SAP ERP vs Oracle ERP: Which is Right for Your Business?
SAP ERP vs Oracle ERP: Choosing the right enterprise resource planning (ERP) system is a critical decision for any business. Both SAP and Oracle are industry giants, offering robust solutions designed to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
But with so many similarities, how do you determine which platform is the best fit for your specific needs?
This article delves into the key differences between SAP ERP and Oracle ERP, exploring their core features, industry focus, deployment options, pricing models, user experience, security, and more. By examining these factors, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of each platform and make an informed decision about which one aligns best with your business goals and objectives.
Introduction
In the contemporary business landscape, the ability to efficiently manage and integrate data across various departments and operations is paramount. This is where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play. ERP systems are comprehensive software solutions that streamline and automate core business processes, including finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
They provide a centralized platform for data storage, analysis, and decision-making, enabling organizations to optimize their operations, improve productivity, and gain a competitive edge.
SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are two of the most prominent and widely used ERP systems globally. Both solutions offer a wide range of features and functionalities, catering to the diverse needs of businesses across industries. Understanding the key differences between SAP ERP and Oracle ERP is crucial for organizations seeking to select the most suitable ERP system for their specific requirements.
Comparison of SAP ERP and Oracle ERP
This comparison aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key features, functionalities, and strengths of both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP. By examining the differences and similarities between these two leading ERP systems, organizations can make informed decisions regarding the best solution for their business needs.
Core Features and Functionalities: Sap Erp Vs Oracle Erp
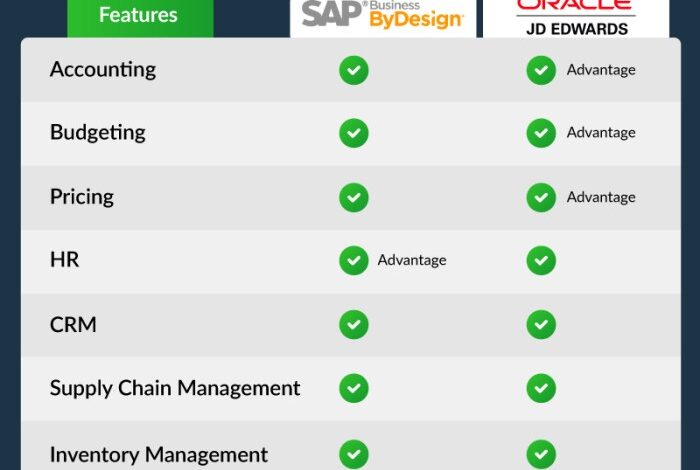
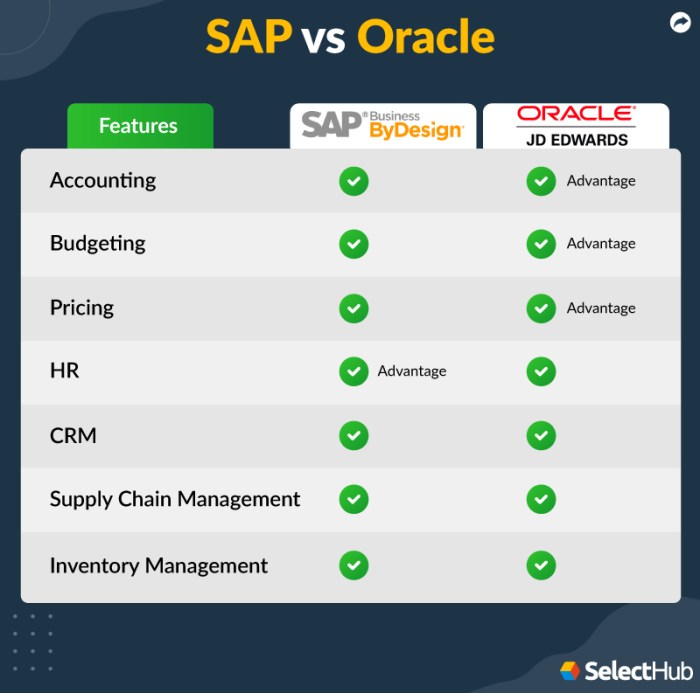
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems that offer a wide range of modules to manage various business functions. They cater to diverse industry needs, helping organizations streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making.
However, they have distinct features and functionalities, which can influence the suitability of each system for specific organizations.
Finance
The finance module is a core component of both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP, encompassing functionalities such as financial accounting, management accounting, and treasury management. Both systems provide comprehensive solutions for financial reporting, budgeting, and forecasting. However, they differ in their strengths and weaknesses.
SAP ERP excels in its robust financial consolidation capabilities, enabling organizations to manage complex financial structures and consolidate data from multiple subsidiaries. Oracle ERP, on the other hand, offers a more user-friendly interface and strong integration with other modules, facilitating seamless data flow across different business units.
Here’s a table comparing the key features of SAP ERP and Oracle ERP in the finance module:
| Feature | SAP ERP | Oracle ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Consolidation | Stronger | Moderate |
| User Interface | Moderate | Stronger |
| Integration with other modules | Moderate | Stronger |
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) is another critical area where both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP offer comprehensive solutions. They cover functionalities such as inventory management, procurement, production planning, and logistics. SAP ERP is renowned for its advanced planning and optimization capabilities, enabling organizations to optimize their supply chains for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing between SAP ERP and Oracle ERP can feel like navigating a complex maze. Both systems offer robust features, but understanding your specific business needs is key. For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, using command line interface Microsoft can provide a deeper level of control and customization.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your organization’s size, industry, and overall IT infrastructure.
Oracle ERP, on the other hand, provides a more flexible and customizable platform, allowing businesses to tailor their SCM processes to specific needs.Here’s a table comparing the key features of SAP ERP and Oracle ERP in the supply chain management module:
| Feature | SAP ERP | Oracle ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Planning and Optimization | Stronger | Moderate |
| Flexibility and Customization | Moderate | Stronger |
| Integration with other modules | Stronger | Moderate |
Human Resources
Human resource management (HRM) is a critical aspect of any organization, and both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP offer comprehensive solutions for managing employee data, payroll, talent management, and other HR-related functions.SAP ERP excels in its robust talent management capabilities, providing advanced tools for recruitment, performance management, and employee development.
Oracle ERP, on the other hand, offers a more user-friendly interface and strong integration with other modules, making it easier to manage HR data and processes.Here’s a table comparing the key features of SAP ERP and Oracle ERP in the human resources module:
| Feature | SAP ERP | Oracle ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Talent Management | Stronger | Moderate |
| User Interface | Moderate | Stronger |
| Integration with other modules | Moderate | Stronger |
Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a critical aspect of any business, and both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP offer comprehensive solutions for managing customer interactions, sales, marketing, and service.SAP ERP is known for its robust CRM capabilities, providing advanced tools for customer segmentation, marketing automation, and sales forecasting.
Oracle ERP, on the other hand, offers a more user-friendly interface and strong integration with other modules, making it easier to manage customer data and processes.Here’s a table comparing the key features of SAP ERP and Oracle ERP in the customer relationship management module:
| Feature | SAP ERP | Oracle ERP |
|---|---|---|
| CRM Capabilities | Stronger | Moderate |
| User Interface | Moderate | Stronger |
| Integration with other modules | Moderate | Stronger |
Industry Focus and Specialization
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are highly versatile platforms catering to a wide range of industries. However, they have developed specific strengths and expertise in certain sectors, making them particularly well-suited for addressing the unique challenges and opportunities within those industries.
Industry Focus and Specialization of SAP ERP
SAP ERP has a strong presence in various industries, but it has established itself as a leader in manufacturing, retail, and services. SAP’s industry-specific solutions are designed to address the complexities of each sector, offering tailored functionalities and best practices to optimize business processes.
- Manufacturing:SAP’s manufacturing solutions help companies manage production planning, materials management, quality control, and maintenance. They enable manufacturers to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Examples of companies using SAP ERP in manufacturing include:
- Siemens:A global technology powerhouse, Siemens leverages SAP ERP for its manufacturing operations, including supply chain management, production planning, and financial reporting.
- Ford Motor Company:Ford uses SAP ERP to manage its global manufacturing network, optimizing production processes and inventory management across its facilities.
- Retail:SAP ERP provides retailers with comprehensive solutions for managing their supply chain, inventory, and customer relationships. They offer tools for point-of-sale systems, merchandising, and customer analytics. Examples of companies using SAP ERP in retail include:
- Walmart:Walmart relies on SAP ERP to manage its massive global supply chain, ensuring efficient inventory management and timely delivery of goods to its stores.
- Nike:Nike uses SAP ERP to manage its global retail operations, including supply chain management, inventory optimization, and customer relationship management.
- Services:SAP ERP provides service-oriented companies with solutions for managing customer interactions, service delivery, and resource allocation. They offer tools for field service management, contract management, and customer relationship management. Examples of companies using SAP ERP in services include:
- Deutsche Telekom:Deutsche Telekom uses SAP ERP to manage its customer service operations, providing efficient support to its millions of subscribers.
Choosing between SAP ERP and Oracle ERP can be a tough decision, especially with the ever-evolving landscape of technology. It’s like trying to decide between two different flavors of ice cream, both delicious but with subtle nuances that make one a better fit for your taste buds.
Speaking of tech, did you hear about how a new version of the Beats Solo headphones was accidentally revealed in the latest version of iOS? Check it out here ! Anyway, back to the ERP debate, both SAP and Oracle offer robust solutions, but ultimately the best choice depends on your specific business needs and priorities.
- Accenture:Accenture, a global consulting firm, leverages SAP ERP to manage its project delivery, resource allocation, and financial reporting.
- Deutsche Telekom:Deutsche Telekom uses SAP ERP to manage its customer service operations, providing efficient support to its millions of subscribers.
Industry Focus and Specialization of Oracle ERP
Oracle ERP has a strong presence in various industries, including finance, banking, and telecommunications. Oracle’s industry-specific solutions are designed to address the unique challenges and opportunities of each sector, offering tailored functionalities and best practices to optimize business processes.
- Finance:Oracle ERP provides financial institutions with comprehensive solutions for managing their core banking operations, including customer relationship management, lending, and treasury management. They offer tools for risk management, regulatory compliance, and fraud detection. Examples of companies using Oracle ERP in finance include:
- Bank of America:Bank of America uses Oracle ERP to manage its core banking operations, including customer relationship management, lending, and treasury management.
- Citigroup:Citigroup leverages Oracle ERP for its global banking operations, including customer relationship management, trade finance, and investment banking.
- Banking:Oracle ERP provides banks with comprehensive solutions for managing their core banking operations, including customer relationship management, lending, and treasury management. They offer tools for risk management, regulatory compliance, and fraud detection. Examples of companies using Oracle ERP in banking include:
- HSBC:HSBC uses Oracle ERP to manage its global banking operations, including customer relationship management, trade finance, and investment banking.
Choosing between SAP ERP and Oracle ERP can be a tough decision, especially when considering the complex integrations and resource management involved. To streamline these processes, implementing a robust cloud project management software solution can be a game-changer. This allows for centralized task management, resource allocation, and real-time progress tracking, ultimately making the transition to either SAP ERP or Oracle ERP smoother and more efficient.
- Wells Fargo:Wells Fargo leverages Oracle ERP for its core banking operations, including customer relationship management, lending, and treasury management.
- HSBC:HSBC uses Oracle ERP to manage its global banking operations, including customer relationship management, trade finance, and investment banking.
- Telecommunications:Oracle ERP provides telecommunications companies with solutions for managing their customer relationships, billing, and network operations. They offer tools for service provisioning, network optimization, and customer analytics. Examples of companies using Oracle ERP in telecommunications include:
- AT&T:AT&T uses Oracle ERP to manage its customer relationships, billing, and network operations, providing efficient service delivery to its subscribers.
- Verizon:Verizon leverages Oracle ERP for its core telecommunications operations, including customer relationship management, billing, and network management.
Companies Using SAP ERP and Oracle ERP
| Company | Industry | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Siemens | Manufacturing | Supply chain management, production planning, financial reporting |
| Ford Motor Company | Manufacturing | Global manufacturing network management, production process optimization, inventory management |
| Walmart | Retail | Global supply chain management, inventory management, point-of-sale systems |
| Nike | Retail | Supply chain management, inventory optimization, customer relationship management |
| Deutsche Telekom | Services | Customer service operations, field service management, contract management |
| Accenture | Services | Project delivery, resource allocation, financial reporting |
| Bank of America | Finance | Core banking operations, customer relationship management, lending, treasury management |
| Citigroup | Finance | Global banking operations, customer relationship management, trade finance, investment banking |
| HSBC | Banking | Global banking operations, customer relationship management, trade finance, investment banking |
| Wells Fargo | Banking | Core banking operations, customer relationship management, lending, treasury management |
| AT&T | Telecommunications | Customer relationship management, billing, network operations, service provisioning |
| Verizon | Telecommunications | Core telecommunications operations, customer relationship management, billing, network management |
Deployment Options and Pricing
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP offer a range of deployment options to cater to different business needs and IT infrastructure preferences. Understanding these options and their associated costs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Deployment Options
The deployment options for SAP ERP and Oracle ERP encompass on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid models. Each option presents unique advantages and considerations, influencing the overall cost and complexity of implementation.
- On-Premise:In this traditional model, the software is installed and managed on the organization’s own servers and infrastructure. On-premise deployments offer greater control over data security and customization, but require significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and ongoing maintenance.
- Cloud-Based:Cloud deployments involve accessing the ERP system through a third-party cloud provider, such as AWS, Azure, or Oracle Cloud. This eliminates the need for on-site infrastructure, reduces upfront costs, and provides scalability and flexibility. However, organizations may have limited control over data security and customization options.
- Hybrid:Hybrid deployments combine elements of both on-premise and cloud-based models. This allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both options, such as greater control over sensitive data while still benefiting from the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud computing.
Pricing Models
The pricing models for SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are complex and vary depending on factors such as deployment option, modules selected, user licenses, and support services.
- Subscription-based:Cloud-based deployments typically follow a subscription-based pricing model, where organizations pay a recurring monthly or annual fee based on the number of users and modules. This model offers predictable costs and eliminates the need for upfront capital expenditure.
- Perpetual License:On-premise deployments often involve purchasing perpetual licenses, granting organizations the right to use the software indefinitely. However, ongoing maintenance fees and support costs are still applicable.
- Usage-based:Some cloud-based offerings may also adopt a usage-based pricing model, where organizations are charged based on actual usage or resource consumption.
Cost Considerations
The total cost of ownership (TCO) for SAP ERP and Oracle ERP encompasses various factors beyond the initial purchase price.
- Implementation Costs:Implementing an ERP system involves significant costs for consulting services, customization, data migration, and training.
- Maintenance Costs:Ongoing maintenance costs include software updates, technical support, and user training.
- Hardware and Infrastructure Costs:On-premise deployments require investments in servers, storage, and networking equipment.
- Licensing Costs:Licensing fees for SAP ERP and Oracle ERP can vary depending on the number of users, modules, and deployment option.
Table Comparing Deployment Options and Pricing Structures
| Deployment Option | SAP ERP | Oracle ERP |
|---|---|---|
| On-Premise | Perpetual license with ongoing maintenance fees | Perpetual license with ongoing maintenance fees |
| Cloud-Based | Subscription-based pricing model | Subscription-based pricing model |
| Hybrid | Combination of perpetual licenses and subscription-based pricing | Combination of perpetual licenses and subscription-based pricing |
Integration and Compatibility
In today’s interconnected business world, seamless integration with other systems is crucial for any ERP solution. Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP offer robust integration capabilities, but their approaches and strengths differ. This section will explore the integration capabilities of both systems, their compatibility with various platforms and technologies, and provide examples of successful integration scenarios.
Integration with Other Business Systems
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP provide extensive integration capabilities with various business systems, including:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):SAP CRM and Oracle Siebel are widely used CRM systems that can be integrated with SAP ERP and Oracle ERP respectively, providing a unified view of customer data and interactions.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM):Integration with SCM systems like SAP SCM and Oracle SCM allows for optimized supply chain planning, execution, and visibility across the entire value chain.
- Human Capital Management (HCM):Integrating with HCM systems like SAP SuccessFactors and Oracle Taleo helps streamline HR processes, manage employee data, and optimize talent acquisition and development.
- Business Intelligence (BI):Both SAP and Oracle offer BI tools that can be integrated with their ERP systems, enabling organizations to analyze data, generate reports, and make informed decisions.
- Enterprise Content Management (ECM):Integration with ECM systems like SAP Document Management and Oracle WebCenter Content facilitates document management, collaboration, and knowledge sharing within the organization.
Compatibility with Platforms and Technologies
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP support a wide range of platforms and technologies, ensuring compatibility with diverse IT environments. Here are some key aspects:
- Operating Systems:Both systems are compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Unix.
- Databases:SAP ERP primarily uses its own database, SAP HANA, while Oracle ERP relies on Oracle Database. However, both systems offer support for other databases like SQL Server and DB2.
- Cloud Computing:Both SAP and Oracle offer cloud-based versions of their ERP systems, enabling organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs.
- API Integration:Both systems provide Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that enable integration with third-party applications and services, fostering a more flexible and adaptable IT environment.
Successful Integration Scenarios
Here are some examples of successful integration scenarios for both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP:
- Manufacturing:A leading automotive manufacturer integrated its SAP ERP system with its supply chain management system to optimize production planning, inventory management, and logistics, resulting in reduced lead times and improved efficiency.
- Retail:A global retail chain integrated its Oracle ERP system with its CRM system to gain a comprehensive view of customer data, personalize marketing campaigns, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Healthcare:A healthcare provider integrated its SAP ERP system with its electronic health records (EHR) system to streamline patient data management, improve billing processes, and enhance patient care.
User Experience and Customization
The user experience and customization options offered by SAP ERP and Oracle ERP play a significant role in determining their suitability for various businesses. Both systems offer distinct approaches to user interface design, configuration flexibility, and ease of use, catering to different organizational needs and preferences.
Ease of Use and User Interface
The ease of use and user interface design of SAP ERP and Oracle ERP vary significantly, influencing the user experience. SAP ERP, known for its robust functionalities and complex architecture, often presents a steeper learning curve for users. The user interface can be perceived as less intuitive, requiring users to navigate through multiple menus and screens to accomplish tasks.
Oracle ERP, on the other hand, emphasizes user-friendliness and simplicity, offering a more intuitive interface and streamlined workflows. The user interface is designed to be intuitive and accessible, making it easier for users to learn and adapt to the system.
Configuration Flexibility
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP provide extensive customization options, allowing organizations to tailor the systems to their specific business requirements. SAP ERP offers a wide range of configuration options, enabling users to adapt various modules, processes, and functionalities to align with their unique needs.
However, the extensive configuration options can be overwhelming for some users, requiring specialized skills and knowledge to effectively implement customizations. Oracle ERP, while providing robust configuration options, prioritizes a more standardized approach, making it easier for users to implement customizations with minimal technical expertise.
The system offers pre-built templates and configurations, simplifying the process of adapting the system to specific business requirements.
Examples of User Interface Customizations and Configurations
- SAP ERP:Users can customize the SAP GUI, the main user interface, to include personalized settings, such as preferred language, color schemes, and screen layouts. The system also allows for the creation of custom reports and dashboards, providing users with tailored insights and information.
Furthermore, SAP ERP enables users to develop custom applications and extensions, enhancing the system’s functionalities to meet specific business needs.
- Oracle ERP:Oracle ERP offers a range of customization options through its Oracle Forms and Reports technology. Users can create custom forms, reports, and interfaces to streamline workflows and improve data visibility. The system also allows for the customization of dashboards and reports, enabling users to visualize data and track key performance indicators (KPIs) according to their preferences.
Additionally, Oracle ERP provides pre-built templates and configurations for various industries, simplifying the customization process and reducing the time and effort required to adapt the system.
Security and Compliance
In the realm of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, security and compliance are paramount considerations. Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP offer robust security features and comprehensive compliance capabilities to safeguard sensitive data and ensure adherence to industry regulations. This section delves into the security and compliance aspects of these leading ERP systems, highlighting their strengths and differences.
Data Protection Measures
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP implement comprehensive data protection measures to secure sensitive information. They employ encryption technologies, access control mechanisms, and data masking techniques to protect data at rest and in transit.
- Data Encryption:Both systems encrypt data at rest, meaning that data stored on databases and files is encrypted, making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption keys. Encryption in transit, using protocols like TLS/SSL, safeguards data transmitted over networks.
- Access Control Mechanisms:SAP ERP and Oracle ERP employ robust access control mechanisms, including role-based access control (RBAC) and granular permissions. This ensures that only authorized users can access specific data and perform specific actions within the system.
- Data Masking:To further protect sensitive data, both systems offer data masking techniques. Data masking replaces sensitive information with non-sensitive values, preventing unauthorized access to critical data while still allowing for testing and analysis.
Security Certifications and Compliance Standards
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP have achieved numerous security certifications and comply with various industry regulations. These certifications and standards attest to the systems’ security posture and their ability to meet stringent compliance requirements.
- SAP ERP:SAP ERP has achieved certifications such as ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System), SOC 1, SOC 2, and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard). It also complies with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act).
- Oracle ERP:Oracle ERP has also obtained several security certifications, including ISO 27001, SOC 1, SOC 2, and PCI DSS. It complies with various regulations, including GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
Implementation and Support
Implementing and supporting an ERP system is a complex and crucial undertaking. The success of an ERP implementation depends heavily on the chosen vendor’s implementation methodology, support services, and the organization’s readiness. Both SAP and Oracle offer a range of implementation and support options tailored to different business needs and organizational sizes.
Implementation Processes
The implementation processes of SAP and Oracle ERP systems share similarities but also have key differences. Both vendors follow a structured approach, involving several phases from initial planning to go-live and ongoing support.
- Planning Phase:This phase involves defining project scope, identifying key stakeholders, and establishing project goals and timelines.
- Requirements Gathering:In this phase, both vendors gather detailed information about the organization’s business processes, existing systems, and desired functionalities.
- Design and Configuration:This phase focuses on designing the ERP system to meet the organization’s specific needs, configuring the system, and developing custom solutions if required.
- Testing and Training:Thorough testing is conducted to ensure the system functions as expected, and users are trained on the new system.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support:The final phase involves transitioning to the new system, monitoring performance, and providing ongoing support to address any issues or enhancements.
However, some differences exist in their implementation approaches:
- SAP:SAP emphasizes a structured, iterative approach with its AcceleratedSAPmethodology. This methodology focuses on rapid deployment through pre-configured solutions and a streamlined implementation process. SAP also offers SAP Activate, which is a guided implementation approach that emphasizes a modular and iterative approach.
- Oracle:Oracle offers a more flexible implementation approach, allowing organizations to choose from various implementation methodologies, including Oracle Rapid Implementation, Oracle Accelerated Implementation, and Oracle Cloud Implementation. Oracle also emphasizes a phased approach, allowing organizations to implement modules incrementally.
Resources and Expertise, Sap erp vs oracle erp
Implementing an ERP system requires significant resources, including dedicated project teams, experienced consultants, and skilled IT professionals. The specific resources and expertise required will vary depending on the complexity of the implementation, the size of the organization, and the chosen implementation methodology.
- Project Team:A dedicated project team consisting of business users, IT professionals, and project managers is essential for successful implementation.
- Consultants:Both SAP and Oracle offer a wide range of consulting services, including implementation, configuration, and integration expertise. These consultants can help guide the implementation process and ensure the system meets the organization’s specific needs.
- IT Professionals:Skilled IT professionals are required for system administration, infrastructure management, and ongoing support.
- Training:Both vendors offer comprehensive training programs for end users, administrators, and IT professionals.
Implementation Methodologies
Both SAP and Oracle offer various implementation methodologies tailored to different needs and organizational sizes. These methodologies aim to streamline the implementation process, reduce risks, and ensure successful adoption.
- SAP:SAP offers a range of implementation methodologies, including AcceleratedSAP, SAP Activate, and SAP S/4HANA Cloud Implementation. These methodologies focus on rapid deployment, pre-configured solutions, and a streamlined implementation process.
- Oracle:Oracle offers several implementation methodologies, including Oracle Rapid Implementation, Oracle Accelerated Implementation, and Oracle Cloud Implementation. These methodologies allow organizations to choose the approach that best suits their needs and timelines.
Support Options
Both SAP and Oracle provide a range of support options to ensure the ongoing success of their ERP systems. These support options include technical support, functional support, and ongoing maintenance.
- Technical Support:Both vendors offer 24/7 technical support to address any technical issues that may arise.
- Functional Support:Both vendors offer functional support to assist with business process issues, system configuration, and user training.
- Maintenance and Upgrades:Both vendors offer maintenance and upgrade services to ensure the system remains up-to-date and secure.
Future Trends and Innovations
The ERP market is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are actively adapting to these changes, incorporating cutting-edge technologies and functionalities to remain competitive. This section delves into the key future trends and innovations shaping the landscape of these ERP giants.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The emergence of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and blockchain is profoundly impacting the ERP market. These technologies are enabling new levels of automation, efficiency, and security in ERP systems.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is revolutionizing ERP systems by automating repetitive tasks, providing real-time insights, and enhancing decision-making. AI-powered features like predictive analytics, chatbots, and intelligent automation are being integrated into both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP. * Predictive Analytics:AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict future trends and outcomes, enabling proactive decision-making in areas like inventory management, supply chain optimization, and risk mitigation.
Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots are being integrated into ERP systems to provide real-time customer support, answer queries, and automate routine tasks, improving user experience and efficiency.
Intelligent Automation
AI is automating tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and order fulfillment, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is transforming ERP deployments, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are increasingly offering cloud-based solutions, enabling businesses to access their ERP systems anytime, anywhere.* Cloud-Based Deployments:Cloud ERP solutions provide a subscription-based model, eliminating the need for upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud ERP systems can easily scale up or down based on changing business needs, providing agility and adaptability.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cloud ERP solutions eliminate the need for on-premises infrastructure, reducing capital expenditure and operational costs.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in the ERP market, offering enhanced security, transparency, and traceability. Blockchain can revolutionize supply chain management, financial transactions, and data security in ERP systems.* Supply Chain Management:Blockchain can provide real-time visibility into the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, improving efficiency and transparency.
Financial Transactions
Blockchain can streamline financial transactions, ensuring secure and tamper-proof record-keeping.
Data Security
Blockchain can enhance data security by providing an immutable and decentralized ledger, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Future Roadmap and Development Plans
Both SAP ERP and Oracle ERP are actively investing in research and development to stay ahead of the curve. Their future roadmaps focus on enhancing existing functionalities, incorporating emerging technologies, and delivering innovative solutions to meet evolving business needs.
SAP ERP
SAP is continuously enhancing its ERP suite with new features and functionalities, driven by the SAP S/4HANA platform. SAP’s future roadmap includes:* Intelligent Enterprise:SAP aims to deliver intelligent ERP solutions that leverage AI, machine learning, and analytics to optimize business processes.
Cloud-First Strategy
SAP is focusing on cloud-based deployments, offering flexible and scalable ERP solutions.
Industry-Specific Solutions
SAP is developing industry-specific solutions to address the unique needs of different sectors.
Oracle ERP
Oracle is also actively developing its ERP solutions, focusing on innovation and integration. Oracle’s future roadmap includes:* Cloud-Native Architecture:Oracle is migrating its ERP solutions to a cloud-native architecture, offering greater scalability and agility.
AI and Machine Learning
Oracle is integrating AI and machine learning capabilities into its ERP solutions to enhance decision-making and automate processes.
Integration with Other Solutions
Oracle is focusing on seamless integration with other Oracle solutions, providing a comprehensive enterprise platform.


