Apple DMA: App Store Changes for Developers
Apple dma app store changes app developers – Apple DMA: App Store Changes for Developers sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The Digital Markets Act (DMA), a landmark European Union legislation, has spurred significant changes to Apple’s App Store, directly impacting app developers and reshaping the competitive landscape of the app market.
This shift, driven by the DMA’s aim to promote fairness and competition, has created a ripple effect across the entire app ecosystem, influencing everything from app discovery to pricing strategies.
The DMA’s key provisions, which include allowing app developers to use alternative payment systems and limiting Apple’s ability to restrict app distribution, have forced Apple to adapt its practices. These changes have the potential to empower app developers, enabling them to reach a wider audience and potentially negotiate more favorable terms with Apple.
However, the transition is not without its challenges, as developers grapple with navigating new regulations and adapting their business models to a more competitive environment.
Apple’s DMA and App Store Changes
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a new set of regulations from the European Union that aims to increase competition in the digital marketplace. The DMA specifically targets large tech companies like Apple, Google, and Amazon, with the goal of making their platforms more open and interoperable.
This legislation has significant implications for Apple’s App Store, as it requires changes to how Apple operates its platform.
Key Provisions of the DMA Impacting Apple’s App Store
The DMA mandates several changes to how Apple operates its App Store, aiming to create a more open and competitive ecosystem.
- Sideloading:The DMA requires Apple to allow users to install apps from sources other than the App Store. This means users can download apps directly from developers’ websites or third-party app stores, bypassing Apple’s App Store entirely.
- Interoperability:The DMA requires Apple to make its messaging and communication services interoperable with other platforms. This means users should be able to communicate with people using other messaging apps without having to switch platforms.
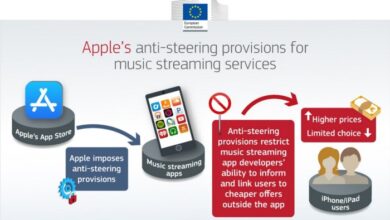
- Payment System Alternatives:The DMA mandates Apple to allow developers to use alternative payment systems in their apps, giving them more control over how they monetize their apps and reducing Apple’s 30% commission on in-app purchases.
- Transparency and Non-Discriminatory Treatment:The DMA requires Apple to be more transparent about its App Store policies and practices. This includes providing developers with clear and non-discriminatory guidelines for app submissions and reviews.
Apple’s Response to the DMA
In response to the DMA, Apple has made several changes to its App Store.
- Sideloading:Apple has announced that it will comply with the DMA’s sideloading requirements, allowing users to install apps from sources other than the App Store. However, Apple plans to implement security measures to protect users from malicious apps.
- Interoperability:Apple has confirmed that it will comply with the DMA’s interoperability requirements, allowing users to communicate with people using other messaging apps. However, Apple is still exploring how to best implement these requirements while maintaining its focus on user privacy and security.
The recent changes to Apple’s DMA App Store policies have certainly shaken things up for app developers, forcing them to adapt and find new ways to reach their audience. It’s like a whole new landscape out there, and just like you might need a fresh pair of stylish glasses to navigate a new environment, developers are searching for new strategies.
Maybe a touch of inspiration from the retro-chic aesthetic of palm springs inspired glasses cases could spark some innovative ideas for app promotion – a splash of color, a touch of vintage charm, and a whole lot of personality!
- Payment System Alternatives:Apple has announced that it will allow developers to use alternative payment systems in their apps, but only for apps that are not offered in the App Store. This means developers can use alternative payment systems for apps they distribute directly to users, but they still need to use Apple’s payment system for apps in the App Store.
- Transparency and Non-Discriminatory Treatment:Apple has published new guidelines for app developers, aiming to provide more transparency and clarity on its App Store policies. Apple has also stated that it will work to ensure that its App Store policies are applied in a fair and non-discriminatory manner.
Comparison of the App Store Before and After DMA Changes
The DMA’s impact on Apple’s App Store is significant, creating a more open and competitive environment.
- Before DMA:Apple had complete control over app distribution and monetization within the App Store. Developers had to comply with Apple’s strict policies and pay a 30% commission on in-app purchases.
- After DMA:Developers will have more options for app distribution and monetization. They can choose to distribute their apps outside the App Store, use alternative payment systems, and negotiate different commission rates with Apple.
Impact on App Developers
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) and the subsequent App Store changes are poised to significantly impact app developers, presenting both opportunities and challenges. The DMA aims to foster competition and give app developers more control over their distribution and monetization strategies.
Potential Benefits
The DMA’s provisions offer potential benefits for app developers by creating a more level playing field and reducing reliance on app stores like the Apple App Store.
The recent changes to Apple’s DMA App Store policies have sparked a lot of discussion about the future of app development. It’s interesting to see how these changes might impact the overall mobile app market, especially in light of the recent Microsoft report on the impact of AI on the UK economy.
It’s clear that technology is rapidly evolving, and developers need to adapt to these changes to stay competitive.
- Increased Competition:The DMA encourages alternative app stores, potentially leading to more choices for developers and users. This competition could drive down app store fees and offer more favorable terms for developers.
- Greater Control over Distribution:Developers may have the option to distribute their apps outside of app stores, giving them more control over pricing, marketing, and user acquisition.
- Monetization Flexibility:The DMA could allow developers to use alternative payment systems, reducing reliance on app store in-app purchase systems and potentially increasing their revenue share.
- Enhanced Transparency:The DMA mandates transparency from app stores regarding their algorithms and data usage, providing developers with valuable insights into app store operations.
Challenges Faced by App Developers
While the DMA presents opportunities, app developers may also face challenges in adapting to the new landscape.
- Compliance Costs:Implementing the DMA’s requirements, such as offering alternative payment systems, may require significant technical and financial resources for developers.
- Navigating Multiple App Stores:Developers may need to adapt their distribution strategies to reach users across different app stores, increasing their workload and marketing expenses.
- Potential for Fragmentation:The emergence of multiple app stores could lead to app fragmentation, making it harder for developers to reach a large user base and manage updates across different platforms.
- Uncertainty in App Store Policies:As the DMA’s implementation unfolds, developers may face uncertainty regarding app store policies and potential changes in the future.
Examples of App Developers Affected by the DMA and App Store Changes
The DMA’s impact on app developers is already being felt.
- Spotify:The music streaming service Spotify has been vocal about its concerns regarding Apple’s App Store fees, arguing that they stifle competition and limit its revenue. The DMA’s provisions could potentially allow Spotify to offer alternative payment systems and reduce its reliance on Apple’s in-app purchase system.
- Epic Games:The developer of Fortnite has been engaged in a long-standing legal battle with Apple over its App Store policies. The DMA’s provisions could provide support for Epic Games’ arguments regarding antitrust concerns and the need for more competition in the app store market.
The Apple DMA App Store changes are forcing app developers to think outside the box. I’m finding myself looking for ways to enhance my productivity and creative workflow, and that’s where a top-notch keyboard like the Razer Huntsman V3 Pro Tenkeyless comes in.
It’s a game-changer for Mac users, providing the precision and responsiveness I need to navigate the new landscape of app development. I’m confident that these changes, combined with the right tools, will lead to a more innovative and exciting future for app development.
Competition and Market Dynamics

The DMA and App Store changes are poised to significantly impact the competitive landscape of the app market, potentially reshaping the power dynamics between Apple and app developers. These changes could usher in a new era of competition, fostering innovation and consumer choice.
Increased Competition
The DMA mandates that Apple open up its App Store to alternative app stores, creating a more competitive environment. This could lead to:
- More app stores:Developers will have more options for distributing their apps, potentially leading to a proliferation of app stores.
- Lower fees:Increased competition among app stores could drive down commission fees, benefiting developers.
- Greater choice for users:Consumers will have access to a wider range of apps and app stores, potentially leading to greater choice and lower prices.
This increased competition could potentially lead to a more fragmented app market, where developers may need to distribute their apps across multiple platforms to reach a wider audience.
Shifting Power Dynamics
The DMA’s provisions could significantly alter the power dynamics between Apple and app developers. By allowing developers to bypass Apple’s App Store and its stringent review process, the DMA could:
- Empower developers:Developers will have more control over how they distribute their apps and interact with users.
- Reduce Apple’s control:Apple’s dominance over the app ecosystem could be diminished, leading to a more level playing field for developers.
- Encourage innovation:With less reliance on Apple’s platform, developers may be more inclined to experiment with new app models and business models.
This shift in power could also lead to increased competition in the development of new technologies and services, as developers explore alternative platforms and distribution channels.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of the DMA and App Store changes are still unfolding. However, some potential outcomes include:
- Increased innovation:With greater freedom and competition, developers may be more likely to innovate and introduce new app categories and features.
- New business models:The changes could lead to the emergence of new business models for app development and distribution, potentially including subscription services and alternative payment systems.
- A more diverse app ecosystem:The changes could foster a more diverse app ecosystem, with a wider range of apps and developers catering to different user needs and preferences.
However, it is important to note that these changes could also lead to challenges, such as increased fragmentation and security concerns.
Consumer Impact
The DMA and App Store changes are designed to create a more competitive and open app ecosystem, which can have significant benefits for consumers. These changes could lead to lower prices, more choices, and improved app discovery.
Increased Competition and Choice
The DMA and App Store changes are intended to increase competition in the app market by allowing developers to distribute their apps through alternative app stores. This could lead to a wider range of apps available to consumers, as developers will be less reliant on Apple’s App Store.
Consumers could also benefit from lower prices as developers compete for customers. For example, a study by the Coalition for App Fairness found that app prices on the Google Play Store are significantly lower than on the Apple App Store, suggesting that increased competition can lead to lower prices for consumers.
Improved App Discovery
The DMA and App Store changes could also improve app discovery for consumers. Currently, Apple’s App Store algorithms can make it difficult for new or smaller apps to gain visibility. By allowing alternative app stores to operate, consumers will have access to a wider range of apps and can discover apps that might not be featured prominently on the Apple App Store.
This could lead to consumers finding apps that better meet their needs and interests.
Examples of Consumer Impact
Several examples illustrate how these changes could impact consumers. For example, Epic Games, the developer of Fortnite, has been a vocal critic of Apple’s App Store policies. Epic Games argued that Apple’s policies were anti-competitive and prevented developers from offering consumers lower prices.
In 2020, Epic Games launched its own payment system in Fortnite, which violated Apple’s App Store guidelines. As a result, Apple removed Fortnite from the App Store. This situation highlights the potential benefits of increased competition in the app market, as it could allow developers to offer consumers alternative payment options and potentially lower prices.
Future of App Stores: Apple Dma App Store Changes App Developers
The DMA and App Store changes are not just about immediate changes in the way apps are distributed. They are laying the foundation for a fundamentally different app store landscape in the future. These changes are likely to influence how app stores operate, the business models they adopt, and the overall experience for developers and consumers.
Potential New Business Models, Apple dma app store changes app developers
The increased competition and flexibility brought about by the DMA could lead to the emergence of new business models for app stores.
- Subscription-based app stores: App stores might offer subscription tiers with varying levels of access to features, content, or even app downloads. This could be particularly attractive for developers who offer a suite of related apps or services.
- App store marketplaces: The DMA could foster the development of app store marketplaces where developers can directly connect with users and sell their apps without relying on a centralized platform. This could allow for more direct relationships and potentially lower fees for developers.
- Specialized app stores: The rise of niche app stores focused on specific industries or user segments could emerge. This could cater to the needs of developers targeting specialized audiences and offer a more curated experience for users.