
Using Apple Devices in a Microsoft-Centric Business
Using apple devices in microsoft centric business – Imagine a world where your business runs smoothly, seamlessly integrating both Apple and Microsoft technologies. While the idea might seem like a tech utopia, the reality is that using Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric business can present unique challenges. From compatibility issues to security concerns, navigating this hybrid landscape requires careful consideration and strategic planning.
But with the right approach, you can unlock a world of possibilities, leveraging the best of both worlds to boost productivity and collaboration.
This article delves into the intricacies of integrating Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric environment, exploring the potential benefits, challenges, and strategies for success. We’ll examine the compatibility and integration challenges, discuss management and security considerations, and explore the impact on productivity, collaboration, and user experience.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the key factors to consider when deciding whether to embrace a mixed-device strategy.
The Challenge of Apple Devices in a Microsoft-Centric Business
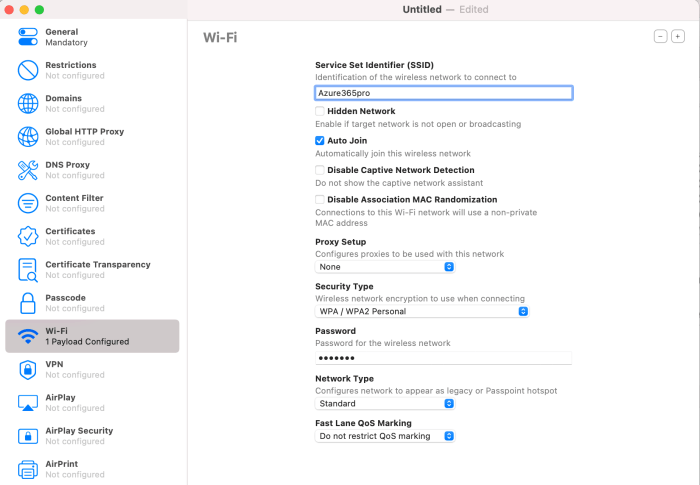
The integration of Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric business environment can present unique challenges, particularly regarding compatibility, management, and security. While Apple products are known for their user-friendliness and design, their integration into a Microsoft-dominated infrastructure can lead to various issues that need to be addressed carefully.
Compatibility Issues
The compatibility between Apple and Microsoft software and hardware can be a significant hurdle. Apple’s macOS and iOS operating systems are distinct from Microsoft’s Windows and its associated applications. This difference can lead to incompatibility issues in various aspects, including:
- File Sharing and Data Transfer:Sharing files between Apple and Windows devices can be problematic due to differing file formats and protocols. For example, Apple’s Pages document format is not natively compatible with Microsoft Word, requiring conversion or compatibility issues. This can lead to data loss or formatting inconsistencies when transferring files between different platforms.
- Application Compatibility:Some Microsoft applications, such as Microsoft Office, are available on macOS, but their functionality and features may be limited compared to their Windows counterparts. Additionally, certain applications, especially those designed for Windows, may not be available on macOS, creating a gap in software accessibility for Apple users.
- Hardware Compatibility:While some peripherals and accessories are compatible with both Apple and Windows devices, others may be exclusive to one platform. For example, some printers may only support Windows drivers, making it difficult for Apple users to print documents seamlessly.
Management and Security Challenges
Managing and securing Apple devices within a Microsoft-dominated infrastructure can pose challenges. Apple’s operating systems and management tools differ significantly from Microsoft’s, leading to potential difficulties in:
- Device Management:Managing Apple devices within a Microsoft environment can be complex, as Microsoft’s management tools, such as Microsoft Endpoint Manager, are primarily designed for Windows devices. Integrating Apple devices into these systems requires additional configurations and tools, such as Apple’s own MDM (Mobile Device Management) solutions.
This can lead to a more fragmented management infrastructure, requiring separate tools and processes for different platforms.
- Security:Security policies and configurations for Apple devices may differ from those implemented for Windows devices. Microsoft’s security solutions, such as Azure Active Directory, may not fully extend to Apple devices, requiring additional security measures to be implemented. This can lead to a more complex security landscape, potentially increasing the risk of security vulnerabilities and data breaches.
- Data Protection:Apple’s data protection features, such as its encryption capabilities and privacy settings, may differ from Microsoft’s. Ensuring consistent data protection across both platforms requires careful planning and configuration, especially when dealing with sensitive data or compliance requirements.
Compatibility and Integration
While Apple devices offer a user-friendly experience, integrating them into a Microsoft-centric business environment presents unique challenges. These challenges arise from the inherent differences between the two ecosystems, particularly in terms of software and hardware compatibility.
Software Compatibility
Software compatibility is a major concern when integrating Apple devices into a Microsoft environment. Many Microsoft applications, especially those designed for Windows, may not run natively on macOS or iOS. While some applications offer limited functionality or are available as web-based alternatives, others may require workarounds or alternative solutions.
- Microsoft Office Suite:While Microsoft Office is available for macOS, the features and functionality may differ slightly from the Windows version. Additionally, some advanced features, such as certain Excel macros, might not be fully compatible.
- Active Directory and Group Policy:Active Directory (AD) is a core component of many Microsoft environments for managing user accounts, permissions, and devices. However, AD integration with macOS is limited, requiring third-party solutions or manual configuration for managing user accounts and security policies.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems:Many businesses rely on ERP systems like SAP or Oracle, which may not have native support for macOS. This can necessitate the use of virtual machines or cloud-based access, potentially impacting performance and user experience.
Hardware Compatibility
Hardware compatibility is another key consideration. Apple devices use different hardware components and protocols compared to Windows devices, leading to potential compatibility issues with peripherals, network devices, and other hardware components.
- Printers:While most modern printers offer drivers for both macOS and Windows, older or specialized printers might not have macOS drivers. This could require finding alternative drivers or relying on network printing solutions.
- Peripherals:Some peripherals, such as USB-C docks or external storage devices, may not be fully compatible with both macOS and Windows. This can lead to limitations in data transfer, power delivery, or functionality.
- Network Infrastructure:Apple devices may not always seamlessly integrate with Microsoft-centric network infrastructure, particularly with older network equipment or security protocols. This can result in issues with network connectivity, authentication, and security.
Workflow Implications
The use of Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric business can also impact workflows and collaboration. While Apple devices offer a user-friendly experience, their integration with Microsoft tools and processes might require adjustments or workarounds.
While Apple devices might not be the first choice for a Microsoft-centric business, it’s possible to integrate them seamlessly. One way to bridge the gap is by mastering the command line interface in Microsoft , which provides a universal language for managing both Windows and macOS systems.
This opens up a world of possibilities for managing and sharing data between different platforms, making Apple devices a viable option even in a Microsoft-dominated environment.
- File Sharing and Collaboration:Sharing files between macOS and Windows devices can be challenging, particularly for larger files or specialized formats. Cloud storage solutions can help bridge the gap, but they may not be suitable for all situations.
- Remote Access and Management:Managing and supporting Apple devices remotely can be more complex compared to Windows devices, as they require different tools and configurations. This can necessitate additional expertise and resources for IT support.
- Security and Compliance:Ensuring security and compliance with Apple devices can be more challenging in a Microsoft-centric environment, as Apple devices may have different security features and configurations. This can require additional measures to ensure data security and regulatory compliance.
Management and Security

Integrating Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric business environment introduces unique challenges in managing and securing these devices. While both platforms offer robust management tools, their approaches and functionalities differ significantly, requiring careful consideration of compatibility, integration, and potential vulnerabilities.
Navigating a Microsoft-centric business with Apple devices can be a unique challenge, especially when it comes to security. It’s crucial to be aware of the various social engineering tactics used by attackers, like those outlined in this article on 6 persuasion tactics used in social engineering attacks , to protect your data.
Understanding these tactics can help you recognize and avoid potential threats, ensuring the smooth integration of your Apple devices within your Microsoft environment.
Management Tools Comparison
The choice of management tools for Apple and Microsoft devices heavily influences the efficiency and effectiveness of managing a mixed IT environment.
- Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM):A comprehensive platform for managing Windows, Android, and iOS devices. While it offers excellent integration with other Microsoft services and robust features for managing Windows devices, its support for Apple devices is less extensive compared to Apple’s own management tools.
- Apple Device Management (Apple MDM):A dedicated solution for managing Apple devices, including iPhones, iPads, and Macs. It provides granular control over device settings, apps, and data, offering superior capabilities for managing Apple devices compared to MEM.
The ideal approach involves leveraging both platforms. MEM can manage Windows and Android devices effectively, while Apple MDM provides comprehensive control over Apple devices. This dual-platform strategy ensures comprehensive management across the entire IT infrastructure.
While Apple devices might not be the first choice in a Microsoft-centric business, the integration of Apple’s ecosystem with Microsoft’s offerings is becoming increasingly seamless. For instance, Microsoft’s commitment to blockchain technology, as seen in their facilitation of automated transactions with blockchain and the COCO framework , could potentially bridge the gap between the two platforms.
This advancement in automated transactions could lead to a more efficient and secure exchange of data between Apple and Microsoft devices, ultimately benefiting businesses operating within a mixed environment.
Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Integrating Apple devices into a Microsoft environment raises security concerns due to the inherent differences in operating systems and security architectures.
- Data Access and Sharing:Data sharing between Apple and Microsoft platforms can be challenging, potentially exposing sensitive information if not properly managed. Implementing strict data access policies, using secure communication protocols, and leveraging encryption technologies are essential for mitigating these risks.
- Malware and Security Threats:Apple devices are generally considered more secure than Windows devices, but they are not immune to malware and security threats. Implementing robust security measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and regular security updates, is crucial for protecting Apple devices within a Microsoft environment.
- Device Management and Control:Managing Apple devices within a Microsoft environment can be complex, particularly when enforcing security policies. Implementing strong password policies, enabling device encryption, and using MDM solutions to restrict device access and data sharing are vital for ensuring security and compliance.
These strategies, along with proactive security monitoring and incident response plans, can help minimize the risks associated with using Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric business environment.
Productivity and Collaboration
The integration of Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric business environment raises questions about the impact on productivity and collaboration. While Apple devices are known for their user-friendly interface and intuitive design, their compatibility with Microsoft tools and services might pose challenges.
Document Sharing
The ability to seamlessly share documents between Apple and Microsoft platforms is crucial for efficient collaboration. Apple’s iWork suite, comprising Pages, Numbers, and Keynote, offers a robust set of productivity tools that can create documents compatible with Microsoft Office. However, some formatting inconsistencies may occur when sharing documents between the two platforms.
Additionally, while Apple’s iCloud offers cloud storage and synchronization capabilities, it lacks the comprehensive features of Microsoft OneDrive, which is deeply integrated with Office 365.
Video Conferencing
Apple’s FaceTime is a popular video conferencing tool known for its ease of use and high-quality video calls. However, Microsoft Teams is the preferred platform for video conferencing in many Microsoft-centric businesses. While FaceTime can be integrated with Teams using third-party apps, the experience may not be as seamless as using Teams’ native features.
Integration with Microsoft Collaboration Tools
Apple devices can be integrated with Microsoft collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams and Office 365. However, the integration may not be as comprehensive as using native Microsoft devices. For instance, while Apple devices can access Microsoft Teams, they may not support all features, such as the ability to join meetings directly from a calendar notification or seamlessly share files within a team channel.
Advantages of Using Apple Devices
- User-Friendly Interface:Apple devices are known for their intuitive design and ease of use, which can improve user productivity.
- Strong Security Features:Apple devices have robust security features, including built-in encryption and a secure operating system, which can enhance data protection in a business environment.
- Seamless Integration with Apple Ecosystem:Apple devices integrate seamlessly with other Apple products and services, such as iCloud, Apple Music, and Apple Pay, which can improve workflow efficiency for users who rely on the Apple ecosystem.
Disadvantages of Using Apple Devices
- Compatibility Issues:Apple devices may experience compatibility issues with certain Microsoft tools and services, leading to potential workarounds and reduced productivity.
- Limited Customization:Apple devices offer limited customization options compared to Windows PCs, which may restrict users’ ability to tailor their devices to their specific needs.
- Higher Cost:Apple devices generally have a higher price point compared to comparable Windows PCs, which can be a significant factor for businesses with budget constraints.
User Experience and Adoption
The user experience of Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric business environment is a complex topic, influenced by factors such as user familiarity, preferences, and the overall integration of the devices into the existing IT infrastructure. The impact on user adoption and satisfaction can be significant, as it affects how employees interact with their work tools and ultimately influences their productivity and overall job satisfaction.
User Familiarity and Preferences
User familiarity and preferences play a crucial role in the adoption of Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric environment. Many employees are accustomed to using Microsoft products and may be hesitant to adapt to a new operating system and interface. The transition can be challenging, especially for users who are not familiar with Apple’s ecosystem and its features.
- User-friendly interface:Apple devices are known for their user-friendly interface, which can be appealing to users who are not tech-savvy. However, the simplicity of Apple’s interface can also be a challenge for users who are accustomed to the more complex features and functionalities of Windows.
- Customization:While Apple devices offer a degree of customization, they are generally less customizable than Windows devices. This can be a drawback for users who prefer to personalize their devices to suit their specific needs and preferences.
- Mobile integration:Apple devices are tightly integrated with Apple’s mobile ecosystem, which can be beneficial for users who rely heavily on mobile devices. However, this integration can also create challenges for users who prefer to use different mobile devices or operating systems.
Impact on User Adoption and Satisfaction
The impact of Apple devices on user adoption and satisfaction depends on several factors, including the company’s IT infrastructure, the level of support provided to employees, and the overall company culture.
- Training and support:Adequate training and support are essential to ensure a smooth transition to Apple devices. Employees should be provided with the necessary resources and guidance to learn how to use the new devices and software.
- Integration with existing infrastructure:Integrating Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric IT infrastructure can be challenging, especially for organizations with complex IT environments. Compatibility issues may arise, requiring additional resources and time to resolve.
- User acceptance:The level of user acceptance depends on factors such as the user’s familiarity with Apple devices, their preferences, and the overall company culture. If employees are not comfortable using Apple devices, it can lead to resistance and lower adoption rates.
Cost and ROI
The decision to integrate Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric business environment necessitates a careful consideration of the associated costs and potential return on investment (ROI). While Apple devices offer a unique user experience and advanced features, their integration into a Microsoft ecosystem can present specific challenges and financial implications.
This section examines the cost factors, potential savings, and ROI considerations when deploying Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric business.
Cost Implications, Using apple devices in microsoft centric business
Understanding the cost implications of using Apple devices within a Microsoft environment is crucial for making informed decisions. The costs associated with Apple devices encompass various aspects, including purchase price, management, support, and integration.
- Purchase Price:Apple devices, particularly Macs and iPads, tend to have a higher purchase price compared to their Windows counterparts. This price difference can be significant, especially when purchasing devices in bulk for an entire organization.
- Management and Support:Managing and supporting Apple devices within a Microsoft environment can present unique challenges. While Apple provides its own management tools, integrating these with existing Microsoft infrastructure might require additional software or services, potentially increasing management costs.
- Integration:Ensuring seamless integration between Apple devices and Microsoft applications and services can be a complex task. This might involve additional software licenses, custom configurations, or specialized expertise, contributing to higher integration costs.
Potential Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
While Apple devices come with a higher upfront cost, they can potentially generate cost savings and efficiency gains in the long run.
- Improved Productivity:Apple devices are known for their user-friendly interface and intuitive design, which can contribute to improved employee productivity. This can translate into higher output, reduced training time, and overall efficiency gains.
- Reduced IT Support Costs:Apple devices are generally considered to be more stable and require less maintenance than their Windows counterparts. This can lead to reduced IT support costs and a more efficient IT department.
- Security Enhancements:Apple devices have strong security features built-in, which can reduce the risk of security breaches and associated costs. The company’s focus on privacy and security can provide a more secure environment for sensitive data.
- Reduced Hardware Replacement Costs:Apple devices are known for their longevity and durability. This can result in reduced hardware replacement costs over time, as devices may last longer than their Windows counterparts.
ROI Analysis
Calculating the ROI of using Apple devices in a Microsoft-centric business requires a comprehensive analysis of the potential costs and benefits.
The ROI can be calculated using the following formula: ROI = (Total Benefits
Total Costs) / Total Costs
To determine the ROI, consider factors such as:
- Increased Productivity:Quantify the potential increase in productivity due to the use of Apple devices, such as increased output or reduced time spent on tasks.
- Reduced IT Support Costs:Calculate the potential savings in IT support costs due to the use of Apple devices, taking into account factors such as fewer support tickets or reduced maintenance requirements.
- Security Enhancements:Assess the potential reduction in security risks and associated costs due to the use of Apple devices, considering factors such as reduced risk of data breaches or malware infections.
- Reduced Hardware Replacement Costs:Estimate the potential savings in hardware replacement costs due to the longer lifespan of Apple devices.
Best Practices and Recommendations: Using Apple Devices In Microsoft Centric Business
Successfully integrating Apple devices into a Microsoft-centric business requires careful planning and execution. This involves addressing compatibility, management, security, and productivity challenges while optimizing user experience and maximizing return on investment.
Compatibility and Integration Strategies
Ensuring seamless integration between Apple and Microsoft environments is crucial for a smooth transition.
- Leverage Cross-Platform Solutions:Utilize solutions like Microsoft Teams, OneDrive, and Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to enable collaboration and data sharing across platforms. Microsoft Teams, for example, offers native support for both iOS and macOS, allowing users to communicate and collaborate regardless of their device type.
- Employ Virtualization:Implement virtualization solutions like Parallels Desktop or VMware Fusion to run Windows applications on macOS devices. This provides a consistent user experience and enables access to applications that may not have native macOS counterparts.
- Explore Cloud-Based Solutions:Utilize cloud-based services like Microsoft 365, which offers access to applications and data across multiple devices, including iOS and macOS. This eliminates the need for local installations and provides a consistent experience across platforms.
Management and Security Best Practices
Managing and securing Apple devices within a Microsoft-centric environment requires a robust approach.
- Utilize Mobile Device Management (MDM) Solutions:Implement an MDM solution like Microsoft Endpoint Manager to manage and secure Apple devices, including enforcing policies, deploying applications, and managing device access. Microsoft Endpoint Manager provides comprehensive management capabilities for both iOS and macOS devices, allowing IT administrators to enforce security policies, deploy applications, and monitor device activity.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):Implement 2FA for all user accounts to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access. This can be achieved through Azure AD, which supports 2FA for both iOS and macOS devices.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP):Utilize DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the corporate network, regardless of the device used. This can be integrated with Microsoft Endpoint Manager to enforce data protection policies across Apple devices.
Productivity and Collaboration Optimization
Optimizing productivity and collaboration in a mixed-device environment requires a strategic approach.
- Promote Cross-Platform Collaboration Tools:Encourage the use of cross-platform collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams, which allows for seamless communication and file sharing across iOS, macOS, Windows, and Android devices.
- Utilize Cloud Storage Solutions:Implement cloud storage solutions like OneDrive and SharePoint to enable access to files and documents from any device, regardless of platform.
- Provide Comprehensive Training:Offer comprehensive training to users on how to effectively utilize cross-platform tools and resources, ensuring they can maximize productivity in a mixed-device environment.


