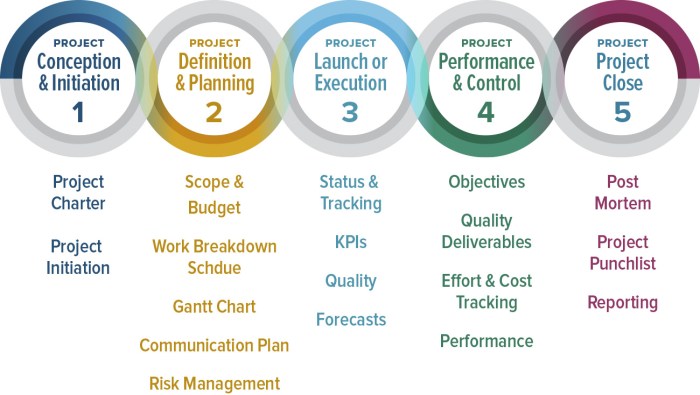
6 Essential Documents for Project Management Success
6 Essential Documents for Project Management Success sets the stage for a successful project, providing a roadmap for clarity, collaboration, and ultimately, achieving your goals. These documents are not just paperwork; they’re the foundation for a well-structured, efficient, and effective project lifecycle.
From defining the project’s purpose and scope to outlining tasks, managing risks, and ensuring everyone is on the same page, these documents serve as a guide, keeping the project on track and preventing costly mistakes. This article will delve into the six essential documents, highlighting their importance, key elements, and how they contribute to overall project success.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a fundamental project management tool that systematically decomposes project deliverables into smaller, manageable tasks. This hierarchical structure provides a clear roadmap for planning, organizing, and executing projects effectively.
Different WBS Structures
The structure of a WBS can vary depending on the type and complexity of the project. Here are some common WBS structures:
- Product-Oriented WBS: This structure is commonly used for projects with a tangible output, such as software development or construction. It breaks down the project into components, sub-components, and tasks, reflecting the final product’s structure.
- Process-Oriented WBS: This structure focuses on the project’s phases and activities, outlining the steps required to complete the project. It is suitable for projects with a defined workflow, such as marketing campaigns or research projects.
- Hybrid WBS: This structure combines elements of both product-oriented and process-oriented WBS, providing a comprehensive view of the project’s deliverables and activities. It is particularly useful for complex projects involving multiple phases and deliverables.
Benefits of Using a WBS
The WBS offers several benefits for project planning and execution:
- Clear Project Scope: By breaking down the project into manageable tasks, the WBS provides a clear understanding of the project’s scope and deliverables.
- Improved Planning and Estimation: The WBS facilitates accurate estimation of time, resources, and costs for each task, leading to more realistic project plans.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: The WBS serves as a common language for project stakeholders, promoting effective communication and collaboration among team members.
- Effective Task Management: The WBS allows for efficient task assignment, tracking, and monitoring, ensuring that all tasks are completed on time and within budget.
- Risk Identification and Mitigation: The WBS helps identify potential risks associated with each task, allowing for proactive risk mitigation strategies.
Project Schedule
A project schedule is a crucial document in project management, outlining the project’s timeline, milestones, and dependencies. It serves as a roadmap, providing a clear picture of when tasks should be completed and helping to ensure the project stays on track.
Having the right documents in place is crucial for project management success, ensuring everyone is on the same page and progress can be tracked effectively. Just like the innovative advancements in the intel lunar lake npu are driving the future of AI, having a clear project scope document, detailed requirements, and a well-defined risk management plan can help your projects achieve their goals and overcome challenges.
A well-defined project schedule helps manage expectations, allocate resources effectively, and identify potential risks and delays.
Having a solid set of project management documents is crucial for success. From project charters outlining objectives to risk assessments mitigating potential roadblocks, these documents act as your roadmap and compass. Speaking of roadmaps, I recently read about how Tim Cook, the CEO of Apple, blind-ranked his top five Apple products of all time, including one of its most controversial sort of, which you can read about here.
Just like those documents helped shape Apple’s iconic products, your project management documents can guide you towards achieving your project goals. So, make sure you have all the essentials in place!
Different Scheduling Techniques
Various scheduling techniques can be used to create a project schedule, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The choice of technique depends on the project’s complexity, the team’s experience, and the available resources.
- Gantt Chart:A Gantt chart is a visual representation of the project schedule, displaying tasks and their durations on a timeline. It provides a clear overview of the project’s progress and helps identify potential conflicts and dependencies between tasks.
- Critical Path Method (CPM):The CPM is a network-based scheduling technique that identifies the critical path, the sequence of tasks that directly impacts the project’s completion date. It helps determine the minimum project duration and highlights tasks that require close monitoring to avoid delays.
From project scope documents to risk assessments, those 6 essential documents can make or break a project. It’s amazing how technology continues to evolve, and with the news that Apple’s iPhone 18 chip technology might have been announced as TSMC touts advanced 16nm fabrication , it’s clear that even the most complex projects rely on thorough documentation to stay on track.
So, before you dive into your next project, make sure you’ve got those key documents in place!
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT):PERT is similar to CPM but considers the uncertainty of task durations. It uses a probabilistic approach to estimate the project’s completion time, taking into account optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimates for each task.
Sample Project Schedule
This sample project schedule illustrates a simple project with milestones and dependencies:
| Task | Duration (Days) | Start Date | End Date | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requirement Gathering | 5 | 2023-10-23 | 2023-10-28 | – |
| Design | 10 | 2023-10-28 | 2023-11-07 | Requirement Gathering |
| Development | 15 | 2023-11-07 | 2023-11-22 | Design |
| Testing | 5 | 2023-11-22 | 2023-11-27 | Development |
| Deployment | 2 | 2023-11-27 | 2023-11-29 | Testing |
The sample schedule demonstrates the use of dependencies. For example, “Design” cannot start until “Requirement Gathering” is completed.
Risk Management Plan: 6 Essential Documents For Project Management Success
A risk management plan is an essential document for project success, as it Artikels the process for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact project objectives. This plan serves as a roadmap for proactively addressing potential threats and maximizing the likelihood of achieving project goals.
Risk Identification
The first step in risk management is to identify potential risks that could affect the project. This involves brainstorming and evaluating various factors that could negatively impact project scope, schedule, budget, or quality.
- Technical Risks:These risks arise from uncertainties related to the project’s technology, tools, or processes. Examples include technology obsolescence, software bugs, or inadequate technical expertise.
- Resource Risks:These risks stem from potential issues with project resources, such as personnel, equipment, or materials. Examples include staff turnover, equipment failures, or material shortages.
- Financial Risks:These risks are associated with project funding and budget constraints. Examples include cost overruns, budget cuts, or delays in funding.
- External Risks:These risks originate from factors outside the project’s control, such as economic downturns, political instability, or natural disasters.
- Legal and Regulatory Risks:These risks are related to compliance with laws, regulations, or contractual obligations. Examples include changes in legislation, licensing issues, or breaches of contract.
Risk Analysis
Once risks have been identified, they need to be analyzed to assess their likelihood and impact. This helps prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively.
- Probability:This refers to the likelihood of a risk occurring. It can be assessed using historical data, expert opinions, or statistical analysis.
- Impact:This refers to the potential consequences of a risk if it occurs. It can be measured in terms of cost, schedule delays, or quality degradation.
Risk assessment is crucial for prioritizing risks and allocating resources effectively.
| Risk | Probability | Impact | Risk Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Bugs | High | High | High |
| Staff Turnover | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Economic Downturn | Low | High | Medium |
Risk Response Planning, 6 essential documents for project management success
After analyzing risks, it’s essential to develop strategies for mitigating, transferring, or accepting them.
- Mitigation:This involves taking steps to reduce the probability or impact of a risk. Examples include implementing quality control measures, training staff, or securing backup resources.
- Transfer:This involves shifting the risk to another party, such as an insurance company or a vendor. Examples include purchasing insurance for equipment failure or outsourcing a critical task.
- Acceptance:This involves accepting the risk and its potential consequences. This is typically done for low-probability or low-impact risks.
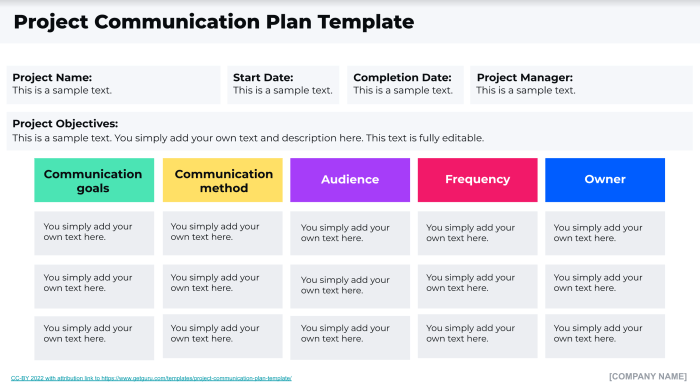
Communication Plan
A well-defined communication plan is crucial for project success. It ensures that all stakeholders are informed, engaged, and aligned throughout the project lifecycle.
Identifying Stakeholder Communication Needs
Understanding the communication needs of different stakeholders is essential for creating a tailored communication plan.
- Project Team:The project team requires frequent updates, task assignments, and clear communication about project progress, risks, and changes.
- Management:Management needs regular reports on project status, budget, and resource allocation. They also require communication regarding any potential risks or deviations from the plan.
- Customers:Customers require clear communication about project deliverables, timelines, and any potential delays or changes. They should also be informed about project progress and milestones.
- Vendors:Vendors require clear communication regarding contract terms, payment schedules, and project requirements. They also need to be informed about any changes or updates to the project plan.
Establishing Communication Channels and Frequency
Selecting the right communication channels and establishing a frequency for communication is vital for ensuring effective information sharing.
- Project Management Software:This tool allows for centralized communication, task management, and document sharing. It can be used for daily updates, progress reports, and discussions.
- Email:Email is suitable for formal communication, sending documents, and scheduling meetings. It can be used for regular updates, notifications, and project-related announcements.
- Instant Messaging:Instant messaging is effective for quick communication, addressing urgent issues, and real-time collaboration. It can be used for quick questions, updates, and discussions.
- Meetings:Meetings provide a platform for collaborative discussions, brainstorming, and decision-making. They are valuable for reviewing project progress, addressing challenges, and ensuring alignment.
Managing Communication Throughout the Project Lifecycle
Effective communication is essential throughout the project lifecycle, from initiation to closure.
- Initiation Phase:Clear communication of project objectives, scope, and deliverables is crucial. Stakeholder expectations should be established and documented.
- Planning Phase:Regular communication about project plans, timelines, and resource allocation is essential. Stakeholders should be informed about any changes or updates to the plan.
- Execution Phase:Frequent updates on project progress, milestones achieved, and any challenges encountered should be communicated. Stakeholders should be kept informed about the project’s status.
- Monitoring and Controlling Phase:Communication regarding project risks, issues, and deviations from the plan should be transparent. Stakeholders should be informed about any corrective actions taken.
- Closure Phase:Communication about project completion, lessons learned, and project outcomes should be shared with stakeholders. Feedback and appreciation for their involvement should be expressed.