Edge Computing & Cloud Computing: A Powerful Duo
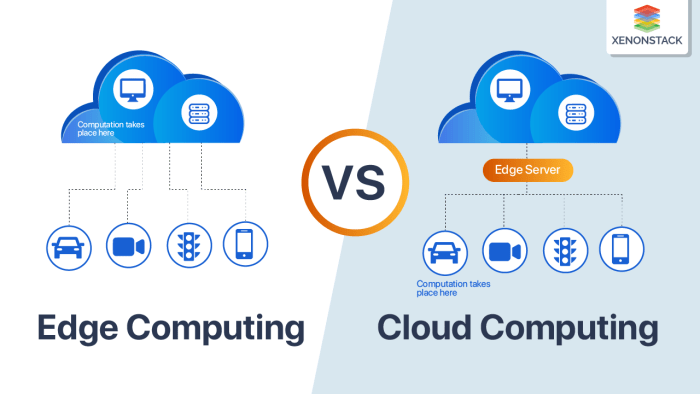
Edge computing cloud computing, a dynamic duo revolutionizing the digital landscape, has emerged as a potent force driving innovation across various industries. Edge computing, in essence, brings processing power closer to the source of data, reducing latency and enhancing real-time responsiveness.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, provides a scalable and flexible infrastructure for storing and managing data in a centralized location. Together, they offer a synergistic approach to data management, enabling businesses to leverage the benefits of both distributed and centralized computing power.
The rise of edge computing has been fueled by the increasing demand for low-latency applications, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and autonomous vehicles. Edge computing allows for faster data processing and analysis, leading to more efficient operations and improved decision-making.
Meanwhile, cloud computing continues to provide a robust foundation for data storage, backup, and large-scale computing tasks. The integration of these two technologies creates a powerful ecosystem that empowers businesses to optimize their operations and unlock new possibilities.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: Edge Computing Cloud Computing
Edge computing and cloud computing are two popular computing paradigms that have revolutionized how we access and process data. While both offer numerous advantages, they differ significantly in their architecture, performance characteristics, and use cases. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right approach for specific applications.
Comparing Edge and Cloud Computing
This table provides a comprehensive comparison of edge computing and cloud computing across key factors:
| Factor | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low latency due to data processing closer to the source. | Higher latency due to data traveling to remote data centers. |
| Security | Enhanced security with data processed locally, reducing exposure to external threats. | Security risks associated with data transmission and storage in remote data centers. |
| Scalability | Scalability limited by the capacity of edge devices and infrastructure. | Highly scalable with the ability to handle large volumes of data and users. |
| Cost | Higher initial deployment costs due to the need for edge infrastructure. | Lower initial costs but potential for higher ongoing costs due to data transfer and storage. |
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Approach
Edge computing excels in scenarios demanding low latency, real-time data processing, and enhanced security. For example, autonomous vehicles rely on edge computing for rapid decision-making based on sensor data. On the other hand, cloud computing shines in applications requiring high scalability, centralized data management, and cost-effectiveness.
For instance, social media platforms leverage cloud computing to manage vast user data and provide global access.
Hybrid Architectures
Hybrid architectures combine the strengths of both edge and cloud computing, offering a balanced approach. For example, a manufacturing plant might use edge computing for real-time process monitoring and control while leveraging cloud computing for data analytics and storage. This approach allows for optimal performance, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Future Trends and Developments in Edge Computing
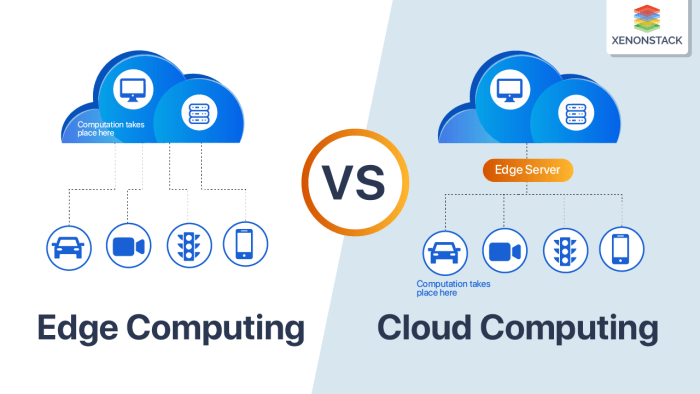
Edge computing is a rapidly evolving field with immense potential to transform various industries and aspects of our lives. Its ability to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time responsiveness, makes it a crucial technology for the future.
This section explores some key trends and developments that are shaping the landscape of edge computing.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The convergence of edge computing with emerging technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) is unlocking new possibilities and driving innovation.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology offers decentralized and secure data storage and management, making it ideal for edge computing environments. This combination can enhance data integrity, security, and transparency, particularly in applications involving sensitive data or transactions. For example, in supply chain management, blockchain on edge devices can track products from origin to delivery, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms, especially those focused on machine learning and deep learning, can be deployed on edge devices to enable real-time analysis and decision-making. This capability is crucial for applications like predictive maintenance, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. Edge AI can analyze sensor data from devices and equipment, detect anomalies, and initiate corrective actions, minimizing downtime and improving efficiency.
Edge Computing in the Metaverse and Emerging Digital Spaces
Edge computing plays a vital role in enabling immersive and interactive experiences in the metaverse and other emerging digital spaces.
- Metaverse: The metaverse, a virtual world where users can interact and experience digital environments, relies heavily on edge computing for low latency and real-time responsiveness. Edge servers can handle data processing and rendering, ensuring smooth and seamless interactions for users.
This is crucial for applications like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), where responsiveness is critical for an immersive experience.
- Extended Reality (XR): Edge computing enables the deployment of XR applications, such as VR and AR, in various industries. For instance, in healthcare, edge-powered XR applications can facilitate remote surgeries and training simulations, while in manufacturing, they can provide interactive guides and support for complex tasks.
Edge Computing for Societal Challenges
Edge computing has the potential to address significant societal challenges, including climate change and resource management.
- Climate Change: Edge computing can contribute to sustainability efforts by enabling efficient energy management and reducing carbon emissions. Smart grids, powered by edge computing, can optimize energy distribution and consumption, minimizing waste and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Edge devices can also monitor environmental conditions and provide real-time data for environmental monitoring and disaster response.
- Resource Management: Edge computing can facilitate efficient resource management in areas like agriculture and water conservation. Smart sensors deployed on edge devices can monitor crop health, soil conditions, and water usage, providing valuable insights for optimizing resource allocation and minimizing waste.
This approach can lead to increased productivity and sustainability in resource-intensive sectors.
Key Areas of Research and Development, Edge computing cloud computing
Several key areas of research and development are crucial for advancing edge computing and unlocking its full potential.
- Security and Privacy: As edge devices become more interconnected and handle sensitive data, ensuring security and privacy is paramount. Research is ongoing to develop robust security protocols and privacy-preserving techniques for edge computing environments.
- Interoperability and Standardization: The lack of standardized protocols and interoperability between different edge computing platforms can hinder adoption. Research and development efforts are focused on establishing industry standards and frameworks to facilitate seamless integration and collaboration.
- Resource Management and Optimization: Efficient resource management is crucial for maximizing the performance and cost-effectiveness of edge computing deployments. Research focuses on developing intelligent resource allocation algorithms and optimization techniques to ensure efficient utilization of computing power, storage, and network bandwidth.
Edge computing and cloud computing are revolutionizing how we access and process data, bringing computing power closer to users and devices. But sometimes, the most powerful tools are the simplest ones. A calming scent can help create a focused environment, and essential oils diffuser blends can be just the thing to enhance productivity and focus, whether you’re working on a complex cloud infrastructure project or simply trying to find a moment of peace in the midst of a busy day.
Just like edge computing brings the power of the cloud closer to the user, these blends bring a sense of tranquility and well-being right into your workspace.
Edge computing and cloud computing are changing the way we interact with the world, and sometimes, even the way we craft our personal projects. Just like edge computing brings processing power closer to the user, a DIY project like this xoxo heart clutch diy allows you to personalize and bring your creativity closer to the finished product.
Ultimately, both edge computing and crafting your own heart clutch are about taking control and making things your own, whether it’s data processing or a fashion statement.
Edge computing and cloud computing are transforming the way we interact with data, bringing processing power closer to the source. This shift is particularly relevant to the field of sustainability, where real-time data analysis and localized action are crucial.
The recent vb special issue on intelligent sustainability explores this intersection, highlighting how edge computing can enable smarter energy management, optimize resource utilization, and foster a more sustainable future. As we move towards a more interconnected world, edge computing will play a critical role in driving intelligent solutions for a greener planet.