
JavaScript Map Set Tutorial: Mastering Essential Data Structures
JavaScript Map Set Tutorial: Dive into the world of JavaScript’s powerful data structures, maps and sets. These versatile tools are essential for efficient data handling, allowing you to organize, access, and manipulate information with ease. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting out, understanding maps and sets will significantly enhance your coding abilities and unlock new possibilities in your JavaScript projects.
This tutorial will guide you through the fundamentals of sets and maps, exploring their unique characteristics, methods, and practical applications. We’ll delve into creating, manipulating, and iterating over these data structures, uncovering their strengths and limitations. By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how to effectively utilize sets and maps to optimize your code and achieve your programming goals.
Introduction to JavaScript Data Structures
JavaScript data structures are fundamental building blocks for organizing and manipulating data effectively. Understanding these structures is crucial for building efficient and scalable JavaScript applications.
Arrays
Arrays are ordered collections of data, allowing you to store multiple values of the same or different data types. They provide a convenient way to represent lists, sequences, or collections of related items.
- Indexed Access:Each element in an array has a unique index, starting from 0, which allows you to access and modify specific elements efficiently.
- Dynamic Size:Arrays in JavaScript are dynamic, meaning their size can change as you add or remove elements.
- Iteration:Arrays support various methods for iterating through their elements, such as loops and array methods like `forEach` and `map`.
Sets
Sets are unordered collections of unique values. They ensure that each element appears only once, eliminating duplicates.
- Uniqueness:Sets guarantee that each element is unique, preventing duplicate entries.
- Efficient Membership Testing:Sets provide efficient methods for checking if an element exists within the collection.
- Set Operations:Sets support various operations like union, intersection, and difference, enabling you to manipulate and combine sets effectively.
Maps
Maps are key-value pairs that associate unique keys with corresponding values. They provide a way to store and retrieve data based on specific keys.
- Key-Value Pairs:Maps allow you to associate values with unique keys, enabling efficient data retrieval based on keys.
- Dynamic Size:Similar to arrays, maps can grow and shrink dynamically as you add or remove key-value pairs.
- Efficient Lookup:Maps provide fast access to values based on their associated keys.
Understanding JavaScript Sets
JavaScript sets are a unique data structure that allows you to store collections of distinct values, where each value can appear only once. This means that sets maintain the uniqueness of elements, eliminating any duplicates. Sets are particularly useful when you need to perform operations that require unique values, such as finding the intersection or union of two sets.
Creating and Initializing Sets
You can create a JavaScript set using the `Set` constructor. To initialize a set with values, you can pass an iterable object, such as an array, to the constructor.“`javascript// Creating an empty setconst mySet = new Set();// Initializing a set with values from an arrayconst numbers = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4];const uniqueNumbers = new Set(numbers); // 1, 2, 3, 4“`
Adding, Deleting, and Checking Elements
Sets provide methods for adding, deleting, and checking the presence of elements.
- `add(value)`:Adds a new element to the set. If the element already exists, it does not add it again.
- `delete(value)`:Removes an element from the set.
- `has(value)`:Checks if an element exists in the set and returns a boolean value.
“`javascript// Adding elementsmySet.add(10);mySet.add(“hello”);mySet.add(10); // Does not add again, as 10 already exists// Deleting elementsmySet.delete(10);// Checking for elementsconsole.log(mySet.has(“hello”)); // trueconsole.log(mySet.has(10)); // false“`
Iterating Over Elements
You can iterate over the elements of a set using a `for…of` loop.“`javascriptfor (const value of uniqueNumbers) console.log(value);“`
Learning about JavaScript’s Map and Set data structures can be really enlightening, especially when you see how they can streamline your code. It’s like discovering a new tool in your toolbox. I was actually reminded of this while reading about Apple’s latest design trick – building a modern-day pyramid in Malaysia ! It’s a fascinating example of how even seemingly complex projects can be broken down into manageable pieces, just like how Map and Set allow you to manage data efficiently.
So, whether you’re building pyramids or complex applications, mastering JavaScript’s Map and Set is a valuable skill.
Use Cases of Sets in JavaScript Development
Sets find applications in various scenarios:
- Unique Value Validation:Sets are ideal for validating the uniqueness of data, such as user IDs or email addresses.
- Intersection and Union Operations:Sets enable efficient intersection and union operations on collections of data.
- Removing Duplicates:Sets can be used to eliminate duplicates from arrays or other iterables.
- Data Deduplication:Sets are helpful for tasks like removing duplicate entries from a database.
“`javascript// Removing duplicates from an arrayconst arrayWithDuplicates = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4];const uniqueArray = […new Set(arrayWithDuplicates)]; // [1, 2, 3, 4]“`
Exploring JavaScript Maps
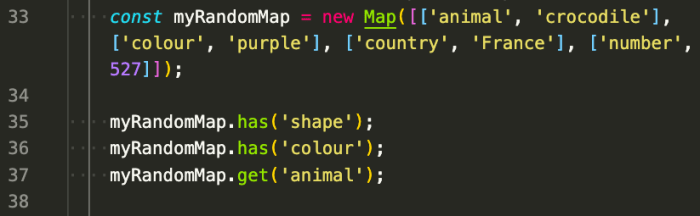
JavaScript maps are a powerful data structure that allows you to store key-value pairs. They are similar to objects, but with some key differences that make them more versatile and efficient for certain tasks.
Creating and Initializing Maps
To create a new map, you use the `new Map()` constructor. You can initialize a map with key-value pairs by passing an array of arrays to the constructor. Each inner array represents a key-value pair. “`javascriptconst myMap = new Map([ [‘name’, ‘John Doe’], [‘age’, 30], [‘occupation’, ‘Software Engineer’]]);“`This creates a map with three key-value pairs: `name` with the value `John Doe`, `age` with the value `30`, and `occupation` with the value `Software Engineer`.
Adding, Deleting, and Retrieving Values
You can add new key-value pairs to a map using the `set()` method. The `set()` method takes two arguments: the key and the value.“`javascriptmyMap.set(‘city’, ‘New York’);“`This adds a new key-value pair to the `myMap` with the key `city` and the value `New York`.To retrieve a value from a map, you use the `get()` method.
The `get()` method takes the key as an argument and returns the corresponding value.“`javascriptconst name = myMap.get(‘name’);console.log(name); // Output: John Doe“`You can delete a key-value pair from a map using the `delete()` method. The `delete()` method takes the key as an argument.“`javascriptmyMap.delete(‘age’);“`This removes the key-value pair with the key `age` from the `myMap`.
Learning about JavaScript’s Map and Set data structures is a great way to build a foundation for more complex projects. You might be surprised how handy they are for keeping track of things, like the different categories in your budget! If you’re looking for a little help organizing your finances, check out some of the best expense tracker apps to streamline your budgeting process.
Once you’ve got your finances in order, you can put your newfound knowledge of JavaScript Maps and Sets to work in building your own custom expense tracker or any other project you have in mind!
Iterating Over Key-Value Pairs
You can iterate over the key-value pairs in a map using the `forEach()` method. The `forEach()` method takes a callback function as an argument. The callback function receives three arguments: the value, the key, and the map itself.“`javascriptmyMap.forEach((value, key) => console.log(`$key: $value`););“`This will print the following output to the console:“`name: John Doeoccupation: Software Engineercity: New York“`
Use Cases of Maps
JavaScript maps are a versatile data structure with numerous use cases in JavaScript development. Here are some examples:
- Caching: Maps can be used to store frequently accessed data in memory to improve performance.
- Data Association: Maps can be used to associate data with specific keys, such as storing user preferences or mapping IDs to user objects.
- Unique Data Storage: Maps can be used to store unique data, as they only allow one value for each key.
- Counting Occurrences: Maps can be used to count the occurrences of elements in an array or string.
Comparing JavaScript Sets and Maps
JavaScript offers two unique data structures: Sets and Maps. While they share similarities in their ability to store collections of data, they differ significantly in how they organize and manage that data. Understanding their distinctions is crucial for choosing the most appropriate structure for your specific needs.
Learning about JavaScript’s Map and Set data structures can be a real game-changer for your coding journey. It’s like having a super-organized toolbox for handling unique values and key-value pairs. Speaking of unique experiences, I recently read this interesting article about how Rivian’s CEO is against adopting CarPlay, rivians ceo says theyre never adopting carplay and i think thats the right move , and it made me think about how important it is to have a distinct and well-defined approach in your own coding projects, just like Rivian is doing with their in-car system.
So, whether you’re building a complex web app or just getting started with JavaScript, understanding Map and Set will give you a powerful edge in your development journey.
Comparing Sets and Maps
Sets and Maps are both powerful tools in JavaScript, but they cater to different use cases. The table below summarizes their key characteristics, methods, and typical applications:
| Characteristic | Set | Map |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Unordered collection of unique values | Collection of key-value pairs |
| Data Type | Any data type | Any data type for keys and values |
| Duplicates | Not allowed | Allowed for values, not for keys |
| Order | Unordered | Unordered |
| Methods | add(), delete(), has(), clear(), size(), forEach(), values() |
set(), get(), delete(), has(), clear(), size(), forEach(), keys(), values(), entries() |
| Use Cases | – Removing duplicates from an array
|
– Storing key-value pairs for efficient lookups
|
Advantages and Disadvantages
Sets
Advantages
- Uniqueness Guarantee:Sets ensure that each element is stored only once, eliminating duplicates.
- Efficient Membership Testing:Checking if a value exists in a Set is very fast, as it uses a hash-based implementation.
- Simple Operations:Sets provide a concise set of methods for common operations like adding, deleting, and checking membership.
Disadvantages
- No Key-Value Association:Sets store only values, making it unsuitable for situations where you need to associate data with keys.
- Limited Functionality:Sets lack methods for retrieving specific elements by index or for sorting the elements.
Maps
Advantages
- Key-Value Pairing:Maps store data as key-value pairs, allowing you to efficiently access and manipulate data based on unique keys.
- Flexible Data Types:Keys and values can be of any data type, including objects and arrays.
- Efficient Lookups:Maps use a hash table to store key-value pairs, resulting in fast retrieval of values based on their keys.
Disadvantages
- Key Uniqueness:Keys within a Map must be unique, while values can be duplicated.
- Increased Memory Consumption:Maps typically consume more memory than Sets due to the need to store both keys and values.
Use Case Scenarios
Sets
- Unique Usernames:You can use a Set to ensure that each user in your application has a unique username.
- Duplicate Removal:A Set can be used to efficiently remove duplicates from an array of data.
- Algorithm Implementation:Sets are valuable for algorithms that require unique elements, such as graph traversal or finding the intersection of two sets.
Maps
- Caching:Maps can be used to store frequently accessed data in memory for faster retrieval, improving application performance.
- Dictionaries:Maps are ideal for representing dictionaries or associative arrays, where data is organized by key-value pairs.
- Object Management:Maps can be used to manage objects based on their unique identifiers, allowing for efficient access and manipulation.
Practical Applications of Sets and Maps
Sets and maps are powerful tools in JavaScript that can be used to solve a variety of problems. They provide efficient ways to store and retrieve data, making them ideal for tasks like removing duplicates from arrays, storing and retrieving data efficiently, implementing unique identifier systems, and tracking user preferences or activity.
Removing Duplicates from an Array
Sets are particularly useful for removing duplicates from arrays. The uniqueness property of sets ensures that each element is stored only once. To remove duplicates from an array, we can convert the array into a set, which automatically eliminates duplicates.
Then, we can convert the set back into an array, resulting in an array with only unique elements.Here’s an example:“`javascriptconst originalArray = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5];const uniqueArray = […new Set(originalArray)];console.log(uniqueArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]“`
Storing and Retrieving Data Efficiently
Maps provide a highly efficient way to store and retrieve data based on key-value pairs. The keys can be any type, including strings, numbers, objects, or even functions, allowing for flexible data organization. The lookup time for values associated with specific keys is very fast, making maps ideal for scenarios where frequent data access is required.For instance, consider a scenario where we need to store user information, such as their name, email address, and profile picture.
Using a map, we can associate each user’s unique ID with their corresponding data.“`javascriptconst users = new Map();users.set(‘user1’, name: ‘Alice’, email: ‘[email protected]’, profilePicture: ‘https://example.com/alice.jpg’ );users.set(‘user2’, name: ‘Bob’, email: ‘[email protected]’, profilePicture: ‘https://example.com/bob.jpg’ );console.log(users.get(‘user1’)); // Output: name: ‘Alice’, email: ‘[email protected]’, profilePicture: ‘https://example.com/alice.jpg’ “`
Implementing Unique Identifier Systems, Javascript map set tutorial
Sets are perfect for generating and managing unique identifiers, ensuring that each identifier is distinct. This is especially useful in applications where you need to track entities uniquely, such as users, products, or transactions.Imagine a system where each user is assigned a unique ID upon registration.
We can use a set to store these IDs, guaranteeing that no two users have the same ID.“`javascriptconst userIDs = new Set();function generateUniqueUserID() let newID; do newID = Math.random().toString(36).substring(2, 15); while (userIDs.has(newID)); userIDs.add(newID); return newID;console.log(generateUniqueUserID()); // Output: A unique IDconsole.log(generateUniqueUserID()); // Output: Another unique ID“`
Tracking User Preferences or Activity
Maps can be used to track user preferences or activity, efficiently storing and retrieving information about individual users. This is useful for personalizing user experiences, providing targeted recommendations, or analyzing user behavior.For example, we can use a map to store user preferences for different products.
Each user’s ID can be the key, and the value can be an object containing their preferred product categories, brands, or specific items.“`javascriptconst userPreferences = new Map();userPreferences.set(‘user1’, preferredCategories: [‘electronics’, ‘books’], preferredBrands: [‘Apple’, ‘Amazon’] );userPreferences.set(‘user2’, preferredItems: [‘iPhone’, ‘Kindle’] );console.log(userPreferences.get(‘user1’)); // Output: preferredCategories: [‘electronics’, ‘books’], preferredBrands: [‘Apple’, ‘Amazon’] “`
Advanced Techniques with Sets and Maps: Javascript Map Set Tutorial
In the previous sections, we explored the fundamentals of JavaScript Sets and Maps. Now, let’s delve into more advanced techniques that leverage these data structures for enhanced functionality and efficiency.
Essential Methods for Sets and Maps
These methods provide the building blocks for manipulating and extracting data from Sets and Maps.
- `has()`: This method checks if a specific element exists in a Set or a key exists in a Map. It returns a Boolean value (true or false) indicating the presence or absence of the element or key.
- `add()`: This method adds a new element to a Set. It returns the Set itself, allowing for method chaining.
- `delete()`: This method removes an element from a Set or a key-value pair from a Map. It returns a Boolean value indicating whether the removal was successful.
- `clear()`: This method removes all elements from a Set or all key-value pairs from a Map.
- `get()`: This method retrieves the value associated with a specific key in a Map.
- `set()`: This method adds a new key-value pair to a Map or updates the value associated with an existing key.
- `forEach()`: This method iterates over the elements in a Set or the key-value pairs in a Map. It takes a callback function as an argument, which is executed for each element or pair.
- `keys()`: This method returns an iterator that iterates over the keys in a Map.
- `values()`: This method returns an iterator that iterates over the values in a Map.
- `entries()`: This method returns an iterator that iterates over the key-value pairs in a Map.
Sets and Maps with Other JavaScript Concepts
Sets and Maps seamlessly integrate with other core JavaScript concepts, extending their capabilities and opening up new possibilities.
Sets and Arrays
- Creating Sets from Arrays: You can easily create a Set from an existing array by passing the array to the `Set` constructor. For example,
const mySet = new Set([1, 2, 3, 4]);creates a Set containing the elements from the array[1, 2, 3, 4]. - Removing Duplicates from Arrays: Sets inherently prevent duplicates. You can leverage this to remove duplicate elements from an array by creating a Set from the array and then converting it back to an array. For example,
const uniqueArray = [...new Set([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4])];creates a new array[1, 2, 3, 4]with only unique elements.
Sets and Asynchronous Operations
- Managing Asynchronous Results: Sets can be useful for storing and processing results from asynchronous operations, such as API calls or database queries. For example, you can use a Set to track unique IDs retrieved from an API, preventing duplicate entries.
- Preventing Race Conditions: Sets can help avoid race conditions in asynchronous operations by ensuring that only unique values are processed, even if multiple asynchronous tasks complete in close succession.
Sets and Higher-Order Functions
- Filtering and Mapping: You can use higher-order functions like `filter()` and `map()` with Sets to manipulate their elements. For example, you can filter a Set to include only elements greater than a certain value or map a Set to a new Set containing transformed values.
- Chaining Operations: Sets can be used with method chaining to perform multiple operations in a concise and readable way. For example, you can filter a Set, map its elements, and then convert it to an array using a single chain of operations.
Resources and Further Learning

This section provides a curated list of resources for delving deeper into JavaScript sets and maps. These resources include official documentation, comprehensive tutorials, and insightful articles that can further enhance your understanding of these powerful data structures.
Official Documentation
The official documentation is the most authoritative source for information on JavaScript sets and maps. It provides detailed descriptions of their methods, properties, and usage examples.
- MDN Web Docs: Set and Map offer comprehensive information on these data structures, including their methods, properties, and usage examples.
Tutorials and Articles
Numerous tutorials and articles provide step-by-step guides and practical examples for using JavaScript sets and maps.
- FreeCodeCamp: JavaScript Sets and Maps Explained presents a clear and concise explanation of these data structures, covering their fundamental concepts and common use cases.
- JavaScript.info: Set and Map offers a comprehensive tutorial that explores the intricacies of sets and maps, providing illustrative examples and practical scenarios.
- Medium: JavaScript Sets and Maps Explained with Examples presents a detailed explanation of sets and maps, accompanied by real-world examples to solidify your understanding.
Additional Topics
Beyond the core concepts of sets and maps, there are other related topics that can further expand your knowledge of JavaScript data structures.
- WeakSets and WeakMaps:These data structures offer a unique way to store objects while avoiding memory leaks by not preventing garbage collection. They are particularly useful for managing references to objects without the need for explicit cleanup.
- Data Structure Performance:Understanding the time and space complexities of different data structures, including sets and maps, is crucial for optimizing your code and choosing the most appropriate structure for your specific use case.
- Advanced Data Structures:Explore advanced data structures like trees, graphs, and heaps, which provide efficient solutions for complex data manipulation and algorithmic problems.




