Apple EU Digital Markets Act: A New Era for App Ecosystems
Apple EU Digital Markets Act sets the stage for a dramatic shift in the app ecosystem. This landmark legislation aims to curb the dominance of large tech companies, like Apple, and foster greater competition and consumer choice. The act’s impact on Apple’s business model, app developers, and consumers alike is profound, and its implications are still unfolding.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a set of rules designed to regulate the behavior of large online platforms in the European Union. The DMA specifically targets companies with “gatekeeper” status, meaning they hold significant market power in key digital services like app stores, online marketplaces, and search engines.
Apple, with its App Store and control over iOS devices, falls squarely within this category. The DMA’s primary goal is to level the playing field, ensuring that consumers have more choices and developers have greater opportunities to reach them.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA)
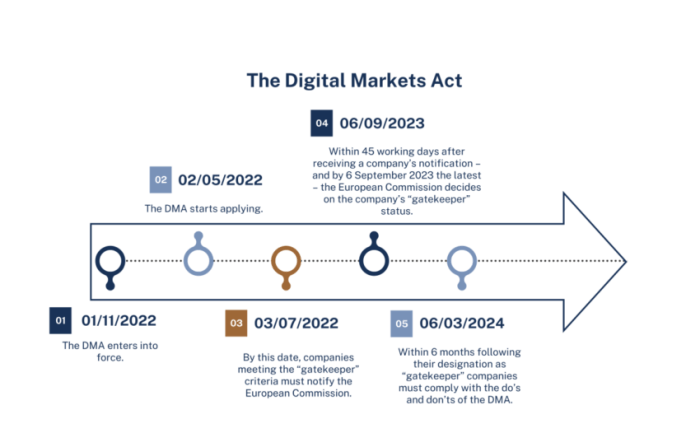
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a landmark piece of legislation adopted by the European Union in 2022, aiming to regulate the behavior of large online platforms and promote a fairer digital marketplace. This regulation is designed to address concerns about the dominance of a few tech giants and their potential to stifle competition and harm consumers.
The DMA’s Key Provisions
The DMA identifies “gatekeeper” platforms that meet specific criteria, including having a significant market share and providing core platform services. These platforms are subject to a range of obligations designed to ensure fair competition and protect consumer rights.
- Interoperability:Gatekeepers must allow users to switch between different platforms and services seamlessly. For example, a messaging app must allow users to communicate with contacts on other platforms without losing functionality.
- Data Access:Gatekeepers must provide users with access to their own data and allow businesses to access data generated on their platforms, enabling them to develop competing services.
- Non-Discriminatory Treatment:Gatekeepers must treat all businesses and users fairly, preventing them from favoring their own services or those of their partners. This includes ensuring equal access to advertising and search results.
- Transparency and Oversight:Gatekeepers must provide clear and transparent information about their algorithms and practices, and they are subject to increased scrutiny by regulators.
Rationale Behind the DMA
The DMA addresses several concerns about the power and influence of large online platforms.
- Market Dominance:The rise of a few dominant platforms has created concerns about reduced competition, limiting consumer choice and potentially leading to higher prices. The DMA aims to create a more level playing field for smaller businesses and startups.
- Consumer Rights:Concerns have been raised about the potential for gatekeepers to exploit their market power to harm consumers, for example, by collecting excessive amounts of personal data or using unfair pricing strategies. The DMA seeks to strengthen consumer rights and ensure fair treatment.
- Innovation:The DMA aims to foster innovation by promoting competition and allowing smaller businesses to access essential resources and data. This can lead to the development of new and exciting products and services.
Impact on Apple’s Business Practices
The DMA has the potential to significantly impact Apple’s business practices, particularly in areas like messaging, app distribution, and data access.
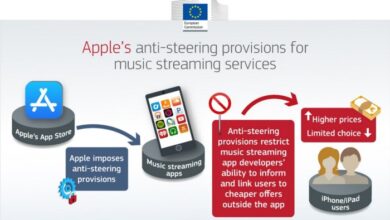
- iMessage Interoperability:The DMA could require Apple to make iMessage interoperable with other messaging platforms, allowing users to communicate with Android users without switching apps. This could potentially erode the walled garden approach that Apple has maintained for iMessage.
- App Store Competition:The DMA could require Apple to allow alternative app stores on iOS devices, potentially increasing competition and reducing Apple’s control over the app distribution process. This could lead to a more diverse app ecosystem and potentially lower prices for consumers.
- Data Access:The DMA could require Apple to provide businesses with access to data generated on iOS devices, enabling them to develop competing services. This could potentially impact Apple’s ability to leverage user data for its own products and services.
Apple’s Business Model and the DMA: Apple Eu Digital Markets Act

The Digital Markets Act (DMA) aims to regulate large online platforms, including Apple, to ensure fair competition and consumer protection. Understanding Apple’s business model is crucial to analyzing how the DMA might impact its operations and revenue streams.
Apple’s Current Business Model
Apple’s business model relies heavily on its control over the app distribution and in-app purchase ecosystem within its iOS operating system. This strategy has been incredibly successful, generating substantial revenue for the company.
- App Store:The App Store is a central platform for distributing apps to iOS devices. Apple controls the distribution process, setting the rules and regulations for app developers. This allows Apple to collect a 30% commission on all app purchases and in-app transactions, generating significant revenue.
- In-App Purchases:Apple’s in-app purchase system allows users to buy digital goods and services within apps. This system also generates a 30% commission for Apple, further contributing to its revenue.
Potential Conflicts with the DMA, Apple eu digital markets act
The DMA’s regulations aim to address potential anti-competitive practices by large online platforms. Some of Apple’s practices might fall under scrutiny under the DMA’s provisions.
- Mandatory App Distribution:The DMA requires large platforms to allow alternative app stores and payment systems. Apple’s current model restricts app distribution to its own App Store, which could be considered a violation of the DMA’s requirement for interoperability.
- High Commission Fees:The DMA might challenge Apple’s 30% commission on app purchases and in-app transactions. This fee has been criticized as being excessive and potentially hindering competition.
- Data Access and Privacy:The DMA emphasizes user data protection and access. Apple’s data collection practices, including its use of user data for targeted advertising, might be subject to scrutiny under the DMA.
Potential Impact on Apple’s Revenue Streams
The DMA’s regulations could potentially impact Apple’s revenue streams in several ways.
- Reduced App Store Revenue:If the DMA forces Apple to allow alternative app stores, it could lead to a decrease in the App Store’s market share and, consequently, lower revenue from app purchases and in-app transactions.
- Lower Commission Fees:The DMA could force Apple to reduce its commission fees on app purchases and in-app transactions, directly impacting its revenue.
- Increased Competition:The DMA’s regulations could encourage more competition in the app distribution and in-app purchase market, potentially leading to lower prices and a decline in Apple’s market share.
The EU Digital Markets Act aims to create a fairer and more competitive digital landscape, and while that’s a serious topic, it’s also a good reminder that sometimes you need a break from the complexities of regulation. If you’re looking for a fun and easy way to unwind, why not check out these last minute costume ideas for couples ?
After all, a little laughter and creativity can go a long way in reminding us that even in the face of complex regulations, there’s always room for a little fun.
The EU’s Digital Markets Act is putting pressure on tech giants like Apple to loosen their grip on their ecosystems, which could have a significant impact on the supply chain for critical materials. This is especially relevant as we see companies like Titan, who recently appointed a new president to bolster their leadership in advancing the U.S.
domestic supply of critical materials , work to secure these resources. The DMA could force Apple to open up its devices to other manufacturers, potentially disrupting the current supply chain and creating opportunities for companies like Titan to fill the void.
The EU Digital Markets Act is definitely shaking things up for Apple, especially when it comes to their mobile gaming ecosystem. It’s interesting to see how Apple is responding with the iPhone 16, and what kind of performance enhancements they’re bringing to the table for gamers.
You can check out every mobile gaming upgrade coming with iPhone 16 so far to get a sense of what’s in store. Ultimately, the EU Digital Markets Act is forcing Apple to become more transparent and open, which could lead to more competition and innovation in the mobile gaming space.