Apple Appeals $19 Billion EU Fine Over App Store Practices
Apple appeals a dollar19 billion eu fine levied following spotifys claims of anti competitive app store behavior – Apple Appeals $19 Billion EU Fine Over App Store Practices, a case that has sent shockwaves through the tech industry. The European Union levied this hefty fine after Spotify, the popular music streaming service, accused Apple of engaging in anti-competitive behavior within its App Store.
This case has raised crucial questions about the power and control that tech giants exert over their platforms, particularly in the realm of app distribution and payment processing.
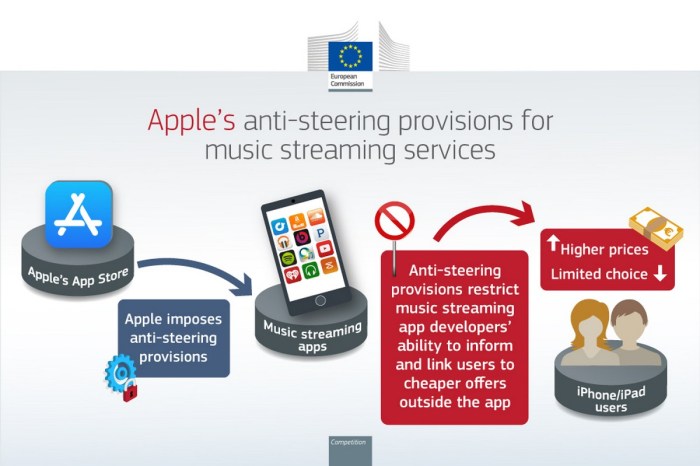
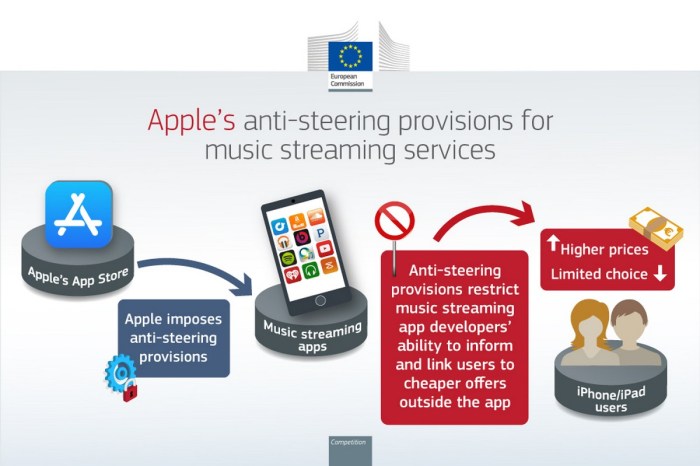
The EU’s decision stems from its investigation into Apple’s App Store policies, which Spotify argued unfairly favor Apple’s own apps and services. Spotify claimed that Apple’s 30% commission on in-app purchases for non-Apple apps, along with its strict guidelines for app development and distribution, created an uneven playing field for competitors.
The EU agreed, finding that Apple’s practices had stifled innovation and limited consumer choice.
The Antitrust Case: Apple Appeals A Dollar19 Billion Eu Fine Levied Following Spotifys Claims Of Anti Competitive App Store Behavior
The European Union (EU) imposed a hefty $19 billion fine on Apple in 2021, alleging that the tech giant’s App Store practices violated antitrust laws. This landmark case highlights the growing scrutiny of tech giants and their control over digital markets.
The EU’s Rationale for the Fine
The EU’s decision to fine Apple stemmed from its investigation into the company’s App Store policies, specifically focusing on how Apple manages app distribution and payments within its ecosystem. The EU’s primary concern was that Apple’s practices unfairly restricted competition and hindered the ability of developers to reach consumers on iOS devices.
Allegations Against Apple
The EU’s investigation revealed a series of practices that Apple implemented on its App Store, which were considered anti-competitive:
- Exclusive App Distribution:Apple’s App Store was the sole authorized channel for distributing apps to iOS users, effectively creating a monopoly. This limited the choices available to consumers and restricted competition among app developers.
- Mandatory In-App Purchase System:Apple mandated that all app developers use its in-app purchase system, which levied a 30% commission on all transactions. This significantly impacted the revenue of app developers, particularly smaller companies, and created a financial barrier to entry.
- Restrictive Developer Guidelines:Apple’s strict guidelines for app development and distribution limited the flexibility of developers and hindered innovation. These guidelines, often perceived as arbitrary and opaque, created a sense of unfairness and stifled competition.
Examples of Anti-Competitive Practices
Spotify, a major music streaming service, was a vocal critic of Apple’s App Store practices and played a key role in bringing the antitrust case to the forefront. Spotify argued that Apple’s practices gave its own music streaming service, Apple Music, an unfair advantage by:
- Preferential Treatment:Apple Music was exempted from the 30% commission on in-app purchases, giving it a significant financial advantage over competitors like Spotify.
- Limited Promotion Opportunities:Apple’s App Store algorithms and promotional efforts favored Apple Music, making it difficult for Spotify to reach users effectively.
- Lack of Transparency:Apple’s lack of transparency in its App Store policies and algorithms created an uneven playing field for developers, making it challenging for them to compete with Apple’s own services.
Apple’s App Store Policies
Apple’s App Store policies are a critical aspect of the company’s business model and have been at the center of ongoing antitrust scrutiny. These policies govern how apps are distributed and monetized within the App Store ecosystem, impacting developers and users alike.
Apple’s appeal of a $19 billion EU fine, levied after Spotify’s claims of anti-competitive App Store practices, highlights the ongoing debate about fair competition in the tech industry. While the legal battle rages on, I’m finding solace in a more hands-on approach, like building my own simple cutting board.
It’s a reminder that even in the midst of complex issues, there’s satisfaction in creating something tangible and useful. Ultimately, I’m curious to see how this legal battle will unfold and what impact it will have on the future of app stores and digital marketplaces.
App Distribution Policies
Apple’s App Store policies dictate the guidelines that developers must adhere to for their apps to be listed and distributed through the App Store. These policies aim to ensure app quality, security, and user experience.
- App Review Process:All apps submitted to the App Store undergo a review process by Apple, which can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks. This process ensures that apps meet Apple’s guidelines for content, functionality, and security.
- Content Restrictions:Apple has strict content restrictions on the App Store, prohibiting apps that contain explicit content, promote illegal activities, or violate user privacy.
- Technical Requirements:Apps must meet specific technical requirements, including compatibility with Apple’s operating system and adherence to Apple’s development guidelines.
- In-App Purchases:Apple requires developers to use its in-app purchase system for all digital goods and services sold within their apps. This system allows Apple to collect a 30% commission on all transactions.
Implications for Developers
Apple’s App Store policies have significant implications for developers, both positive and negative.
- Access to a Large User Base:The App Store provides developers with access to a vast user base of millions of iPhone and iPad users worldwide. This potential market reach is a major advantage for app developers.
- Brand Recognition and Trust:The App Store’s reputation for quality and security enhances the credibility of apps listed on the platform, potentially boosting user trust and adoption.
- Revenue Restrictions:Apple’s 30% commission on in-app purchases can significantly reduce developers’ revenue. This commission structure has been a major point of contention for developers, who argue that it is excessive and unfair.
- Limited Flexibility:Apple’s strict policies can limit developers’ flexibility in terms of app functionality and monetization strategies. This can be particularly challenging for developers who want to offer alternative payment methods or experiment with innovative business models.
Implications for App Users
Apple’s App Store policies also have implications for app users.
- App Quality and Security:Apple’s review process and content restrictions aim to ensure the quality and security of apps available on the App Store. This helps to protect users from malicious apps and malware.
- User Experience:Apple’s guidelines promote a consistent user experience across all apps on the App Store. This can make it easier for users to navigate and interact with apps, even if they are unfamiliar with them.
- Limited Choice and Competition:Apple’s policies can limit user choice and competition in the app market. By requiring developers to use its in-app purchase system and enforcing strict content restrictions, Apple may be hindering the emergence of alternative app stores and payment methods.
Apple’s Arguments Defending its App Store Practices
Apple argues that its App Store policies are necessary to protect user privacy, security, and a consistent user experience.
- User Privacy and Security:Apple maintains that its review process and content restrictions are crucial for safeguarding user privacy and security. They argue that these measures help to prevent the spread of malware and protect users from harmful content.
- Quality Control:Apple emphasizes the importance of its App Store review process in ensuring the quality and functionality of apps. They believe that this process helps to maintain a high standard for apps available on the platform.
- Consistent User Experience:Apple argues that its guidelines for app design and functionality promote a consistent user experience across all apps on the App Store. This, they claim, makes it easier for users to navigate and interact with apps, regardless of the developer.
It’s fascinating to see how Apple is fighting back against the EU’s $19 billion fine for its App Store practices. The whole situation reminds me of our own little battle against overpriced store-bought signs – we ended up making our own rope light sign and saved a ton of money! Maybe Apple should consider some DIY solutions to its legal woes, too.
- Revenue Model:Apple maintains that its revenue model, which includes a 30% commission on in-app purchases, is essential for funding the development and maintenance of the App Store ecosystem. They argue that this model allows them to invest in security, infrastructure, and customer support, ultimately benefiting both developers and users.
The Impact on the Tech Industry
The EU’s decision to fine Apple $19 billion for anti-competitive app store practices has significant implications for the tech industry, potentially triggering a domino effect across various platforms and ecosystems. The case has raised critical questions about the power dynamics within app stores and the future of app distribution models.
Implications for Other App Stores and Platforms, Apple appeals a dollar19 billion eu fine levied following spotifys claims of anti competitive app store behavior
The EU’s ruling sets a precedent for other app stores and platforms, potentially prompting similar investigations and legal challenges. This could lead to increased scrutiny of app store policies and practices, particularly in areas like commission fees, payment processing, and developer restrictions.
- Google Play Store:Google’s app store, which faces similar antitrust concerns, could be subject to increased regulatory pressure, particularly in Europe. The EU’s ruling might encourage regulators to investigate Google’s practices and potentially impose similar fines.
- Amazon Appstore:Amazon’s app store, though smaller than Apple’s and Google’s, could also face scrutiny. The EU’s decision could embolden developers and regulators to challenge Amazon’s app store policies, potentially leading to changes in its commission structure and developer agreements.
Potential Changes in App Distribution and Payment Models
The EU’s decision could drive significant changes in app distribution and payment models, impacting both developers and users.
The recent news of Apple appealing a $19 billion EU fine levied following Spotify’s claims of anti-competitive App Store behavior highlights the ongoing debate about the power and practices of tech giants. This situation brings to mind the positive initiative of Cisco and the University of Ottawa, who are equipping engineering students with job-ready IT and cybersecurity skills , addressing the growing demand for skilled professionals in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
As Apple fights to maintain its control over its App Store, it’s crucial to remember that the future of technology relies on well-prepared individuals who can navigate the complexities of a digital world.
- Alternative App Stores:The ruling could encourage the emergence of alternative app stores that offer developers more favorable terms, such as lower commission fees or greater control over their apps. This could create a more competitive landscape for app distribution, potentially benefiting developers and users.
- Direct Payment Options:Developers may explore alternative payment methods to bypass app store fees, such as direct payment options through their own websites or other platforms. This could give developers greater control over their revenue and potentially lead to lower prices for users.
- Open Source App Stores:Open-source app stores, which allow for greater transparency and community involvement, could gain traction as developers seek alternatives to traditional app stores. This could lead to a more decentralized and democratic app ecosystem.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape
The Apple-Spotify case highlights the evolving legal and regulatory landscape surrounding antitrust issues in the tech industry. This landscape is characterized by a growing focus on the power of dominant tech platforms and the potential for their practices to stifle competition.
The EU’s approach to antitrust enforcement, as seen in the Apple case, is a significant example of this shift.
Comparison of Antitrust Enforcement Approaches
The EU’s approach to antitrust enforcement differs significantly from that of other jurisdictions. The EU has a long history of aggressive antitrust enforcement, particularly in the tech sector. The EU’s approach is characterized by a broad interpretation of antitrust laws and a willingness to take action against companies that are perceived to be abusing their dominant market positions.
In contrast, the US approach to antitrust enforcement has traditionally been more focused on consumer welfare and less likely to intervene in cases involving large tech companies.
- The EU’s approach to antitrust enforcement is often seen as more proactive and interventionist than that of the US. The EU’s competition authorities have a broader mandate to intervene in markets and are more likely to scrutinize mergers and acquisitions, particularly those involving tech companies.
- The US, on the other hand, has historically taken a more hands-off approach to antitrust enforcement in the tech sector, often relying on market forces to regulate competition. However, this approach is being challenged by the growing concerns over the dominance of tech giants and their potential to stifle innovation.
- Other jurisdictions, such as China and South Korea, are also increasingly adopting a more aggressive approach to antitrust enforcement in the tech sector, reflecting the global trend towards greater scrutiny of the power of tech giants.
Implications for Future Antitrust Litigation
The Apple-Spotify case could have significant implications for future antitrust litigation. It is likely to encourage other companies to challenge the app store policies of dominant tech platforms. The case could also lead to greater scrutiny of the practices of these platforms by regulators around the world.
- The EU’s decision to fine Apple could embolden other companies to challenge similar practices by dominant tech platforms. This could lead to a wave of antitrust lawsuits against tech giants, particularly in jurisdictions where antitrust laws are being interpreted more broadly.
- The case is likely to increase the scrutiny of app store policies by regulators around the world. Regulators are increasingly concerned about the potential for dominant tech platforms to use their market power to stifle competition and innovation. The Apple-Spotify case could provide a roadmap for regulators to investigate similar practices by other tech giants.
- The case could also lead to changes in the way app stores operate. Tech companies may be forced to make changes to their app store policies to address antitrust concerns. This could include allowing developers to offer in-app purchases through alternative payment systems or reducing the fees charged to developers.
Consumer Impact
The EU’s decision to fine Apple $19 billion for anti-competitive App Store practices could have a significant impact on consumers. The case raises concerns about the potential for increased app prices, reduced app availability, and limitations on consumer choice.
App Pricing and Availability
The potential impact of the EU’s decision on app pricing and availability is a complex issue. The ruling could lead to changes in Apple’s App Store policies, potentially affecting the way developers price their apps. * Increased Competition:One potential outcome is increased competition among app developers, as they may feel less restricted by Apple’s policies.
This could lead to more affordable app prices, as developers compete for consumers’ attention.
Reduced App Availability
On the other hand, some developers might choose to withdraw their apps from the App Store if they disagree with Apple’s new policies. This could lead to a reduction in the number of apps available to consumers.
Alternative App Stores
The ruling could also encourage the development of alternative app stores, offering consumers more choices and potentially leading to lower prices.
Consumer Choice and Competition
The EU’s decision is likely to affect consumer choice and competition in the app market. By potentially loosening Apple’s grip on the App Store, the ruling could create a more open and competitive environment for app developers.* Greater Flexibility:Consumers might have more flexibility in choosing apps, as they are no longer limited to the App Store.
This could lead to a wider range of apps available, with varying features and prices.
Innovation
Increased competition could also lead to greater innovation in the app market, as developers strive to create unique and compelling apps to attract consumers.
The EU’s decision is a significant step towards promoting competition and consumer choice in the app market.







