VMware Cloud vs Microsoft Azure: Choosing the Right Cloud Platform
VMware Cloud vs Microsoft Azure: the battle for cloud supremacy rages on, each platform offering a compelling suite of services to cater to diverse business needs. Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure have carved out their niches in the cloud computing landscape, providing infrastructure, platforms, and software as a service to businesses of all sizes.
This article dives into the key differences and similarities between these two giants, helping you navigate the complexities of cloud adoption and make an informed decision for your organization.
From infrastructure models and service offerings to security considerations and pricing strategies, we’ll explore the nuances of each platform, providing a comprehensive comparison that empowers you to choose the best fit for your specific requirements.
Introduction: Vmware Cloud Vs Microsoft Azure

Cloud computing has become an indispensable tool for businesses of all sizes, revolutionizing the way they operate and interact with their customers. It offers a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to access and manage computing resources, enabling organizations to adapt to ever-changing market demands and innovate at a rapid pace.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of cloud computing, exploring two prominent players: VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure. These platforms provide a comprehensive suite of cloud services, each catering to specific needs and target audiences.
VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure: Key Features and Target Audiences
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer a wide range of cloud services, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). However, they differ in their core features and target audiences.
- VMware Cloud: VMware Cloud is a hybrid cloud platform that seamlessly integrates with on-premises VMware environments, offering a familiar experience for IT professionals accustomed to VMware technologies. It is particularly well-suited for organizations seeking to extend their existing VMware infrastructure to the cloud, enabling a smooth transition and reducing the learning curve for their IT teams.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure is a public cloud platform that provides a comprehensive set of cloud services, including computing, storage, networking, databases, analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI). It is designed for organizations looking for a flexible and scalable cloud platform with a wide range of services and tools.
Azure’s strong integration with Microsoft products and services makes it an attractive option for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Infrastructure and Services
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer a comprehensive range of infrastructure and services to support various workloads and application deployments. Understanding the differences in their infrastructure models, compute, storage, and networking options, as well as the specific services they provide, is crucial for making informed decisions about which platform best suits your needs.
Infrastructure Models
The infrastructure models offered by VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure are distinct and cater to different preferences and requirements. VMware Cloud primarily focuses on extending the familiar on-premises VMware environment to the cloud, while Microsoft Azure provides a broader range of services encompassing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
- VMware Cloud: VMware Cloud primarily offers Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) solutions, extending the familiar VMware vSphere environment to the cloud. This approach is particularly beneficial for organizations already invested in VMware technologies, seeking a seamless transition to the cloud with minimal disruption to existing infrastructure and workflows.
It offers a consistent experience across on-premises and cloud environments, simplifying management and reducing the learning curve for IT teams.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure offers a more comprehensive range of infrastructure models, encompassing IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. This flexibility allows organizations to choose the level of control and management they desire.
- IaaS: Azure’s IaaS offerings provide virtual machines, storage, networking, and other infrastructure components, giving users granular control over their environment.
Choosing between VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure is a big decision, especially when you consider the ever-evolving landscape of customer identity management. The latest trends in this area, as outlined in this article on okta customer identity trends , highlight the need for robust, flexible solutions.
Whether you choose VMware Cloud’s emphasis on on-premises integration or Azure’s cloud-native approach, ensuring a seamless and secure customer identity experience should be a top priority.
- PaaS: Azure’s PaaS offerings provide a platform for developing and deploying applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. These services include databases, web apps, and container services, simplifying application development and deployment.
- SaaS: Azure’s SaaS offerings provide complete software solutions, such as Office 365 and Dynamics 365, which are accessed through the cloud and managed by Microsoft.
- IaaS: Azure’s IaaS offerings provide virtual machines, storage, networking, and other infrastructure components, giving users granular control over their environment.
Compute Options
Both platforms offer a wide array of compute options to cater to various workload requirements, ranging from small, cost-effective virtual machines to powerful, high-performance instances.
- VMware Cloud: VMware Cloud leverages the familiar vSphere architecture, offering a wide range of virtual machine types and configurations. These virtual machines can be customized to meet specific performance and resource needs. For example, you can choose from different CPU types, memory configurations, and storage options.
VMware Cloud also supports the deployment of vSphere clusters, providing high availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure offers a diverse set of virtual machine sizes and types, including general-purpose, memory-optimized, and compute-optimized instances. This allows users to select the best-suited option for their specific workloads. Azure also provides options for deploying virtual machines with different operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and other specialized distributions.
Furthermore, Azure offers advanced features like spot instances and dedicated hosts, which can be leveraged for cost optimization and enhanced security, respectively.
Storage Options
Storage is a critical component of any cloud infrastructure, and both platforms offer a range of storage options to suit different performance and cost requirements.
- VMware Cloud: VMware Cloud leverages the storage capabilities of the underlying cloud provider, offering various storage options, including block storage, file storage, and object storage. These options provide flexibility in choosing the appropriate storage solution for different workloads and data types.
For instance, block storage is suitable for high-performance applications requiring low latency, while object storage is ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure offers a comprehensive storage portfolio, including block storage (Azure Disk), file storage (Azure Files), object storage (Azure Blob), and managed databases (Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB). These storage options provide flexibility in terms of performance, cost, and scalability, enabling users to select the most appropriate solution for their needs.
Azure also provides advanced storage features like data replication, backup, and disaster recovery, ensuring data availability and resilience.
Networking Options
Networking is essential for connecting cloud resources and enabling communication between applications and users. Both platforms offer robust networking capabilities, including virtual networks, load balancers, and firewalls.
- VMware Cloud: VMware Cloud leverages the networking capabilities of the underlying cloud provider, offering virtual networks, load balancers, and firewalls. These networking components enable users to create secure and isolated networks for their cloud deployments.
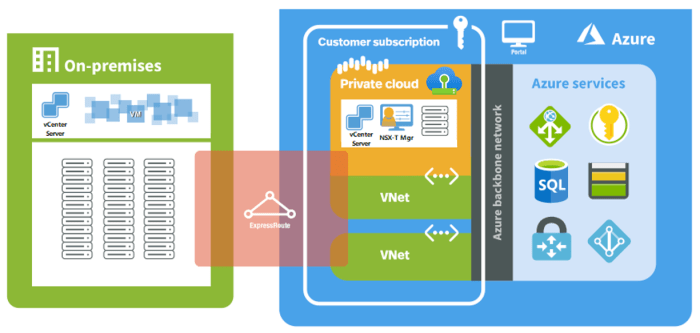
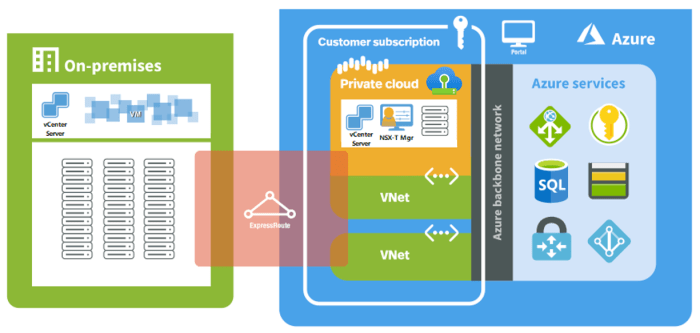
- Microsoft Azure: Azure provides a comprehensive networking platform with features like virtual networks, subnets, network security groups, and load balancers. This allows users to create highly customized and secure network environments for their cloud deployments. Azure also offers advanced networking features like VPN gateways, ExpressRoute, and Azure Firewall, providing enhanced connectivity and security capabilities.
Services
Beyond the core infrastructure components, both platforms offer a wide array of services to enhance application development, deployment, and management.
- VMware Cloud: VMware Cloud provides services like VMware vCenter Server, VMware NSX, and VMware Cloud Director. These services simplify management and automation tasks, enabling users to efficiently deploy and manage their cloud environments.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure offers a vast ecosystem of services, including databases (Azure SQL Database, Azure Cosmos DB), web services (Azure App Service), container services (Azure Kubernetes Service), and artificial intelligence (Azure Cognitive Services). These services provide a comprehensive platform for developing, deploying, and managing various types of applications.
Deployment and Management
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer comprehensive tools and methodologies for deploying and managing applications. However, their approaches differ significantly in terms of ease of use, flexibility, and overall experience.
Choosing between VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure can be tough, especially when you’re trying to balance cost, features, and ease of use. But while I’m busy pondering that decision, I’m also excited about the upcoming adaptation of William Gibson’s cyberpunk classic, Neuromancer on Apple TV+.
It’s a reminder that even with all the tech talk, sometimes the best stories are about humanity’s struggle in a rapidly changing world, which is a struggle that applies equally to the cloud infrastructure we choose.
Deployment Tools and Methodologies
The deployment tools and methodologies employed by VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure reflect their respective origins and target audiences. VMware Cloud, being a cloud-based extension of VMware’s on-premises virtualization platform, leverages familiar tools and concepts for VMware users. Azure, on the other hand, offers a more integrated and cloud-native approach.
Choosing between VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure can be a tough decision, especially when considering security. It’s important to understand the tactics social engineers use to exploit vulnerabilities, and how they can be applied to cloud environments. Take a look at 6 persuasion tactics used in social engineering attacks to better understand how these tactics could be used to gain access to your cloud infrastructure.
Knowing these tactics can help you implement stronger security measures for both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
- VMware Cloud:VMware Cloud leverages familiar tools like vCenter Server, vSphere, and NSX-T for managing virtual machines, networks, and security. These tools provide a consistent experience for VMware users migrating to the cloud.
- Microsoft Azure:Azure offers a comprehensive suite of deployment and management tools, including Azure Portal, Azure CLI, PowerShell, and Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates. These tools provide a unified platform for managing all aspects of your Azure infrastructure and applications.
Ease of Use and Flexibility
The ease of use and flexibility of deployment and management tools vary between VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
- VMware Cloud:VMware Cloud’s familiarity and consistency with on-premises VMware environments make it easier for existing VMware users to transition to the cloud. The platform’s focus on virtualization and traditional infrastructure management offers a familiar and comfortable experience. However, this familiarity may also limit flexibility and agility compared to cloud-native solutions.
- Microsoft Azure:Azure’s cloud-native approach and extensive suite of tools provide greater flexibility and agility. The platform’s focus on automation, orchestration, and declarative configuration allows for rapid deployment and scaling of applications. However, the learning curve for Azure’s tools and methodologies can be steeper for users unfamiliar with cloud-native concepts.
Hypothetical Deployment Scenario
Consider a hypothetical scenario where you need to deploy a simple web application.
Deployment on VMware Cloud
- You would start by creating a virtual machine (VM) using vCenter Server. You would then install the necessary software on the VM, configure the web server, and deploy your application.
- To manage the application, you would use vCenter Server to monitor the VM’s health, performance, and resource utilization. You could also use NSX-T to configure network security and traffic routing for the application.
Deployment on Microsoft Azure
- You would use Azure Portal or Azure CLI to create a virtual machine (VM) with the necessary operating system and software pre-installed.
- You could then use Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates to automate the deployment of the application, including the configuration of the web server, database, and other required resources.
- Azure Monitor would provide comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities, and Azure Security Center would offer security and compliance features for the application.
Security and Compliance
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer robust security features and compliance certifications, crucial for organizations of all sizes. These platforms implement different security models and best practices to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Security Features
VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure provide a wide range of security features to protect your data and applications. These features include:
- Data Encryption:Both platforms offer data encryption at rest and in transit, ensuring data confidentiality even if the underlying infrastructure is compromised.
- Network Security:VMware Cloud and Azure provide network security features like firewalls, network segmentation, and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to prevent unauthorized access to your resources.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):Both platforms offer robust IAM solutions that allow you to control access to your resources based on user roles and permissions.
- Vulnerability Management:Both platforms offer vulnerability scanning and patching tools to help you identify and address security vulnerabilities in your infrastructure.
- Security Monitoring and Logging:VMware Cloud and Azure provide comprehensive security monitoring and logging capabilities to detect and respond to security incidents.
Compliance Certifications
VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure have obtained numerous industry-standard compliance certifications, demonstrating their commitment to security and data protection. Some of the key certifications include:
- ISO 27001:Both platforms are certified to ISO 27001, demonstrating their adherence to international best practices for information security management.
- SOC 2:Both platforms are SOC 2 certified, demonstrating their ability to protect customer data and ensure the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of data.
- PCI DSS:Both platforms are PCI DSS compliant, ensuring the secure processing, storage, and transmission of credit card data.
- HIPAA:Both platforms are HIPAA compliant, allowing healthcare organizations to store and process sensitive patient data securely.
Security Models
VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure implement different security models to address various security needs:
- Shared Responsibility Model:Both platforms operate on a shared responsibility model, where the cloud provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for securing their applications and data.
- Zero Trust Security:Azure adopts a zero-trust security model, where no user or device is trusted by default. This model requires strict authentication and authorization for every access request, enhancing security.
- Defense-in-Depth:VMware Cloud implements a defense-in-depth strategy, employing multiple layers of security controls to protect against various threats. This approach includes network segmentation, access control, and intrusion detection systems.
Best Practices
To further enhance security on both platforms, consider implementing these best practices:
- Regular Security Assessments:Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
- Strong Password Policies:Enforce strong password policies for all user accounts, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible.
- Least Privilege Principle:Grant users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks, minimizing the impact of potential security breaches.
- Regular Security Updates:Ensure that all software and operating systems are updated regularly to address known vulnerabilities.
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response:Implement robust security monitoring and incident response plans to detect and respond to security threats effectively.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities
While both VMware Cloud and Azure offer robust security features, potential vulnerabilities can still arise. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to your resources:
- Misconfigurations:Incorrect configuration of security settings can leave your resources vulnerable to attack.
- Outdated Software:Outdated software can contain known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Unsecured Applications:Applications with weak security controls can be exploited to gain access to sensitive data.
- Phishing Attacks:Users can be tricked into revealing their credentials through phishing attacks, compromising their accounts.
- Social Engineering:Attackers can use social engineering techniques to manipulate users into granting them access to sensitive data or resources.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate potential security vulnerabilities, both VMware Cloud and Azure offer various tools and best practices:
- Security Best Practices:Adhering to security best practices like strong password policies, least privilege principle, and regular security updates can significantly reduce the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Security Monitoring and Logging:Implementing comprehensive security monitoring and logging solutions can help detect and respond to security threats in a timely manner.
- Security Training:Providing security training to users can help them understand common threats and how to protect themselves from attacks.
- Regular Security Assessments:Regularly assessing your security posture can help identify vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
- Vulnerability Management Tools:Utilizing vulnerability management tools can help identify and remediate vulnerabilities in your infrastructure.
Pricing and Cost Optimization
Understanding the pricing models and cost structures of VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing cloud expenses. Both platforms offer a variety of pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot instances, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
By carefully analyzing your workload requirements and utilizing cost-effective strategies, you can significantly reduce your cloud spending.
Pricing Models and Cost Structures
VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer a range of pricing models to cater to different needs and budgets.
- Pay-as-you-go:This model allows you to pay for the resources you use on an hourly or per-minute basis. It provides flexibility and scalability, making it ideal for short-term projects or unpredictable workloads.
- Reserved instances:These offer discounts for committing to using specific resources for a set period.
Reserved instances are a cost-effective option for predictable workloads, such as production applications or databases.
- Spot instances:These are surplus compute capacity available at a significantly lower price than on-demand instances. Spot instances are ideal for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
Cost-Effective Solutions and Strategies
Several strategies can help optimize cloud expenses on both platforms.
- Right-sizing instances:Choose the appropriate instance size for your workloads to avoid overprovisioning.
- Utilizing reserved instances:Commit to using specific resources for a set period to get discounted pricing.
- Leveraging spot instances:Utilize spot instances for non-critical workloads to save costs.
- Optimizing storage:Choose the appropriate storage tier for your data based on access frequency and performance requirements.
- Auto-scaling:Automatically scale your resources up or down based on demand to avoid paying for unused capacity.
- Cost management tools:Utilize cost management tools provided by both platforms to monitor and analyze spending patterns.
Pricing Comparison
Here’s a table comparing the pricing of common services on VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure:
| Service | VMware Cloud | Microsoft Azure |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Machines (Standard) | Varies based on instance type and region | Varies based on instance type and region |
| Storage (Standard HDD) | $0.01 per GB per month | $0.01 per GB per month |
| Network Bandwidth (Outbound) | Varies based on region and usage | Varies based on region and usage |
Note:Pricing is subject to change. Please refer to the official VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure pricing pages for the most up-to-date information.
Integration and Interoperability
In the world of cloud computing, seamless integration and interoperability are paramount for businesses seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure and leverage the power of different technologies. Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer robust integration capabilities, allowing them to work cohesively with existing IT environments and a wide range of third-party services.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure, Vmware cloud vs microsoft azure
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure excel at facilitating the integration of existing IT infrastructure. This is crucial for organizations looking to migrate their workloads to the cloud without disrupting their existing systems.
VMware Cloud
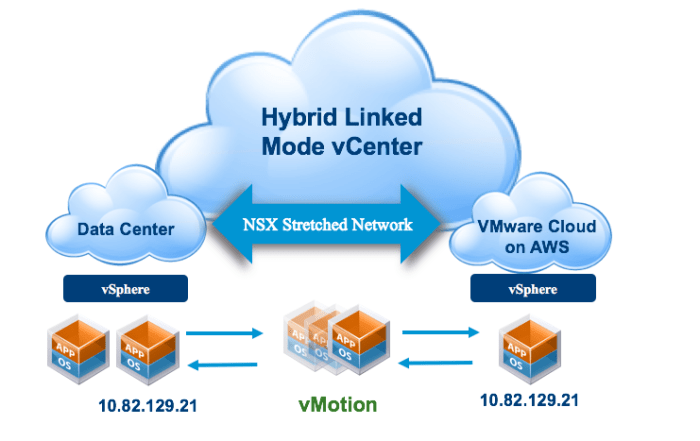
VMware Cloud, being built upon VMware’s virtualization technology, seamlessly integrates with existing VMware environments. Organizations can extend their on-premises vSphere infrastructure to the cloud with minimal effort. This allows them to migrate virtual machines (VMs) to VMware Cloud on AWS or VMware Cloud on Azure, leveraging familiar tools and processes.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure offers a comprehensive suite of tools and services that enable integration with various on-premises infrastructure components. Azure Site Recovery, for instance, facilitates disaster recovery by replicating on-premises VMs to Azure, ensuring business continuity. Azure ExpressRoute provides a dedicated, private connection between on-premises networks and Azure, enabling low-latency access to cloud resources.
Integration with Third-Party Services
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer extensive integration capabilities with third-party services, enabling businesses to build comprehensive and tailored solutions.
VMware Cloud
VMware Cloud integrates with a vast ecosystem of third-party services, including popular monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana, security solutions like Palo Alto Networks, and data management platforms like Snowflake. This allows organizations to leverage the best-of-breed solutions for their specific needs, creating a flexible and adaptable cloud environment.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure boasts a robust integration ecosystem with a wide range of third-party services. Azure Marketplace, for example, offers a vast catalog of pre-built solutions and integrations, simplifying the process of connecting Azure with various services. Azure Logic Apps enables the creation of automated workflows that integrate Azure with external systems, automating business processes and streamlining operations.
Real-World Integration Scenarios
The integration capabilities of VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure are essential for addressing various real-world scenarios:
Hybrid Cloud Deployment
Organizations often adopt a hybrid cloud strategy, combining on-premises infrastructure with cloud services. VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure facilitate this by enabling seamless communication and data exchange between on-premises and cloud environments. This allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both worlds, optimizing resource utilization and enhancing agility.
Multi-Cloud Strategy
In a multi-cloud environment, organizations utilize multiple cloud providers to diversify their IT resources and mitigate vendor lock-in. VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure support multi-cloud strategies by enabling interoperability with other cloud platforms. For example, organizations can utilize VMware Cloud to connect their AWS and Azure environments, facilitating data transfer and workload migration.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture, a modern approach to software development, involves breaking down applications into smaller, independent services. VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer tools and services that support microservices deployments, enabling organizations to build and deploy microservices efficiently. These platforms integrate with container orchestration tools like Kubernetes, simplifying the management of microservices-based applications.
Use Cases and Best Practices
Choosing between VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure often boils down to understanding their specific strengths and how they align with your business needs. This section explores common use cases, best practices, and industry-specific benefits to guide your decision-making process.
Common Use Cases and Platform Strengths
Understanding the core strengths of each platform is crucial for aligning them with your specific use cases. The table below Artikels common scenarios and the respective strengths of VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure:
| Use Case | VMware Cloud Strengths | Microsoft Azure Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Migrating existing on-premises workloads | Seamless migration with minimal disruption due to compatibility with existing VMware infrastructure. | Wide range of migration tools and services, including Azure Migrate, for a comprehensive migration experience. |
| Developing and deploying new cloud-native applications | Offers a familiar VMware environment for developers, enabling easier transition to the cloud. | Provides a rich ecosystem of cloud-native services, including Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), for building and deploying modern applications. |
| Running high-performance computing (HPC) workloads | Offers dedicated hardware and optimized configurations for demanding workloads, ensuring high performance. | Provides scalable and flexible infrastructure, including Azure High-Performance Computing (HPC) solutions, for handling complex computations. |
| Data warehousing and analytics | Offers robust data storage and management capabilities, ideal for large-scale data operations. | Provides a comprehensive suite of data analytics services, including Azure Synapse Analytics, for data warehousing and insights. |
| Disaster recovery and business continuity | Provides a familiar disaster recovery solution, leveraging existing VMware technologies and expertise. | Offers various disaster recovery solutions, including Azure Site Recovery, for quick and efficient recovery in case of outages. |
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Platform
The choice between VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure depends on your specific business needs, existing infrastructure, and future goals. Consider the following best practices:
- Assess your current infrastructure:Evaluate your existing VMware environment, including your applications, operating systems, and dependencies. VMware Cloud offers a smooth transition for organizations already heavily invested in VMware.
- Analyze your application requirements:Consider the specific needs of your applications, including performance, scalability, and security. Azure excels in providing a wide range of cloud-native services and tools for modern application development.
- Evaluate your team’s skills and experience:Assess your team’s familiarity with VMware or Azure technologies. Choosing a platform that aligns with your team’s existing expertise can streamline implementation and management.
- Consider your long-term goals:Look beyond immediate needs and consider your future plans for cloud adoption. Azure offers a comprehensive cloud platform with a vast array of services, while VMware Cloud provides a familiar environment for gradual migration.
Industry-Specific Benefits
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer tailored solutions for various industry verticals. Here are some examples:
- Finance:VMware Cloud provides a secure and compliant platform for financial institutions, adhering to regulations like PCI DSS. Azure offers robust security features and compliance certifications for managing sensitive financial data.
- Healthcare:VMware Cloud offers HIPAA-compliant solutions for managing patient data and ensuring data privacy. Azure provides a comprehensive healthcare platform with services like Azure Healthcare APIs and Azure Sentinel for healthcare security.
- Retail:VMware Cloud enables retailers to run critical applications with high availability and performance. Azure offers omnichannel solutions and analytics services for optimizing customer experiences and driving sales.
Future Trends and Considerations
The cloud computing landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging at a rapid pace. These advancements will undoubtedly have a significant impact on both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure, influencing their future direction and how they are used by organizations.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rise of edge computing, serverless computing, and other emerging technologies will influence the evolution of both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
- Edge Computing:Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure are both actively expanding their edge computing capabilities, offering solutions for deploying and managing applications at the edge.
This trend will continue to grow, particularly in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and retail, where real-time data processing and low latency are crucial. For example, a manufacturing plant can use edge computing to monitor and analyze sensor data from machines in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing production processes.
- Serverless Computing:Serverless computing allows developers to run code without managing the underlying infrastructure. Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer serverless platforms, such as VMware Cloud Functions and Azure Functions, respectively. This trend is expected to gain momentum as organizations seek to reduce operational overhead and focus on application development.
For instance, a retail company can use serverless functions to trigger personalized promotions based on customer behavior in real-time, without having to manage the underlying servers.
Future Direction and Evolution
Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure are continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses.
- Increased Focus on Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments:As organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy, both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure are enhancing their hybrid and multi-cloud capabilities. VMware Cloud provides a consistent platform for managing workloads across on-premises and cloud environments, while Microsoft Azure offers tools and services for connecting and managing workloads across different clouds.
This trend will likely accelerate as businesses seek to leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers and maintain flexibility in their IT infrastructure.
- Emphasis on Security and Compliance:Security and compliance are becoming increasingly important for cloud providers. Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure are investing heavily in security features and compliance certifications to meet the stringent requirements of organizations in regulated industries. For example, VMware Cloud offers features like vSphere Trust Authority and VMware Cloud on AWS, which are designed to enhance security and compliance.
Similarly, Microsoft Azure has a comprehensive set of security and compliance services, including Azure Security Center and Azure Sentinel, to protect customer data and meet regulatory requirements.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML are transforming various industries, and cloud providers are integrating these technologies into their platforms. Both VMware Cloud and Microsoft Azure offer AI and ML services, enabling organizations to leverage these technologies for tasks such as predictive analytics, automation, and customer insights.
For instance, a financial institution can use Azure Machine Learning to detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, improving security and reducing losses.