This approach adds an extra layer of security by diversifying data storage locations and making it more difficult for attackers to access sensitive information.
- Resilience:The distributed nature of multicloud infrastructure enhances resilience, ensuring that even if one cloud provider experiences an outage, other providers can seamlessly take over, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Industry-Specific Benefits
Multicloud offers tailored advantages for various industries, addressing specific needs and driving innovation.
- Financial Services:Multicloud solutions can enhance compliance and security in financial services, enabling organizations to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive customer data.
- Healthcare:Multicloud facilitates secure storage and analysis of patient data, enabling healthcare providers to improve patient care and conduct groundbreaking research.
- Manufacturing:Multicloud enables manufacturers to optimize production processes, improve supply chain management, and accelerate product development through data-driven insights and real-time analytics.
- Retail:Multicloud empowers retailers to personalize customer experiences, optimize inventory management, and enhance online shopping through data-driven insights and flexible cloud infrastructure.
Challenges of Multicloud
Adopting a multicloud strategy brings numerous benefits, but it also presents a unique set of challenges that organizations must address. Managing a multicloud environment involves navigating complexities across multiple cloud providers, each with its own infrastructure, services, and tools. This complexity can lead to challenges in areas such as data management, security, and compliance.
Data Management in Multicloud
Managing data across multiple cloud environments requires a strategic approach to ensure consistency, accessibility, and security. The following points highlight key challenges and solutions:
- Data Consistency and Synchronization:Maintaining data consistency across multiple cloud platforms is crucial. Data replication and synchronization tools help ensure data integrity and availability across different clouds. This involves establishing data governance policies and implementing data replication solutions that can handle large volumes of data and ensure consistent updates.
- Data Portability and Migration:Organizations need to consider data portability when transitioning between cloud providers or migrating data to a different cloud platform. Data migration tools and strategies are essential for transferring data securely and efficiently, minimizing downtime and ensuring data integrity. This involves choosing the right migration tools and strategies based on data size, format, and security requirements.
- Data Backup and Recovery:Establishing a robust backup and recovery strategy is critical in a multicloud environment. Organizations need to ensure that data backups are replicated across multiple clouds for disaster recovery purposes. This involves implementing a multi-cloud backup and recovery solution that can handle data backups across different cloud platforms, ensuring data redundancy and quick recovery in case of failures.
Security in Multicloud
Securing a multicloud environment requires a comprehensive approach to address the unique security challenges posed by multiple cloud providers.
- Security Policy Enforcement:Implementing consistent security policies across all cloud environments is crucial. This involves defining and enforcing security policies that cover areas like access control, data encryption, and threat detection, ensuring consistent security practices across all cloud platforms. This requires adopting a centralized security management platform that can enforce policies and monitor security events across multiple cloud providers.
- Threat Detection and Response:Detecting and responding to security threats across multiple clouds can be challenging. Organizations need to implement threat detection and response solutions that can monitor and analyze security events across different cloud platforms. This involves integrating security information and event management (SIEM) solutions with cloud security tools to provide a unified view of security events and enable proactive threat detection and response.
Navigating the world of multicloud can feel like a constant game of Tetris, trying to fit different workloads and services into the right cloud environments. But just like finding the perfect bra, knowing where to look for the best deals can make all the difference.
That’s where a resource like hunkemoller uk new and upcoming offers comes in handy, providing insights on the latest offers and promotions. And just as you’d carefully consider the fit and support of your lingerie, you should choose your cloud providers based on your specific needs and budget, maximizing efficiency and value.
- Compliance and Regulations:Meeting compliance requirements in a multicloud environment can be complex, as different cloud providers may have different compliance certifications. Organizations need to ensure that their cloud deployments meet relevant industry standards and regulations. This involves conducting thorough compliance audits, implementing appropriate security controls, and working with cloud providers to ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
Compliance in Multicloud
Navigating compliance requirements in a multicloud environment can be complex due to differing regulations and certifications across cloud providers.
- Data Privacy Regulations:Organizations need to comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, which may have different requirements for data storage, processing, and transfer. This involves understanding the specific requirements of each regulation, implementing appropriate data governance policies, and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws across all cloud platforms.
- Industry-Specific Compliance Standards:Different industries have specific compliance standards, such as HIPAA for healthcare or PCI DSS for payment card processing. Organizations need to ensure that their multicloud deployments meet these standards. This involves conducting thorough compliance audits, implementing appropriate security controls, and working with cloud providers to ensure compliance with industry-specific standards.
- Auditing and Reporting:Compliance audits and reporting are essential to demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards. Organizations need to establish a process for regular auditing and reporting on their multicloud environment. This involves implementing tools and processes for tracking compliance activities, generating reports, and providing evidence of compliance to auditors.
Key Considerations for Multicloud Adoption: Multicloud The Smart Persons Guide
Adopting a multicloud strategy requires careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure success. Organizations must assess their infrastructure, security posture, data management practices, and cost implications to navigate the complexities of multicloud effectively.
Infrastructure Considerations
Infrastructure forms the foundation of any multicloud deployment. Organizations must carefully evaluate their existing infrastructure and identify the best cloud providers for their specific needs.
- Cloud Provider Selection:Choosing the right cloud providers is crucial. Consider factors such as service offerings, pricing models, global reach, and compliance certifications.
- Hybrid Cloud Integration:Integrating on-premises infrastructure with cloud services requires careful planning. Organizations must ensure seamless data transfer, application compatibility, and security protocols across different environments.
- Network Connectivity:Establishing secure and reliable network connections between cloud providers and on-premises infrastructure is essential for optimal performance and data transfer.
- Capacity Planning:Accurately estimating resource requirements is critical to avoid performance bottlenecks and ensure scalability. Organizations must consider factors such as peak workloads, application dependencies, and data storage needs.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in multicloud environments, where data and applications are distributed across multiple platforms. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Data Encryption:Encrypting data at rest and in transit is essential to prevent unauthorized access. Organizations should leverage encryption tools and protocols offered by cloud providers.
- Access Control:Implementing granular access controls to restrict user permissions based on roles and responsibilities is crucial. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Security Monitoring:Continuous security monitoring is essential to detect and respond to threats proactively. Organizations should utilize security information and event management (SIEM) tools to analyze logs and identify anomalies.
- Compliance and Governance:Meeting industry-specific compliance regulations is crucial. Organizations must ensure their multicloud deployments adhere to relevant standards and frameworks.
Data Management Considerations
Managing data effectively across multiple cloud platforms is a key challenge. Organizations must ensure data consistency, availability, and security.
- Data Replication:Replicating data across multiple cloud providers ensures data availability and resilience. Organizations should consider strategies such as multi-region replication or disaster recovery.
- Data Governance:Establishing clear data governance policies is crucial to manage data access, ownership, and compliance. This ensures data integrity and consistency across different cloud environments.
- Data Backup and Recovery:Implementing robust backup and recovery strategies is essential to protect data from accidental deletion or hardware failures. Organizations should leverage cloud-native backup solutions or third-party tools.
- Data Migration:Migrating data to the cloud requires careful planning and execution. Organizations must ensure data integrity, minimize downtime, and address potential security risks.
Cost Considerations
Managing costs in a multicloud environment can be complex due to varying pricing models and service offerings. Organizations must carefully analyze costs and optimize their cloud spending.
- Cloud Cost Optimization:Regularly monitoring and optimizing cloud spending is crucial. Organizations should leverage cost management tools and implement strategies such as right-sizing resources and using reserved instances.
- Cloud Provider Contracts:Negotiating favorable contracts with cloud providers is essential to secure competitive pricing and avoid hidden fees. Organizations should consider factors such as usage patterns, service level agreements (SLAs), and support options.
- Cost Allocation:Accurately allocating cloud costs to different departments or projects is crucial for budgeting and accountability. Organizations should implement cost allocation models based on usage patterns and resource consumption.
- Cost Transparency:Cloud providers should offer clear and transparent pricing models. Organizations should understand the cost implications of different services and ensure they are aligned with their budget constraints.
Multicloud Architecture and Design

Multicloud architecture is the blueprint for how organizations structure and manage their cloud resources across multiple cloud providers. This strategic approach allows businesses to leverage the strengths of different platforms, optimize costs, and mitigate risks associated with single-vendor dependence.
Components of a Multicloud Architecture
A multicloud architecture consists of several key components that work together to ensure seamless operation and efficient resource utilization.
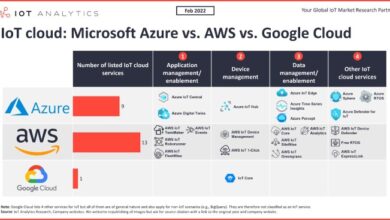
- Cloud Providers:The core of a multicloud architecture are the cloud providers themselves, such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and others. Each provider offers a unique set of services, including compute, storage, networking, databases, and more. Selecting the right combination of providers is crucial for meeting specific business needs and achieving optimal performance.
- Networking:Connecting cloud resources across different providers is essential for data flow and communication. Multicloud networking solutions involve establishing secure and reliable connections between cloud environments. This can be achieved through various methods, including VPNs, direct connections, and cloud-based networking services.
- Security:Ensuring data security and compliance is paramount in a multicloud environment. Implementing robust security measures across all cloud providers is critical. This includes access control, encryption, threat detection, and incident response mechanisms.
- Management and Orchestration:Managing and orchestrating resources across multiple cloud providers can be complex. Multicloud management tools and platforms provide centralized visibility, automation, and control over resources, simplifying operations and improving efficiency.
Multicloud Integration and Orchestration
Integrating and orchestrating cloud services across different providers is essential for achieving the full potential of a multicloud strategy.
- API Integration:Cloud providers offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow applications and services to interact with each other. By leveraging APIs, businesses can integrate cloud services from different providers seamlessly, enabling data sharing, workflow automation, and enhanced functionality.
- Multicloud Management Platforms:These platforms provide a centralized console for managing resources across multiple cloud providers. They offer features such as resource monitoring, cost optimization, security management, and automated deployment.
- Cloud-Native Technologies:Adopting cloud-native technologies like containers and microservices can simplify multicloud integration. These technologies enable applications to be deployed and managed consistently across different cloud environments, fostering agility and scalability.
Visual Representation of a Typical Multicloud Architecture
[Image of a multicloud architecture with different cloud providers, networking connections, and security elements]This image illustrates a typical multicloud architecture with resources distributed across multiple cloud providers. Each provider is connected through secure network links, enabling data exchange and application communication.
Security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, are implemented at various levels to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Multicloud, the smart person’s guide to navigating the complex world of cloud computing, can sometimes feel overwhelming. But just like the “sister style nothing fancy” approach to fashion, sister style nothing fancy , multicloud can be approached with a focus on simplicity and practicality.
By understanding your core needs and choosing the right cloud providers for each, you can build a robust and flexible multicloud strategy that fits your specific requirements.
Multicloud Management Tools and Technologies
Managing multiple cloud environments effectively is a complex challenge. This is where multicloud management tools and technologies come into play, providing a unified platform to streamline operations, optimize resource utilization, and enhance security across diverse cloud providers.
Popular Multicloud Management Tools and Technologies
A wide array of tools and technologies cater to the needs of multicloud management.
- Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs):These comprehensive platforms offer centralized control and visibility across multiple clouds, providing a single pane of glass for managing infrastructure, applications, and resources. Examples include:
- VMware Cloud Director:A popular CMP that extends VMware’s virtualization capabilities to multicloud environments, enabling unified management of virtual machines, networks, and storage across various cloud providers.
- Red Hat CloudForms:A comprehensive CMP that provides automation, orchestration, and self-service capabilities for managing multicloud infrastructure, applications, and services.
- Microsoft Azure Stack Hub:An on-premises solution that extends Azure services to hybrid and multicloud environments, enabling consistent management and deployment across on-premises and cloud resources.
- Configuration Management Tools:These tools automate the configuration and management of infrastructure and applications, ensuring consistency and compliance across multiple clouds. Examples include:
- Ansible:An open-source tool that uses YAML-based playbooks to automate configuration tasks, infrastructure provisioning, and application deployment across various cloud providers.
- Chef:A powerful tool that uses a domain-specific language (DSL) to define infrastructure configurations and automate deployments across multicloud environments.
- Puppet:A robust configuration management tool that uses declarative language to define desired states for infrastructure and applications, ensuring consistency and compliance across multiple clouds.
- Cloud Orchestration Platforms:These platforms facilitate the automation and orchestration of cloud resources, enabling efficient provisioning, scaling, and management of applications across multiple cloud providers. Examples include:
- Kubernetes:An open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications across multiple cloud providers.
- Docker Swarm:A native container orchestration platform for Docker, enabling the management and scaling of containerized applications across multicloud environments.
- Cloud Foundry:An open-source platform-as-a-service (PaaS) that provides a unified platform for deploying and managing applications across multiple cloud providers.
- Cloud Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):These tools provide centralized logging, monitoring, and analysis of security events across multiple cloud environments, enabling proactive threat detection and response. Examples include:
- Splunk:A comprehensive SIEM solution that aggregates security logs from various cloud providers, providing real-time threat detection, incident response, and security analytics.
- Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana (ELK):An open-source SIEM stack that offers log collection, analysis, and visualization capabilities for security monitoring across multicloud environments.
- IBM QRadar:A robust SIEM solution that provides threat intelligence, security analytics, and incident response capabilities for managing security risks across multiple clouds.
- Cloud Cost Management Tools:These tools provide insights into cloud spending, helping organizations optimize resource utilization and reduce costs. Examples include:
- CloudHealth by VMware:A comprehensive cloud cost management platform that provides insights into cloud spending, resource utilization, and cost optimization opportunities across multiple cloud providers.
- AWS Cost Explorer:A built-in tool within AWS that provides detailed insights into cloud spending, enabling organizations to identify cost optimization opportunities and track budgets.
- Azure Cost Management + Billing:A comprehensive cost management tool within Azure that provides insights into cloud spending, resource utilization, and cost optimization recommendations.
Comparing and Contrasting Multicloud Management Tools
Each multicloud management tool has its strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial to carefully evaluate their features, functionalities, and use cases before selecting the most suitable option.
- Functionality:CMPs offer comprehensive management capabilities, while configuration management tools focus on automation and consistency. Cloud orchestration platforms excel at containerized application deployment and scaling, while SIEM tools prioritize security monitoring and threat detection. Cloud cost management tools provide insights into cloud spending and optimization opportunities.
- Integration:Some tools offer native integration with specific cloud providers, while others provide broader support for multiple cloud platforms. Compatibility with existing infrastructure and applications is essential for seamless integration and reduced complexity.
- Scalability:The ability to scale management capabilities to accommodate growing cloud environments is crucial. Consider the tool’s scalability, performance, and ability to handle increasing workloads and data volumes.
- Cost:Different tools have varying pricing models, ranging from free open-source solutions to subscription-based services. Evaluate the cost of ownership, including licensing fees, maintenance costs, and potential training requirements.
Best Practices for Selecting and Implementing Multicloud Management Tools
Selecting and implementing the right multicloud management tools is essential for achieving success in a multicloud environment.
- Define Clear Objectives:Clearly define the goals and objectives for multicloud management, such as simplifying operations, optimizing costs, enhancing security, or improving application performance. This will help narrow down the selection of tools and technologies that best align with your specific needs.
- Evaluate Existing Infrastructure:Assess the current infrastructure and applications, including the cloud providers used, the types of workloads deployed, and the security posture. This will inform the selection of tools that are compatible with your existing environment and address your specific requirements.
- Consider Scalability and Flexibility:Choose tools that can scale with your cloud environment and offer flexibility to adapt to changing needs. Consider the ability to integrate with new cloud providers or technologies as your multicloud strategy evolves.
- Prioritize Security:Select tools that prioritize security and compliance, offering features like encryption, access control, and auditing capabilities. Ensure the tools meet industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Focus on User Experience:Choose tools with intuitive interfaces, robust documentation, and adequate training resources to facilitate adoption and ease of use across your organization.
- Implement a Phased Approach:Implement multicloud management tools in a phased manner, starting with a pilot project to test and refine the approach before rolling out across the organization. This minimizes risks and allows for continuous improvement.
Multicloud Security Best Practices
Securing multicloud environments presents a unique set of challenges due to the distributed nature of resources and the complexities of managing security across multiple cloud providers. This section explores a comprehensive set of best practices for securing multicloud environments, encompassing key considerations like data encryption, access control, and threat detection.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a crucial aspect of multicloud security, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information stored and transmitted across multiple cloud providers. Implementing robust encryption strategies involves the following steps:
- Encrypt data at rest:Encrypt data stored in cloud storage services, databases, and other data repositories using encryption-at-rest capabilities offered by cloud providers or by deploying your own encryption solutions. This ensures that data is protected even if the underlying storage infrastructure is compromised.
- Encrypt data in transit:Encrypt data transmitted between applications, services, and users using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols. This safeguards data from eavesdropping and tampering during network transmission.
- Use strong encryption algorithms:Choose strong encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a key length of at least 256 bits to ensure data is protected against brute-force attacks and advancements in cryptography.
- Implement key management solutions:Securely manage encryption keys using dedicated key management solutions offered by cloud providers or by deploying your own key management systems. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of encryption keys, preventing unauthorized access and use.
Access Control
Access control is a fundamental security principle that restricts access to resources based on user identity and permissions. Implementing effective access control in multicloud environments requires:
- Implement least privilege principle:Grant users and applications the minimum access privileges necessary to perform their tasks. This principle helps to limit the potential damage caused by unauthorized access or compromised accounts.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA):Require users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as passwords, tokens, or biometrics, before granting access to sensitive resources. This significantly enhances security by making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Enforce strong password policies:Establish strong password policies that mandate the use of complex passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. This makes it more difficult for attackers to guess or crack passwords.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC):Define roles and assign permissions to those roles based on job functions. This simplifies access management and ensures that users have appropriate access to the resources they need to perform their duties.
- Regularly review and audit access permissions:Regularly review and audit user access permissions to identify and remove any unnecessary or outdated permissions. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive resources.
Threat Detection and Response
Threat detection and response is essential for identifying and mitigating security threats in multicloud environments. This involves:
- Implement security information and event management (SIEM):Use SIEM solutions to collect, analyze, and correlate security events from multiple cloud providers. This provides a centralized view of security threats across the multicloud environment and facilitates timely threat detection and response.
- Deploy security monitoring tools:Utilize security monitoring tools to continuously monitor cloud resources for suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and data exfiltration. This enables proactive threat detection and response.
- Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS):Deploy IDS/IPS solutions to detect and prevent malicious network traffic targeting cloud resources. These systems can identify and block known attacks and suspicious activities, enhancing the security posture of the multicloud environment.
- Use cloud security posture management (CSPM):Implement CSPM tools to assess the security posture of cloud resources, identify vulnerabilities, and recommend remediation actions. This helps to maintain a high level of security across the multicloud environment.
- Develop incident response plans:Establish clear incident response plans that Artikel the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. This ensures a coordinated and effective response to security threats, minimizing potential damage and downtime.
Multicloud Use Cases and Success Stories
Multicloud adoption is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a reality for organizations across industries. Businesses are increasingly realizing the benefits of a multicloud strategy, leveraging the strengths of different cloud providers to achieve specific business outcomes. This section delves into real-world examples of successful multicloud deployments, highlighting the advantages and challenges encountered.
We’ll explore how organizations have harnessed multicloud to gain a competitive edge and achieve strategic goals.
Multicloud in Retail
The retail industry is undergoing a digital transformation, and multicloud plays a crucial role in this evolution. Retailers are leveraging multicloud to enhance customer experiences, improve operational efficiency, and gain insights from data.
- Walmart: Walmart, a global retail giant, utilizes a multicloud strategy to power its e-commerce platform and manage its vast supply chain. They leverage Azure for their cloud-based services, Google Cloud for analytics, and AWS for their core infrastructure. This approach enables Walmart to scale its operations efficiently and deliver a seamless customer experience.
- Target: Target, another leading retailer, has embraced multicloud to enhance its digital presence and provide personalized shopping experiences. They use AWS for their website and mobile applications, Google Cloud for data analytics, and Azure for security and compliance. This multicloud approach allows Target to optimize costs, improve performance, and gain valuable insights from customer data.
Multicloud in Financial Services, Multicloud the smart persons guide
The financial services industry is highly regulated and demands robust security and compliance measures. Multicloud provides a solution for financial institutions to meet these demands while innovating and delivering new services.
- Capital One: Capital One, a major financial institution, has adopted a multicloud strategy to modernize its infrastructure and enhance customer service. They leverage AWS for their core banking systems, Azure for data analytics, and Google Cloud for machine learning. This multicloud approach enables Capital One to improve agility, enhance security, and deliver personalized financial services to its customers.
- JP Morgan Chase: JP Morgan Chase, another leading financial institution, utilizes multicloud to streamline its operations and improve risk management. They leverage AWS for their trading platforms, Azure for their cloud-based services, and Google Cloud for data analytics. This multicloud strategy allows JP Morgan Chase to optimize costs, enhance performance, and mitigate risks across its diverse operations.
Multicloud in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is increasingly embracing digital technologies to improve patient care and operational efficiency. Multicloud provides a flexible and scalable platform for healthcare providers to meet these demands.
- Mayo Clinic: Mayo Clinic, a renowned healthcare provider, utilizes a multicloud strategy to manage patient data, enhance research capabilities, and improve operational efficiency. They leverage AWS for their cloud-based services, Azure for data analytics, and Google Cloud for machine learning.
This multicloud approach enables Mayo Clinic to deliver personalized care, conduct groundbreaking research, and optimize their operations.
- Cleveland Clinic: Cleveland Clinic, another leading healthcare provider, has adopted a multicloud strategy to enhance patient engagement and improve clinical outcomes. They use AWS for their patient portal and mobile applications, Azure for their electronic health records, and Google Cloud for data analytics.
This multicloud approach allows Cleveland Clinic to provide a seamless patient experience, gain insights from data, and optimize their clinical workflows.
The Future of Multicloud

The multicloud landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs. Emerging trends and technologies are shaping the future of multicloud, paving the way for more sophisticated and dynamic deployments.
Impact of Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. In the multicloud context, edge computing will play a crucial role in extending multicloud deployments to the edge, enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of multicloud in geographically dispersed locations.
This will be particularly important for applications that require low latency, such as real-time analytics, autonomous vehicles, and IoT devices.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing allows developers to focus on writing code without managing the underlying infrastructure. In a multicloud environment, serverless computing can simplify deployment and management, enabling businesses to scale resources on demand and pay only for what they use. Serverless computing will further enhance the flexibility and agility of multicloud deployments, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to changing needs.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various industries, and its impact on multicloud is significant. AI-powered tools can automate tasks, optimize resource allocation, and improve security in multicloud environments. For example, AI-driven security solutions can detect and respond to threats in real time, ensuring the security of sensitive data across multiple clouds.