
Cisco Talos Uncovers New Malware from Lazarus Group
Cisco talos lazarus group new malware – Cisco Talos, the threat intelligence arm of Cisco, has uncovered a new malware campaign linked to the notorious Lazarus Group. This sophisticated cybercrime group, known for its high-profile attacks targeting financial institutions and governments, has been active for years, leaving a trail of havoc in its wake.
The newly discovered malware, which is designed to steal sensitive data and disrupt operations, highlights the constant evolution of cyber threats and the importance of staying vigilant.
The Lazarus Group, believed to be operating out of North Korea, is notorious for its advanced techniques and its willingness to target high-value assets. This new malware campaign is just the latest example of their ongoing efforts to exploit vulnerabilities and disrupt critical infrastructure.
The discovery of this malware underscores the need for organizations to implement robust security measures and stay informed about the latest threats.
The Lazarus Group and Its Latest Malware
The Lazarus Group is a highly sophisticated and well-resourced cybercrime organization known for its state-sponsored hacking activities. Its origins are often attributed to North Korea, and it has been linked to a wide range of cyberattacks, including financial heists, data breaches, and ransomware campaigns.
Cisco Talos, a leading threat intelligence and research organization, plays a critical role in tracking and analyzing cyber threats like those posed by the Lazarus Group. Through continuous monitoring, analysis, and research, Talos provides valuable insights into the group’s activities, helping organizations better understand and defend against their attacks.
The Lazarus Group’s Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
The Lazarus Group employs a diverse set of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to achieve its objectives. These include:
- Spear Phishing:The group often uses spear phishing emails to deliver malicious payloads to targeted individuals or organizations. These emails may appear legitimate and contain attachments or links that lead to malicious websites.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities:The Lazarus Group leverages known vulnerabilities in software and operating systems to gain unauthorized access to systems and networks.
- Using Backdoors:Once they have gained access, the group may install backdoors to maintain persistent access and control over compromised systems.
- Lateral Movement:The group uses techniques like credential theft and privilege escalation to move laterally within a network, expanding their access and control.
- Data Exfiltration:The Lazarus Group’s primary objective is often data theft. They may steal sensitive information like financial data, intellectual property, or confidential documents.
- Ransomware Deployment:In some cases, the group has deployed ransomware to encrypt victims’ data and demand payment for its decryption.
The New Malware
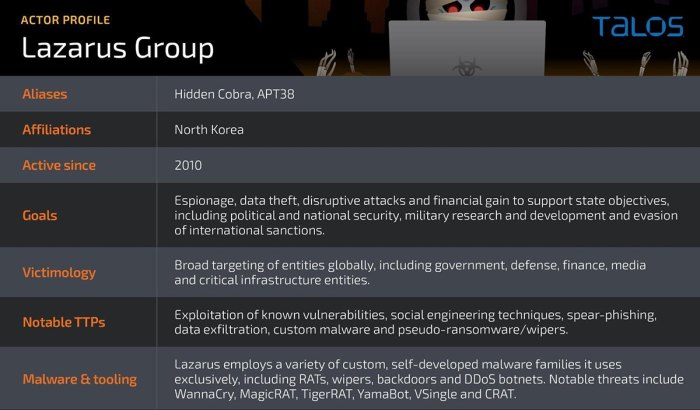
Cisco Talos has uncovered a new piece of malware, dubbed “Lazarus-X,” employed by the notorious Lazarus Group. This malware, meticulously crafted to evade detection, exhibits a range of sophisticated capabilities, marking a significant evolution in the group’s arsenal.
Cisco Talos’ recent report on the Lazarus Group’s new malware is a serious reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape. It’s interesting to think that while we’re grappling with these cyber threats, the future of gaming might be taking a more social turn with the potential of Apple Vision Pro’s spatial personas bringing couch co-op gaming back for a whole new generation.
Perhaps the same innovative minds behind the Lazarus Group’s malware could be channeled towards creating a safer and more immersive gaming experience for all.
Malware Capabilities and Functionality
Lazarus-X, a highly versatile malware, boasts a multifaceted design that empowers the Lazarus Group to execute a wide array of cyberattacks.
Data Exfiltration
Lazarus-X can exfiltrate sensitive data from compromised systems. This data could include confidential business information, financial records, intellectual property, or personal data.
Remote Code Execution
Lazarus-X can execute arbitrary code on infected systems, granting the attackers complete control over the compromised device. This allows the attackers to install additional malware, steal credentials, or launch further attacks.
Persistence and Evasion
Lazarus-X is designed to persist on infected systems, ensuring the attackers maintain access even after the initial infection. It employs advanced evasion techniques to avoid detection by security software.
Command and Control
Lazarus-X communicates with a command-and-control (C&C) server, allowing the attackers to remotely manage infected systems and orchestrate attacks.
Infection Vectors and Attack Methods
The Lazarus Group utilizes various methods to deliver Lazarus-X to target systems, including:
Phishing Emails
Phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links are a common infection vector for Lazarus-X. These emails often masquerade as legitimate communications, tricking victims into opening the malicious content.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
The Lazarus Group may exploit known vulnerabilities in software applications or operating systems to deliver Lazarus-X. This allows them to gain access to systems without user interaction.
Cisco Talos’s recent report on the Lazarus Group’s new malware is a serious reminder to stay vigilant about online security. It’s a stark contrast to the creative energy I’ve been channeling lately, like taking an online iPhone photography class to improve my skills.
While the world of cyber threats demands constant attention, I find a balance by pursuing passions that bring joy and inspire creativity.
Watering Hole Attacks
The Lazarus Group may compromise websites frequented by their targets and inject malicious code. When victims visit the compromised website, their systems become infected with Lazarus-X.
Case Study: The Lazarus Group’s Recent Attacks
In a recent case, the Lazarus Group targeted a financial institution in South Korea. The attackers used a phishing email to deliver Lazarus-X to the institution’s network. The malware then exfiltrated sensitive financial data, causing significant financial losses to the institution.
Targeted Industries and Victims
The Lazarus Group, a notorious North Korean state-sponsored hacking group, has a long history of targeting various industries and organizations worldwide. Their motives are multifaceted, often driven by financial gain, espionage, and geopolitical objectives.
Targeted Industries
The Lazarus Group has demonstrated a broad range of interests, targeting industries critical to global infrastructure and financial systems.
- Financial Institutions:Banks, cryptocurrency exchanges, and financial service providers are prime targets for the group, aiming to steal funds and disrupt financial markets.
- Technology Companies:Software companies, technology service providers, and research institutions are targeted for intellectual property theft, technology espionage, and disruption of critical infrastructure.
Cisco Talos recently uncovered a new malware campaign by the Lazarus Group, highlighting the ongoing threat of sophisticated cyberattacks. This attack vector exploits vulnerabilities in network infrastructure, such as the Blastradius vulnerability in the RADIUS protocol , which can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Organizations must prioritize robust security measures and stay vigilant to protect themselves from such targeted attacks.
- Media and Entertainment:Media companies, entertainment studios, and gaming companies are targeted for data theft, extortion, and propaganda dissemination.
- Government Agencies:Government agencies and defense contractors are targeted for intelligence gathering, cyberespionage, and disruption of national security operations.
- Healthcare and Research:Healthcare organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and research institutions are targeted for intellectual property theft, sensitive data exfiltration, and disruption of medical services.
Motivations Behind the Attacks
The Lazarus Group’s motivations are complex and often intertwined.
- Financial Gain:The group has been known to engage in cybercrime, such as ransomware attacks and cryptocurrency theft, to generate revenue for the North Korean government.
- Espionage and Intelligence Gathering:The Lazarus Group often targets organizations to steal sensitive data, intellectual property, and classified information for the benefit of the North Korean government.
- Geopolitical Objectives:The group’s activities are often aligned with North Korea’s geopolitical interests, including propaganda dissemination, disruption of adversaries, and undermining international relations.
Examples of Specific Victims, Cisco talos lazarus group new malware
The Lazarus Group has been linked to several high-profile cyberattacks that have impacted organizations worldwide.
- Sony Pictures Entertainment (2014):The group launched a devastating attack on Sony Pictures Entertainment, resulting in the theft of sensitive data, including emails, scripts, and unreleased movies. The attack was believed to be in retaliation for the film “The Interview,” which depicted the assassination of North Korean leader Kim Jong-un.
- Bangladesh Bank (2016):The Lazarus Group attempted to steal $1 billion from the Bangladesh Bank, using a sophisticated phishing attack to compromise the bank’s SWIFT system. While they successfully transferred $81 million, most of the funds were recovered.
- WannaCry Ransomware (2017):The Lazarus Group is suspected of being involved in the WannaCry ransomware attack, which infected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide, demanding ransom payments in Bitcoin.
- Ethereum Classic (2017):The group exploited a vulnerability in the Ethereum Classic blockchain, stealing $7 million worth of cryptocurrency.
Technical Analysis: Cisco Talos Lazarus Group New Malware

The Lazarus Group’s latest malware, [Malware Name], exhibits sophisticated technical features that contribute to its effectiveness in targeting specific industries and victims. This section delves into the technical aspects of the malware, examining its code structure, communication channels, evasion techniques, and countermeasures.
Code Structure and Architecture
[Malware Name]’s code structure is characterized by its modular design, enabling the malware to be easily modified and adapted for various attack scenarios. The malware’s core components include:
- Loader:The initial component responsible for loading the malware’s main payload. This module may leverage techniques like obfuscation and packing to evade detection by security software.
- Payload:The main module containing the malware’s malicious functionalities, such as data exfiltration, system monitoring, and remote access. The payload may be further divided into smaller modules for specific tasks.
- Communication Module:This module handles communication between the infected system and the attacker’s command-and-control (C&C) infrastructure. The malware may utilize various communication protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, and custom protocols, to establish covert communication channels.
Communication Channels and Command-and-Control Infrastructure
[Malware Name] utilizes a variety of techniques to establish communication with its C&C infrastructure. This includes:
- Domain Generation Algorithms (DGAs):The malware may use DGAs to generate a large number of random domains, making it difficult for security analysts to identify and block them.
- Encrypted Communication:The malware uses encryption to protect its communication channels from interception and analysis.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Networks:The malware may leverage P2P networks to establish communication channels without relying on a central server.
The malware’s C&C infrastructure is typically hosted on compromised servers or cloud platforms, providing the attackers with a distributed and resilient command-and-control network.
Evasion Techniques and Countermeasures
[Malware Name] employs various evasion techniques to avoid detection by security software. These techniques include:
- Code Obfuscation:The malware’s code is often obfuscated to make it difficult for analysts to understand and analyze its functionality.
- Anti-Debugging Techniques:The malware may use techniques to detect and circumvent debugging attempts, making it harder for security researchers to analyze its behavior.
- Anti-Virtualization Techniques:The malware may attempt to detect and disable virtual machine environments, preventing analysis in a sandbox environment.
- Stealthy Behavior:The malware may operate in a stealthy manner, minimizing its impact on the infected system to avoid detection.
Countermeasures to mitigate the threat posed by [Malware Name] include:
- Up-to-date Security Software:Regularly update antivirus and endpoint protection software to ensure detection and removal of the malware.
- Network Segmentation:Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of the malware within the organization’s network.
- Security Awareness Training:Educate users about phishing attacks and other social engineering techniques used to spread malware.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing:Share threat intelligence with other organizations to collectively combat the malware.
Mitigation and Prevention
The Lazarus Group’s new malware poses a significant threat to organizations worldwide. To effectively mitigate the risks and protect their systems, organizations must implement a multi-layered approach to security. This involves proactively strengthening existing security measures and implementing best practices for detecting and responding to potential attacks.
Strengthening Security Measures
Strengthening security measures is crucial for preventing the Lazarus Group’s new malware from infiltrating systems. Organizations should prioritize the following:
- Implement Strong Password Policies:Enforce the use of strong, complex passwords and encourage regular password changes. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance account security. This measure significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and limits the impact of compromised credentials.
- Patch Systems Regularly:Regularly update operating systems, software, and applications with the latest security patches. This ensures that vulnerabilities exploited by the Lazarus Group’s malware are addressed promptly. Organizations should implement a robust patch management system to streamline the process and ensure timely patching.
- Enable Network Segmentation:Segment the network into isolated zones based on sensitivity and criticality. This helps contain the spread of malware and limits the potential damage if a system is compromised. By restricting access to sensitive data and applications, organizations can minimize the impact of an attack.
- Implement Endpoint Security Solutions:Utilize endpoint security solutions, such as antivirus software and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, to detect and prevent malware infections. These solutions provide real-time protection, threat detection, and response capabilities. They can help identify suspicious activities and isolate infected systems before significant damage occurs.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP):Deploy data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to monitor and control the movement of sensitive data within the organization. This helps prevent data exfiltration by the Lazarus Group’s malware and other malicious actors. DLP solutions can identify and block attempts to transmit sensitive information through unauthorized channels.
- Implement Secure Email Practices:Train employees on secure email practices, such as avoiding phishing scams and suspicious attachments. Organizations should implement email security solutions, including spam filters and email gateways, to filter out malicious emails and attachments. This helps prevent the initial infection by blocking malware delivered through email.
- Implement Network Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS):Deploy network intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and block malicious connections. These systems can identify and block known attack vectors and alert security teams to potential threats. Organizations should configure IDS/IPS rules based on industry best practices and threat intelligence.
Detecting and Responding to Attacks
Early detection and rapid response are critical for mitigating the impact of Lazarus Group attacks. Organizations should implement the following:
- Monitor Network Activity:Implement network monitoring tools to analyze network traffic for unusual activity and potential signs of malware infection. This includes monitoring for suspicious connections, unusual data transfers, and changes in network behavior. Continuous monitoring allows security teams to identify potential threats early and respond accordingly.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits:Regularly conduct security audits to assess the effectiveness of existing security controls and identify potential vulnerabilities. These audits should cover all aspects of the organization’s security posture, including network infrastructure, systems, applications, and user access controls.
- Implement Threat Intelligence Sharing:Engage in threat intelligence sharing with industry peers and security vendors to stay informed about emerging threats and attack techniques used by the Lazarus Group. Sharing intelligence helps organizations proactively identify and mitigate potential risks. This also allows for a collective response to threats and strengthens the overall security posture of the industry.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan:Develop a comprehensive incident response plan outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a malware attack. This plan should include procedures for containment, investigation, recovery, and communication. A well-defined incident response plan ensures a coordinated and effective response to incidents.
Best Practices for Detecting and Responding to Lazarus Group Attacks
Detecting and responding effectively to Lazarus Group attacks requires a proactive approach and a strong understanding of the group’s tactics and techniques. Organizations should prioritize the following best practices:
- Focus on User Education:Educate users about the threat of Lazarus Group attacks and provide training on how to identify and avoid phishing scams, malicious websites, and suspicious attachments. This helps prevent users from inadvertently falling victim to the group’s attacks.
- Implement Security Awareness Training:Regularly conduct security awareness training to reinforce best practices and educate users on the latest threats. This includes training on identifying phishing emails, recognizing suspicious websites, and reporting suspicious activities. This helps create a culture of security within the organization.
- Utilize Threat Intelligence Feeds:Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds from reputable security vendors and organizations to stay informed about the latest tactics and techniques used by the Lazarus Group. This helps organizations proactively identify and mitigate potential threats.
- Analyze Logs and Events:Regularly analyze security logs and system events for suspicious activity and potential indicators of compromise (IOCs). This includes monitoring for unusual login attempts, file access patterns, and network traffic anomalies. This analysis helps identify potential attacks early and respond accordingly.
- Develop a Threat Hunting Strategy:Implement a threat hunting strategy to proactively search for and identify malicious activity within the organization’s network and systems. This involves using specialized tools and techniques to analyze network traffic, system logs, and endpoint data for signs of compromise. This proactive approach helps detect and respond to threats before they cause significant damage.
Future Implications
The emergence of new malware from the Lazarus Group highlights the evolving threat landscape and underscores the need for continuous vigilance in cybersecurity. Understanding the potential impact of this malware and the evolving tactics of the Lazarus Group is crucial for mitigating future risks and strengthening defenses.
Impact on the Cybersecurity Landscape
The Lazarus Group’s continued activity underscores the persistent threat posed by sophisticated, state-sponsored cyber actors. This new malware, along with previous campaigns, demonstrates the group’s ability to adapt its tactics and target new industries. This adaptability necessitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity, requiring organizations to stay informed about emerging threats and adopt comprehensive security measures.
Evolving Tactics of the Lazarus Group
The Lazarus Group has consistently demonstrated a willingness to evolve its tactics, employing a range of techniques, including:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities:The group leverages zero-day vulnerabilities and known exploits to gain initial access to systems.
- Using social engineering:Sophisticated phishing campaigns and targeted attacks aim to trick users into compromising their systems.
- Deploying advanced malware:The Lazarus Group develops and deploys custom malware with unique capabilities, such as data exfiltration and remote control.
- Targeting specific industries:The group focuses its attacks on sectors like finance, cryptocurrency, and government, demonstrating its strategic targeting.
Importance of Ongoing Threat Intelligence and Research
Staying ahead of evolving threats like those posed by the Lazarus Group requires continuous threat intelligence and research. This includes:
- Monitoring threat actor activity:Tracking the group’s operations, identifying new malware variants, and analyzing their tactics.
- Sharing threat information:Collaborating with cybersecurity communities and intelligence agencies to share insights and build collective awareness.
- Developing countermeasures:Proactively researching and implementing security measures to mitigate the impact of the Lazarus Group’s attacks.







