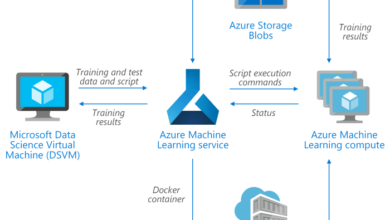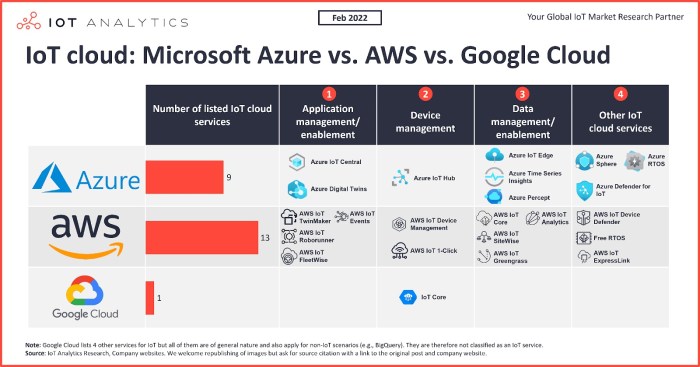
Azure vs Google Cloud: Which Cloud Platform Reigns Supreme?
Azure vs Google Cloud: This age-old question has been a constant debate in the tech world, each platform vying for the top spot. Both offer a vast array of services, from computing and storage to AI and security, catering to a diverse range of businesses and developers.
But which one truly reigns supreme? Let’s dive into the heart of this cloud computing showdown and see who emerges as the champion.
This blog post will be your guide through the intricacies of Azure and Google Cloud, offering a comprehensive comparison of their features, strengths, and weaknesses. We’ll explore key areas like compute power, storage solutions, networking capabilities, database services, AI and machine learning, security, pricing, integration, and customer support.
By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which platform best aligns with your needs and goals.
Overview
Azure and Google Cloud are two of the leading cloud computing platforms, offering a wide range of services to businesses of all sizes. They provide the infrastructure, tools, and services needed to build, deploy, and manage applications in the cloud.
This overview will explore the key features and services offered by both platforms, and highlight their target audiences and market positioning.
Key Features and Services
Azure and Google Cloud offer a wide array of services, including:
- Compute:Both platforms provide virtual machines (VMs), containers, and serverless computing options for running applications.
- Storage:Azure and Google Cloud offer a variety of storage options, including object storage, block storage, and file storage, to meet different needs.
- Networking:Both platforms provide robust networking capabilities, including virtual networks, load balancing, and firewalls, to ensure secure and reliable connectivity.
- Databases:Azure and Google Cloud offer a range of database services, including relational databases, NoSQL databases, and data warehousing solutions.
- Analytics and Machine Learning:Both platforms offer powerful analytics and machine learning tools and services to help businesses gain insights from their data.
- Security:Both platforms provide a comprehensive set of security features and tools to protect data and applications.
Target Audiences and Market Positioning
While both platforms cater to a wide range of businesses, they have distinct target audiences and market positioning.
- Azureis often favored by businesses that are already heavily invested in Microsoft technologies, such as Windows Server and Office 365. It also has a strong presence in the enterprise market, with a focus on hybrid cloud deployments.
- Google Cloudis known for its innovative and cutting-edge technologies, particularly in areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. It also has a strong presence in the developer community, with a focus on open source technologies and agile development methodologies.
Computing Services
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a comprehensive suite of computing services to cater to diverse workloads and requirements. These services enable businesses to run applications, process data, and perform various computational tasks in the cloud. Let’s delve into the core computing options offered by each provider, comparing their strengths and weaknesses.
Virtual Machines
Virtual machines (VMs) provide a traditional approach to cloud computing, offering a dedicated environment for running applications. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a wide array of VM types, each optimized for specific workloads, such as general-purpose, memory-intensive, or high-performance computing.Azure’s VM offerings include the standard A-series, the high-performance D-series, and the memory-optimized E-series.
Google Cloud offers similar options, such as the N1 series, the M1 series, and the E2 series. Both providers also offer specialized VM types for specific tasks, such as GPU-accelerated VMs for machine learning and data analysis.
- Performance: The performance of VMs depends heavily on the chosen VM type, the underlying hardware, and the application’s requirements. Both Azure and Google Cloud provide high-performance VMs with dedicated resources, enabling demanding workloads.
- Scalability: Both providers offer elastic scaling, allowing you to adjust the number of VMs based on demand. This enables you to scale up or down resources quickly, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Pricing: VM pricing varies depending on the chosen VM type, operating system, and region. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, enabling you to pay only for the resources you consume.
Advantages of VMs:
- Familiar environment for traditional applications.
- Full control over the operating system and software.
- Flexibility to customize and optimize performance.
Disadvantages of VMs:
- Higher management overhead compared to serverless options.
- Can be more expensive than serverless options for infrequent workloads.
Containers
Containers offer a lightweight and portable way to package and deploy applications. Both Azure and Google Cloud provide comprehensive container orchestration services to manage and scale containerized applications.Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) is a fully managed Kubernetes service, providing a platform for deploying and managing containerized applications at scale.
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a similar service on Google Cloud, offering a robust and scalable Kubernetes platform.
- Performance: Containers offer excellent performance by sharing the host operating system’s kernel, reducing overhead and resource consumption. Both AKS and GKE provide optimized environments for containerized applications, ensuring high performance and efficiency.
- Scalability: Container orchestration services like AKS and GKE enable effortless scaling of containerized applications. They automatically handle resource allocation, load balancing, and failover, ensuring high availability and scalability.
- Pricing: The pricing for container services is based on the underlying infrastructure, including VMs, storage, and network resources. Both AKS and GKE offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, making them cost-effective for various workloads.
Advantages of Containers:
- Improved portability and consistency across environments.
- Faster deployment and scaling compared to VMs.
- Efficient resource utilization and lower overhead.
Disadvantages of Containers:
- Requires familiarity with containerization technologies and tools.
- Can be more complex to manage than VMs.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing eliminates the need for managing servers, allowing developers to focus on writing code. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer serverless computing platforms, enabling developers to run code without provisioning or managing any infrastructure.Azure Functions is a serverless compute service that enables you to execute code on demand.
Google Cloud Functions is a similar service on Google Cloud, offering a platform for running serverless functions.
- Performance: Serverless platforms scale automatically based on demand, ensuring optimal performance for both high-traffic and low-traffic applications.
- Scalability: Serverless platforms are highly scalable, allowing you to handle spikes in traffic without manual intervention. They automatically adjust resources to meet changing demand, ensuring high availability and performance.
- Pricing: Serverless platforms typically follow a pay-per-execution model, charging only for the time your code is running. This makes them cost-effective for applications with intermittent workloads.
Advantages of Serverless Computing:
- Simplified development and deployment.
- Reduced management overhead and costs.
- Automatic scaling and high availability.
Disadvantages of Serverless Computing:
- Limited control over the underlying infrastructure.
- Cold starts can impact performance for infrequent workloads.
Storage Solutions
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a comprehensive suite of storage services, catering to diverse data management needs. These services are designed to handle various data types, from unstructured data like images and videos to structured data like databases and logs.
Choosing the right storage solution is crucial for optimizing performance, cost, and data availability.
Object Storage
Object storage is ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as images, videos, and backups. It provides a highly scalable and cost-effective solution for data that is accessed infrequently. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer robust object storage services:
- Azure Blob Storage: Offers a highly scalable and durable object storage service. It supports various storage tiers based on access frequency, enabling cost optimization. Blob storage is ideal for storing media files, backups, and other unstructured data.
- Google Cloud Storage (GCS): GCS is a highly scalable and durable object storage service that provides a wide range of features, including multi-region storage for high availability and data redundancy. It is suitable for storing media files, backups, and other unstructured data.
Comparison of Features, Performance, and Pricing
| Feature | Azure Blob Storage | Google Cloud Storage ||—|—|—|| Scalability | Highly scalable | Highly scalable || Durability | High durability | High durability || Pricing | Tiered pricing based on access frequency | Tiered pricing based on access frequency || Features | Supports various storage tiers, including hot, cool, and archive | Supports multi-region storage, object lifecycle management, and data encryption || Performance | High performance | High performance |
Best Use Cases
* Media Storage: Storing images, videos, and other media files for content delivery networks (CDNs) or media streaming services.
Backups and Archives
Storing backups of data for disaster recovery or long-term archiving.
Data Lakes
Storing large amounts of unstructured data for analytics and machine learning.
Block Storage
Block storage is designed for storing data as blocks, making it suitable for applications that require high I/O performance and low latency. This storage type is often used for virtual machine disks, databases, and other performance-critical applications.
- Azure Managed Disks: Azure Managed Disks provide a highly scalable and performant block storage solution. They are available in different performance tiers, allowing you to choose the right balance between performance and cost. Managed Disks are ideal for virtual machine disks, databases, and other performance-critical applications.
- Google Persistent Disk: Google Persistent Disk is a highly scalable and durable block storage service. It offers various performance tiers and storage types, including standard, premium, and SSD, to meet diverse performance requirements. Persistent Disk is suitable for virtual machine disks, databases, and other performance-critical applications.
Comparison of Features, Performance, and Pricing
| Feature | Azure Managed Disks | Google Persistent Disk ||—|—|—|| Scalability | Highly scalable | Highly scalable || Durability | High durability | High durability || Pricing | Tiered pricing based on performance and storage capacity | Tiered pricing based on performance and storage capacity || Features | Supports various performance tiers, including standard, premium, and ultra | Supports various performance tiers, including standard, premium, and SSD || Performance | High performance | High performance |
Best Use Cases
* Virtual Machine Disks: Providing persistent storage for virtual machines running applications.
Databases
Storing data for relational databases, NoSQL databases, and other database systems.
High-Performance Computing
Providing storage for applications that require high I/O performance and low latency.
Choosing between Azure and Google Cloud can be a tough decision, especially when you consider the ever-evolving landscape of security threats. The recent vb special issue intelligent_security highlighted the importance of proactive security measures, and both Azure and Google Cloud offer robust solutions to address these concerns.
Ultimately, the best platform for you depends on your specific needs and the level of security sophistication you require.
File Storage
File storage provides a familiar file-based interface for accessing data, making it suitable for applications that require shared access to files. This storage type is often used for sharing files among users, storing application data, and supporting traditional file-based applications.
- Azure File Share: Azure File Share provides a fully managed file storage service that allows you to access files using the standard SMB protocol. It is highly scalable and offers high availability and durability. File Share is ideal for sharing files among users, storing application data, and supporting traditional file-based applications.
- Google Cloud Filestore: Google Cloud Filestore is a fully managed file storage service that offers a high-performance and scalable file system. It supports both NFS and SMB protocols, providing flexibility for various applications. Filestore is suitable for sharing files among users, storing application data, and supporting traditional file-based applications.
Comparison of Features, Performance, and Pricing
| Feature | Azure File Share | Google Cloud Filestore ||—|—|—|| Scalability | Highly scalable | Highly scalable || Durability | High durability | High durability || Pricing | Tiered pricing based on storage capacity and throughput | Tiered pricing based on storage capacity and throughput || Features | Supports SMB protocol | Supports NFS and SMB protocols || Performance | High performance | High performance |
Best Use Cases
* File Sharing: Sharing files among users in a collaborative environment.
Application Data
Storing application data that requires shared access.
Traditional File-Based Applications
Supporting applications that rely on file-based storage.
Networking Capabilities
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer robust networking capabilities that are essential for building and deploying modern cloud applications. Understanding the nuances of each provider’s networking infrastructure is crucial for architects and developers to make informed decisions about their cloud strategy.
This section will delve into the key networking features and capabilities of Azure and Google Cloud, comparing their virtual networks, load balancing, and firewalls. We’ll also examine the security and performance implications of each provider’s networking infrastructure.
Virtual Networks
Virtual networks (VNet) provide a logical isolation layer for your cloud resources, enabling you to segment your network traffic and enhance security. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer comprehensive virtual network features:Azure Virtual Networks:
Regional Scope
Azure VNets are defined within a specific Azure region, providing a logical boundary for your resources.
Subnet Management
VNets can be divided into subnets, allowing for granular control over resource placement and network segmentation.
Connectivity Options
Azure offers various connectivity options, including VPN gateways, ExpressRoute, and Azure Firewall.
Network Security Groups (NSGs)
NSGs provide granular control over inbound and outbound traffic to virtual machines and other resources within a subnet.Google Cloud Virtual Private Networks (VPNs):
Global Scope
Google Cloud VPNs are global in scope, allowing you to connect resources across different regions.
Subnet Management
Similar to Azure, Google Cloud allows you to create subnets within your VPNs for network segmentation.
Cloud Router
Google Cloud’s Cloud Router provides advanced routing capabilities, including BGP support and dynamic routing.
Cloud Armor
Cloud Armor acts as a web application firewall (WAF) and can be used to protect your applications from DDoS attacks and other threats.
Load Balancing, Azure vs google cloud
Load balancing is crucial for distributing traffic across multiple instances of your application, ensuring high availability and scalability. Both Azure and Google Cloud provide robust load balancing solutions:Azure Load Balancer:
Basic and Standard Load Balancers
Azure offers two main types of load balancers: Basic for simple load balancing needs and Standard for more advanced scenarios.
Internal and External Load Balancers
Both types of load balancers can be internal (for traffic within your virtual network) or external (for traffic from the internet).
Health Probes
Azure load balancers support health probes to ensure that only healthy instances are receiving traffic.Google Cloud Load Balancing:
Global and Regional Load Balancing
Google Cloud provides both global and regional load balancing options, catering to different use cases.
HTTP(S), TCP, and SSL Load Balancing
Google Cloud offers load balancing for various protocols, including HTTP(S), TCP, and SSL.
Traffic Management
Google Cloud Load Balancing allows you to configure traffic management policies for advanced routing and distribution.
Firewalls
Firewalls play a critical role in protecting your cloud resources from unauthorized access. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a range of firewall options:Azure Firewall:
Managed Firewall Service
Azure Firewall is a fully managed firewall service that provides stateful inspection, intrusion detection, and threat intelligence.
Network Security Groups (NSGs)
NSGs are a more basic firewall solution that can be used to control inbound and outbound traffic at the subnet level.
Azure Application Gateway
Azure Application Gateway can act as a web application firewall (WAF) to protect your web applications from attacks.Google Cloud Firewalls:
Cloud Armor
Cloud Armor is a managed WAF that can protect your applications from DDoS attacks and other threats.
Cloud Firewall
Google Cloud Firewall is a managed network firewall service that provides stateful inspection and advanced security features.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Firewalls
Google Cloud VPC Firewalls can be used to control traffic within your VPC network.
Networking Capabilities Comparison
| Feature | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Networks | Regional scope, Subnet management, Connectivity options, Network Security Groups | Global scope, Subnet management, Cloud Router, Cloud Armor |
| Load Balancing | Basic and Standard Load Balancers, Internal and External Load Balancers, Health Probes | Global and Regional Load Balancing, HTTP(S), TCP, and SSL Load Balancing, Traffic Management |
| Firewalls | Azure Firewall, Network Security Groups, Azure Application Gateway | Cloud Armor, Cloud Firewall, VPC Firewalls |
Database Services: Azure Vs Google Cloud
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a comprehensive suite of database services to cater to various needs, from simple applications to complex data warehousing solutions. This section delves into the different database services provided by both platforms, comparing their performance, scalability, and pricing.
Relational Databases
Relational databases are the most traditional type of database, organizing data into tables with rows and columns. They are well-suited for structured data and applications that require ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).Azure and Google Cloud offer a range of relational database services, including:
- Azure SQL Database:A fully managed SQL database service with high availability, scalability, and security features. It offers various deployment options, including single databases, elastic pools, and managed instances.
- Google Cloud SQL:A fully managed MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server database service. It provides high availability, scalability, and built-in security features. Google Cloud SQL also offers a variety of deployment options, including single databases, instances, and clusters.
Both Azure SQL Database and Google Cloud SQL offer similar features and capabilities. The choice between the two often comes down to factors like preferred database engine, existing infrastructure, and pricing.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases are designed to handle unstructured data and high volumes of data at scale. They are often used for applications like social media, e-commerce, and real-time analytics.Azure and Google Cloud provide various NoSQL database services, including:
- Azure Cosmos DB:A fully managed, globally distributed NoSQL database service that supports multiple data models, including document, key-value, graph, and table. It offers high availability, scalability, and low latency, making it suitable for applications demanding high performance and global reach.
- Google Cloud Firestore:A fully managed NoSQL database service that provides a document database with strong consistency and automatic scaling. It is ideal for mobile and web applications requiring real-time data synchronization and offline capabilities.
- Azure Table Storage:A NoSQL key-value store service that offers high scalability and availability. It is well-suited for storing structured data like user profiles, settings, and other metadata.
- Google Cloud Datastore:A NoSQL database service that provides a scalable and highly available data store for web and mobile applications. It offers features like automatic scaling, strong consistency, and ACID properties.
Azure Cosmos DB and Google Cloud Firestore are both popular choices for modern applications requiring high performance and scalability. Azure Table Storage and Google Cloud Datastore offer more specialized solutions for specific use cases.
Data Warehousing Solutions
Data warehousing solutions are designed to store and analyze large volumes of data from various sources. They are often used for business intelligence, reporting, and data analytics.Azure and Google Cloud offer various data warehousing solutions, including:
- Azure Synapse Analytics:A fully managed data warehousing service that provides a unified platform for data ingestion, transformation, and analysis. It offers high performance, scalability, and integration with other Azure services.
- Google BigQuery:A serverless data warehouse that provides a scalable and cost-effective solution for analyzing large datasets. It offers a powerful SQL engine, integration with other Google Cloud services, and built-in machine learning capabilities.
Both Azure Synapse Analytics and Google BigQuery are powerful data warehousing solutions with their strengths and weaknesses. Azure Synapse Analytics offers a more integrated approach with other Azure services, while Google BigQuery excels in its serverless architecture and machine learning capabilities.
Performance, Scalability, and Pricing
The performance, scalability, and pricing of database services can vary significantly between Azure and Google Cloud.
- Performance:Both platforms offer high-performance database services. However, the actual performance can vary depending on the specific service, configuration, and workload. For example, Azure Cosmos DB and Google Cloud Firestore are known for their low latency and high throughput, while Azure Synapse Analytics and Google BigQuery are optimized for large-scale data analysis.
- Scalability:Both Azure and Google Cloud offer highly scalable database services. They allow you to adjust resources based on your application’s needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. Azure Cosmos DB and Google Cloud Firestore provide automatic scaling, while Azure Synapse Analytics and Google BigQuery offer manual scaling options.
- Pricing:The pricing models for database services can differ between Azure and Google Cloud. Both platforms offer pay-as-you-go pricing, but they may have different pricing tiers, discounts, and usage-based charges. It is essential to compare pricing models carefully based on your specific needs and usage patterns.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Choosing between Azure and Google Cloud for database services depends on specific requirements and priorities.
- Azure:
- Advantages:Strong integration with other Azure services, comprehensive security features, wide range of database options, and a robust ecosystem of partners and tools.
- Disadvantages:Can be more expensive than Google Cloud for some services, and its interface might be less intuitive for some users.
- Google Cloud:
- Advantages:Cost-effective pricing for some services, strong focus on machine learning and data analytics, and a user-friendly interface.
- Disadvantages:Less extensive database offerings compared to Azure, and its integration with other services might be less seamless.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer comprehensive AI and ML solutions, catering to various needs from simple model training to complex deployments. This section explores the strengths and weaknesses of each platform’s AI and ML offerings, including pre-trained models, machine learning platforms, and AI services.
Pre-trained Models
Pre-trained models are a valuable resource for developers looking to quickly build AI applications. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a wide range of pre-trained models, each tailored for specific tasks like image classification, natural language processing, and object detection.Azure’s pre-trained models are available through Azure Machine Learning, Azure Cognitive Services, and Azure OpenAI Service.
Google Cloud offers pre-trained models through Google Cloud AI Platform, Vertex AI, and TensorFlow Hub.
Key Differences
- Azure’s pre-trained models are often tailored to specific industry verticals, while Google Cloud’s models are more general-purpose.
- Azure offers pre-trained models from various sources, including Microsoft, third-party providers, and the open-source community, while Google Cloud focuses primarily on its own models.
Machine Learning Platforms
Machine learning platforms provide a comprehensive environment for building, training, and deploying machine learning models. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer robust machine learning platforms with features such as data preparation, model training, model deployment, and model monitoring.Azure Machine Learning and Google Cloud AI Platform are the primary machine learning platforms for their respective cloud providers.
Key Differences
- Azure Machine Learning offers a more user-friendly interface and a wider range of pre-built components, while Google Cloud AI Platform provides a more flexible and powerful platform for advanced users.
- Azure Machine Learning integrates seamlessly with other Azure services, while Google Cloud AI Platform offers a more independent platform with a strong focus on open-source technologies.
AI Services
AI services offer pre-built AI capabilities that can be easily integrated into applications. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a wide range of AI services, including computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, and translation.Azure Cognitive Services and Google Cloud AI Platform are the primary providers of AI services for their respective cloud providers.
Key Differences
- Azure Cognitive Services offers a broader range of services, including some specialized services like Anomaly Detection and Content Moderator, while Google Cloud AI Platform focuses on a more curated set of services with a strong emphasis on open-source technologies.
- Azure Cognitive Services is often more tightly integrated with other Azure services, while Google Cloud AI Platform offers a more independent set of services that can be easily integrated with other platforms.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-trained Models | Azure Machine Learning, Azure Cognitive Services, Azure OpenAI Service | Google Cloud AI Platform, Vertex AI, TensorFlow Hub |
| Machine Learning Platforms | Azure Machine Learning | Google Cloud AI Platform |
| AI Services | Azure Cognitive Services | Google Cloud AI Platform |
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are paramount concerns for businesses when choosing a cloud provider. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer robust security features and compliance certifications to ensure the protection of customer data and applications.
Security Features
Both Azure and Google Cloud implement a wide range of security features to protect customer data and applications.
- Data Encryption:Both platforms offer data encryption at rest and in transit using industry-standard algorithms like AES-256. They also provide tools for key management and control. For example, Azure Key Vault and Google Cloud Key Management Service (KMS) allow users to manage encryption keys securely.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM) provide granular control over access to resources. Users can be assigned specific roles with defined permissions, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and applications.
- Network Security:Both platforms offer a range of network security features, including firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and intrusion detection systems (IDS). Azure Firewall and Google Cloud Armor provide comprehensive network security solutions.
- Threat Detection and Response:Azure Security Center and Google Cloud Security Command Center offer advanced threat detection and response capabilities. They use machine learning algorithms to analyze security data and identify potential threats, providing real-time alerts and remediation guidance.
Compliance Certifications
Both Azure and Google Cloud have obtained numerous compliance certifications, demonstrating their commitment to meeting industry standards.
- Azure:Azure has achieved certifications from various regulatory bodies, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. These certifications ensure that Azure meets specific security and privacy requirements for handling sensitive data.
- Google Cloud:Google Cloud has also obtained numerous compliance certifications, including ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. They also have certifications specific to certain industries, such as FedRAMP for government agencies.
Key Compliance Standards
Both Azure and Google Cloud comply with key industry standards, including:
- ISO 27001:This standard specifies requirements for an information security management system (ISMS). It ensures that organizations have implemented appropriate controls to protect sensitive information.
- SOC 2:This standard focuses on the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data. It provides assurance that organizations have adequate controls in place to protect sensitive information.
- HIPAA:This standard sets requirements for the protection of health information. It ensures that organizations comply with specific regulations for handling patient data.
- PCI DSS:This standard focuses on the protection of credit card data. It ensures that organizations have implemented security controls to prevent fraud and data breaches.
- GDPR:This regulation sets requirements for the protection of personal data in the European Union. It ensures that organizations handle personal data responsibly and transparently.
Pricing and Cost Optimization
Choosing the right cloud provider often comes down to cost. Azure and Google Cloud offer a range of pricing models and cost optimization strategies to help businesses manage their cloud expenses. This section will compare the pricing models and cost optimization strategies of Azure and Google Cloud, analyzing the different pricing options available for various services and discussing the factors to consider when choosing between the two based on pricing and cost optimization.
Choosing between Azure and Google Cloud is a tough call, especially when you consider the ever-present threat of cyberattacks. The recent Sandworm threat actor disrupting power in Ukraine highlights the need for robust security measures, which both platforms offer, but with different strengths.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and the level of security you require.
Pricing Models
Azure and Google Cloud utilize different pricing models for their services, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
- Pay-as-you-go: This is the most common pricing model, where you pay for the resources you use. This model is ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads or those who want to pay only for what they use. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer pay-as-you-go pricing for most of their services.
Choosing between Azure and Google Cloud can be a tough decision, especially when considering factors like cost, security, and scalability. But sometimes, even the most complex technology decisions get overshadowed by news in the financial world. For instance, CMC Metals Ltd’s announcement of a proposed amendment of warrants could be a hot topic for investors.
Ultimately, though, the choice between Azure and Google Cloud comes down to your specific needs and priorities, and it’s worth exploring both platforms to find the best fit for your organization.
- Reserved Instances: Both Azure and Google Cloud offer reserved instances for specific services like virtual machines (VMs) and databases. This model allows you to commit to using a certain amount of resources for a specific period, in return for a discounted rate.
Reserved instances can be a good option for businesses with predictable workloads or those who want to reduce their costs.
- Spot Instances: Spot instances are a more cost-effective option for workloads that can tolerate interruptions. They offer significant discounts compared to on-demand instances but can be terminated with little notice. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer spot instances, but the specific availability and pricing vary.
- Preemptible Instances: Similar to spot instances, preemptible instances are offered at a lower cost, but they can be terminated with a short notice. Google Cloud offers preemptible instances, while Azure offers similar functionality with their low-priority VMs.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a range of cost optimization strategies to help businesses reduce their cloud expenses. These strategies can be categorized into three main areas:
- Rightsizing Resources: This involves ensuring that you are using the appropriate resources for your workloads. For example, if you have a VM that is underutilized, you can downsize it to a smaller instance to save money. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer tools and recommendations to help you rightsize your resources.
- Optimizing Usage: This involves reducing your overall resource consumption. For example, you can schedule your workloads to run during off-peak hours when prices are lower. Both Azure and Google Cloud offer features like auto-scaling and scheduled tasks to help you optimize usage.
- Leveraging Discounts and Credits: Both Azure and Google Cloud offer various discounts and credits to help businesses save money. These can include discounts for sustained use, reserved instances, and volume discounts.
Cost Comparison
Comparing the pricing of Azure and Google Cloud is challenging, as the pricing of specific services can vary significantly depending on the region, instance type, and other factors. However, some general observations can be made:
- Compute Services: For virtual machines, Google Cloud tends to be more cost-effective than Azure, particularly for preemptible instances. However, Azure offers more flexibility with reserved instances and spot instances.
- Storage Services: Azure and Google Cloud offer similar pricing for storage services, but Google Cloud might be more cost-effective for large-scale storage needs.
- Database Services: The pricing for database services can vary significantly depending on the specific database type and usage patterns. It is important to compare the pricing of specific database services on both platforms before making a decision.
Factors to Consider
When choosing between Azure and Google Cloud based on pricing and cost optimization, several factors should be considered:
- Workload Requirements: The type and scale of your workloads will influence the pricing model and cost optimization strategies that are most suitable.
- Budget and Cost Sensitivity: Consider your budget constraints and how sensitive you are to cost fluctuations.
- Long-Term Strategy: If you anticipate your cloud needs to grow, consider the long-term pricing and cost optimization capabilities of each platform.
- Specific Service Needs: Compare the pricing of specific services that are critical to your business on both platforms.
- Cost Optimization Tools and Resources: Evaluate the cost optimization tools and resources offered by each platform.
Conclusion
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer a range of pricing models and cost optimization strategies to help businesses manage their cloud expenses. The best platform for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, you can choose the cloud provider that offers the most cost-effective solution for your business.
Integration and Ecosystem
The integration capabilities and ecosystem of cloud providers are crucial factors to consider when choosing a platform. A robust ecosystem with seamless integration options allows for greater flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in deploying and managing cloud solutions.
Integration with Other Technologies and Services
The integration capabilities of Azure and Google Cloud are extensive, encompassing a wide range of technologies and services.
- Azureoffers integration with various third-party tools and platforms, including popular DevOps tools like Jenkins, GitHub, and GitLab, as well as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems such as SAP and Oracle. Azure also seamlessly integrates with Microsoft’s suite of products, including Windows Server, Office 365, and Active Directory.
- Google Cloudexcels in integrating with open-source technologies and platforms, including Kubernetes, Apache Spark, and Hadoop. Google Cloud also has strong integrations with Google’s own services, such as Google Workspace, Google Maps, and Google Analytics.
Ecosystem and Integration Options
Both Azure and Google Cloud boast comprehensive ecosystems with a wide range of services, tools, and partners.
- Azurehas a mature ecosystem with a large number of partners, including independent software vendors (ISVs), system integrators (SIs), and managed service providers (MSPs). Azure’s ecosystem offers a wide range of solutions for various industries, including finance, healthcare, and retail.
- Google Cloudis rapidly expanding its ecosystem, particularly in areas like AI and machine learning. Google Cloud’s ecosystem includes a strong developer community, numerous open-source projects, and partnerships with leading technology companies.
Strengths and Weaknesses
- Azure‘s strength lies in its deep integration with Microsoft’s products and services, making it a preferred choice for organizations already heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. However, Azure’s reliance on proprietary technologies can limit flexibility and interoperability with other platforms.
- Google Cloud‘s strengths lie in its open-source focus, strong developer community, and innovative AI and ML capabilities. Google Cloud’s ecosystem offers a high degree of flexibility and interoperability with other platforms. However, Google Cloud’s ecosystem is still evolving and may not be as mature as Azure’s.
Customer Support and Documentation
Both Azure and Google Cloud offer robust customer support and comprehensive documentation to assist users in navigating their platforms. These resources are crucial for developers, IT professionals, and businesses to troubleshoot issues, learn best practices, and maximize the value of their cloud solutions.
Customer Support Channels
The availability and quality of support channels play a significant role in user satisfaction and problem resolution. Both Azure and Google Cloud provide a variety of support options, catering to different needs and technical expertise levels.
- Azureoffers several support channels, including:
- Online resources:Azure documentation, tutorials, and FAQs are readily available on the Microsoft website and within the Azure portal.
- Technical support:Azure provides various support plans, ranging from basic to premium, with different levels of response times and technical expertise.
- Community forums:Azure has active community forums where users can connect with peers, share knowledge, and seek assistance from Microsoft experts.
- Google Cloudalso offers a comprehensive set of support channels, including:
- Online resources:Google Cloud documentation, tutorials, and FAQs are available on the Google Cloud website and within the Google Cloud console.
- Technical support:Google Cloud provides various support packages, including basic, standard, and premium, with different levels of response times and technical expertise.
- Community forums:Google Cloud has a vibrant community forum where users can connect with peers, share knowledge, and seek assistance from Google Cloud experts.
Documentation Quality and Comprehensiveness
Comprehensive and well-structured documentation is essential for users to understand the capabilities, features, and best practices of a cloud platform. Both Azure and Google Cloud provide extensive documentation, but their strengths and weaknesses differ.
- Azuredocumentation is known for its comprehensiveness and depth, covering a wide range of topics, from fundamental concepts to advanced technical details. It also provides detailed examples and code snippets to illustrate concepts and best practices. However, some users find the documentation to be overly technical and dense, making it challenging to navigate for beginners.
- Google Clouddocumentation is generally praised for its clarity and user-friendliness. It often presents information in a more concise and accessible manner, making it easier for users to find the information they need. However, some users find the documentation to be less comprehensive than Azure’s, with fewer examples and code snippets.