UK Teachers Cybersecurity Training: Protecting Students and Data
UK teachers cybersecurity training sets the stage for a vital discussion about protecting our students and their data in the digital age. With cyberattacks on schools and universities becoming increasingly common, it’s more important than ever for educators to understand the threats and learn how to defend against them.
This training is not just about technical skills; it’s about fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness within the classroom. By equipping teachers with the knowledge and tools they need, we can create a safer and more secure learning environment for everyone.
The Importance of Cybersecurity Training for UK Teachers
The UK education sector is increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. As schools and universities rely more heavily on technology, they become more attractive targets for cybercriminals. Cybersecurity training for UK teachers is crucial for protecting sensitive data, safeguarding students, and maintaining the smooth operation of educational institutions.
The Growing Need for Cybersecurity Training in the UK Education Sector
The reliance on technology in schools and universities has grown significantly, making them more susceptible to cyberattacks. Cybercriminals are constantly developing new tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in networks and systems. Schools and universities are facing a growing number of cyberattacks, including phishing scams, malware infections, and ransomware attacks.
Statistics on Cyberattacks Targeting Schools and Universities
- The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) reported a significant increase in cyberattacks targeting UK schools and universities in recent years.
- A study by the UK government found that 70% of schools and universities have experienced at least one cyberattack in the past year.
- The NCSC has issued numerous warnings about the growing threat of ransomware attacks against schools and universities.
The Potential Consequences of Data Breaches and Security Incidents
Data breaches and security incidents can have severe consequences for schools and universities, including:
- Loss of sensitive student data, such as personal information, academic records, and financial details.
- Disruption of learning and teaching activities, including access to online resources and systems.
- Damage to the reputation of the institution and loss of public trust.
- Significant financial losses due to recovery costs, legal fees, and potential fines.
Key Cybersecurity Concepts for UK Teachers
In today’s digital world, cybersecurity is paramount for everyone, including educators. UK teachers handle sensitive student data, manage school resources, and interact with online platforms. Understanding key cybersecurity concepts can significantly enhance their ability to protect themselves, their students, and the school community from cyber threats.
Phishing
Phishing attacks are a common form of social engineering where attackers attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, or personal data. They do this by sending emails, text messages, or creating fake websites that appear legitimate.
In the context of education, phishing attacks can target teachers, students, and parents, aiming to steal access credentials or compromise school systems.
Malware
Malware refers to malicious software designed to harm computer systems or steal data. It can take various forms, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. Teachers need to be aware of malware threats as they can affect school computers, networks, and student devices.
UK teachers are on the front lines of digital learning, and their cybersecurity training is essential. They handle sensitive student data, and protecting it requires robust solutions like Netskope data loss prevention. This technology helps schools prevent accidental or malicious data leaks, ensuring student information stays secure.
By incorporating these measures, UK teachers can confidently navigate the digital landscape and provide a safe learning environment for all.
Malware can disrupt learning, steal sensitive data, or even hold systems hostage for ransom.
Social Engineering
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into performing actions or revealing information that benefits the attacker. This can be done through various methods, such as impersonation, pretexting, or baiting. In the education sector, social engineering attacks can target teachers to gain access to school networks or sensitive student data.
Data Privacy
Data privacy is crucial in education, as schools collect and manage sensitive information about students, teachers, and staff. The UK’s Data Protection Act 2018 (DPA 2018) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provide legal frameworks for protecting personal data.
Teachers must be aware of data privacy regulations and their responsibilities in handling student data.
Password Security
Strong passwords are essential for protecting accounts and sensitive information. Teachers should avoid using weak passwords, such as common words or personal details. They should also use different passwords for different accounts and enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for UK Teachers

In today’s digital world, teachers are increasingly relying on technology in the classroom. This brings numerous benefits, but it also introduces new cybersecurity risks. To ensure a safe and secure learning environment for both students and teachers, adopting strong cybersecurity practices is essential.
This section will explore several key best practices for UK teachers to follow when using technology in the classroom.
Secure Password Management
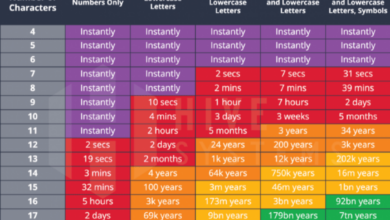
Strong passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive information. Teachers should use unique, complex passwords for all their online accounts, including school accounts, email, and social media platforms. A strong password typically includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Use a password manager: Password managers are tools that securely store and manage all your passwords. They can generate strong, unique passwords for each of your accounts and automatically fill in login details, making it easier to maintain good password hygiene.
- Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts: If one account is compromised, attackers can potentially gain access to other accounts using the same password.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to their phone, in addition to their password.
Safe Browsing Habits
Teachers should be cautious about the websites they visit and the information they share online. They should be aware of the potential risks associated with clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links: Be wary of emails or messages that contain links that seem too good to be true, or that ask you to click on a link to claim a prize or update your account.
- Be cautious about downloading files from untrusted sources: Only download files from reputable sources and always scan them for malware before opening them.
- Keep your software up to date: Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities.
- Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks can be insecure, making it easy for attackers to intercept your data. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it more secure.
Recognizing and Avoiding Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a common type of cybercrime where attackers try to trick users into giving up sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card details, or personal information.
UK teachers are increasingly facing the challenge of protecting themselves and their students from cyber threats. It’s a complex issue, but one that requires a proactive approach. Just like learning a new skill, like crochet basics slip knots foundation chains , requires a solid foundation, cybersecurity training should be a fundamental part of any teacher’s professional development.
By understanding the basics of online safety, teachers can empower themselves and their students to navigate the digital world with confidence.
- Be aware of the signs of a phishing attack: Phishing emails often have grammatical errors, use generic greetings, or ask for personal information that the sender shouldn’t need.
- Hover over links before clicking on them: This will show you the actual URL of the website you’re being redirected to. If it looks suspicious, don’t click on it.
- Report phishing emails: If you receive a phishing email, report it to your school’s IT department or the relevant authorities.
Reporting Suspicious Activity
Teachers should be vigilant about reporting any suspicious activity they encounter online. This includes reporting phishing attacks, malware infections, or any other security breaches.
- Report suspicious activity to your school’s IT department: Your school’s IT department is responsible for handling cybersecurity incidents. They can investigate the issue and take appropriate action to protect your data.
- Report cybercrime to the police: If you believe you have been a victim of cybercrime, you should report it to the police.
Protecting Student Data
Teachers have a responsibility to protect the privacy and security of student data. This includes ensuring that student data is stored securely and only accessed by authorized individuals.
- Only collect and store necessary student data: Don’t collect any student data that isn’t absolutely necessary for educational purposes.
- Use strong passwords and access controls: Restrict access to student data to authorized individuals.
- Follow your school’s data protection policies: Schools have data protection policies in place to ensure that student data is handled responsibly. Make sure you are familiar with and follow these policies.
Cybersecurity Resources for UK Teachers
Navigating the digital landscape requires a strong understanding of cybersecurity, and for UK teachers, access to reliable resources is crucial. This section will guide you to various sources that can help you enhance your cybersecurity knowledge and skills.
Government Websites
The UK government provides comprehensive resources on cybersecurity, offering guidance and support specifically for educators. These websites serve as valuable hubs for information, best practices, and relevant policies.
| Resource Name | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) | The NCSC is the UK’s national cybersecurity authority, providing guidance and support for individuals, organizations, and educators. | https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/ |
| Department for Education (DfE) | The DfE offers resources and guidance on data protection, online safety, and cybersecurity for schools and colleges. | https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/department-for-education |
| Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) | The ICO is responsible for upholding information rights in the UK, providing guidance on data protection and cybersecurity regulations. | https://ico.org.uk/ |
Educational Institutions
Several educational institutions in the UK offer dedicated cybersecurity programs and resources for teachers, equipping them with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate the digital world effectively.
| Resource Name | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| University of Oxford | Oxford University’s Department of Computer Science offers online courses and resources on cybersecurity for educators. | https://www.cs.ox.ac.uk/ |
| Imperial College London | Imperial College London provides a range of cybersecurity programs and resources, including online courses and workshops for teachers. | https://www.imperial.ac.uk/ |
| University of Cambridge | Cambridge University offers a variety of cybersecurity-related programs and resources, including online courses and workshops. | https://www.cam.ac.uk/ |
Industry Organizations
Industry organizations play a vital role in promoting cybersecurity best practices and offering resources to educators. These organizations often provide guidance, training materials, and networking opportunities.
| Resource Name | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Information Security Forum (ISF) | The ISF is a global information security membership organization, providing resources and guidance on cybersecurity for various sectors, including education. | https://www.isforum.org/ |
| National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) | NIST is a US government agency that develops and promotes standards and guidelines for cybersecurity, including resources relevant to education. | https://www.nist.gov/ |
| Cybersecurity Information Sharing and Analysis Center (CISAC) | CISAC is a non-profit organization that facilitates the sharing of cybersecurity information and best practices, including resources for educators. | https://www.cisac.org/ |
Online Training Platforms
Online training platforms offer a convenient and flexible way for UK teachers to enhance their cybersecurity knowledge and skills. These platforms provide a variety of courses, certifications, and resources to cater to different learning styles and needs.
| Resource Name | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Training by NCSC | The NCSC offers a range of online training courses and resources on cybersecurity, specifically tailored for educators. | https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/training |
| Coursera | Coursera is an online learning platform that offers a variety of cybersecurity courses from leading universities and institutions. | https://www.coursera.org/ |
| Udemy | Udemy is another online learning platform that offers a wide range of cybersecurity courses, including those specifically designed for educators. | https://www.udemy.com/ |
Cybersecurity Training Programs for UK Teachers

Cybersecurity training is essential for UK teachers to ensure the safety and security of themselves, their students, and the school network. Various programs are available, each offering different advantages and disadvantages.
Online Courses, Uk teachers cybersecurity training
Online courses offer flexibility and accessibility, allowing teachers to learn at their own pace and on their schedule. These courses are often self-paced and can cover a wide range of cybersecurity topics.
- Advantages:
- Flexibility and convenience: Teachers can learn at their own pace and on their schedule, making it easier to fit training into busy schedules.
- Accessibility: Online courses are available to teachers across the UK, regardless of location.
- Cost-effective: Online courses are often more affordable than in-person workshops.
- Variety of topics: Online courses cover a wide range of cybersecurity topics, from basic concepts to advanced techniques.
- Disadvantages:
- Lack of interaction: Online courses can be isolating, and teachers may miss out on the opportunity to interact with other teachers.
- Technical difficulties: Technical issues can arise, interrupting the learning process.
- Limited hands-on experience: Online courses may not offer the same level of hands-on experience as in-person workshops.
In-Person Workshops
In-person workshops provide a more interactive and engaging learning experience, allowing teachers to interact with instructors and other teachers.
- Advantages:
- Interactive learning: In-person workshops provide opportunities for teachers to interact with instructors and other teachers, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
- Hands-on experience: Workshops often include hands-on activities and simulations, allowing teachers to apply their knowledge in a practical setting.
- Networking opportunities: In-person workshops provide opportunities for teachers to network with other educators and share best practices.
- Disadvantages:
- Time commitment: In-person workshops require teachers to commit to attending sessions at specific times and locations.
- Cost: In-person workshops can be more expensive than online courses.
- Limited accessibility: In-person workshops may not be accessible to teachers in remote areas.
Teacher-Led Training Sessions
Teacher-led training sessions offer a tailored approach to cybersecurity education, allowing teachers to focus on specific topics relevant to their needs and the school environment.
Speaking of important things to keep safe, I’m really happy that UK teachers are getting more cybersecurity training. It’s crucial for them to understand how to protect themselves and their students online. And since Valentine’s Day is coming up, I’ve been playing around with some new makeup looks.
I’ve been loving this my favorite non toxic makeup for a shimmery valentines day look – it’s perfect for a romantic evening out! Anyway, back to cybersecurity – I think it’s great that teachers are getting the tools they need to stay safe online.
- Advantages:
- Targeted content: Training sessions can be tailored to address the specific needs and challenges of a particular school or group of teachers.
- Practical application: Teachers can learn about cybersecurity best practices in the context of their own school environment.
- Cost-effective: Teacher-led training sessions can be more cost-effective than external training programs.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited expertise: Teacher-led training sessions may be limited by the expertise of the teachers leading the sessions.
- Time commitment: Teacher-led training sessions can require teachers to dedicate time outside of their regular teaching responsibilities.
- Limited resources: Teacher-led training sessions may not have access to the same resources as external training programs.
Integrating Cybersecurity into the Curriculum: Uk Teachers Cybersecurity Training
Cybersecurity is no longer a niche topic confined to tech experts. It’s a fundamental skill everyone needs to navigate the digital world safely. Integrating cybersecurity concepts into the curriculum equips students with the knowledge and skills to protect themselves and their data in an increasingly interconnected world.
Cybersecurity Across Subjects
Integrating cybersecurity concepts across different subjects allows students to understand its relevance in real-world contexts. Here’s how to weave cybersecurity into various subjects:
- Mathematics:Explore data encryption algorithms, such as Caesar cipher, and discuss their role in securing information. Analyze the effectiveness of different encryption methods through mathematical calculations. Students can also learn about data analysis techniques used to detect cybersecurity threats.
- English Language Arts:Analyze news articles, blog posts, and social media posts related to cybersecurity breaches and data privacy. Students can also write persuasive essays advocating for responsible online behavior and digital citizenship.
- Science:Explore the science behind cybersecurity, including cryptography, network security, and digital forensics. Students can learn about the hardware and software used to protect computer systems and data.
- Social Studies:Discuss the social and economic impact of cybersecurity breaches. Analyze the ethical implications of hacking and data privacy violations. Students can also learn about the role of government agencies in cybersecurity and data protection.
- Computer Science:Provide hands-on experience with cybersecurity tools and techniques. Students can learn about coding, programming, and ethical hacking practices.
The Role of Technology in Cybersecurity Training
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity training for UK teachers, providing interactive and engaging learning experiences that cater to diverse learning styles. By leveraging innovative tools and platforms, training programs can be made more effective, accessible, and relevant to the real-world challenges teachers face.
Utilizing Technology for Effective Cybersecurity Training
Technology offers numerous opportunities to enhance cybersecurity training for UK teachers, making it more interactive, engaging, and effective. Here are some key ways technology can be leveraged:
- Interactive Learning Platforms:Platforms like Moodle, Canvas, and Google Classroom can be used to deliver online cybersecurity training modules, quizzes, and assessments. These platforms allow for self-paced learning, personalized feedback, and tracking of progress.
- Simulation and Gaming:Cybersecurity simulations and games provide realistic scenarios where teachers can practice their skills in a safe and controlled environment. These tools help develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities in a fun and engaging way. Examples include CyberLympics and Capture the Flag (CTF) competitions.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR):VR and AR technologies offer immersive experiences that can bring cybersecurity concepts to life. Teachers can be placed in virtual environments where they can experience real-world threats and learn how to respond effectively.
- Mobile Learning Apps:Mobile apps offer flexibility and accessibility, allowing teachers to access cybersecurity training materials anytime, anywhere. These apps can provide bite-sized learning modules, quizzes, and resources that fit into busy schedules.
Innovative Tools and Platforms for Cybersecurity Training
Here is a table showcasing different technologies and their potential applications in cybersecurity training:
| Technology | Application in Cybersecurity Training |
|---|---|
| Interactive Learning Platforms | Delivering online training modules, quizzes, and assessments. Providing personalized feedback and tracking progress. |
| Simulation and Gaming | Creating realistic scenarios for practicing cybersecurity skills. Developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making abilities. |
| Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) | Offering immersive experiences that bring cybersecurity concepts to life. Providing realistic simulations of real-world threats. |
| Mobile Learning Apps | Delivering bite-sized learning modules, quizzes, and resources. Providing flexibility and accessibility for learning on the go. |
| Gamification | Making cybersecurity training more engaging and fun through game mechanics. Encouraging participation and motivating learners. |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Personalizing learning experiences based on individual needs and progress. Providing adaptive assessments and feedback. |
The Future of Cybersecurity Training for UK Teachers
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, demanding that educators stay ahead of the curve. As technology advances, so do the threats, making it crucial for UK teachers to have a robust understanding of cybersecurity principles and best practices. This section explores emerging trends and challenges in cybersecurity training for UK teachers, discusses the impact of new technologies on cybersecurity education, and offers a vision for the future of cybersecurity training in the UK education sector.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies on Cybersecurity Training
The emergence of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT), presents both opportunities and challenges for cybersecurity training.
- AI-powered tools can automate tasks and improve efficiency in cybersecurity training. For instance, AI-driven simulations can provide teachers with realistic scenarios to practice their skills and develop their understanding of cybersecurity threats.
- Cloud computing allows for greater accessibility and scalability of cybersecurity training resources. This can enable teachers to access online courses, workshops, and simulations from anywhere with an internet connection.
- The increasing adoption of IoT devices creates new security vulnerabilities that require teachers to understand the unique security challenges associated with connected devices.
Teachers need to be equipped with the knowledge and skills to navigate these emerging technologies safely and effectively.