AWS vs Google Cloud: Choosing the Right Cloud Platform
AWS vs Google Cloud: These two titans of the cloud computing world dominate the landscape, offering a vast array of services and tools to power modern businesses. But with so much overlap, how do you choose the right platform for your needs?
This comparison dives deep into the core offerings, strengths, and weaknesses of each, helping you make an informed decision.
Whether you’re a seasoned developer looking to optimize your infrastructure or a startup venturing into the cloud for the first time, understanding the differences between AWS and Google Cloud is crucial. This guide will explore the key features, pricing models, and use cases of each platform, highlighting their unique advantages and potential drawbacks.
AWS vs. Google Cloud: A Comprehensive Comparison
In today’s digital landscape, cloud computing has become an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. Two dominant players in this space are Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Both platforms offer a wide range of services, from infrastructure and storage to data analytics and artificial intelligence.
Choosing between AWS and Google Cloud can feel like navigating a virtual world, and just like in the metaverse, security is paramount. But is the metaverse safe? This article dives into the potential risks and considerations. Back to the cloud platforms, both AWS and Google Cloud offer robust security features, but their strengths lie in different areas.
AWS excels in compliance, while Google Cloud shines in AI and machine learning, which are crucial for building secure and reliable metaverse experiences.
This comparison aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of their key features, strengths, and weaknesses, helping you make informed decisions about which platform best suits your specific needs.
The significance of comparing these two cloud giants lies in their influence on the technology landscape. Both AWS and GCP are constantly innovating, expanding their service offerings, and driving the adoption of cloud computing. Understanding their differences and similarities is crucial for businesses looking to leverage the power of cloud for scalability, cost optimization, and competitive advantage.
Key Offerings and Target Audiences
AWS and GCP cater to a diverse range of users and industries. While both platforms offer core cloud services like compute, storage, and networking, their focus and strengths differ. Understanding their target audiences can help you determine which platform aligns better with your specific requirements.
- AWS: AWS is known for its extensive service portfolio, catering to a broad range of customers, from startups to large enterprises. It excels in infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), offering a wide array of virtual machines, storage options, and networking tools. AWS is also a popular choice for businesses with complex IT environments and a need for high scalability and flexibility.
- Google Cloud: GCP focuses on providing a comprehensive platform for data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI). Its strengths lie in data warehousing, big data processing, and AI/ML tools. GCP is particularly attractive to data-driven businesses, research institutions, and organizations with a strong emphasis on AI and data science.
Computing Services
Both AWS and Google Cloud offer a comprehensive suite of computing services to cater to diverse workloads and business needs. From virtual machines to serverless computing and container orchestration, these platforms provide developers and organizations with the flexibility and scalability required for modern application development and deployment.
Virtual Machines, Aws vs google cloud
AWS EC2 and Google Compute Engine (GCE) are the core virtual machine offerings of their respective platforms. Both services allow users to create and manage virtual machines with varying specifications, including CPU, memory, storage, and networking configurations.
- Instance Types: Both EC2 and GCE offer a wide range of instance types optimized for specific workloads, such as general-purpose, compute-optimized, memory-optimized, and GPU-accelerated instances. EC2 boasts a larger selection of instance types, including specialized instances for specific use cases like machine learning and high-performance computing.
GCE focuses on a more streamlined selection of instance types, emphasizing efficiency and cost optimization.
- Pricing Models: Both AWS and Google Cloud employ pay-as-you-go pricing models for their virtual machines, charging based on the instance type, usage time, and resources consumed. EC2 offers a variety of pricing options, including on-demand, reserved instances, and spot instances. GCE provides a simpler pricing structure with on-demand instances and sustained use discounts.
- Performance: Both EC2 and GCE provide high-performance virtual machines with robust networking capabilities. However, EC2 generally boasts superior performance for certain workloads, particularly those requiring high I/O throughput or low latency. GCE excels in providing cost-effective solutions for applications that require moderate performance and scalability.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing platforms like AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions allow developers to run code without managing servers, simplifying application development and deployment.
- AWS Lambda: Lambda excels in handling event-driven workloads and provides a broad range of integrations with other AWS services. Its mature ecosystem and extensive documentation make it a popular choice for serverless applications.
- Google Cloud Functions: Cloud Functions offer a simple and scalable serverless environment with strong support for containerized applications. Its seamless integration with Google Cloud services and its focus on efficiency make it a compelling option for serverless workloads.
Container Orchestration
Container orchestration services automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- AWS ECS/EKS: AWS offers two container orchestration services: ECS (Elastic Container Service) and EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service). ECS provides a managed container orchestration platform with built-in features for scaling and load balancing. EKS, on the other hand, is a fully managed Kubernetes service, offering greater flexibility and control over container deployments.
Choosing between AWS and Google Cloud can be a tough decision, especially when considering factors like pricing and performance. But it’s crucial to remember that a level playing field is essential for any technology to truly thrive. That’s why the recent net neutrality wins again are a welcome development.
A truly open internet ensures that both AWS and Google Cloud can compete fairly, ultimately benefiting developers and businesses alike.
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE): GKE is a fully managed Kubernetes service that provides a robust and scalable platform for containerized applications. It offers a wide range of features, including automatic scaling, load balancing, and security enhancements.
Storage Solutions
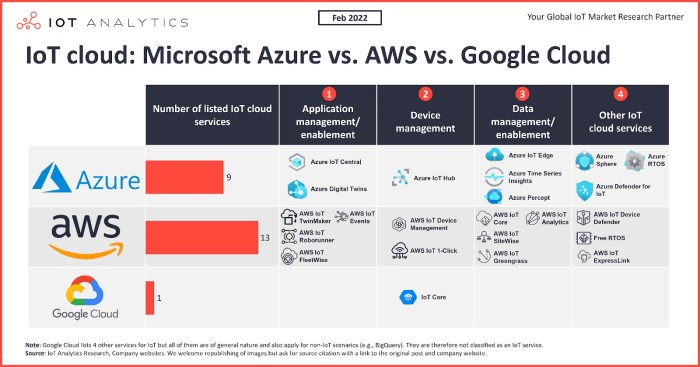
Both AWS and Google Cloud offer a comprehensive suite of storage solutions to cater to diverse data management needs. These solutions include object storage, block storage, and NoSQL databases, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Object Storage: AWS S3 vs Google Cloud Storage (GCS)
AWS S3 and Google Cloud Storage (GCS) are object storage services that provide highly scalable and durable storage for various data types, including images, videos, and backups.
- Storage Classes: Both services offer different storage classes with varying pricing and performance characteristics. AWS S3 provides options like Standard, Standard-IA, Glacier, and Glacier Deep Archive, while GCS offers Standard, Nearline, Coldline, and Archive.
- Pricing: The pricing for both services is based on storage capacity, data retrieval, and data transfer. AWS S3 generally offers slightly lower storage costs compared to GCS, but GCS provides competitive pricing for data retrieval and transfer.
- Data Durability: Both services guarantee high data durability with a 99.999999999% annual durability rate, meaning that data is highly protected from loss or corruption.
Block Storage: AWS EBS vs Google Persistent Disk
AWS EBS and Google Persistent Disk are block storage services that provide persistent storage volumes for virtual machines.
- Performance: AWS EBS offers different volume types, including General Purpose SSD, Provisioned IOPS SSD, and Magnetic, each with varying performance characteristics. Google Persistent Disk provides Standard, Premium, and Extreme types, with performance optimized for different workloads.
- Integration: AWS EBS integrates seamlessly with AWS EC2 instances, providing a unified platform for compute and storage. Google Persistent Disk integrates well with Google Compute Engine instances, offering a similar integration experience.
- Pricing: The pricing for both services is based on storage capacity and I/O operations. AWS EBS generally offers slightly lower pricing for storage capacity, while Google Persistent Disk provides competitive pricing for I/O operations.
NoSQL Databases: AWS DynamoDB vs Google Cloud Spanner
AWS DynamoDB and Google Cloud Spanner are NoSQL databases that offer high scalability, availability, and performance for managing large volumes of data.
- Data Model: DynamoDB is a key-value store, while Spanner is a relational database that offers a more structured data model.
- Scalability: Both services are highly scalable, capable of handling massive data volumes and traffic. DynamoDB excels in horizontal scalability, while Spanner provides both horizontal and vertical scalability.
- Consistency: DynamoDB offers eventual consistency, while Spanner provides strong consistency, ensuring that all data is synchronized across the database.
- Pricing: The pricing for both services is based on storage capacity, read/write operations, and other factors. DynamoDB offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, while Spanner provides a more fixed pricing structure.
Networking and Security
In the realm of cloud computing, robust networking and security are paramount. Both AWS and Google Cloud offer comprehensive solutions to manage network traffic and protect sensitive data. This section delves into the intricacies of their networking and security features, providing a comparative analysis to help you make informed decisions.
AWS VPC and Google Cloud VPC
AWS VPC and Google Cloud VPC are virtual networking environments that provide network isolation and security. Both services enable you to create private networks within the public cloud, allowing you to control network access and configure security policies.
- AWS VPC: AWS VPC allows you to create custom networks, subnets, and routing tables. You can configure security groups to control inbound and outbound traffic to instances within your VPC. AWS also provides Network Load Balancers, Application Load Balancers, and Classic Load Balancers to distribute traffic across multiple instances.
- Google Cloud VPC: Google Cloud VPC offers similar features to AWS VPC, enabling you to create custom networks, subnets, and firewalls. Google Cloud’s firewall rules are more granular than AWS security groups, allowing you to control traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
Google Cloud also offers a variety of load balancers, including HTTP(S) Load Balancing, TCP Proxy Load Balancing, and SSL Proxy Load Balancing.
AWS IAM and Google Cloud IAM
AWS IAM and Google Cloud IAM are identity and access management services that control user access to cloud resources. Both services enable you to create users, groups, and roles, and assign permissions to specific resources.
- AWS IAM: AWS IAM allows you to create users and groups, and assign policies that define their permissions. You can also use IAM roles to grant temporary access to resources without requiring users to have their own credentials. AWS IAM also offers multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security.
- Google Cloud IAM: Google Cloud IAM provides similar capabilities to AWS IAM, enabling you to create users, groups, and roles. Google Cloud IAM also supports conditional access policies, which allow you to control access based on device type, location, and other factors.
Google Cloud IAM also offers MFA and integration with third-party identity providers.
AWS WAF and Google Cloud Armor
AWS WAF and Google Cloud Armor are web application firewalls (WAFs) that protect web applications from common attacks. Both services provide protection against SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other vulnerabilities.
- AWS WAF: AWS WAF is a managed service that provides a set of rules to protect web applications. AWS WAF rules can be customized to block specific attacks based on HTTP requests, such as IP addresses, user agents, and request headers.
AWS WAF also integrates with other AWS services, such as CloudFront and Lambda.
- Google Cloud Armor: Google Cloud Armor is a managed service that offers advanced protection against DDoS attacks, web application attacks, and other threats. Google Cloud Armor uses a combination of rules, machine learning, and Google’s global network to protect web applications. It also provides visibility into attack patterns and allows you to configure custom rules to meet your specific security requirements.
Choosing between AWS and Google Cloud can feel like picking the right leather for a bracelet. Both offer a range of tools and services, but ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs. If you’re looking for a hands-on project, you might want to check out how to make leather stud bracelets – it’s a fun way to get creative! Just like crafting a bracelet, choosing the right cloud platform requires careful consideration of your project’s requirements and your own comfort level.
Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Aws Vs Google Cloud
Data analytics and machine learning are crucial aspects of modern cloud computing, enabling businesses to extract insights from their data and build intelligent applications. Both AWS and Google Cloud offer a comprehensive suite of services for data analytics and machine learning, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
AWS Redshift vs. Google BigQuery
AWS Redshift and Google BigQuery are fully managed data warehouse services designed for large-scale data analysis. Redshift is a columnar data warehouse service that optimizes query performance by storing data in columns instead of rows. BigQuery, on the other hand, is a serverless data warehouse that uses a columnar storage format and a powerful query engine.
- Scalability and Performance:Both Redshift and BigQuery offer high scalability and performance. Redshift excels in handling large data volumes and complex queries, while BigQuery is known for its fast query speeds and ease of use.
- Pricing:Redshift uses a pay-per-use pricing model, while BigQuery charges based on data storage and query execution. The pricing structure can vary depending on usage patterns.
- Integration:Redshift integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, such as S3 and EMR. BigQuery integrates with Google Cloud services, such as Cloud Storage and Dataproc.
AWS SageMaker vs. Google Cloud AI Platform
AWS SageMaker and Google Cloud AI Platform are fully managed machine learning platforms that simplify the process of building, training, and deploying machine learning models.
- Features:Both platforms offer a wide range of features, including data preprocessing, model training, model deployment, and model monitoring. SageMaker provides tools for building custom machine learning algorithms, while AI Platform offers pre-trained models and AutoML capabilities for automated model development.
- Ease of Use:AI Platform is generally considered more user-friendly due to its intuitive interface and pre-built components. SageMaker offers a more comprehensive set of tools for advanced machine learning tasks.
- Scalability:Both platforms scale seamlessly to handle large datasets and complex models. AI Platform leverages Google’s infrastructure for high-performance computing, while SageMaker offers various instance types and scaling options.
AWS Athena vs. Google Cloud Dataproc
AWS Athena and Google Cloud Dataproc are services designed for data exploration and analysis. Athena is a serverless query service that allows users to analyze data stored in S3 using SQL. Dataproc is a managed Hadoop and Spark service that provides a cluster environment for running data processing jobs.
- Use Cases:Athena is well-suited for ad-hoc data exploration and analysis, while Dataproc is ideal for large-scale batch processing and complex data transformations.
- Performance:Athena is known for its fast query speeds, while Dataproc provides high-performance computing for data-intensive tasks.
- Integration:Athena integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, such as S3 and Glue. Dataproc integrates with Google Cloud services, such as Cloud Storage and Cloud Dataproc.
Developer Tools and Services
Modern cloud platforms like AWS and Google Cloud offer comprehensive developer tools and services to streamline application development, deployment, and management. These tools facilitate seamless integration with cloud infrastructure, enabling developers to focus on building innovative solutions.
AWS CodePipeline vs. Google Cloud Build
AWS CodePipeline and Google Cloud Build are both powerful CI/CD tools that automate the software release process. They provide a robust framework for building, testing, and deploying applications to the cloud.Both platforms offer a similar set of features, including:
- Source Code Integration:Both services can connect to popular source code repositories like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket.
- Build and Test Automation:They provide tools for automating the build and test phases of the CI/CD pipeline, including support for various programming languages and frameworks.
- Deployment Automation:Both platforms enable automated deployments to different environments, such as development, testing, and production.
- Pipeline Orchestration:They allow developers to define and manage complex pipelines with multiple stages and dependencies.
- Integration with Other Services:Both platforms integrate with other cloud services, such as AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions for serverless computing.
However, some key differences exist between the two platforms:
- AWS CodePipeline:CodePipeline is a more mature and feature-rich CI/CD platform, offering a wider range of integrations and customization options. It excels in managing complex deployments with multiple environments and stages. CodePipeline provides a visual interface for building and managing pipelines, making it user-friendly.
- Google Cloud Build:Google Cloud Build is known for its simplicity and ease of use. It focuses on providing a streamlined experience for deploying containerized applications. Cloud Build is well-integrated with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), making it ideal for deploying microservices and containerized applications.
AWS CloudFormation vs. Google Cloud Deployment Manager
AWS CloudFormation and Google Cloud Deployment Manager are infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tools that allow developers to define and manage cloud infrastructure using declarative templates. They offer a way to automate infrastructure provisioning, configuration, and updates, ensuring consistency and repeatability.
- AWS CloudFormation:CloudFormation uses YAML or JSON templates to describe the desired infrastructure. It excels in managing complex AWS resources, including EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and Lambda functions. CloudFormation provides a robust mechanism for managing dependencies between resources and ensuring infrastructure consistency.
- Google Cloud Deployment Manager:Deployment Manager uses YAML templates to define infrastructure. It supports a wide range of Google Cloud resources, including Compute Engine instances, Cloud Storage buckets, and Cloud SQL instances. Deployment Manager provides a powerful mechanism for managing complex infrastructure deployments and updates.
Both platforms offer advantages and disadvantages:
| Feature | AWS CloudFormation | Google Cloud Deployment Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Language | YAML or JSON | YAML |
| Resource Support | Comprehensive support for AWS resources | Comprehensive support for Google Cloud resources |
| Template Complexity | Can handle complex infrastructure definitions | Can handle complex infrastructure definitions |
| Version Control Integration | Integrates with version control systems like Git | Integrates with version control systems like Git |
| User Interface | Provides a user-friendly console for managing templates | Provides a user-friendly console for managing templates |
| Community Support | Large and active community with extensive documentation and resources | Active community with growing documentation and resources |
AWS API Gateway vs. Google Cloud Endpoints
AWS API Gateway and Google Cloud Endpoints are API management platforms that enable developers to create, manage, and secure APIs. They provide a centralized gateway for API traffic, offering features like rate limiting, authentication, and monitoring.
- AWS API Gateway:API Gateway is a mature and feature-rich API management platform that supports various protocols, including REST, WebSocket, and HTTP. It offers robust features for managing API traffic, including request validation, throttling, and caching. API Gateway also integrates with other AWS services, such as Lambda functions and DynamoDB.
- Google Cloud Endpoints:Google Cloud Endpoints is a powerful API management platform that focuses on providing a seamless experience for managing and securing APIs. It offers features like request validation, authentication, and authorization. Endpoints are well-integrated with other Google Cloud services, such as Cloud Functions and Cloud Run.
Both platforms offer a similar set of features, but some key differences exist:
- Deployment Models:AWS API Gateway supports both on-premises and cloud deployments, while Google Cloud Endpoints is primarily a cloud-based solution.
- Pricing Models:AWS API Gateway charges based on API calls and data transfer, while Google Cloud Endpoints charges based on API calls and usage of other services.
- Integrations:AWS API Gateway offers a wider range of integrations with other AWS services, while Google Cloud Endpoints is well-integrated with other Google Cloud services.






