Israel Threat Actors Target Organizations with Email Attacks
Israel threat actors email attacks are a growing concern for organizations in the region. These attacks often leverage sophisticated phishing campaigns and malware delivery methods to steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, and inflict financial damage. Understanding the motivations, tactics, and impact of these attacks is crucial for safeguarding against them.
The threat actors operating in Israel are diverse, ranging from nation-state actors to financially motivated cybercriminals. Each group has its own objectives and tactics, making it essential to stay informed about the latest threats. This blog delves into the specifics of these attacks, exploring the common attack vectors, the consequences they bring, and the best practices for defending against them.
Threat Actor Groups Operating in Israel
Israel, a technologically advanced nation, faces a unique set of cyber threats. Numerous threat actor groups target Israeli organizations, aiming to disrupt operations, steal sensitive information, and advance political agendas.
Prominent Threat Actor Groups
Several prominent threat actor groups have been identified as posing significant cyber threats to Israeli entities. These groups employ various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to achieve their objectives.
- APT34 (OilRig): This Iranian-backed group is known for its advanced persistent threats targeting energy, government, and financial sectors in Israel and the Middle East. They employ sophisticated malware, phishing campaigns, and social engineering tactics to gain access to sensitive information.
- APT35 (Charming Kitten): This Iranian threat actor group specializes in espionage and information gathering. They target individuals, government organizations, and media outlets in Israel, primarily focused on intelligence gathering and propaganda dissemination.
- APT36 (MuddyWater): A suspected Iranian group known for targeting government, military, and energy sectors in Israel and the Middle East. They leverage custom malware, phishing, and spear-phishing campaigns to gain access and steal sensitive information.
- APT37 (BlackTech): This group, believed to be North Korean, has been linked to cyberattacks against Israeli organizations. Their activities involve data theft, espionage, and financial fraud.
- APT29 (Cozy Bear): A Russian intelligence group known for its extensive espionage activities. They have been linked to cyberattacks against Israeli government and military entities, aiming to gather sensitive information and disrupt operations.
Motivations and Objectives
The motivations and objectives of threat actor groups targeting Israel are diverse, ranging from espionage and information gathering to disruption of critical infrastructure and political influence.
- Espionage and Intelligence Gathering: Some groups, such as APT35, prioritize gaining access to sensitive information, including classified documents, military strategies, and economic data. This information is used to enhance intelligence capabilities, gain strategic advantage, and influence decision-making.
- Disruption and Sabotage: Groups like APT34 have targeted critical infrastructure, including energy facilities, to disrupt operations and cause economic damage. These attacks can have significant consequences for national security and economic stability.
- Political Influence and Propaganda: Threat actors often engage in information manipulation and propaganda campaigns to influence public opinion, sow discord, and undermine trust in government institutions. These activities aim to advance specific political agendas or destabilize the region.
- Financial Gain: Some groups, such as APT37, are motivated by financial gain, engaging in cybercrime activities like data theft, ransomware attacks, and financial fraud.
Tactic, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
Threat actor groups targeting Israel employ a wide range of tactics, techniques, and procedures to achieve their objectives. These methods evolve constantly, requiring continuous adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Israel-based threat actors are increasingly using sophisticated email attacks to target individuals and organizations. These attacks often involve phishing emails that trick victims into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software. To protect yourself from these threats, it’s crucial to use a strong password manager and a reputable best no log vpn service.
A no-log VPN encrypts your internet traffic and hides your IP address, making it harder for attackers to track your online activity and target you with personalized attacks.
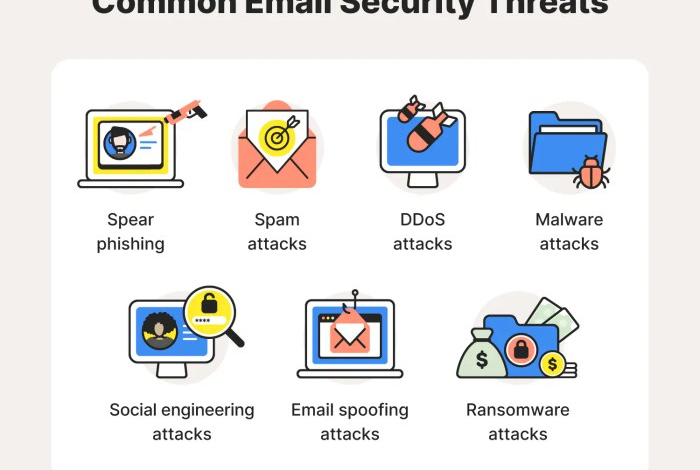
- Phishing and Spear-Phishing: These techniques involve sending malicious emails or messages designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links. They often exploit social engineering tactics and current events to increase the likelihood of success.
- Malware Deployment: Threat actors use various malware, including trojans, ransomware, and spyware, to gain access to systems, steal data, or disrupt operations. They leverage sophisticated techniques to evade detection and exploit vulnerabilities.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Threat actors actively scan for and exploit vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and networks to gain unauthorized access to systems. They often target known vulnerabilities and exploit zero-day exploits to gain an advantage.
- Social Engineering: Threat actors use psychological manipulation techniques to gain access to systems or sensitive information. This includes impersonating trusted individuals, exploiting social connections, and leveraging social media platforms.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: These attacks aim to overwhelm systems with traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate users. They can disrupt critical services, cause financial losses, and damage reputation.
Common Email Attack Vectors Targeting Israel: Israel Threat Actors Email Attacks
Israel is a prime target for cyberattacks due to its advanced technology sector, critical infrastructure, and geopolitical significance. Email is a common vector for these attacks, as it is a widely used communication method and can be easily manipulated by attackers.
Israel-based threat actors have been known to use sophisticated email attacks, often targeting businesses and government entities. These attacks can be difficult to detect and often involve phishing scams or malware disguised as legitimate communications. It’s interesting to note how regulations can influence tech companies, like Apple, who have decided to stop including chargers with their high-end iPad Pro, blaming the EU regulations for the change.
This type of regulatory pressure could potentially influence how threat actors adapt their tactics, forcing them to find new ways to bypass security measures.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, or personal details. Attackers often use email to lure victims into clicking malicious links or opening attachments that lead to phishing websites or malware downloads.
Examples of Phishing Attacks
- Subject:Urgent Action Required – Your Account is Suspended Content:This email informs the recipient that their account has been suspended due to suspicious activity and directs them to a fake website to verify their account details. Attachment:None
- Subject:You Have a New Message Content:This email appears to be a notification from a legitimate service like a bank or social media platform, but it contains a malicious link that redirects the user to a phishing website. Attachment:None
Spear Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing attacks are highly targeted phishing campaigns that specifically target individuals or organizations. Attackers gather information about their victims to create personalized emails that appear legitimate and increase the chances of successful attacks.
Examples of Spear Phishing Attacks
- Subject:Meeting Confirmation – [Victim’s Name] Content:This email appears to be a meeting confirmation from a known colleague or business partner, but it contains a malicious link that leads to a phishing website or malware download. Attachment:None
- Subject:Important Information Regarding [Specific Project/Event] Content:This email discusses a project or event that the victim is involved in, but it contains a malicious link or attachment that steals sensitive information or installs malware. Attachment:A malicious document or executable file disguised as a legitimate document related to the project or event.
Malware Delivery
Malware delivery attacks use email to distribute malicious software that can steal data, disrupt operations, or take control of the victim’s computer. Attackers often use email attachments, malicious links, or drive-by downloads to infect victims’ devices.
Examples of Malware Delivery Attacks
- Subject:Invoice – [Invoice Number] Content:This email appears to be a legitimate invoice from a supplier or vendor, but it contains a malicious attachment that installs malware on the victim’s computer. Attachment:A malicious document or executable file disguised as an invoice.
Israel-based threat actors are notorious for their sophisticated email attacks, often targeting organizations with highly sensitive information. These attacks often utilize advanced phishing techniques and exploit vulnerabilities in email security systems. Fortunately, tools like Google Chronicle Security Operations Preview Duet AI can help organizations detect and respond to these threats more effectively.
By leveraging AI and machine learning, Duet AI can analyze email traffic patterns and identify suspicious activity, potentially preventing these attacks before they cause significant damage.
- Subject:You Have Won a Prize! Content:This email informs the recipient that they have won a prize and directs them to a website to claim their prize. However, the website is actually a malware distribution site. Attachment:None
Impact of Email Attacks on Israeli Organizations

Email attacks pose a significant threat to Israeli organizations, potentially leading to substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and disruptions to critical operations. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in email security and human error, allowing malicious actors to gain access to sensitive information and compromise systems.
Data Breaches
Data breaches are a major consequence of successful email attacks. Phishing emails, for example, can trick users into revealing sensitive credentials, such as login details or financial information, which attackers can then use to gain unauthorized access to systems and databases.
Once inside, attackers can steal valuable data, including customer information, intellectual property, financial records, and confidential documents. This stolen data can be used for various illicit purposes, such as identity theft, fraud, and blackmail.
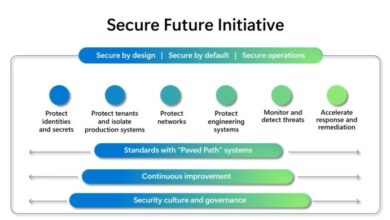
Defensive Measures Against Email Attacks
In the face of sophisticated email attacks, Israeli organizations must implement robust defensive measures to protect their sensitive data and operations. These measures involve a multi-layered approach, encompassing employee training, advanced email security solutions, and a culture of vigilance.
Employee Training and Awareness
Employee training plays a crucial role in bolstering email security. It empowers individuals to identify and avoid malicious emails, reducing the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks and other threats.
- Phishing Awareness:Training programs should educate employees about the tactics used in phishing attacks, including spoofed sender addresses, urgent requests, and deceptive links. They should be encouraged to verify the authenticity of emails, especially those requesting sensitive information or directing them to unfamiliar websites.
- Social Engineering:Employees need to understand the various methods used in social engineering attacks, such as impersonation, baiting, and pretexting. They should be aware of the potential for attackers to exploit their curiosity, trust, or sense of urgency.
- Best Practices:Training should emphasize best practices for handling emails, including avoiding opening attachments from unknown senders, reporting suspicious emails to security teams, and being cautious about clicking on links in emails.
Email Security Solutions
Implementing advanced email security solutions is essential for safeguarding against email attacks. These solutions offer a comprehensive approach to detecting and mitigating threats.
- Spam Filters:Spam filters are designed to identify and block unsolicited or malicious emails, including those containing malware, phishing attempts, and spam messages. They utilize various techniques, such as content analysis, sender reputation scoring, and blacklists.
- Anti-Malware Software:Anti-malware software protects against malicious attachments and links within emails. It scans incoming emails for known malware signatures and can block or quarantine suspicious content.
- Email Authentication Mechanisms:Email authentication mechanisms, such as Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC), help verify the authenticity of emails. They prevent attackers from spoofing sender addresses and ensure that emails originate from legitimate sources.
Security Awareness Culture, Israel threat actors email attacks
A strong security awareness culture within an organization is critical for effective email security. This culture involves promoting ongoing training, fostering a sense of responsibility among employees, and encouraging open communication about potential threats.
- Regular Training:Organizations should provide regular training to keep employees updated on emerging threats and best practices.
- Open Communication:Employees should be encouraged to report any suspicious emails or activities to security teams. Open communication channels help ensure that threats are identified and addressed promptly.
- Security Awareness Campaigns:Organizations can implement security awareness campaigns to reinforce best practices and raise employee awareness about email security.
Case Studies of Notable Email Attacks in Israel
Israel has been a frequent target of cyberattacks, with email attacks being a prominent vector. These attacks have targeted individuals, businesses, and government entities, causing significant damage and disruption. Examining notable email attack case studies reveals valuable insights into attack methodologies, victim profiles, and the impact on Israeli organizations.
The 2019 Israeli Election Campaign Email Attacks
This attack involved a sophisticated phishing campaign targeting Israeli political parties and individuals involved in the 2019 Israeli elections. The attackers used spear phishing emails designed to appear legitimate, mimicking official communications from political parties or government institutions. These emails contained malicious attachments or links that, when clicked, infected the victims’ computers with malware.
The malware then allowed the attackers to steal sensitive data, including personal information, campaign strategies, and financial records.The attack was attributed to a foreign state-sponsored hacking group, which aimed to influence the election outcome by undermining public trust in the political process.
The attack highlights the vulnerability of political campaigns to sophisticated email attacks and the importance of implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information.
The 2020 Israeli Hospital Email Attack
In 2020, a major Israeli hospital was hit by a ransomware attack that disrupted critical services and caused significant financial losses. The attack started with a phishing email that targeted hospital staff. The email contained a malicious attachment disguised as a legitimate document.
When clicked, the attachment infected the hospital’s network with ransomware, encrypting sensitive data and demanding a ransom payment for decryption.The attack caused widespread disruption, forcing the hospital to cancel appointments, delay surgeries, and rely on manual systems for critical functions.
The incident highlighted the significant impact of ransomware attacks on healthcare organizations, particularly their reliance on digital infrastructure for patient care and operations.
The 2021 Israeli Energy Company Email Attack
A major Israeli energy company was targeted by a supply chain attack in 2021, where the attackers exploited vulnerabilities in the company’s software supply chain to gain access to its systems. The attack started with a phishing email targeting a software vendor that supplied the energy company.
The email contained a malicious attachment that compromised the vendor’s network, allowing the attackers to install malware on the vendor’s software.The malware then spread to the energy company’s network, granting the attackers access to sensitive data and control over critical infrastructure.
The attack highlighted the vulnerability of organizations to supply chain attacks, where attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in third-party software to gain access to their systems.