Best Open Source IAM Tools: Secure Your Digital Assets
Best open source IAM tools are the unsung heroes of the digital world, quietly safeguarding our data and access rights. They’re the backbone of secure systems, allowing us to manage user identities and permissions with precision and control. From simple logins to complex multi-factor authentication, these tools empower us to build robust security architectures that protect our most valuable assets.
In today’s interconnected world, where data breaches are a constant threat, having a solid IAM solution is more important than ever. Open source IAM tools offer a compelling alternative to proprietary software, providing flexibility, customization, and cost-effectiveness. These tools empower developers and administrators to tailor security solutions to their specific needs, fostering a culture of secure development practices.
Popular Open Source IAM Tools
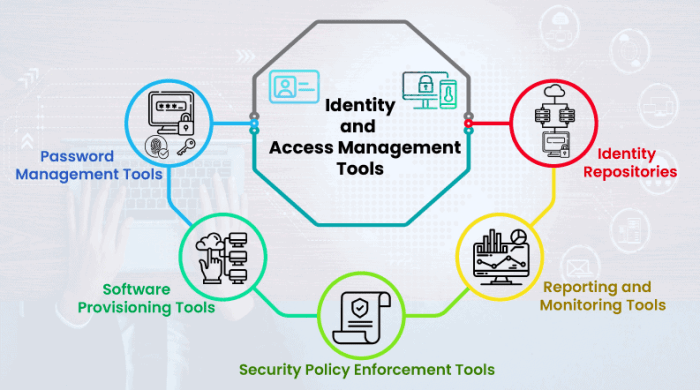
Open-source IAM tools offer a flexible and cost-effective way to manage access control within your organization. These tools provide a range of features to manage users, roles, permissions, and policies, allowing you to enforce granular access controls across your applications and infrastructure.
Popular Open Source IAM Tools
Here are some of the most popular open-source IAM tools:
| Tool | Description | Primary Features | Licensing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keycloak | Keycloak is a comprehensive identity and access management solution that provides a range of features for user authentication, authorization, and single sign-on (SSO). |
|
Apache License 2.0 |
| OAuth2-Proxy | OAuth2-Proxy is a reverse proxy that enables authentication and authorization using OAuth 2.0 protocols. It acts as a gateway between your applications and external identity providers. |
|
Apache License 2.0 |
| Casbin | Casbin is a powerful and flexible authorization library that supports various access control models, including RBAC, ABAC, and ACL. |
|
Apache License 2.0 |
| Auth0 | Auth0 is a comprehensive identity and access management platform that offers a wide range of features, including user authentication, authorization, and API security. |
|
Proprietary |
Deployment and Configuration of Open Source IAM Tools
Open source Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools offer flexibility and control over user access to resources. Choosing the right deployment strategy and configuring the tool effectively are crucial for securing your environment. This section explores the different deployment options and provides a step-by-step guide for configuring an open source IAM tool.
Finding the right open-source IAM tools can be a bit of a journey, but it’s worth the effort for the flexibility and control they offer. It’s almost like finding the perfect accessory for your smartwatch, like this Apple Watch band that gives you hands-free gesture controls – it makes interacting with your device a whole lot easier.
Similarly, the right IAM tools can streamline your access management and security processes, making it simpler to manage your users and resources.
Deployment Options for Open Source IAM Tools
The deployment of open source IAM tools can be tailored to suit various infrastructure setups. Here are the most common options:
- On-Premises Deployment: This option involves installing and managing the IAM tool within your own data center. It provides complete control over the infrastructure and data, ensuring compliance with internal security policies. However, it requires significant resources for setup, maintenance, and ongoing updates.
- Cloud-Based Deployment: Cloud providers offer various IAM solutions that can be easily integrated with existing infrastructure. These services handle the underlying infrastructure, updates, and security, simplifying deployment and management. However, it involves relying on a third-party provider for security and data control.
Choosing the right open-source IAM tools can be a real game-changer for your project. But sometimes, you just need a break from all the technical stuff and get creative. If you’re looking for a fun project, why not try transferring a photo to fabric?
There are lots of cool techniques out there, like using iron-on transfer paper or even fabric paint. Check out this great guide on how to transfer a photo to fabric for some inspiration. Once you’ve finished your masterpiece, you can get back to exploring the world of open-source IAM tools with renewed energy.
- Hybrid Deployment: This approach combines both on-premises and cloud-based components. It offers flexibility by leveraging the strengths of both options, allowing organizations to manage sensitive data on-premises while utilizing cloud services for scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Configuring Open Source IAM Tools
Configuring an open source IAM tool involves several steps, each contributing to a secure and robust access control system. Here’s a step-by-step guide for configuring Keycloak, a popular open source IAM tool, for a specific use case:
Step 1: Installation and Setup
- Download and install Keycloak on a suitable server. This can be done through a package manager or by compiling from source code.
- Configure the database connection for storing user data and configurations. Keycloak supports various databases, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, and H2.
- Set up the Keycloak server with the necessary configuration parameters, such as the admin console URL, realm name, and default language.
Step 2: Defining Realms
- A realm represents a distinct security domain within Keycloak, typically corresponding to a specific application or organization. Create a realm for your application.
- Configure the realm’s security settings, including the authentication mechanisms (e.g., username/password, social logins), authorization policies, and user management options.
Step 3: Creating Users and Roles
- Add users to the realm, defining their credentials, roles, and permissions. You can create users manually or through automated provisioning mechanisms.
- Define roles within the realm, representing different levels of access and privileges. Each role can be assigned specific permissions to access resources or perform actions.
Step 4: Integrating with Applications
- Integrate Keycloak with your application by configuring it to use Keycloak’s authentication and authorization services.
- Use Keycloak’s adapter libraries to simplify the integration process for various programming languages and frameworks.
- Configure Keycloak to handle user logins, validate user permissions, and enforce access control policies based on defined roles.
Step 5: Monitoring and Maintenance
- Monitor Keycloak’s performance and security logs to identify potential issues and vulnerabilities.
- Regularly update Keycloak to benefit from security patches and new features.
- Implement backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability and resilience.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating open-source IAM tools with existing systems is crucial for seamless identity and access management across your infrastructure. This integration allows for centralized control and consistent security policies, regardless of the systems involved.
Choosing the right open source IAM tool can be a challenge, especially when considering the rapid pace of innovation in the tech world. For example, ios 18 will feature one of the most relatable iphone features of all time , which highlights how user-centricity is becoming increasingly important.
So, when evaluating open source IAM solutions, it’s crucial to factor in features that prioritize user experience and security.
Common Integration Points
Open-source IAM tools typically integrate with various systems through APIs and protocols, facilitating communication and data exchange. Common integration points include:
- Databases:IAM tools often rely on databases to store user information, permissions, and audit logs. They integrate with databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MongoDB to manage user data and access control policies.
- Authentication Services:Integration with authentication services like LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) or SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) allows users to authenticate using existing credentials and provides single sign-on (SSO) capabilities. This simplifies the login process for users and streamlines access control.
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs):IAM tools often expose APIs to enable integration with other applications and services. This allows for programmatic access control, automation, and integration with custom workflows.
- Other IAM Tools:Some IAM tools can be integrated with other existing IAM solutions, either for centralized management or to leverage specific features. This approach helps bridge gaps between different systems and offers flexibility in managing identities and access control.
Integration Scenarios and Challenges
Successful integration scenarios often involve using open-source IAM tools to enhance existing security measures or to implement new security policies across various systems.
- Centralized User Management:Integrating an open-source IAM tool with multiple applications and databases can provide a centralized platform for managing user accounts, permissions, and access control policies. This eliminates the need for managing user accounts in multiple systems and reduces the risk of inconsistencies.
- Single Sign-On (SSO):Integrating with authentication services allows users to authenticate once and access multiple applications and services. This improves user experience and reduces administrative overhead.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):Integrating with MFA services enhances security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access systems.
- Audit and Compliance:Integrating with logging and monitoring tools enables comprehensive auditing and compliance reporting, ensuring that all access activities are tracked and analyzed.
Challenges often arise during integration, requiring careful planning and execution:
- Data Synchronization:Maintaining data consistency between the IAM tool and other systems can be challenging, especially when dealing with large datasets and frequent updates. Implementing robust data synchronization mechanisms is essential.
- Security Considerations:Integration requires careful security considerations to ensure that sensitive data is protected and that access is properly controlled. This involves secure communication channels, authentication protocols, and authorization mechanisms.
- Compatibility Issues:Ensuring compatibility between the open-source IAM tool and existing systems can be challenging, particularly when dealing with legacy systems or custom integrations. Thorough testing and validation are crucial.
- Complexity:Integrating IAM tools with existing systems can be complex, requiring technical expertise and a deep understanding of the involved technologies.
Methods for Integration
Various methods can be employed to integrate open-source IAM tools with existing infrastructure.
- API Integration:This involves using APIs to exchange data and commands between the IAM tool and other systems. API integration offers flexibility and allows for custom integrations.
- Protocol Integration:Using industry-standard protocols like LDAP, SAML, or OAuth enables seamless integration with existing authentication services and applications.
- Connector Integration:Some open-source IAM tools offer pre-built connectors for popular applications and services, simplifying the integration process.
- Custom Development:Custom development can be necessary for integrating with unique or legacy systems that lack standard integration options. This approach requires specialized skills and resources.
Security Considerations for Open Source IAM Tools: Best Open Source Iam Tools
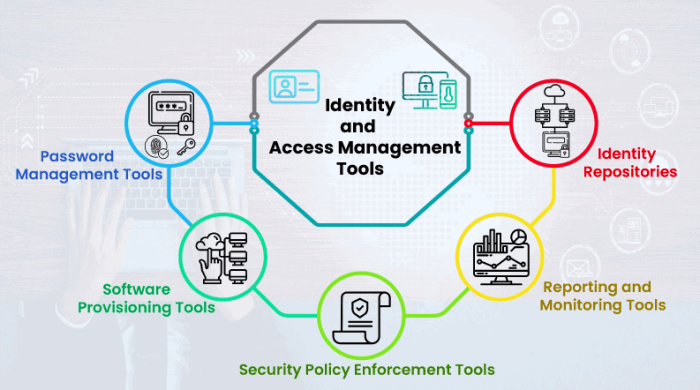
Open source IAM tools offer flexibility and customization, but they also introduce unique security challenges. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial for implementing a robust and secure IAM solution.
Security Risks Associated with Open Source IAM Tools
Open source IAM tools, while offering flexibility and customization, present specific security risks that require careful consideration.
- Vulnerabilities in the Codebase:Open source software is often subject to public scrutiny, which can lead to the identification of vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or systems.
- Lack of Security Audits:Not all open source IAM tools undergo rigorous security audits, which can leave them vulnerable to known and unknown security flaws.
- Dependency on Third-Party Libraries:Open source IAM tools often rely on third-party libraries, which can introduce vulnerabilities if those libraries are not properly vetted and maintained.
- Configuration Errors:Improper configuration of open source IAM tools can create security loopholes that attackers can exploit. This can include weak passwords, insecure permissions, or missing security controls.
- Limited Support:While open source IAM tools offer community support, the level of support may not be as comprehensive as commercial solutions. This can make it difficult to identify and address security issues promptly.
Best Practices for Securing Open Source IAM Solutions
Implementing best practices is essential to mitigate security risks associated with open source IAM tools.
- Choose Secure and Well-Maintained Tools:Select open source IAM tools with a strong track record of security audits and active community support.
- Regularly Update and Patch:Regularly update the open source IAM tools and their dependencies to address known vulnerabilities.
- Implement Strong Authentication:Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance user authentication and prevent unauthorized access.
- Minimize Privileges:Implement the principle of least privilege, granting users only the permissions they need to perform their tasks.
- Secure Configuration:Carefully configure the open source IAM tools to enforce security best practices, such as strong passwords, secure communication protocols, and access control policies.
- Regular Security Audits:Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in the open source IAM tools.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity:Implement monitoring and logging systems to detect and investigate suspicious activity related to the open source IAM tools.
Common Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Understanding common security vulnerabilities and their mitigation strategies is crucial for securing open source IAM solutions.
| Vulnerability | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Implement input validation and output encoding to prevent malicious scripts from being injected into the application. |
| SQL Injection | Use parameterized queries and input validation to prevent attackers from manipulating SQL queries. |
| Authentication Bypass | Implement robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to prevent attackers from bypassing authentication controls. |
| Authorization Bypass | Enforce access control policies based on the principle of least privilege to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data or resources. |
| Insecure Direct Object References | Use indirect object references to prevent attackers from accessing sensitive data or resources directly. |
| Log Injection | Validate and sanitize log messages to prevent attackers from injecting malicious code into log files. |
| Denial of Service (DoS) | Implement rate limiting and other security measures to prevent attackers from overwhelming the system with requests. |
Future Trends in Open Source IAM
The realm of open-source Identity and Access Management (IAM) is constantly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for secure, flexible, and adaptable solutions. This evolution is fueled by advancements in technology, evolving security landscapes, and the growing adoption of cloud-native architectures.
The Rise of AI and Machine Learning in IAM
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize open-source IAM solutions. These technologies can automate tasks, improve security posture, and enhance user experience.
- Automated Threat Detection and Response: AI-powered IAM systems can analyze user behavior patterns and identify anomalies that may indicate potential threats. This proactive approach can help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Adaptive Access Control: AI algorithms can dynamically adjust access permissions based on real-time factors like user location, device type, and network conditions. This ensures that access is granted only when necessary and in a secure manner.
- Enhanced User Experience: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can streamline user authentication processes, provide personalized support, and automate password reset procedures. This simplifies user interactions and reduces the burden on IT teams.
Blockchain’s Impact on IAM
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and immutable ledger that can enhance security and transparency in IAM.
- Secure Identity Management: Blockchain can be used to store and manage digital identities, ensuring their authenticity and integrity. This can help prevent identity theft and fraud.
- Decentralized Access Control: Blockchain-based IAM systems can enable decentralized access control, allowing organizations to grant and manage permissions without relying on a central authority. This fosters greater autonomy and reduces the risk of single points of failure.
- Auditable and Transparent Operations: All IAM actions and transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing a permanent and immutable audit trail. This enhances accountability and transparency within the organization.
The Future of Open Source IAM, Best open source iam tools
Open-source IAM solutions are expected to become even more sophisticated, integrated, and user-friendly in the future.
- Increased Focus on Zero Trust: Open-source IAM tools will embrace zero-trust principles, requiring continuous authentication and authorization for every user and device. This will strengthen security posture and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Interoperability: Open-source IAM solutions will become more interoperable with other systems and platforms, enabling seamless integration across different environments. This will facilitate the adoption of a holistic approach to security.
- Greater Customization and Flexibility: Open-source IAM tools will offer greater flexibility and customization options, allowing organizations to tailor their solutions to meet specific needs and requirements.