VMware vSphere: The Smart Persons Guide
Vmware vsphere the smart persons guide – VMware vSphere: The Smart Person’s Guide is your ultimate resource for mastering this powerful virtualization platform. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just starting your journey into the world of virtualization, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to leverage vSphere’s full potential.
From the fundamentals of virtualization to advanced concepts like automation and high availability, we’ll explore the key components of vSphere, including ESXi, vCenter Server, and vSphere Client. We’ll dive into practical scenarios, best practices, and troubleshooting tips to help you navigate the complexities of vSphere and achieve your virtualization goals.
Introduction to VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere is a comprehensive virtualization platform that empowers organizations to optimize their IT infrastructure, enhance application performance, and achieve significant cost savings. It’s a powerful suite of products designed to simplify server management, improve resource utilization, and enhance business agility.
So, you’re looking to master VMware vSphere? It’s a powerful tool for managing your virtualized infrastructure, and my guide aims to make it accessible to everyone. While we’re on the topic of powerful worlds, have you heard about the upcoming adaptation of William Gibson’s cyberpunk classic, Neuromancer on Apple TV+ ?
It’s sure to be a visual feast, just like mastering vSphere can be a rewarding experience. Back to our guide, let’s dive into the intricacies of vCenter Server and explore the depths of virtual machine management.
Core Concepts of VMware vSphere
Virtualization is the core concept behind vSphere. It allows you to run multiple operating systems and applications on a single physical server, creating virtual machines (VMs). This separation of software from hardware offers numerous benefits, including improved server utilization, reduced hardware costs, and enhanced flexibility.A hypervisor is the software layer that sits between the physical hardware and the virtual machines.
VMware vSphere is a powerful virtualization platform, and mastering it can be a game-changer for IT professionals. But with its depth and complexity, it’s easy to get lost in the details. That’s where “VMware vSphere: The Smart Person’s Guide” comes in, providing a clear and concise roadmap for navigating this complex world.
It’s a far cry from the tech-heavy world of vSphere, but it’s interesting to see how the world of technology is evolving, like with Apple’s Vision Pro, as seen in this recent interview with Tim Cook in Vanity Fair apple ceo pictured wearing vision pro for the first-time tim cook dons spatial computer in vanity fair interview.
Whether it’s virtualizing your servers or exploring new frontiers in computing, the key is to keep learning and adapting, just like the smart person’s guide to VMware vSphere encourages.
It acts as a virtual machine monitor, managing the allocation of resources and providing a platform for running virtual machines. VMware vSphere uses a type 1 hypervisor, also known as a bare-metal hypervisor, which runs directly on the server’s hardware.The vSphere suite of products encompasses a range of components that work together to provide a comprehensive virtualization solution.
These components include:
- ESXi: The hypervisor responsible for running virtual machines. It provides a secure and stable platform for virtualized workloads.
- vCenter Server: A central management console that allows you to monitor, manage, and automate your virtual infrastructure. It provides a unified view of your virtual environment, enabling you to perform tasks such as provisioning VMs, managing storage, and configuring networking.
- vSphere Client: A web-based interface that allows you to interact with your vSphere environment. It provides access to various management features, including VM creation, configuration, and monitoring.
- vSphere Update Manager: A tool that helps you manage updates and patches for your vSphere components. It streamlines the update process, ensuring that your environment remains secure and up-to-date.
Benefits of Using VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere offers numerous benefits for organizations, including:
- Improved Server Utilization: By consolidating multiple workloads onto fewer physical servers, vSphere reduces hardware footprint and maximizes resource utilization, leading to significant cost savings.
- Reduced Hardware Costs: With fewer physical servers required, organizations can reduce their hardware investment, leading to lower capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Enhanced Flexibility: vSphere allows you to quickly provision and deploy virtual machines, providing greater agility in responding to changing business needs. You can easily scale your infrastructure up or down based on demand, eliminating the need for long lead times for hardware procurement.
- Increased Availability: vSphere provides high availability features that ensure business continuity. With features like fault tolerance and vMotion, you can minimize downtime and ensure that applications remain accessible even in the event of server failures.
- Improved Disaster Recovery: vSphere facilitates disaster recovery by allowing you to replicate virtual machines to secondary locations, ensuring business continuity in the event of a disaster.
Real-World Examples of VMware vSphere
VMware vSphere is widely adopted across various industries and organizations, including:
- Financial Services: Financial institutions leverage vSphere to virtualize their critical applications, ensuring high availability and performance for online banking, trading, and other core operations.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers utilize vSphere to manage patient records, medical imaging systems, and other critical applications, ensuring data security and compliance with regulations.
- Education: Educational institutions rely on vSphere to virtualize their desktops and applications, providing students and faculty with access to resources from anywhere, anytime.
- Retail: Retailers use vSphere to virtualize their point-of-sale systems, inventory management applications, and e-commerce platforms, ensuring seamless operations and scalability.
Understanding vSphere Components
vSphere is a powerful virtualization platform that enables organizations to manage and optimize their virtualized infrastructure. It consists of various components, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of the platform. This section will delve into the key components of vSphere, their roles, and how they interact with each other.
ESXi
ESXi is the hypervisor at the heart of vSphere. It is a type 1 hypervisor, meaning it runs directly on the server hardware and provides a layer of abstraction between the hardware and the virtual machines. ESXi is responsible for managing the hardware resources of the server and providing a secure and reliable platform for running virtual machines.
- Hardware Virtualization:ESXi virtualizes the hardware resources of the server, allowing multiple virtual machines to share the same physical hardware. This includes resources such as CPU, memory, storage, and network interfaces.
- Virtual Machine Management:ESXi manages the lifecycle of virtual machines, including creation, deployment, power management, and resource allocation.
- Security and Isolation:ESXi provides a secure environment for running virtual machines, isolating them from each other and from the underlying hardware. This helps to protect virtual machines from malicious attacks and ensures that each virtual machine has its own dedicated resources.
vCenter Server
vCenter Server is the central management component of vSphere. It provides a single point of control for managing all the virtualized infrastructure, including ESXi hosts, virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- Centralized Management:vCenter Server provides a centralized platform for managing all aspects of the vSphere environment. This includes tasks such as monitoring, configuration, provisioning, and troubleshooting.
- Inventory and Configuration:vCenter Server maintains an inventory of all the components in the vSphere environment, including ESXi hosts, virtual machines, and storage devices. It also allows administrators to configure and manage the settings of these components.
- Workflow Automation:vCenter Server provides tools for automating common tasks, such as deploying virtual machines, creating templates, and managing updates. This helps to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of errors.
vSphere Client
vSphere Client is the graphical user interface (GUI) for managing vSphere. It provides a user-friendly interface for accessing and managing all the components of the vSphere environment.
- Access to vCenter Server:vSphere Client connects to vCenter Server, providing a single point of access for managing the entire vSphere infrastructure.
- Virtual Machine Management:vSphere Client provides a comprehensive set of tools for managing virtual machines, including creating, deploying, powering on/off, and migrating virtual machines.
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting:vSphere Client provides tools for monitoring the performance of ESXi hosts and virtual machines, as well as troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
vSphere Components Interaction
The components of vSphere work together to provide a comprehensive and robust virtualization platform. Here is a diagram illustrating the interaction between the key components:
[Image Description: A diagram depicting the interaction between different vSphere components. The diagram shows ESXi hosts at the bottom, connected to vCenter Server in the middle. vCenter Server acts as a central management point for all ESXi hosts and virtual machines. On the top, vSphere Client connects to vCenter Server, allowing administrators to manage the entire vSphere environment. Arrows indicate the flow of information and control between the components.]
Installing and Configuring vSphere
This section delves into the practical aspects of setting up your vSphere environment, covering the installation of ESXi on physical servers and the configuration of vCenter Server. We’ll also explore best practices for securing and managing your vSphere infrastructure.
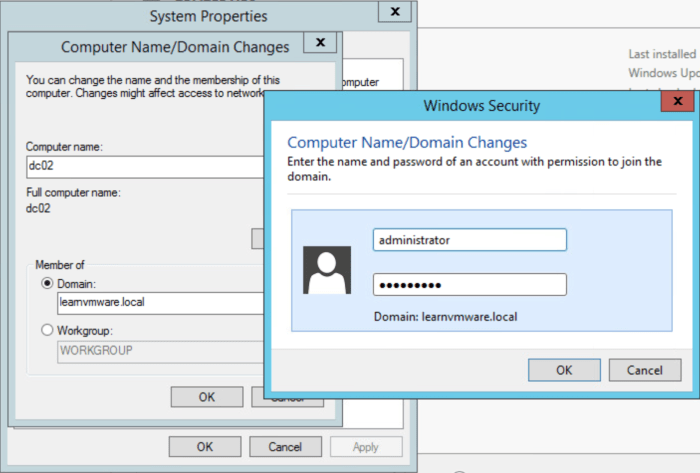
Installing ESXi on a Physical Server
Installing ESXi on a physical server is the foundation of your vSphere infrastructure. This process involves booting the server from the ESXi installation media and following a guided setup.
- Download the ESXi installer:Obtain the latest ESXi installer from the VMware website, ensuring compatibility with your server hardware.
- Create bootable media:Create a bootable USB drive or DVD using the downloaded ESXi installer.
- Boot the server:Configure the server’s BIOS to boot from the created bootable media.
- Start the installation:Follow the on-screen instructions to install ESXi. This typically involves selecting the desired installation options, such as disk partitioning and network configuration.
- Set the root password:Configure a strong password for the root user account. This password is essential for accessing the ESXi host via SSH or the vSphere client.
- Complete the installation:Once the installation process is complete, the server will reboot and boot into the ESXi operating system.
Configuring vCenter Server
vCenter Server is the central management component of vSphere, providing a unified interface for managing ESXi hosts, virtual machines, and other vSphere components.
- Install vCenter Server:Download the vCenter Server installer from the VMware website and install it on a dedicated server.
- Configure the database:vCenter Server requires a database to store its configuration data. Choose a suitable database, such as SQL Server or PostgreSQL, and configure it according to the vCenter Server installation requirements.
- Connect to ESXi hosts:After installing vCenter Server, add your ESXi hosts to the inventory by providing their hostname or IP address and credentials.
- Configure networking:Define the network settings for vCenter Server, including its IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Configure licenses:Apply the appropriate licenses to your vCenter Server installation to activate the desired vSphere features.
Securing and Managing vSphere Infrastructure
Maintaining a secure and well-managed vSphere environment is crucial for operational stability and data protection.
- Enable SSH access:Enable SSH access to ESXi hosts for remote management and troubleshooting, but ensure that you use strong passwords and enable SSH key authentication.
- Configure firewall rules:Configure the ESXi host firewall to allow only necessary traffic, such as SSH, vCenter Server communication, and network traffic for virtual machines.
- Implement strong passwords:Use strong passwords for all vSphere accounts, including root, administrator, and user accounts.
- Enable logging and monitoring:Configure logging and monitoring tools to track system events, identify potential security threats, and diagnose issues.
- Regularly patch and update:Keep your vSphere infrastructure up-to-date by applying the latest security patches and software updates to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC):Define specific roles and permissions for users to restrict access to sensitive resources and enforce security policies.
- Utilize vSphere features for security:Leverage built-in vSphere features such as vSphere Distributed Switch, vSphere Network I/O Control, and vSphere Storage I/O Control to enhance security and performance.
Creating and Managing Virtual Machines
Virtual machines are the heart of VMware vSphere, enabling you to run multiple operating systems and applications on a single physical server. This section delves into the process of creating and managing virtual machines within the vSphere environment, covering essential configuration aspects and lifecycle management techniques.
Creating Virtual Machines
Creating a virtual machine in vSphere is a straightforward process that involves specifying the virtual machine’s hardware configuration and selecting the desired operating system. This process is initiated through the vSphere Client, a graphical interface for managing vSphere infrastructure.
- Select a Host:Begin by selecting the ESXi host where you want to deploy the virtual machine. This host will provide the physical resources for the virtual machine to run.
- Specify Virtual Machine Name and Location:Assign a unique name to the virtual machine, ensuring it’s descriptive and easy to identify. Choose the location where the virtual machine files will be stored, such as a shared datastore accessible by the ESXi host.
- Define Virtual Machine Hardware:Configure the virtual machine’s hardware resources, including:
- CPU:Allocate the number of virtual CPUs for the virtual machine, considering the application’s requirements and available host resources.
- Memory:Specify the amount of RAM (in GB) to be assigned to the virtual machine. Ensure sufficient memory is allocated for optimal performance.
- Storage:Create a virtual disk for the virtual machine, defining its size and storage type (thin provisioned or thick provisioned).
- Networking:Connect the virtual machine to the desired virtual network, enabling communication with other virtual machines and the physical network.
- Select Operating System:Choose the operating system to be installed on the virtual machine. vSphere supports a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and other server operating systems.
- Customize Installation Options:Depending on the chosen operating system, you may need to configure additional settings during the installation process, such as the network configuration, time zone, and user accounts.
Configuring Virtual Machine Settings
Once a virtual machine is created, you can fine-tune its settings to optimize performance and resource utilization.
- CPU and Memory:Adjust the number of virtual CPUs and RAM allocated to the virtual machine. You can increase or decrease these resources based on the application’s demands and available host resources.
- Storage:Expand the virtual disk size if necessary, or create additional virtual disks to provide more storage space for the virtual machine.
- Networking:Modify the virtual machine’s network settings, such as changing the network adapter type or connecting it to a different virtual network.
- Power Management:Configure power-saving options, such as setting the virtual machine to automatically power on or off at specific times.
Managing Virtual Machine Lifecycle
vSphere provides tools for managing the lifecycle of virtual machines, ensuring smooth operation and efficient resource utilization.
- Cloning:Create identical copies of existing virtual machines, simplifying deployment and reducing configuration time. Cloning replicates the virtual machine’s settings and files, enabling rapid deployment of new instances.
- Snapshots:Capture a point-in-time snapshot of a virtual machine’s state, allowing you to revert to a previous configuration if needed. Snapshots can be used for testing, recovery, or as a backup mechanism.
- Migration:Move virtual machines between ESXi hosts or datastores without disrupting their operation. This allows for load balancing, resource optimization, or physical server maintenance.
- High Availability (HA):Configure high availability for critical virtual machines, ensuring automatic failover in case of host failure. This minimizes downtime and maintains service availability.
vSphere Networking and Storage: Vmware Vsphere The Smart Persons Guide

VMware vSphere provides a comprehensive set of networking and storage options to meet the diverse needs of virtualized environments. This chapter delves into the key networking and storage technologies supported by vSphere, including VLANs, distributed switches, NSX, shared storage, local storage, and cloud storage.
Understanding these technologies and their best practices is crucial for designing and implementing a robust and efficient vSphere infrastructure.
vSphere Networking
vSphere offers a variety of networking options to connect virtual machines (VMs) and manage network traffic. These options provide flexibility and control over the network environment, allowing you to tailor it to your specific requirements.
VLANs
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. Each VLAN is a broadcast domain, meaning that devices within the same VLAN can communicate with each other, while devices in different VLANs cannot. VLANs offer several benefits, including:
- Improved Security: By isolating traffic, VLANs prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Enhanced Performance: VLANs can reduce network congestion by separating traffic from different departments or applications.
- Flexible Network Management: VLANs simplify network administration by allowing you to manage groups of devices as a single unit.
Distributed Switches
Distributed switches are logical switches that provide centralized management and control over network connectivity within a vSphere environment. They offer several advantages over traditional physical switches, including:
- Centralized Management: Distributed switches allow you to configure and manage network settings from a single point, simplifying administration.
- Scalability: Distributed switches can handle large numbers of VMs and virtual networks, enabling scalability.
- High Availability: Distributed switches can be configured for redundancy, ensuring network availability in case of failures.
NSX
VMware NSX is a software-defined networking (SDN) solution that provides a comprehensive platform for managing and securing virtual networks. NSX offers several features, including:
- Network Virtualization: NSX allows you to create and manage virtual networks independent of the underlying physical infrastructure.
- Micro-Segmentation: NSX enables fine-grained control over network access, enhancing security by isolating traffic at the VM level.
- Automated Network Provisioning: NSX simplifies network configuration and deployment through automation, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
vSphere Storage, Vmware vsphere the smart persons guide
vSphere supports various storage technologies, allowing you to choose the best option based on your performance, capacity, and budget requirements. These technologies provide different levels of flexibility, scalability, and availability.
Shared Storage
Shared storage is a storage solution that allows multiple servers to access the same storage devices. Shared storage offers several benefits, including:
- Data Sharing: VMs can share data and resources, enabling collaboration and efficient data management.
- High Availability: Shared storage can be configured for redundancy, ensuring data availability in case of failures.
- Scalability: Shared storage allows you to easily expand storage capacity as your needs grow.
Local Storage
Local storage refers to storage devices directly connected to a server, such as hard drives or SSDs. Local storage is typically used for smaller workloads or when high performance is required.
- High Performance: Local storage can provide faster access to data compared to shared storage.
- Lower Cost: Local storage is generally less expensive than shared storage.
- Limited Scalability: Local storage is less scalable than shared storage, as it is tied to a specific server.
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage refers to storage services provided by third-party providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Cloud storage offers several benefits, including:
- Scalability: Cloud storage allows you to easily scale storage capacity on demand.
- Pay-as-you-go Pricing: Cloud storage is typically priced on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing you to only pay for the storage you use.
- High Availability: Cloud storage providers offer high availability and redundancy, ensuring data reliability.
vSphere Security and High Availability
In the world of virtualization, ensuring the security and reliability of your virtual infrastructure is paramount. vSphere offers a robust set of features to address these critical aspects, providing a secure and highly available environment for your virtual machines.
vSphere Security Features
vSphere incorporates several security features to protect your virtual infrastructure from unauthorized access and potential threats.
- User Authentication: vSphere utilizes strong authentication mechanisms, such as Active Directory integration, to verify user identities and grant access to specific resources. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access and manage the virtual environment.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC allows you to define granular permissions for different user roles, restricting their access to specific resources based on their responsibilities. This principle of least privilege helps to minimize the risk of unauthorized actions.
- Encryption: vSphere provides encryption capabilities to protect sensitive data, such as virtual machine files and configuration settings. This helps to safeguard data confidentiality and integrity, even in the event of unauthorized access or data breaches.
vSphere High Availability Options
vSphere offers various high availability options to ensure business continuity and minimize downtime in the event of hardware failures.
- vSphere HA: This feature automatically restarts virtual machines on a different host if the original host fails. It achieves this by monitoring the health of ESXi hosts and automatically migrating virtual machines to a healthy host in case of a failure.
- vSphere Fault Tolerance: This advanced high availability solution provides continuous availability for critical virtual machines. It creates a secondary virtual machine (a replica) that runs in parallel with the primary virtual machine. In case of a host failure, the replica automatically takes over, ensuring uninterrupted service.
Fault Tolerance is ideal for mission-critical applications where even a brief outage is unacceptable.
Configuring Security and High Availability Solutions
Implementing security and high availability solutions in vSphere involves configuring the appropriate settings and features.
VMware vSphere is a powerful tool for managing virtualized environments, but it comes with its fair share of complexity. One aspect that often trips people up is managing user accounts and passwords. That’s where the concept of password managers built teams, like the ones discussed in this article , can be invaluable.
By streamlining password management, you can focus on the bigger picture of efficiently running your vSphere environment.
- User Authentication: You can configure Active Directory integration to enable centralized user authentication and management. This ensures that users are authenticated against a trusted directory service.
- RBAC: You can define custom roles and assign permissions based on the responsibilities of different user groups. This allows you to control access to specific resources and actions.
- Encryption: You can enable encryption for virtual machine files and configuration settings. This helps to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or data breaches.
- vSphere HA: You can configure vSphere HA to monitor the health of ESXi hosts and automatically migrate virtual machines in case of a failure. This ensures that virtual machines remain operational even if a host becomes unavailable.
- vSphere Fault Tolerance: You can enable Fault Tolerance for critical virtual machines to ensure continuous availability. This creates a replica virtual machine that runs in parallel, providing instant failover in case of a host failure.
vSphere Automation and Management
Automating tasks and managing your vSphere infrastructure efficiently is crucial for any organization. vSphere provides a powerful set of tools and APIs that enable you to streamline operations and enhance your overall environment.
vSphere APIs and Scripting
vSphere APIs allow you to interact with the vSphere environment programmatically, providing a flexible way to automate tasks. These APIs are available in various languages, such as Python, PowerShell, and Java.
- vSphere REST API: Provides a modern, web-based interface for managing vSphere resources. It allows you to perform various tasks such as creating virtual machines, managing storage, and configuring networking.
- vSphere SDK for Python: A powerful library that simplifies interacting with vSphere using Python. It provides a comprehensive set of classes and methods for managing virtual machines, hosts, and other vSphere components.
- PowerShell vSphere SDK: Allows you to manage vSphere from PowerShell scripts. It provides cmdlets for performing common vSphere tasks, such as creating and managing virtual machines, managing storage, and configuring networking.
vCenter Server: Centralized Management
vCenter Server acts as the central management hub for your vSphere environment. It provides a single point of control for managing and monitoring all your vSphere components, including hosts, virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- Centralized Monitoring: vCenter Server provides a comprehensive view of your vSphere environment, allowing you to monitor the health and performance of your hosts, virtual machines, and other components. This helps you identify potential issues proactively and take corrective actions.
- Resource Allocation and Optimization: vCenter Server allows you to manage and optimize resource allocation across your vSphere environment. You can configure policies and rules to ensure that resources are used efficiently and meet the needs of your applications.
- Automated Task Execution: vCenter Server provides features for automating tasks, such as virtual machine provisioning, patching, and backups. This helps you reduce manual intervention and improve efficiency.
Automating Common vSphere Tasks
Automating common vSphere tasks can significantly improve efficiency and reduce manual errors. Here are some best practices for automating tasks:
- Virtual Machine Provisioning: Automate the process of creating and configuring new virtual machines. This can involve tasks such as creating virtual machine templates, deploying virtual machines from templates, and configuring networking and storage.
- Patching and Updates: Automate the process of applying patches and updates to your hosts and virtual machines. This helps ensure that your environment is secure and up-to-date.
- Backup and Recovery: Automate the process of backing up your virtual machines and data. This helps protect your data from loss in case of a disaster.
Advanced vSphere Concepts

This chapter delves into the advanced features of vSphere, which empower administrators to optimize resource utilization, ensure high availability, and simplify management tasks. We will explore key concepts such as vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), vSphere Storage vMotion, and vSphere Update Manager, along with their benefits and practical applications.
vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS)
DRS automates the process of balancing workloads across multiple ESXi hosts within a cluster. It leverages real-time monitoring and resource utilization data to dynamically migrate virtual machines, ensuring optimal performance and resource allocation.DRS offers several benefits:
- Optimized Resource Utilization:DRS ensures that all available resources are utilized efficiently, preventing resource bottlenecks and maximizing performance.
- High Availability:DRS enables automatic failover by migrating virtual machines away from failing hosts, ensuring continuous service availability.
- Simplified Management:DRS automates the process of workload balancing, reducing the need for manual intervention and simplifying cluster management.
DRS can be configured to operate in different modes:
- Fully Automated:DRS automatically migrates virtual machines based on predefined rules and resource utilization data.
- Manually Controlled:DRS provides recommendations for virtual machine migrations, allowing administrators to manually initiate the process.
vSphere Storage vMotion
vSphere Storage vMotion allows administrators to migrate virtual machine data from one storage location to another without disrupting service. This feature is essential for tasks such as storage upgrades, storage consolidation, and disaster recovery.Key benefits of vSphere Storage vMotion include:
- Zero Downtime:Storage vMotion enables storage migrations without interrupting virtual machine operations, ensuring continuous service availability.
- Flexible Storage Management:Administrators can easily migrate virtual machines to different storage systems, optimizing storage utilization and simplifying management.
- Disaster Recovery:Storage vMotion can be used to replicate virtual machine data to a secondary storage location, providing a mechanism for disaster recovery.
vSphere Update Manager
vSphere Update Manager streamlines the process of updating and patching ESXi hosts and virtual machines. It provides a centralized platform for managing updates, ensuring consistency and reducing the risk of downtime.vSphere Update Manager offers several key advantages:
- Automated Patching:Update Manager automates the process of applying updates and patches to ESXi hosts and virtual machines, simplifying management and reducing manual errors.
- Reduced Downtime:Update Manager allows administrators to schedule updates and patches during off-peak hours, minimizing downtime and service disruptions.
- Enhanced Security:By keeping ESXi hosts and virtual machines up to date with the latest patches, Update Manager strengthens the security posture of the vSphere environment.
vSphere Troubleshooting and Best Practices
Troubleshooting and maintaining a robust vSphere environment requires a proactive approach, encompassing both identifying and resolving issues and implementing preventative measures. This chapter delves into common vSphere challenges, effective troubleshooting strategies, and best practices for optimizing performance and ensuring high availability.
Common vSphere Issues and Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting vSphere issues often involves analyzing logs, monitoring system performance, and isolating the root cause. Common issues include:
- Virtual Machine Performance Degradation:This can manifest as slow response times, application hangs, or high CPU/memory utilization. Analyzing performance counters for the virtual machine, the host, and the underlying storage can pinpoint the source of the problem. Common causes include insufficient resources, storage I/O bottlenecks, or network connectivity issues.
- Host Connectivity Issues:Loss of connectivity between ESXi hosts and vCenter Server can disrupt management and monitoring. Checking network connectivity, verifying firewall rules, and ensuring proper vCenter Server configuration are crucial steps in resolving such issues.
- Storage Access Problems:Storage access issues can arise from various factors, including faulty hardware, network connectivity problems, or storage array configuration errors. Examining storage logs, checking network connectivity, and verifying storage array configuration can help identify the source of the problem.
- vCenter Server Availability:vCenter Server downtime can significantly impact the entire vSphere environment. Monitoring vCenter Server health, implementing high availability solutions, and regularly performing backups are crucial for minimizing downtime.
Best Practices for vSphere Performance Optimization
Optimizing vSphere performance involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing resource allocation, storage configuration, and network management.
- Resource Allocation:Proper resource allocation is critical for efficient virtual machine performance. Over-provisioning resources can lead to wasted capacity, while under-provisioning can result in performance bottlenecks. Monitoring resource utilization and adjusting resource allocation based on actual needs can significantly improve performance.
- Storage Configuration:Choosing the right storage solution and configuring it appropriately is essential for optimal performance. Factors to consider include storage type (SAN, NAS, or local), storage capacity, and I/O performance. Implementing technologies like RAID and SSDs can enhance storage performance.
- Network Management:Effective network management is crucial for maintaining vSphere performance. This includes optimizing network bandwidth, minimizing network latency, and implementing network segmentation to isolate traffic flows. Using dedicated network adapters for virtual machines and implementing network load balancing can further improve performance.
Monitoring and Logging in vSphere Environments
Proactive monitoring and logging are essential for maintaining vSphere health and troubleshooting issues.
- Monitoring:vSphere provides built-in monitoring tools that track key performance indicators (KPIs) for hosts, virtual machines, and other components. These tools allow for real-time performance analysis, identification of potential issues, and proactive intervention. Monitoring tools like vCenter Server, vSphere Performance Charts, and ESXi Performance Graphs provide valuable insights into system health and performance.
- Logging:Logging is critical for identifying and diagnosing issues. vSphere generates logs for various components, including ESXi hosts, vCenter Server, and virtual machines. Analyzing logs can reveal error messages, performance bottlenecks, and other critical information. Effective logging practices include configuring log levels, rotating logs regularly, and using log analysis tools to extract meaningful insights.
Future of vSphere
VMware vSphere, a virtualization platform that has revolutionized data centers for over two decades, continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing landscape of modern IT. As we move further into the era of cloud computing, software-defined infrastructure, and emerging technologies, vSphere is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of data centers.
Cloud Integration
vSphere’s integration with cloud platforms is a key area of focus. VMware’s hybrid cloud strategy aims to provide a seamless bridge between on-premises and cloud environments, enabling organizations to leverage the benefits of both.
- VMware Cloud on AWS: This service allows organizations to run vSphere workloads directly on AWS infrastructure, providing a familiar management experience and access to AWS services.
- VMware Cloud Foundation: This software-defined data center platform simplifies the deployment and management of vSphere, NSX, and vSAN across on-premises and cloud environments.
These integrations offer organizations flexibility and scalability, allowing them to deploy applications where they make the most sense, whether in their own data centers or in the cloud.