Linux Project Management Software: Streamlining Your Workflows
Linux project management software offers a powerful and flexible approach to managing projects in diverse environments. These tools, designed for the open-source operating system, empower teams with features tailored for collaboration, task organization, and efficient project execution.
From agile methodologies to traditional project management frameworks, Linux project management software caters to a wide range of needs. Its open-source nature fosters innovation and community-driven development, leading to constant improvements and a wealth of customizable options.
Introduction to Linux Project Management Software
Linux project management software refers to applications designed for planning, organizing, and managing projects within a Linux operating system environment. These tools provide a comprehensive suite of features that streamline project workflows, enhance collaboration, and facilitate efficient task management. Linux-based project management tools offer a wide range of functionalities, including task assignment, progress tracking, resource allocation, communication channels, and reporting capabilities.
They are highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs and project requirements.
Advantages of Using Linux-Based Project Management Tools
Linux project management software presents several advantages for project teams, making it a compelling choice for organizations seeking efficient and robust project management solutions.
- Open Source Nature:Linux-based project management tools are often open-source, meaning the source code is freely available for inspection, modification, and distribution. This fosters transparency and allows users to customize the software to their specific needs, enhancing flexibility and control.
- Cost-Effectiveness:Open-source software eliminates the need for licensing fees, making it a cost-effective option for businesses and individuals. This financial advantage is particularly attractive for organizations with limited budgets or those seeking to maximize their return on investment.
- Security and Stability:Linux is renowned for its robust security features and stable operating environment. This translates to enhanced security and reliability for project management software, minimizing the risk of data breaches and system failures.
- Community Support:Open-source projects benefit from a large and active community of developers and users. This provides a rich source of support, documentation, and troubleshooting resources, ensuring users have access to assistance when needed.
- Platform Compatibility:Linux-based project management tools are generally compatible with various platforms, including Windows, macOS, and other Linux distributions. This cross-platform compatibility enables seamless collaboration among team members using different operating systems.
Popular Linux Project Management Software Options
Linux offers a diverse range of project management software solutions, catering to various needs and preferences. These tools empower teams to streamline workflows, track progress, and effectively manage projects.
Linux project management software offers a robust and flexible environment for managing complex projects. While keeping your projects on track is essential, securing your online activity while traveling is equally important. For that, you’ll want to explore the best VPN for travel , ensuring your data stays private and secure, even when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks.
Once you’ve got your online security sorted, you can return to your Linux project management software with peace of mind, knowing your data is protected.
Popular Linux Project Management Software Options
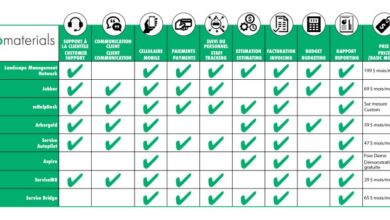
The following table highlights five popular Linux project management software options, each with its distinct features and benefits:
| Name | Description | Key Features | Pricing Model | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taskwarrior | A command-line task management tool known for its simplicity and flexibility. |
|
Open source (free) | All major Linux distributions |
| Redmine | A web-based project management tool offering comprehensive features for project planning, tracking, and collaboration. |
|
Open source (free) | All major Linux distributions |
| OpenProject | A feature-rich project management platform with a focus on collaboration and communication. |
|
Open source (free) and paid plans available | All major Linux distributions |
| Freeplane | A mind mapping and knowledge management tool that can be used for project planning and organization. |
|
Open source (free) | All major Linux distributions |
| KanbanTool | A web-based Kanban tool that simplifies project management and workflow visualization. |
|
Free plan available, paid plans for additional features | Web-based, accessible from any browser |
Features and Capabilities of Linux Project Management Software

Linux project management software offers a comprehensive suite of tools designed to streamline project planning, execution, and monitoring. These applications empower teams to manage tasks efficiently, foster seamless collaboration, generate insightful reports, and integrate with other essential business tools.
Task Management
Effective task management is the cornerstone of any successful project. Linux project management software excels in this domain, providing a range of features that simplify task creation, assignment, prioritization, and tracking.
- Task Creation and Assignment: Users can easily create tasks, define clear descriptions, set due dates, and assign tasks to specific team members. This ensures that everyone is aware of their responsibilities and deadlines.
- Task Prioritization: Many tools allow for task prioritization using methods like Kanban boards or priority levels. This helps teams focus on the most critical tasks first, maximizing productivity.
- Subtasks and Dependencies: Complex projects often involve breaking down large tasks into smaller subtasks. Linux project management software enables users to create subtasks, define dependencies between tasks, and track their progress.
- Task Tracking and Progress Monitoring: Real-time task tracking provides a clear overview of project progress. Users can monitor task completion status, identify potential roadblocks, and adjust plans accordingly.
Collaboration Tools
Collaboration is crucial for project success, and Linux project management software provides a range of features to facilitate seamless communication and teamwork.
- Team Communication: Integrated chat features, forums, and comment sections allow team members to communicate effectively, discuss project updates, and resolve issues quickly.
- File Sharing: Centralized file storage and sharing capabilities enable teams to access and collaborate on project documents, presentations, and other relevant materials easily.
- Real-time Collaboration: Some software offers real-time co-editing features, allowing multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously, improving efficiency and reducing version conflicts.
- Notifications and Alerts: Users can set up notifications and alerts for task updates, deadline reminders, and important announcements, ensuring that everyone stays informed.
Reporting Capabilities, Linux project management software
Data-driven insights are essential for informed decision-making in project management. Linux project management software provides robust reporting capabilities to analyze project performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Project Status Reports: Generate comprehensive reports that provide a clear overview of project progress, task completion rates, and resource utilization. This helps stakeholders track project health and identify potential risks.
- Time Tracking and Reporting: Accurately track time spent on tasks and generate detailed reports on resource allocation, effort estimates, and project timelines. This information can be used to optimize resource utilization and improve future project planning.
- Customizable Reports: Most software offers customizable reporting options, allowing users to create reports tailored to specific project needs and data visualization preferences.
- Data Export and Integration: Export reports in various formats (e.g., PDF, CSV, Excel) for easy sharing and integration with other business intelligence tools.
Integrations
Linux project management software often integrates with other essential business applications, streamlining workflows and improving data consistency.
- Calendar and Scheduling Integration: Integrate with popular calendar applications (e.g., Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar) to sync project deadlines and meetings, ensuring everyone stays on track.
- CRM Integration: Integrate with customer relationship management (CRM) systems to manage customer interactions, track project leads, and streamline sales processes.
- Accounting Software Integration: Integrate with accounting software to track project expenses, manage budgets, and generate financial reports, providing a complete financial picture of project performance.
- Communication Platforms Integration: Integrate with popular communication platforms (e.g., Slack, Microsoft Teams) to facilitate seamless communication and collaboration within the project team.
Benefits of Using Linux Project Management Software
Linux-based project management software offers a range of advantages that can significantly enhance project efficiency, collaboration, and overall success. These benefits stem from the open-source nature of Linux, its flexibility, customization options, and robust security features.
Open-Source Nature
Open-source software is freely available for anyone to use, modify, and distribute. This accessibility fosters a collaborative environment where developers and users can contribute to the software’s development and improvement. This collaborative approach leads to a wider range of features, bug fixes, and security enhancements.
- Cost-Effective:Open-source software eliminates the need for expensive licensing fees, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes. This cost-effectiveness allows organizations to allocate resources to other critical areas, such as project development or training.
- Transparency and Community Support:The open-source nature of Linux-based project management software ensures transparency in the software’s code. This transparency allows users to inspect the code, identify potential vulnerabilities, and contribute to its improvement. Moreover, the active community surrounding open-source software provides a platform for users to seek support, share knowledge, and collaborate on solutions.
- Customization and Flexibility:Open-source software grants users the freedom to customize the software to meet their specific project management needs. This flexibility allows organizations to adapt the software to their workflows, processes, and reporting requirements, maximizing its effectiveness.
Flexibility and Customization Options
Linux-based project management software is known for its flexibility and customization options. This adaptability allows organizations to tailor the software to their specific workflows, processes, and reporting requirements, enhancing project efficiency and collaboration.
- Integration with Other Tools:Linux-based project management software seamlessly integrates with other open-source tools and applications. This interoperability allows organizations to create a unified project management ecosystem, enhancing data flow, automation, and overall efficiency.
- Workflow Customization:Organizations can customize workflows to match their specific project management methodologies, such as Agile, Scrum, or Kanban. This customization ensures that the software aligns with the organization’s project management practices, promoting efficiency and consistency.
- Reporting and Analytics:Linux-based project management software provides extensive reporting and analytics capabilities. Organizations can generate custom reports and dashboards to track project progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. This data-driven approach helps organizations optimize their project management processes and achieve better outcomes.
Security
Linux is renowned for its robust security features, making it an ideal platform for managing sensitive project data. The open-source nature of Linux fosters a collaborative security environment where developers and users can identify and address vulnerabilities quickly.
- Strong Security Features:Linux incorporates robust security features, including user access controls, file system permissions, and intrusion detection systems. These features help protect project data from unauthorized access, malware attacks, and other security threats.
- Regular Security Updates:The open-source community actively develops and releases security updates to address vulnerabilities. This proactive approach ensures that Linux-based project management software remains secure and protected against emerging threats.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches:By leveraging Linux’s strong security features, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches and protect sensitive project information. This enhanced security helps maintain project integrity and build trust with stakeholders.
Best Practices for Choosing and Implementing Linux Project Management Software
Choosing and implementing the right Linux project management software is crucial for any organization or project seeking to streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and improve overall efficiency. This process involves a careful evaluation of needs, thorough research, and a strategic approach to integration and user training.
Defining Requirements and Goals
Before embarking on the software selection process, it is essential to clearly define the specific requirements and goals of your organization or project. This involves understanding the project management methodologies used, the size and complexity of projects, the number of users, and the desired functionalities.
- Project Management Methodologies:Identify the project management methodologies used by your organization, such as Agile, Waterfall, or a hybrid approach. This will help narrow down the software options that best align with your workflow.
- Project Size and Complexity:Consider the size and complexity of projects typically undertaken. Some software may be better suited for small, simple projects, while others offer advanced features for managing large, complex initiatives.
- Number of Users:Determine the number of users who will be accessing the software. This will influence the choice of software with appropriate scalability and user management features.
- Desired Functionalities:Identify the essential functionalities needed, such as task management, time tracking, collaboration tools, reporting, and integrations with other systems. This will help prioritize software options that meet your specific needs.
Researching and Evaluating Software Options
Once you have defined your requirements and goals, it’s time to research and evaluate available Linux project management software options. This involves exploring various software solutions, comparing features and functionalities, and considering factors like pricing, support, and user reviews.
Linux project management software offers a wealth of tools for keeping projects on track, but sometimes you need a boost in processing power. That’s where the new Intel Lunar Lake NPU comes in. With its dedicated neural processing capabilities, it could revolutionize how we handle complex tasks like resource allocation and risk analysis, making Linux project management even more efficient.
- Explore Software Options:Conduct thorough research on popular Linux project management software solutions, including open-source and commercial options. Explore online resources, industry reviews, and vendor websites to gather information.
- Compare Features and Functionalities:Create a comparison table to analyze the features and functionalities of different software options. This will help you identify the best fit based on your specific requirements.
- Consider Pricing and Support:Evaluate pricing models, including subscription fees, per-user costs, and potential add-on features. Consider the level of support offered by vendors, such as documentation, online forums, and customer service.
- Read User Reviews:Gather insights from user reviews on platforms like G2 Crowd, Capterra, and TrustRadius. These reviews provide valuable perspectives on the software’s usability, performance, and overall user experience.
Implementing and Integrating the Software
After selecting the appropriate software, it’s crucial to implement and integrate it effectively into existing workflows. This involves planning the implementation process, providing user training, and addressing potential challenges.
Linux project management software offers a powerful and customizable approach to managing projects, but sometimes you need the flexibility and accessibility of cloud-based solutions. If you’re looking for a platform that can be accessed from anywhere, consider exploring the world of cloud project management software.
While these platforms may not have the same level of customization as their Linux counterparts, they offer a range of features and integrations that can streamline your workflow and boost productivity.
- Plan the Implementation Process:Develop a comprehensive implementation plan that Artikels the steps involved, timelines, and responsibilities. This plan should include data migration, user onboarding, and system testing.
- Provide User Training:Offer comprehensive training sessions for users to familiarize them with the software’s features and functionalities. This training should be tailored to different user roles and levels of experience.
- Address Potential Challenges:Anticipate potential challenges during implementation, such as data migration issues, user adoption resistance, and system integration complexities. Develop strategies to mitigate these challenges and ensure a smooth transition.
Training and Support
Providing adequate training and support for users is crucial for successful adoption and utilization of Linux project management software. This includes offering comprehensive training materials, establishing support channels, and providing ongoing assistance.
- Offer Comprehensive Training Materials:Provide users with access to comprehensive training materials, such as online tutorials, user manuals, and video guides. This will enable them to learn the software at their own pace and access information whenever needed.
- Establish Support Channels:Create multiple support channels for users to seek assistance, such as email, phone, live chat, and online forums. This will ensure prompt and efficient resolution of any issues or queries.
- Provide Ongoing Assistance:Offer ongoing support to users through regular updates, troubleshooting guidance, and knowledge sharing sessions. This will foster continuous learning and ensure the software remains effective over time.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples

The effectiveness of Linux project management software is best demonstrated through real-world applications. By examining successful implementations across various industries, we can gain valuable insights into how these tools have helped organizations achieve their project goals.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
This section will showcase case studies of companies that have successfully leveraged Linux project management software to streamline their operations, enhance collaboration, and improve project outcomes.
- Open Source Software Development:Red Hat, a leading provider of open-source software solutions, utilizes its own internal project management tools based on Linux. These tools enable Red Hat to manage complex software development projects, track progress effectively, and ensure collaboration across distributed teams.
The company’s experience demonstrates the power of open-source project management solutions in handling large-scale software development initiatives.
- Education and Research:Universities and research institutions heavily rely on Linux systems for their computing infrastructure. Many institutions utilize open-source project management tools like Kanban boards and task management systems to manage research projects, organize academic collaborations, and track research progress. The flexibility and customization capabilities of Linux-based project management tools make them ideal for research environments with unique requirements.
- Financial Services:Financial institutions are increasingly adopting Linux-based project management software for managing critical projects related to compliance, risk management, and data analysis. These institutions benefit from the security and stability of Linux systems, as well as the ability to integrate project management tools with existing financial applications.
Real-World Examples of Project Success
This section will provide specific examples of how Linux project management software has helped organizations achieve their project goals.
- Improved Project Visibility and Communication:A large multinational corporation implemented a Linux-based project management system to improve project visibility and communication across its global teams. The system allowed project managers to track progress in real-time, identify potential roadblocks early on, and facilitate effective communication between team members.
This resulted in improved project coordination, reduced delays, and ultimately, successful project completion.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Teamwork:A software development company adopted a collaborative project management tool based on Linux to enhance teamwork and improve productivity. The tool enabled team members to share files, track tasks, and communicate seamlessly, fostering a collaborative environment that boosted team morale and increased efficiency.
This resulted in faster development cycles and higher-quality software releases.
- Streamlined Project Management Processes:A non-profit organization implemented a Linux-based project management system to streamline its project management processes. The system provided a centralized platform for managing tasks, deadlines, and resources, reducing administrative overhead and improving project efficiency. This allowed the organization to focus on its core mission and achieve its objectives more effectively.
Future Trends in Linux Project Management Software
The landscape of Linux project management software is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user needs. Emerging trends are shaping the future of project management in Linux environments, offering both opportunities and challenges.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize project management by automating repetitive tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing overall efficiency. Linux project management software is expected to incorporate these technologies to provide:
- Automated task prioritization:AI algorithms can analyze project data and prioritize tasks based on factors like urgency, dependencies, and resource availability.
- Predictive analytics:Machine learning models can analyze historical project data to predict potential risks, delays, and resource bottlenecks, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
- Resource optimization:AI-powered systems can optimize resource allocation based on skills, availability, and project requirements, ensuring efficient utilization of personnel.
Cloud-Based Project Management
Cloud computing is transforming the way project management software is accessed and deployed. Linux project management software is increasingly adopting cloud-based models, offering:
- Scalability and flexibility:Cloud-based solutions can easily scale to accommodate growing project needs and provide access from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Reduced infrastructure costs:Users can avoid the costs associated with hardware, software licenses, and maintenance by utilizing cloud-based services.
- Enhanced collaboration:Cloud platforms facilitate real-time collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location.
Agile and DevOps Integration
Agile and DevOps methodologies are gaining widespread adoption in software development, and Linux project management software is adapting to support these approaches. Key trends include:
- Kanban boards and sprint tracking:Software is incorporating visual tools like Kanban boards to facilitate agile workflows and track progress in sprints.
- Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines:Project management software is integrating with CI/CD pipelines to streamline the development and deployment process.
- Automated testing and deployment:AI-powered tools are being integrated to automate testing and deployment processes, improving software quality and reducing time to market.
Open Source Collaboration and Innovation
The open-source nature of Linux fosters a collaborative environment, encouraging innovation and community-driven development. Linux project management software is benefitting from this collaborative spirit, leading to:
- Rapid feature development:Open-source communities contribute to rapid feature development and bug fixes, ensuring continuous improvement.
- Increased transparency and accountability:Open-source projects are transparent, allowing users to scrutinize code and contribute to the development process.
- Cost-effective solutions:Open-source software is typically free to use, reducing the cost of project management tools.