EU Antitrust Chief: Apples DMA Compliance Still Under Scrutiny
EU still not happy with Apples dma compliance antitrust chief says we will be investigating new marketplace fees. The European Union’s antitrust chief has expressed continued dissatisfaction with Apple’s compliance with the Digital Markets Act (DMA), specifically targeting the company’s new marketplace fees.
The EU’s concerns stem from potential anti-competitive practices that could stifle competition within the digital marketplace.
The EU’s investigation focuses on the fairness and transparency of these new fees, questioning their potential impact on both app developers and consumers. The DMA, designed to promote competition and consumer choice in the digital market, aims to regulate the behavior of large tech companies like Apple.
The EU’s investigation into Apple’s DMA compliance raises critical questions about the future of competition in the digital landscape.
EU’s Concerns Regarding Apple’s DMA Compliance
The European Union’s antitrust chief has expressed dissatisfaction with Apple’s compliance with the Digital Markets Act (DMA), raising concerns about the company’s practices and their potential impact on competition within the digital marketplace. The EU’s concerns are centered around Apple’s implementation of certain provisions of the DMA, specifically related to interoperability and the introduction of new marketplace fees.
Apple’s Interoperability Compliance
The EU’s concerns regarding Apple’s interoperability compliance stem from the company’s perceived reluctance to fully embrace the spirit of the DMA. While Apple has made some changes to its operating system to comply with the law, the EU believes that these changes are insufficient and do not go far enough to ensure true interoperability between Apple’s ecosystem and other platforms.The EU’s concerns are rooted in the potential for Apple’s limited interoperability to create a closed ecosystem that hinders competition.
By restricting the ability of third-party apps to seamlessly integrate with Apple’s services, the company could potentially give its own apps and services an unfair advantage. For example, if a messaging app cannot fully integrate with Apple’s iMessage, users may be less inclined to switch away from Apple’s default messaging platform.
The EU’s antitrust chief has made it clear that they’re not happy with Apple’s compliance with the Digital Markets Act (DMA) and will be investigating their new marketplace fees. While that’s going on, it’s worth checking out the exciting new designs from Leigh Tucker Willow, now available at Dunnes Stores, new from leigh tucker willow at dunnes stores.
Back to Apple, the EU’s scrutiny of their practices is likely to continue as they push for a fairer digital landscape.
This could stifle innovation and limit consumer choice in the messaging app market.
Apple’s Marketplace Fees
The EU’s concerns extend to Apple’s introduction of new marketplace fees, which the antitrust chief believes could be used to further entrench Apple’s dominant position in the digital marketplace. The EU is concerned that these fees could disproportionately impact smaller app developers, making it more difficult for them to compete with larger companies that have more resources.The EU’s concerns are based on the potential for Apple to use its market power to extract higher fees from app developers, ultimately squeezing their profit margins.
This could lead to a situation where only the largest app developers can afford to operate on Apple’s platform, further reducing competition and innovation.
Examples of Apple’s Practices
The EU has provided specific examples of Apple’s practices that raise concerns about its compliance with the DMA. For example, the EU has expressed concerns about Apple’s continued use of its own proprietary messaging platform, iMessage, which limits the ability of third-party messaging apps to seamlessly integrate with Apple’s ecosystem.
The EU’s antitrust chief is clearly not happy with Apple’s compliance with the Digital Markets Act, and the investigation into their new marketplace fees is just the beginning. It seems like the tech giants are playing a game of cat and mouse with regulators, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s acceptable.
It reminds me of that article I read about ” the ai in a jar ” – a clever metaphor for how AI is being boxed in and controlled by powerful corporations. The EU’s stance on Apple’s practices is a crucial step towards ensuring a fairer digital landscape, and hopefully, it will set a precedent for holding tech giants accountable for their actions.
This practice could potentially give Apple an unfair advantage in the messaging app market.The EU has also raised concerns about Apple’s introduction of new marketplace fees for developers, which the EU believes could be used to further entrench Apple’s dominant position in the digital marketplace.
The EU is concerned that these fees could disproportionately impact smaller app developers, making it more difficult for them to compete with larger companies that have more resources.
The Investigation of New Marketplace Fees: Eu Still Not Happy With Apples Dma Compliance Antitrust Chief Says We Will Be Investigating New Marketplace Fees

The European Union (EU) has expressed its ongoing concerns about Apple’s compliance with the Digital Markets Act (DMA), particularly focusing on the company’s new marketplace fees. The EU’s antitrust chief has confirmed that investigations are underway to scrutinize these fees and their potential impact on app developers and consumers.The EU’s investigation delves into the fairness and transparency of Apple’s newly implemented fees for app developers who utilize the App Store.
These fees, which are charged on in-app purchases, have been met with resistance from developers who argue that they are excessive and disadvantageous. The EU’s primary concern lies in ensuring a level playing field for developers and preventing Apple from abusing its dominant market position.
The Nature of the New Marketplace Fees
The new fees imposed by Apple on app developers involve a commission on in-app purchases. These fees are levied on transactions made within apps, such as subscriptions, digital goods, and virtual currency purchases. While Apple has previously charged a 30% commission, the new fees vary based on the app’s revenue and subscription model.
The Potential Impact on App Developers and Consumers
The potential impact of these fees on app developers is significant. Developers argue that the fees significantly reduce their profits, making it challenging to compete and invest in app development. This could lead to fewer innovative apps being developed and a decrease in the overall quality of the App Store.The impact on consumers is also a matter of concern.
Higher fees for developers could result in increased app prices, subscription costs, or in-app purchase prices. Consumers may ultimately bear the burden of these increased costs, leading to a less competitive and less affordable app ecosystem.
The EU’s antitrust chief has made it clear that they’re not happy with Apple’s compliance with the Digital Markets Act (DMA), and they’re launching a new investigation into the company’s marketplace fees. It’s a complicated issue, but it reminds me of how we often try to make the best of imperfect situations.
For example, when I’m scrapbooking, I’ve learned to embrace those not-so-perfect photos – this article has some great tips! Ultimately, the goal is to find a way to move forward, whether it’s by finding creative solutions to technical challenges or by using those “less than perfect” photos to tell a story.
So, while the EU’s investigation is likely to continue, it’s a reminder that we can always find ways to make the most of things, even when they’re not ideal.
The EU’s Concerns about Fairness and Transparency, Eu still not happy with apples dma compliance antitrust chief says we will be investigating new marketplace fees
The EU’s primary concern regarding Apple’s new marketplace fees is their fairness and transparency. The EU believes that the fees should be fair, transparent, and non-discriminatory. The EU is investigating whether Apple is using its dominant market position to unfairly advantage itself at the expense of app developers and consumers.The EU’s investigation will focus on several key aspects, including:
- The justification for the new fees and whether they are proportionate to the services provided by Apple.
- The transparency of the fee structure and whether developers have sufficient information to understand the costs involved.
- The potential for the fees to stifle competition and innovation in the app market.
- The impact of the fees on consumer prices and choice.
The DMA and its Impact on Apple
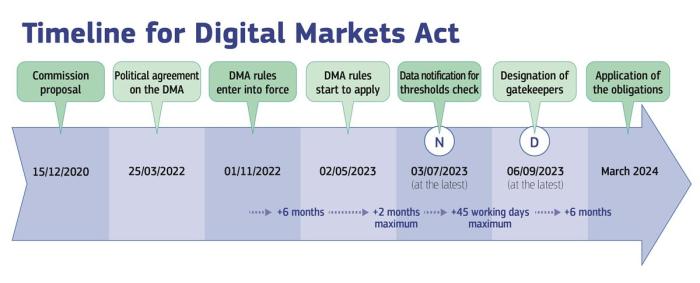
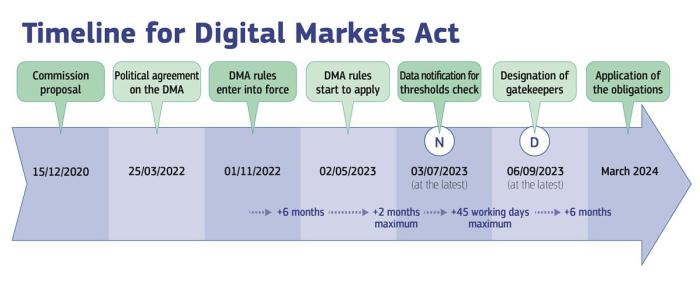
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is a landmark piece of legislation that aims to regulate the behavior of large online platforms in the European Union. The DMA’s goal is to promote competition and consumer choice in the digital marketplace, ultimately empowering users and businesses alike.
This legislation is particularly relevant to companies like Apple, which hold significant market power and influence over how users access and interact with digital services.
The DMA’s Key Provisions
The DMA Artikels a set of rules that apply to companies designated as “gatekeepers” – those with a dominant position in key digital markets. These rules aim to ensure fair competition and protect users’ rights. The DMA mandates that gatekeepers must comply with specific requirements, including:
- Interoperability: Gatekeepers must allow users to access and use apps and services from other providers without any restrictions. This provision aims to break down walled gardens and allow users to choose from a wider range of options.
- Data Portability: Users should be able to easily transfer their data from one platform to another. This promotes competition by enabling users to switch platforms without losing their data.
- Transparency: Gatekeepers must provide clear and transparent information about their algorithms and data practices. This enhances user understanding of how these platforms operate and allows for greater control over personal data.
- Non-discrimination: Gatekeepers must treat all businesses and users fairly, without giving preference to their own products or services. This ensures that all players have a fair chance to compete in the market.
The DMA’s Goals of Promoting Competition and Consumer Choice
The DMA’s ultimate goal is to foster a more competitive and vibrant digital marketplace. By promoting interoperability, data portability, and transparency, the DMA aims to empower users and businesses to choose from a wider range of options and engage in a more level playing field.
This, in turn, is expected to lead to:
- Lower prices: Increased competition can drive down prices for digital services, benefiting consumers.
- More innovation: By creating a more open and accessible marketplace, the DMA can encourage innovation and the emergence of new competitors.
- Improved user experience: Users will have greater control over their data and can choose from a wider range of apps and services, ultimately leading to a more personalized and satisfying digital experience.
The DMA’s Regulation of Large Tech Companies
The DMA directly addresses the concerns regarding the dominance of large tech companies like Apple. The legislation seeks to regulate their behavior and ensure they do not abuse their market power. The DMA’s provisions aim to:
- Prevent anti-competitive practices: The DMA prohibits gatekeepers from engaging in activities that stifle competition, such as tying their own products and services to their platforms or favoring their own offerings over those of competitors.
- Promote fair competition: The DMA ensures that all businesses have a fair chance to compete in the market, regardless of their size or resources.
- Protect user rights: The DMA empowers users by giving them more control over their data and allowing them to choose from a wider range of options.
The Role of the EU’s Antitrust Chief
The EU’s antitrust chief plays a crucial role in ensuring fair competition in the digital market, a sphere that is rapidly evolving and presenting new challenges. The chief, currently Margrethe Vestager, is responsible for enforcing the EU’s competition rules, which aim to prevent monopolies and protect consumers from unfair practices.
This role has become increasingly significant as tech giants like Apple exert growing influence over various aspects of our digital lives.The EU’s investigation into Apple’s compliance with the DMA, the Digital Markets Act, could have significant consequences for the tech giant.
If Apple is found to be violating the DMA’s provisions, it could face substantial fines, potentially running into billions of euros. Furthermore, the EU could impose behavioral remedies, forcing Apple to change its practices in order to promote competition and protect consumers.
This could involve making its operating system more open to competing apps, allowing users to choose their default browser and app store, or offering more transparency regarding its algorithms and data collection practices.
The EU’s Enforcement of Antitrust Regulations Against Tech Giants
The EU has a history of taking action against tech giants for antitrust violations. In 2017, the EU fined Google €2.42 billion for abusing its dominant position in the online search market. The commission found that Google favored its own comparison shopping service in its search results, giving it an unfair advantage over competitors.
This case was a landmark decision, demonstrating the EU’s willingness to challenge the dominance of tech giants. In 2019, the EU fined Google another €1.49 billion for its Android operating system. The commission concluded that Google had illegally bundled its search app and Chrome browser with its Android operating system, hindering competition in the mobile market.
This decision further solidified the EU’s stance on promoting fair competition in the digital space. In 2021, the EU fined Amazon €746 million for favoring its own products in its online marketplace. The commission found that Amazon used data from its own sellers to gain an unfair advantage in its retail business.
These actions highlight the EU’s commitment to ensuring that tech giants operate fairly and do not stifle competition. The EU’s investigations and enforcement actions against tech giants are not merely symbolic gestures. They are crucial steps in shaping a digital market that is fair, competitive, and ultimately beneficial to consumers.
The EU’s antitrust chief plays a vital role in this endeavor, ensuring that the digital landscape remains open and accessible to all.
Potential Outcomes of the Investigation
The EU’s investigation into Apple’s marketplace fees could have significant consequences for the tech giant and the broader digital marketplace. The potential outcomes range from minor adjustments to Apple’s business practices to more substantial changes impacting the company’s revenue and market position.
Impact on Apple’s Business Practices
The investigation could lead to various outcomes impacting Apple’s business practices. These outcomes could range from minor adjustments to more substantial changes impacting the company’s revenue and market position.
- Requirement to lower marketplace fees:The EU could require Apple to lower its commission on app sales, potentially impacting its revenue stream.
- Increased transparency in fee calculation:The EU might mandate Apple to provide more transparency regarding how its marketplace fees are calculated, potentially impacting its pricing strategy.
- Restrictions on self-preferencing:The EU could restrict Apple from favoring its own apps and services over those of competitors, potentially impacting its app store’s curated experience.
- Mandatory interoperability:The EU might require Apple to allow alternative app stores and payment systems on its devices, potentially impacting its control over the iOS ecosystem.
Implications for the Digital Marketplace
The investigation’s outcome could have significant implications for the broader digital marketplace and competition within it.
- Increased competition:Lowering marketplace fees could incentivize more app developers to enter the iOS ecosystem, leading to increased competition and potentially benefiting consumers.
- Greater consumer choice:Allowing alternative app stores and payment systems could provide consumers with more choices and potentially lower prices for digital goods and services.
- Level playing field:Restricting self-preferencing and ensuring transparency in fee calculation could create a more level playing field for app developers, fostering a more competitive digital marketplace.