How Companies Determine Cybersecurity Budgets
How companies determine cybersecurity budgets is a crucial aspect of modern business strategy. In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, organizations must prioritize cybersecurity investments to protect their sensitive data, infrastructure, and reputation. The allocation of cybersecurity resources is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including company size, industry, regulatory compliance, risk assessments, and growth strategies.
Understanding how companies approach cybersecurity budgeting is essential for both business leaders and cybersecurity professionals. This article will delve into the factors influencing cybersecurity budget allocation, key components of a cybersecurity budget, different methods for determining budget, best practices for management, and emerging trends shaping future strategies.
Factors Influencing Cybersecurity Budget Allocation: How Companies Determine Cybersecurity Budgets
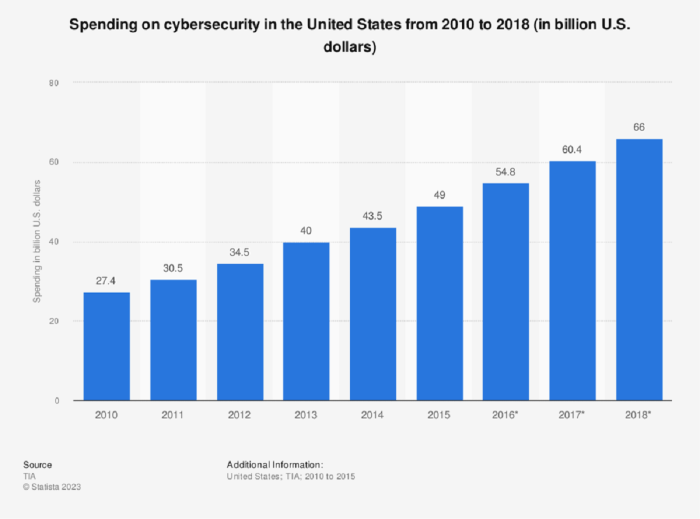
The cybersecurity budget is a crucial component of any organization’s overall security strategy. A well-defined budget ensures that resources are allocated effectively to protect against evolving cyber threats. Several factors play a significant role in determining the size and allocation of a cybersecurity budget.
Company Size and Industry
Company size and industry significantly influence cybersecurity budget priorities. Larger organizations typically have more complex IT infrastructures and greater exposure to cyberattacks, leading to larger cybersecurity budgets. Similarly, industries with sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, and government, require higher levels of security and therefore allocate more resources to cybersecurity.
For example, a small retail business might prioritize basic security measures like firewalls and antivirus software, while a large financial institution would invest in more sophisticated security solutions like intrusion detection systems and security information and event management (SIEM) tools.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Regulatory compliance requirements play a crucial role in driving cybersecurity investments. Industries with stringent data privacy regulations, such as the healthcare industry (HIPAA) and financial services (PCI DSS), must comply with specific security standards. These regulations often dictate the types of security controls that organizations must implement, which can significantly impact cybersecurity budgets.
Companies determine cybersecurity budgets by assessing risk, considering the value of their assets, and analyzing potential threats. Just like you might choose a terrarium planter table runner to enhance your home’s aesthetic appeal, cybersecurity measures are an investment in protecting your business’s digital environment.
By understanding the potential impact of cyberattacks, companies can allocate resources effectively to build a robust defense system.
For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union mandates data protection measures that organizations must implement, including encryption, data access controls, and data breach notification procedures.
Risk Assessments
Risk assessments are essential in determining cybersecurity budget needs. By identifying and evaluating potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities, organizations can prioritize security investments based on the likelihood and impact of potential attacks. A comprehensive risk assessment helps determine the resources needed to mitigate identified risks, such as implementing security controls, training employees, and acquiring security tools.
For example, if a risk assessment identifies a high risk of a ransomware attack, the organization might prioritize investments in data backup and recovery solutions, as well as employee training on ransomware prevention.
Companies typically determine their cybersecurity budgets based on a risk assessment, considering factors like the value of their data, potential threats, and regulatory compliance. But sometimes, you just have to splurge on a good deal, like those incredible iclothing Black Friday deals that offer huge discounts.
Once the shopping spree is over, though, it’s back to the business of securing your data, which means revisiting your cybersecurity budget and ensuring it’s adequate to address any emerging threats.
Company Growth and Expansion Strategies, How companies determine cybersecurity budgets
Company growth and expansion strategies can significantly influence cybersecurity spending. As organizations grow and expand their operations, they often acquire new technologies, systems, and data, increasing their attack surface and cybersecurity needs. Expansion into new markets or geographies may also require adapting cybersecurity measures to comply with local regulations and address specific threats.
For example, a company expanding into a new country with stricter data privacy laws might need to invest in additional security controls and data protection measures to comply with local regulations.
Key Components of a Cybersecurity Budget
A comprehensive cybersecurity budget encompasses various key components that ensure a holistic approach to safeguarding an organization’s digital assets. These components are not mutually exclusive, and their allocation often overlaps.
Infrastructure
Infrastructure spending includes the hardware and software necessary to support cybersecurity operations. This category includes:* Network security devices:Firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and network segmentation tools are essential for controlling network access and detecting malicious activity.
Endpoint security
This includes antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and data loss prevention (DLP) tools to protect individual devices from threats.
Cloud security
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, investing in cloud security solutions like cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), and cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools is crucial.
Physical security
Protecting physical assets, such as servers and data centers, from unauthorized access is essential. This includes security cameras, access control systems, and environmental monitoring systems.
Software
Software spending encompasses the tools and applications used to manage and improve cybersecurity operations. This category includes:* Security information and event management (SIEM):SIEM solutions collect, analyze, and correlate security events from various sources to identify potential threats.
Vulnerability management
Vulnerability scanners and management tools help organizations identify and prioritize security vulnerabilities in their systems and applications.
Security awareness training
Training software provides interactive modules and simulations to educate employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
Incident response
Incident response software helps organizations manage and investigate security incidents, automate incident response processes, and provide forensic analysis.
Personnel
Personnel costs represent the largest portion of most cybersecurity budgets. This category includes:* Salaries and benefits:Hiring and retaining skilled cybersecurity professionals, such as security analysts, engineers, and architects, is essential.
Training and certifications
Providing ongoing training and certifications to cybersecurity staff ensures they stay up-to-date on the latest threats and technologies.
Recruitment and retention
The cybersecurity talent pool is highly competitive, so organizations need to invest in recruitment and retention strategies to attract and retain top talent.
Training
Training investments are crucial for educating employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices. This category includes:* Security awareness training:Regular training programs that cover topics such as phishing, social engineering, and password security help employees understand how to protect themselves and the organization from cyberattacks.
Technical training
Providing technical training to IT staff on security tools and best practices ensures they can effectively implement and maintain cybersecurity controls.
Incident response training
Training employees on incident response procedures, such as reporting suspected breaches and following escalation protocols, helps ensure a coordinated response to security incidents.
Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is essential for understanding the evolving threat landscape and predicting potential attacks. This category includes:* Threat intelligence feeds:Subscription services that provide real-time threat intelligence data from various sources, including security researchers, government agencies, and industry partners.
Threat intelligence platforms
Platforms that aggregate and analyze threat intelligence data to provide actionable insights for security teams.
Figuring out a cybersecurity budget is a balancing act. You need to consider the threats your company faces, the critical assets you need to protect, and the resources available. It’s like planning a home renovation: you have to prioritize projects based on their urgency and impact.
A good example is the abm studio the entryway progress project, where they carefully considered the flow of the space and its overall impact on the home’s functionality. Just like that, cybersecurity budgets require a strategic approach to ensure you’re investing in the right solutions to safeguard your company.
Threat hunting
Dedicated teams or individuals who proactively search for and investigate potential threats in an organization’s network and systems.
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating security vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and applications. This category includes:* Vulnerability scanners:Automated tools that scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability management platforms
Platforms that manage the entire vulnerability management lifecycle, from vulnerability discovery to remediation.
Penetration testing
Simulated attacks conducted by security professionals to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems.
Incident Response
Incident response is the process of responding to security incidents, such as data breaches and malware infections. This category includes:* Incident response planning:Developing and documenting incident response plans that Artikel procedures for responding to security incidents.
Incident response tools
Tools that help organizations manage and investigate security incidents, automate incident response processes, and provide forensic analysis.
Incident response teams
Dedicated teams of security professionals who are responsible for responding to security incidents.
Typical Cybersecurity Budget Allocation
| Category | Typical Percentage Allocation ||—|—|| Infrastructure | 20-30% || Software | 15-25% || Personnel | 40-50% || Training | 5-10% || Threat Intelligence | 5-10% || Vulnerability Management | 5-10% || Incident Response | 5-10% |
Note:These percentages are just estimates, and the actual allocation will vary depending on factors such as the organization’s size, industry, and risk profile.
Methods for Determining Cybersecurity Budget
Determining the appropriate cybersecurity budget is crucial for organizations of all sizes. It involves a careful assessment of risks, vulnerabilities, and potential financial losses. There are various methods that organizations can employ to calculate their cybersecurity budget, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is a common method for determining cybersecurity budgets. It involves evaluating the potential costs of implementing security measures against the potential benefits of preventing security breaches. The cost of implementing security measures can include hardware, software, personnel, and training.
The benefits of implementing security measures can include reduced risk of data breaches, improved customer trust, and compliance with regulations.
A cost-benefit analysis can be expressed as a simple equation:
Benefits
Costs = Net Benefit
For example, an organization might implement a new intrusion detection system (IDS) that costs $10,000. The IDS is expected to prevent $50,000 worth of damage from a potential data breach. The net benefit of implementing the IDS would be $40,000.
- Advantages: Cost-benefit analysis provides a quantifiable method for evaluating the return on investment (ROI) of cybersecurity investments. It can help organizations prioritize security measures that offer the greatest value.
- Disadvantages: Cost-benefit analysis can be challenging to implement accurately, as it can be difficult to quantify the costs and benefits of cybersecurity measures. The analysis may also fail to account for intangible benefits, such as improved customer trust and brand reputation.
Risk-Based Budgeting
Risk-based budgeting is a method that prioritizes security investments based on the likelihood and impact of different risks. This approach involves identifying the most critical assets and vulnerabilities, and allocating resources to mitigate the most significant risks. Risk-based budgeting can be used to develop a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that addresses the most pressing security concerns.
- Advantages: Risk-based budgeting is a more proactive approach to cybersecurity, as it focuses on mitigating the most significant risks. It can help organizations allocate resources more effectively and prioritize security investments based on their potential impact.
- Disadvantages: Risk-based budgeting can be complex and time-consuming to implement, as it requires a thorough assessment of risks and vulnerabilities. It may also be difficult to quantify the impact of some risks, such as reputational damage.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing an organization’s cybersecurity practices and budget to those of similar organizations. This method can help organizations identify areas where they may be under-investing in cybersecurity. Benchmarking can also provide insights into best practices and industry standards.
- Advantages: Benchmarking can provide valuable insights into industry trends and best practices. It can help organizations identify areas where they may be under-investing in cybersecurity and benchmark their performance against their peers.
- Disadvantages: Benchmarking can be difficult to implement accurately, as it can be challenging to find comparable organizations. The data used for benchmarking may not be accurate or complete.
Table: Comparison of Methods for Determining Cybersecurity Budgets
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages ||—|—|—|| Cost-Benefit Analysis | Quantifiable method for evaluating ROI; Helps prioritize security measures that offer the greatest value | Can be challenging to implement accurately; May fail to account for intangible benefits || Risk-Based Budgeting | Proactive approach to cybersecurity; Focuses on mitigating the most significant risks | Can be complex and time-consuming to implement; May be difficult to quantify the impact of some risks || Benchmarking | Provides valuable insights into industry trends and best practices; Helps identify areas where an organization may be under-investing | Can be difficult to implement accurately; Data used for benchmarking may not be accurate or complete |
Best Practices for Cybersecurity Budget Management
Effective cybersecurity budget management is crucial for organizations of all sizes. By optimizing budget allocation and measuring the impact of investments, businesses can ensure their cybersecurity posture is robust and aligned with their overall risk tolerance.
Key Metrics for Measuring Cybersecurity Investment Effectiveness
To assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity investments, organizations need to track and measure key performance indicators (KPIs). These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of security controls, the impact of security incidents, and the overall health of the organization’s security posture.
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD):This metric measures the average time it takes to identify a security incident after it occurs. A lower MTTD indicates a more proactive and efficient security posture.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR):This metric measures the average time it takes to contain and remediate a security incident after it is detected. A lower MTTR signifies a faster and more effective incident response capability.
- Security Incident Rate:This metric tracks the frequency of security incidents within a specific period. A lower incident rate indicates a more secure environment and a successful security strategy.
- Security Awareness Training Completion Rate:This metric measures the percentage of employees who complete mandatory security awareness training. A higher completion rate indicates a greater awareness of security threats and best practices among employees.
- Vulnerability Remediation Rate:This metric measures the percentage of vulnerabilities that are patched or mitigated within a specified timeframe. A higher remediation rate indicates a more proactive approach to addressing security vulnerabilities.
- Return on Security Investment (ROSI):This metric measures the financial benefits of cybersecurity investments against the associated costs. A positive ROSI indicates that security investments are generating a return on investment and contributing to the organization’s bottom line.
Tracking and Monitoring Cybersecurity Budget Spending
Effective budget management requires ongoing tracking and monitoring of spending to ensure that funds are allocated efficiently and effectively. Organizations can use various tools and techniques to track their cybersecurity budget, including:
- Budgeting Software:Dedicated budgeting software provides features for creating budgets, tracking expenses, and generating reports. These tools can automate the process of budget management and provide real-time insights into spending patterns.
- Spreadsheets:While less sophisticated than dedicated software, spreadsheets can still be used to track budget spending effectively. By using formulas and charts, organizations can monitor their budget, identify areas of overspending, and make adjustments as needed.
- Project Management Tools:Project management tools can be used to track the progress of cybersecurity projects and associated expenses. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing tasks, deadlines, and budgets.
- Regular Budget Reviews:Organizations should conduct regular budget reviews to ensure that spending aligns with strategic priorities and that resources are being allocated effectively. These reviews should involve key stakeholders, including IT, security, and finance departments.
Optimizing Cybersecurity Budget Allocation
To maximize the effectiveness of their cybersecurity investments, organizations should prioritize the following recommendations:
- Focus on High-Risk Areas:Organizations should prioritize their budget towards addressing the most critical security risks. This involves conducting risk assessments and identifying vulnerabilities that pose the greatest threat to the organization’s operations and data.
- Invest in a Comprehensive Security Strategy:A robust cybersecurity strategy encompasses multiple layers of defense, including preventive, detective, and corrective controls. Organizations should allocate budget across all aspects of their security strategy to ensure a holistic approach to security.
- Prioritize Security Awareness Training:Employees are often the weakest link in an organization’s security posture. Investing in security awareness training can help employees understand security threats, best practices, and their role in protecting the organization’s data and systems.
- Automate Security Processes:Automating repetitive security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and incident response, can free up security teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. Organizations should allocate budget towards implementing automation solutions that can improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Embrace Security as a Shared Responsibility:Cybersecurity is not solely the responsibility of the IT or security department. Organizations should foster a culture of security awareness and encourage all employees to participate in protecting the organization’s data and systems.
- Regularly Review and Adjust the Budget:The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, and organizations need to adapt their budget accordingly. Regular reviews and adjustments to the budget can ensure that resources are allocated effectively to address emerging threats and technologies.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Budgeting
Cybersecurity budgeting is a dynamic process that constantly adapts to the evolving threat landscape and technological advancements. The rapid pace of innovation and the sophistication of cyberattacks necessitate a proactive approach to cybersecurity budget planning.
Impact of Evolving Cyber Threats
The ever-changing nature of cyber threats significantly influences cybersecurity budget strategies. As attackers become more sophisticated, organizations must allocate resources to counter evolving attack vectors. This includes investing in advanced security technologies, training security professionals, and implementing robust incident response plans.
The rise of ransomware attacks, data breaches, and supply chain vulnerabilities necessitates a shift in focus toward proactive security measures and robust incident response capabilities.
For example, the emergence of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) has made it easier for attackers to launch sophisticated attacks. Companies need to budget for solutions that can detect and prevent ransomware attacks, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools and threat intelligence platforms.