Gartner Global Software Trends: Shaping the Future of Technology
Gartner Global Software Trends are a roadmap for businesses and technology leaders, offering insights into the forces shaping the digital landscape. These trends, meticulously researched and analyzed by Gartner, a leading research and advisory firm, provide a comprehensive overview of the evolving software market and its impact on various industries.
From cloud computing and artificial intelligence to blockchain and edge computing, Gartner’s report delves into the latest advancements and their potential to transform business operations. Understanding these trends is crucial for organizations to remain competitive and adapt to the rapidly changing technological landscape.
Gartner’s Role in Software Trends
Gartner is a leading research and advisory firm in the technology industry, providing insights and analysis to help businesses make informed decisions about technology investments. The firm’s global software trends reports are highly regarded by businesses and technology leaders worldwide, offering valuable guidance on the latest developments and future directions in the software landscape.
The Significance of Gartner’s Global Software Trends Reports
Gartner’s software trends reports are crucial for businesses and technology leaders for several reasons. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of the evolving software landscape, highlighting emerging technologies, market trends, and potential disruptions. They offer insights into the future of software development, deployment, and consumption, enabling businesses to:
- Stay Ahead of the Curve:Gartner’s reports help businesses identify emerging technologies and trends that could impact their operations, allowing them to adapt and innovate proactively.
- Make Informed Technology Decisions:The reports provide valuable insights into the market landscape, helping businesses choose the right software solutions and technologies to meet their specific needs.
- Develop Effective Strategies:By understanding the key trends and challenges in the software industry, businesses can develop more effective strategies for technology adoption, deployment, and management.
Key Areas of Impact on the Software Market
Gartner’s insights have historically influenced the software market in several key areas, shaping the industry’s trajectory and driving innovation. These include:
- Cloud Computing:Gartner’s early adoption of the term “cloud computing” and its subsequent research on cloud adoption trends have played a significant role in the widespread adoption of cloud services.
- Software as a Service (SaaS):Gartner’s analysis of the SaaS market has helped businesses understand the benefits and challenges of SaaS adoption, driving growth in this segment.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):Gartner’s research on AI trends has helped businesses understand the potential of AI, driving investments and adoption in this rapidly evolving field.
- DevOps:Gartner’s insights into DevOps practices have helped businesses streamline software development and delivery processes, improving efficiency and time to market.
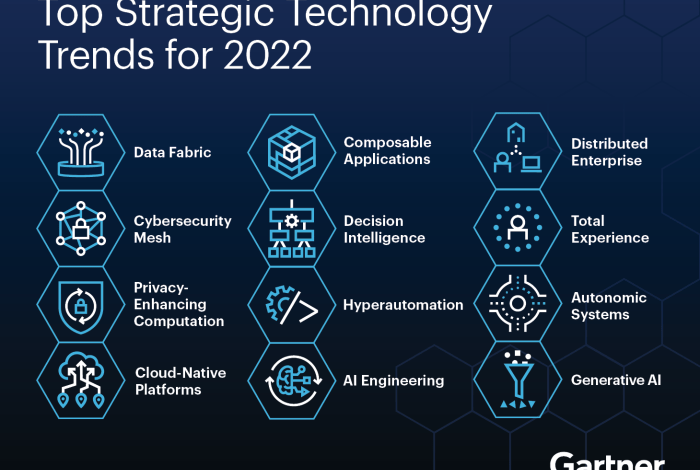
Top Global Software Trends
Gartner’s top 10 global software trends provide insights into the evolving technological landscape and their impact on businesses. These trends represent the most significant shifts in software development, deployment, and utilization, shaping the future of technology and its role in various industries.
The Rise of the Composite Application
The composite application trend signifies a shift towards building software applications by combining different functionalities from various sources, including pre-built components, APIs, and even other applications. This approach enables businesses to rapidly develop and deploy applications tailored to their specific needs, leveraging the power of existing technologies.
The key drivers behind this trend include:
- Increased Demand for Customization:Businesses require software solutions that cater to their unique requirements and workflows, making customization essential. Composite applications offer flexibility by integrating different functionalities, enabling tailoring to specific business needs.
- Rapid Innovation and Agility:The speed of innovation in the software industry necessitates rapid development and deployment of applications. Composite applications enable faster development cycles by leveraging pre-built components and APIs, reducing the time and effort required to build new applications.
- Improved Integration and Interoperability:Integrating different systems and applications is crucial for seamless data flow and efficient operations. Composite applications facilitate integration by leveraging APIs and other technologies, allowing different systems to communicate and share data effectively.
The potential impact of this trend on businesses is significant:
- Enhanced Business Agility:Composite applications enable businesses to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands by integrating new functionalities and features as needed.
- Improved Operational Efficiency:By integrating different systems and applications, businesses can streamline workflows, reduce redundancy, and improve overall efficiency.
- Increased Innovation:The ability to quickly combine and integrate different functionalities empowers businesses to experiment with new ideas and develop innovative solutions.
Examples of how leading organizations are implementing this trend include:
- Salesforce:Salesforce’s platform leverages a composite application approach, allowing businesses to integrate various functionalities, such as CRM, marketing automation, and customer service, into a single platform.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS):AWS provides a wide range of pre-built services and APIs that businesses can use to build composite applications. This allows businesses to leverage AWS’s infrastructure and services without needing to develop everything from scratch.
Impact of Trends on Business Strategy
The global software trends Artikeld by Gartner have profound implications for business strategy and decision-making. These trends represent both opportunities and challenges for organizations to adapt and thrive in the rapidly evolving technological landscape. By embracing these trends, organizations can gain a competitive edge, enhance customer experiences, and unlock new avenues for growth.
Adapting to the Rise of Composable Applications, Gartner global software trends
Composable applications, built from independent, reusable components, are fundamentally changing how organizations develop and deploy software. This shift empowers businesses to be more agile and responsive to evolving market demands.
- Increased Agility and Speed:Composable applications allow organizations to rapidly assemble and deploy new functionalities, adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs with unprecedented speed. This agility enables businesses to launch new products and services quickly, gain a competitive advantage, and respond to emerging trends.
- Enhanced Customization and Personalization:By combining pre-built components, organizations can tailor applications to specific business needs and customer preferences, offering personalized experiences that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. This level of customization allows businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors and cater to the unique requirements of individual customers.
Gartner’s Global Software Trends report highlights the constant evolution of the tech landscape, emphasizing the need for innovation and adaptability. While we’re immersed in the world of cloud computing and AI, sometimes it’s the simple things that make a difference.
Take, for instance, this iPhone app, this iphone app is a treasure trove of photo filters , which shows how a creative tool can add a touch of magic to our digital lives. This kind of user-centric approach, focusing on intuitive and impactful experiences, aligns perfectly with Gartner’s predictions for the future of software development.
- Reduced Development Costs and Time:Reusing pre-built components significantly reduces the time and resources required for software development. This allows organizations to focus on innovation and core business functions, leading to cost savings and faster time-to-market for new solutions.
Key Technologies Driving Trends
The software trends identified by Gartner are driven by a convergence of key technologies, each contributing to the evolving landscape of software development and deployment. These technologies are not isolated but interact and complement each other, shaping the future of software.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are foundational to many of the trends discussed, enabling automation, optimization, and intelligent decision-making. They are crucial for:
- Hyperautomation:AI and ML power automation tools, enabling the automation of complex tasks, including those that were previously considered too intricate for traditional automation. This allows for increased efficiency and productivity, freeing up human resources for more strategic tasks.
- Composable Applications:AI and ML are used to analyze data and identify patterns that inform the design and development of composable applications. They can help in understanding user behavior, predicting future needs, and automating the process of assembling and configuring application components.
- Citizen Development:AI and ML-powered tools are simplifying software development, making it accessible to non-technical users. These tools can help with code generation, testing, and deployment, allowing citizens developers to contribute to software development efforts.
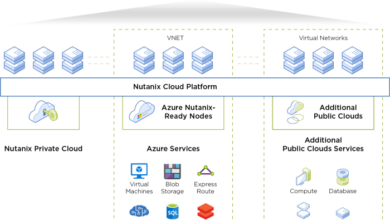
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and platform for many of the software trends. It offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it an essential foundation for:
- Cloud-Native Development:Cloud computing provides the infrastructure and platform for building and deploying cloud-native applications, which are designed to leverage the benefits of cloud computing. These applications are highly scalable, resilient, and can be deployed quickly and easily.
- Serverless Computing:Serverless computing, a cloud-based model, allows developers to focus on writing code without managing servers. It provides on-demand computing resources, scaling automatically based on application needs, and offers a pay-per-use pricing model. This approach further accelerates development and deployment.
- Edge Computing:Edge computing brings computing power closer to the source of data, enabling faster processing and reduced latency. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time data analysis and decision-making, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The increasing number of connected devices is driving the adoption of software solutions that can manage and analyze data from these devices. IoT is a key driver for:
- Real-Time Analytics:IoT devices generate massive amounts of data, requiring real-time analytics capabilities to extract insights and make informed decisions. AI and ML play a critical role in analyzing this data and identifying patterns and trends.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN):SDN enables the automation and orchestration of network resources, making it easier to manage and control the growing number of connected devices. This is essential for ensuring secure and reliable connectivity for IoT applications.
- Digital Twins:Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, enabling organizations to monitor and optimize their performance. This technology is used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation, to improve efficiency and reduce downtime.
Emerging Software Trends

The software landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging at a rapid pace. While some trends gain widespread adoption quickly, others take time to mature and prove their worth. This section explores emerging software trends that are not yet widely adopted but have the potential for significant impact on the future of software development and business operations.
These trends represent innovative approaches to solving complex problems and unlocking new opportunities for organizations.
Gartner’s Global Software Trends report highlights the growing importance of personalized experiences, which is why I’m excited to try my hand at creating some unique home decor. I’m particularly drawn to the idea of making DIY clay cactus candle holders – they’re both trendy and practical.
The report also emphasizes the need for organizations to embrace agility and innovation, and I think this DIY project perfectly embodies that spirit.
Emerging Trends and Their Potential Applications
The following emerging trends are poised to reshape the software landscape in the coming years:
- Generative AI:Generative AI, powered by large language models (LLMs) and deep learning algorithms, has the ability to create new content, such as text, code, images, and audio. This technology has the potential to revolutionize software development by automating tasks, generating code, and improving user experiences.
For example, developers can use generative AI to create code snippets, generate documentation, and even design user interfaces. The technology is also being used in creative fields, such as writing, music composition, and art generation.
- Quantum Computing:Quantum computing is a rapidly developing field that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to solve complex problems that are intractable for traditional computers. This technology has the potential to revolutionize fields such as drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling.
While still in its early stages, quantum computing is expected to have a significant impact on software development in the future.
- Edge Computing:Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. This approach reduces latency, improves responsiveness, and enhances security. Edge computing is expected to be particularly important for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and smart cities.
Gartner’s global software trends are constantly evolving, reflecting the rapid pace of technological innovation. It’s a world where AI is transforming industries and cloud computing is reshaping how we work. Sometimes, though, it’s good to take a break from all that tech and enjoy a simpler pleasure, like a brunch farmers market date.
Fresh air, local produce, and good company can be a refreshing reminder of what really matters. Then, with renewed energy, you can dive back into the fascinating world of Gartner’s software trends and see how you can leverage them to your advantage.
- Cybersecurity Mesh:As organizations adopt a more distributed and cloud-based approach to IT, traditional cybersecurity approaches are becoming less effective. Cybersecurity mesh is an emerging approach that focuses on securing data and applications across the entire IT ecosystem, regardless of location or device.
This approach uses a combination of technologies, including zero-trust security, microsegmentation, and artificial intelligence, to create a more resilient and adaptable security posture.
- Composable Software:Composable software is an approach to building applications by combining pre-built, independent components or microservices. This approach allows organizations to create applications more quickly and efficiently, and to adapt to changing business needs more easily. Composable software is expected to become increasingly popular as organizations seek to accelerate their digital transformation initiatives.
Benefits and Challenges of Emerging Trends
While emerging software trends offer significant benefits, they also present challenges that need to be addressed.
Benefits
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity:Emerging trends like generative AI and composable software can automate tasks, reduce development time, and improve overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Innovation and Creativity:These trends empower developers to create new and innovative solutions by providing access to advanced technologies and tools.
- Improved User Experiences:Emerging trends can enhance user experiences by providing personalized and context-aware interactions.
- New Business Opportunities:Emerging trends create opportunities for businesses to develop new products and services, enter new markets, and gain a competitive advantage.
Challenges
- Skills Gap:Adopting emerging trends requires organizations to invest in training and development to ensure their workforce has the necessary skills.
- Security and Privacy Concerns:Emerging technologies, such as generative AI, raise concerns about data privacy and security. Organizations need to implement robust security measures to mitigate these risks.
- Ethical Considerations:Emerging trends, such as quantum computing and generative AI, raise ethical considerations that need to be carefully addressed.
- Complexity and Integration:Integrating emerging technologies into existing systems can be complex and challenging.
Trends in Specific Software Categories
The global software landscape is continuously evolving, with emerging trends impacting various software categories. Understanding how these trends influence specific software categories is crucial for businesses to adapt and leverage new opportunities. This section will delve into the impact of these trends on cloud computing, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and artificial intelligence (AI), highlighting unique challenges and opportunities within each category.
Cloud Computing
The adoption of cloud computing continues to accelerate, driven by trends like edge computing, serverless computing, and cloud-native development. These trends are transforming how businesses design, deploy, and manage applications.
Challenges
- Security concerns: Migrating sensitive data to the cloud raises concerns about data security and privacy. Businesses need to implement robust security measures and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Vendor lock-in: Choosing a specific cloud provider can lead to vendor lock-in, making it difficult to switch providers in the future. Businesses should carefully evaluate their options and consider multi-cloud strategies.
- Complexity of cloud management: Managing cloud resources across multiple environments can be complex and require specialized skills. Businesses need to invest in training and tools to effectively manage their cloud infrastructure.
Opportunities
- Scalability and agility: Cloud computing provides businesses with the flexibility to scale their resources up or down as needed, enabling rapid response to changing market demands.
- Cost optimization: Cloud services can help businesses optimize costs by paying only for the resources they use, reducing upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
- Innovation and disruption: Cloud computing empowers businesses to experiment with new technologies and develop innovative solutions faster, leading to increased competitiveness.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems are undergoing a significant transformation, driven by trends like cloud-based ERP, mobile ERP, and artificial intelligence (AI). These trends are enhancing ERP functionality, improving user experience, and enabling businesses to make better decisions.
Challenges
- Integration complexities: Integrating ERP systems with other business applications can be challenging, requiring careful planning and coordination. Businesses need to ensure seamless data flow between systems.
- Change management: Implementing a new ERP system can be disruptive, requiring significant change management efforts. Businesses need to effectively communicate the benefits of the new system and provide adequate training to users.
- Data security and privacy: ERP systems store critical business data, making data security and privacy a top priority. Businesses need to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
Opportunities
- Improved efficiency and productivity: Cloud-based ERP systems offer real-time access to data, enabling better decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
- Enhanced visibility and insights: AI-powered analytics can provide businesses with valuable insights into their operations, helping them identify areas for improvement and optimize processes.
- Mobile accessibility: Mobile ERP applications allow employees to access critical data and perform tasks from anywhere, enhancing productivity and flexibility.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming various software categories, including ERP, customer relationship management (CRM), and cybersecurity. AI-powered applications are automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing customer experiences.
Challenges
- Data quality and bias: AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on. Businesses need to ensure data quality and address potential biases in their AI models.
- Ethical considerations: The use of AI raises ethical concerns about data privacy, job displacement, and algorithmic fairness. Businesses need to carefully consider the ethical implications of AI applications.
- Explainability and transparency: Understanding how AI algorithms make decisions can be challenging. Businesses need to develop mechanisms for explainability and transparency to ensure accountability.
Opportunities
- Automation and efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities and improving overall efficiency.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI-powered analytics can provide businesses with real-time insights, enabling better decision-making and improved outcomes.
- Personalized customer experiences: AI can be used to personalize customer interactions, delivering tailored experiences that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Comparison of Trends Across Software Categories
| Trend | Cloud Computing | ERP | AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edge Computing | Increased adoption for real-time data processing and IoT applications. | Limited impact, primarily focused on data collection and analysis. | Emerging applications in edge AI for localized decision-making and analytics. |
| Serverless Computing | Growing popularity for scalable and cost-effective application development. | Limited adoption, primarily for specific workloads like data processing. | Emerging use cases in AI model training and inference for efficient resource utilization. |
| Cloud-Native Development | Driving a shift towards microservices architectures and containerization. | Increasing adoption for modernizing ERP systems and improving agility. | Enabling the development of AI-powered applications optimized for cloud environments. |
Implications for Software Development: Gartner Global Software Trends
The rapid evolution of global software trends has a profound impact on software development practices and methodologies. Developers are challenged to adapt to new technologies, approaches, and the increasing complexity of software systems. This section explores the key implications of these trends for software development, highlighting the need for continuous learning and the adoption of innovative solutions.
The Need for Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Software developers must embrace a culture of continuous learning to keep pace with the ever-changing landscape of technology. This involves staying informed about emerging trends, acquiring new skills, and adapting to new development paradigms. For instance, the rise of low-code and no-code platforms necessitates developers to understand their capabilities and limitations, as well as their potential to empower citizen developers.
Similarly, the increasing adoption of cloud-native technologies requires developers to gain proficiency in containerization, microservices, and serverless computing.
Evolving Software Development Processes
The global software trends are driving significant changes in software development processes. The shift towards agile methodologies, DevOps, and continuous delivery has become essential for organizations seeking to deliver software faster and more efficiently. Moreover, the adoption of AI-powered tools and automation is transforming various aspects of the software development lifecycle, from code generation to testing and deployment.
Workflow Diagram Illustrating Evolving Software Development Processes
The following workflow diagram illustrates how software development processes may evolve in response to global software trends: [Workflow Diagram]The diagram depicts a modern software development process that incorporates elements of agile methodologies, DevOps, and AI-powered tools. The process begins with requirements gathering and analysis, followed by design and development.
Automated testing and code review are integrated throughout the process, ensuring high-quality code. Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines enable rapid deployment and feedback loops. AI-powered tools assist in tasks such as code generation, security analysis, and performance optimization.
Future of Software Trends
The software landscape is in a constant state of flux, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving user demands. Understanding the future trajectory of software trends is crucial for businesses to stay ahead of the curve and leverage emerging opportunities.
This section explores the potential evolution of current trends, identifies emerging technologies that will shape the future, and Artikels a timeline for their anticipated impact over the next 5-10 years.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future
Emerging technologies are constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in software development. These advancements are not only driving innovation but also influencing the future direction of software trends.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI is rapidly transforming software development, enabling intelligent automation, personalized experiences, and predictive analytics. AI-powered tools are already being used for code generation, testing, and bug detection. In the future, AI will play a more prominent role in software design, development, and maintenance.
For instance, AI-powered chatbots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of handling complex customer interactions and providing personalized support.
- Quantum Computing:Quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize software by enabling faster and more efficient algorithms for complex problems. This technology could significantly impact fields like drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling. While still in its early stages, quantum computing is expected to become more accessible and impactful in the coming years.
- Extended Reality (XR):XR encompasses technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), creating immersive and interactive experiences. XR is already being used in various industries, from training and education to gaming and entertainment. In the future, XR will likely become more integrated into software applications, providing more engaging and realistic user interfaces.
- Edge Computing:Edge computing brings data processing and computation closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This technology is particularly important for applications that require real-time data processing, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. Edge computing is expected to play a significant role in the development of distributed and decentralized software architectures.