
Gartner Trends Impact Enterprise Teams: Navigating the Future
Gartner trends impact enterprise teams in profound ways, shaping the technology landscape and driving innovation across industries. As organizations grapple with rapid technological advancements, understanding these trends is crucial for making strategic decisions and staying ahead of the curve.
From the ever-evolving Gartner Hype Cycle to the emergence of transformative technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain, this exploration delves into the key trends that are influencing enterprise technology strategies and their implications for different teams within organizations.
Gartner Hype Cycle and its Impact
The Gartner Hype Cycle is a widely recognized framework that helps enterprises understand the maturity and adoption potential of emerging technologies. This framework, developed by Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, provides a visual representation of the typical lifecycle of a technology, from its initial hype to its eventual plateau of productivity.
Gartner’s trends are constantly shaping the way enterprise teams operate, forcing them to adapt and innovate. One recent example of this is the impact of EU regulations on Apple’s product packaging. As you can see in this article, Apple’s $1299 iPad Pro doesn’t come with a charger in some countries, a direct result of EU legislation.
While this might seem like a small detail, it highlights the larger trend of governments and regulatory bodies influencing even the most minute aspects of product design and distribution, a trend that enterprise teams need to be aware of and prepared to navigate.
Stages of the Hype Cycle
The Gartner Hype Cycle consists of five distinct stages that represent the evolution of a technology’s adoption:
- Technology Trigger:This initial stage marks the emergence of a new technology, often accompanied by significant media attention and excitement. Early adopters and innovators explore its potential, but there is limited understanding of its practical applications.
- Peak of Inflated Expectations:As the technology gains popularity, expectations soar, fueled by optimistic projections and exaggerated claims. However, at this stage, the technology often lacks maturity and may not meet the hype.
- Trough of Disillusionment:This stage is characterized by a decline in interest as the limitations of the technology become apparent. Some organizations may abandon the technology due to unmet expectations or challenges in implementation.
- Slope of Enlightenment:The technology starts to prove its value through successful implementations and the development of practical use cases. The focus shifts from hype to real-world applications and refinements.
- Plateau of Productivity:This final stage represents the maturity of the technology, where it becomes widely adopted and integrated into mainstream business operations. The technology has proven its value and delivers tangible benefits.
Examples of Technologies Traversing the Hype Cycle
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI has traversed the Hype Cycle, starting as a futuristic concept and reaching the Slope of Enlightenment, with practical applications in areas like automation, customer service, and data analysis.
- Cloud Computing:Cloud computing has reached the Plateau of Productivity, becoming a fundamental part of IT infrastructure for businesses of all sizes. Its benefits, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, have been widely recognized.
- Blockchain:Blockchain is currently in the Trough of Disillusionment, facing challenges in scalability and regulatory uncertainty. However, it has the potential to revolutionize industries like finance and supply chain management in the future.
Leveraging the Hype Cycle for Strategic Technology Decisions
- Identify Emerging Technologies:The Hype Cycle helps enterprises identify emerging technologies with potential for disruption and innovation. This allows organizations to stay ahead of the curve and explore new opportunities.
- Manage Expectations:Understanding the stages of the Hype Cycle helps manage expectations and avoid overhyping technologies. Enterprises can make informed decisions based on realistic assessments of technology maturity and capabilities.
- Optimize Investment Strategies:The Hype Cycle provides insights into the right time to invest in emerging technologies. By understanding the technology’s maturity and adoption rate, organizations can make strategic investment decisions that align with their business goals.
- Evaluate Risks and Opportunities:The Hype Cycle highlights potential risks and opportunities associated with emerging technologies. This helps enterprises make informed decisions about technology adoption, considering factors like market maturity, competitive landscape, and potential impact on business operations.
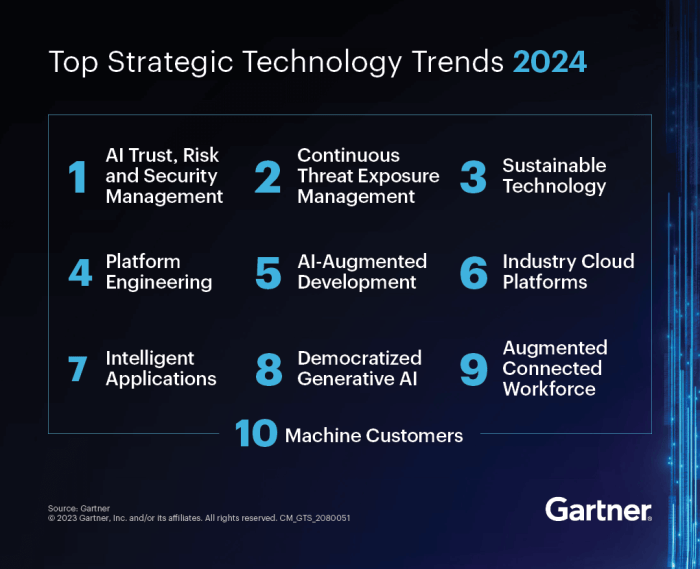
Top Gartner Trends for Enterprise Teams
Gartner’s annual list of top strategic technology trends is a valuable resource for organizations seeking to stay ahead of the curve. These trends not only shape the future of technology but also have a profound impact on how enterprise teams operate.
Understanding and adapting to these trends is crucial for success in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
Gartner trends can dramatically impact enterprise teams, forcing them to adapt and innovate to stay competitive. One key area of focus is financial performance, where understanding the difference between gross profit vs net profit becomes crucial. This distinction allows teams to assess their profitability accurately, identify areas for cost reduction, and ultimately make informed decisions that drive sustainable growth.
Gartner’s Top Trends and Their Impact
The following table highlights some of the key Gartner trends that are shaping the future of enterprise technology and their potential impact on various enterprise teams:
| Trend | Description | Impact on Enterprise Teams | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperautomation | The use of advanced technologies like AI and machine learning to automate complex processes, end-to-end. |
|
|
| Composable Applications | A modular approach to application development, allowing businesses to assemble applications from pre-built components and APIs. |
|
|
| Total Experience (TX) | Focuses on creating seamless and personalized experiences for customers, employees, and partners across all touchpoints. |
|
|
| The Metaverse | A persistent, shared virtual world where users can interact with each other and digital objects in a realistic and immersive way. |
|
|
Emerging Technologies and their Implications
The rise of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing is transforming the way enterprises operate, impacting every aspect of their business, from internal workflows to customer interactions. These technologies are driving innovation, improving efficiency, and creating new opportunities for competitive advantage.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence
AI is revolutionizing enterprise operations by automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and personalizing customer experiences.
Gartner’s trends are constantly shaping how enterprise teams operate, especially in the realm of cloud computing. A recent study, research eyes misconfiguration issues at Google, Amazon, and Microsoft cloud , highlights a critical area of concern: misconfiguration. This research underscores the importance of proactive security measures and proper configuration management to mitigate risks and ensure the smooth operation of cloud environments, aligning with Gartner’s emphasis on security and risk management in today’s digital landscape.
- Automation: AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees to focus on more strategic work. For example, AI-powered chatbots can handle customer inquiries, while AI-powered systems can automate data entry and processing.
- Decision-Making: AI algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify patterns and trends, providing valuable insights to support informed decision-making. For example, AI-powered predictive analytics can help businesses forecast demand, optimize pricing, and identify potential risks.
- Customer Experience: AI can personalize customer interactions by analyzing data about individual preferences and behaviors. For example, AI-powered recommendation engines can suggest products or services that are relevant to individual customers, while AI-powered chatbots can provide personalized support.
Impact of Blockchain
Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and secure nature, is transforming enterprise processes, particularly in areas related to supply chain management, financial transactions, and data security.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can track goods and materials throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and accountability. This can help businesses reduce fraud, improve efficiency, and enhance customer trust.
- Financial Transactions: Blockchain can streamline financial transactions by eliminating intermediaries and reducing processing time. This can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Data Security: Blockchain can enhance data security by creating a tamper-proof record of transactions. This can help businesses protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and manipulation.
Impact of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a nascent technology with the potential to revolutionize fields like drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling. While still in its early stages, it holds immense promise for enterprises.
- Drug Discovery: Quantum computers can simulate complex molecular interactions, accelerating the process of drug discovery and development.
- Materials Science: Quantum computers can help design new materials with enhanced properties, leading to advancements in areas like energy storage and electronics.
- Financial Modeling: Quantum computers can handle complex financial calculations, enabling more accurate risk assessments and portfolio optimization.
Gartner’s Recommendations for Enterprise Technology Strategies
Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, provides valuable insights and recommendations to help enterprises navigate the complex landscape of technology adoption. Their recommendations focus on aligning technology strategies with business goals, adopting a strategic approach to technology implementation, and leveraging emerging technologies to gain a competitive edge.
Aligning Technology with Business Goals
Aligning technology strategies with business goals is crucial for ensuring that technology investments deliver tangible value. Gartner emphasizes the importance of a clear understanding of business objectives and how technology can contribute to their achievement. They recommend:
- Defining a clear business strategy and identifying the key technology enablers.
- Conducting a thorough assessment of current technology capabilities and identifying gaps.
- Developing a technology roadmap that aligns with the business strategy and addresses identified gaps.
- Establishing metrics to track the impact of technology investments on business outcomes.
Technology Adoption Models
Gartner suggests various technology adoption models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right model depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the enterprise.
- Incremental Adoption:This model involves gradually adopting new technologies, starting with small-scale pilots and expanding adoption based on results. This approach is suitable for organizations with limited resources or a high tolerance for risk.
- Transformational Adoption:This model involves a more radical approach, adopting new technologies on a large scale to achieve significant business transformation.
This approach is suitable for organizations with a high tolerance for risk and a clear vision for the future.
- Agile Adoption:This model involves iteratively developing and deploying new technologies, using a rapid prototyping and testing approach. This approach is suitable for organizations that need to be responsive to changing market conditions.
Emerging Technologies and their Implications
Gartner highlights the importance of staying informed about emerging technologies and their potential impact on businesses. They recommend:
- Investing in research and development:This will help enterprises stay ahead of the curve and identify new opportunities.
- Experimenting with emerging technologies:This will allow enterprises to gain firsthand experience and evaluate their potential.
- Developing a strategic approach to emerging technologies:This will ensure that enterprises are prepared to leverage these technologies effectively.
Key Recommendations for Enterprise Technology Strategies, Gartner trends impact enterprise teams
Gartner provides several key recommendations for enterprise technology strategies:
- Focus on business outcomes:Technology investments should be driven by the need to achieve specific business goals.
- Adopt a strategic approach to technology:Technology adoption should be planned and executed in a way that maximizes value and minimizes risk.
- Embrace agility and innovation:Enterprises should be prepared to adapt to changing market conditions and embrace new technologies.
- Prioritize cybersecurity:Cybersecurity should be a top priority for all enterprises, given the increasing threat of cyberattacks.
- Develop a strong technology talent pool:Enterprises need to attract and retain skilled technology professionals to support their technology initiatives.
Importance of a Technology Architecture
Gartner emphasizes the importance of a well-defined technology architecture to support the enterprise’s technology strategy. They recommend:
- Establishing a clear technology vision:This should define the desired future state of the enterprise’s technology landscape.
- Developing a technology architecture roadmap:This should Artikel the steps required to achieve the technology vision.
- Implementing a technology governance framework:This should ensure that technology decisions are aligned with business goals and that technology risks are managed effectively.
Key Considerations for Technology Implementation
Gartner highlights several key considerations for technology implementation:
- Change management:Implementing new technologies often requires significant changes to business processes and employee behavior.
- Data management:Enterprises need to ensure that their data is managed effectively to support their technology initiatives.
- Security:Cybersecurity should be a top priority for all technology implementations.
- Integration:New technologies need to be integrated with existing systems to avoid creating silos.
The Future of Enterprise Technology: Gartner Trends Impact Enterprise Teams
Gartner’s insights and industry trends paint a vibrant picture of the future of enterprise technology, where innovation and disruption will continue to reshape the business landscape. The coming years will see a convergence of emerging technologies, driving transformative changes in how businesses operate, interact with customers, and manage their operations.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rapid evolution of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will profoundly impact enterprise teams. These technologies will not only automate tasks and improve efficiency but also create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
- AI and Machine Learning:AI and machine learning (ML) will play a crucial role in automating tasks, optimizing processes, and enhancing decision-making. Enterprise teams will leverage AI to personalize customer experiences, predict maintenance needs, and automate repetitive tasks, leading to significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
For example, in the financial sector, AI-powered fraud detection systems are already being deployed to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions, reducing financial losses and enhancing security.
- Blockchain:Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to track transactions and data, paving the way for decentralized and trustless systems. Enterprise teams can leverage blockchain to improve supply chain transparency, enhance data security, and streamline financial transactions. For example, in the healthcare industry, blockchain can be used to securely store and manage patient medical records, ensuring data privacy and facilitating interoperability between different healthcare providers.
- Internet of Things (IoT):The IoT connects physical devices to the internet, enabling real-time data collection and analysis. Enterprise teams can use IoT to monitor assets, optimize operations, and improve customer experiences. For example, in manufacturing, IoT sensors can monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes, leading to reduced downtime and improved efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of enterprise technology is not without its challenges. Enterprise teams will need to navigate evolving security threats, address ethical considerations, and adapt to a rapidly changing technological landscape. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth.



