
IBM Data Breach Cost: A Deep Dive
IBM data breach cost is a topic that should be on the minds of every business leader. Data breaches can be incredibly costly, impacting not just a company’s bottom line, but also its reputation and customer trust. From lost revenue and legal fees to the time and effort needed to recover from a breach, the financial implications can be staggering.
The cost of a data breach varies greatly depending on several factors, including the type of data compromised, the size and scope of the breach, and the organization’s response. This blog post explores the complexities of IBM data breach cost, examining the financial impact, legal consequences, and strategies for mitigation.
We’ll also delve into the role of technology in preventing and responding to these incidents.
IBM Data Breach Cost Overview

An IBM data breach refers to a security incident where sensitive information belonging to IBM or its clients is compromised, leading to unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of data. These breaches can have significant financial and reputational consequences for IBM and its clients.The cost of an IBM data breach is influenced by various factors, including the type of data compromised, the number of individuals affected, the time taken to detect and contain the breach, and the resulting legal and regulatory penalties.
Types of IBM Data Breaches
Different types of data breaches can occur at IBM, each with its unique characteristics and potential impact. Here’s a breakdown:
- Data Leakage:Unauthorized disclosure of sensitive data, often through accidental or unintentional means. For example, a company employee might accidentally email confidential information to an external recipient.
- Malware Attacks:Malicious software, such as ransomware or viruses, can infiltrate IBM’s systems, encrypt data, and demand a ransom for its release. This type of breach can disrupt operations and cause significant financial losses.
- Phishing Attacks:These attacks target individuals within IBM by sending deceptive emails or messages designed to trick them into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Insider Threats:Malicious or negligent actions by authorized IBM employees or contractors can lead to data breaches. For example, an employee might intentionally steal data for personal gain or inadvertently share confidential information with unauthorized parties.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks:These attacks aim to disrupt IBM’s services by flooding its systems with excessive traffic, making it difficult or impossible for legitimate users to access resources.
- Cloud Security Breaches:IBM’s cloud computing services are vulnerable to data breaches if security measures are not implemented properly. For example, misconfigured cloud storage buckets can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access.
Financial Impact of IBM Data Breaches
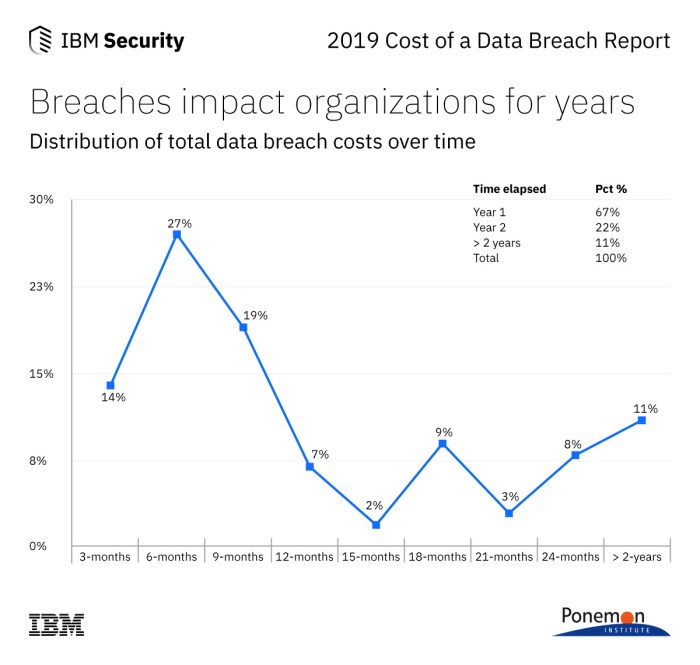
Data breaches can have a significant financial impact on companies, and IBM, being a global technology giant, is not immune to this risk. The costs associated with data breaches can be substantial, encompassing various aspects like incident response, legal fees, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
This section delves into the financial implications of data breaches on IBM, exploring real-world examples and their associated costs.
The cost of an IBM data breach can be astronomical, impacting not only financial resources but also reputation and customer trust. While I’m trying to wrap my head around the sheer scale of those numbers, I can’t help but think about a completely different kind of investment – a pair of stylish boots from Harvey Nichols.
Maybe a little retail therapy could help me process the stress of data security risks, even if it doesn’t directly address the issue of IBM data breach costs.
Impact on IBM’s Revenue, Reputation, and Market Share
Data breaches can negatively affect IBM’s revenue, reputation, and market share in several ways. For instance, a breach could lead to a loss of customer trust, resulting in decreased sales and market share. The cost of recovering from a data breach can also significantly impact IBM’s profitability.
Additionally, the negative publicity associated with a data breach can damage IBM’s reputation, leading to a decline in investor confidence and stock value.
Real-World Examples of IBM Data Breaches and Their Associated Costs
- In 2014, IBM experienced a data breach that affected approximately 1.5 million customers. The breach, which involved the theft of customer data, resulted in significant costs for IBM, including legal fees, regulatory fines, and customer remediation efforts. The exact financial impact of this breach was not publicly disclosed, but estimates suggest it cost IBM millions of dollars.
- In 2017, IBM was involved in a data breach that affected a large number of its employees. The breach, which involved the theft of employee data, resulted in a significant financial impact on IBM. The company had to invest heavily in security measures to prevent future breaches and to mitigate the impact of the breach on its employees.
The estimated cost of this breach was in the millions of dollars.
Impact of Data Breaches on IBM’s Customers and Stakeholders
Data breaches can have a significant impact on IBM’s customers and stakeholders. For example, a breach could lead to the theft of sensitive customer data, resulting in identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage for the affected individuals. This could also lead to legal action against IBM by affected customers, further increasing the company’s financial burden.
The cost of data breaches is a major concern for companies like IBM, and recent events like the kaser focus lay off highlight the potential for significant financial and reputational damage. While layoffs can be a necessary cost-cutting measure, it’s crucial for businesses to prioritize cybersecurity investments to prevent breaches that could ultimately lead to even greater losses.
Furthermore, data breaches can damage IBM’s reputation among stakeholders, including investors, partners, and employees, leading to decreased trust and confidence in the company.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences of IBM Data Breaches
IBM, as a global technology giant, operates within a complex web of legal and regulatory frameworks that govern data protection and privacy. Data breaches can trigger significant legal and regulatory consequences, potentially impacting IBM’s financial stability, reputation, and business operations.
The cost of an IBM data breach can be staggering, affecting not just finances but also reputation. Sometimes, the best antidote to stress is a simple act of creativity. If you’re looking for a thoughtful gift for someone dealing with the aftermath of a data breach, consider a gift idea a simple diy scarf – a project that’s both relaxing and rewarding.
The cost of a data breach might be a significant burden, but the gift of a handmade scarf can offer a small touch of warmth and comfort.
Potential Penalties and Legal Actions
Data breaches can expose IBM to a range of legal and regulatory actions, including civil lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and criminal charges.
- Civil Lawsuits: Individuals whose data is compromised in a data breach can file civil lawsuits against IBM, seeking compensation for damages such as identity theft, financial losses, emotional distress, and reputational harm. These lawsuits can be costly to defend, leading to significant financial settlements or judgments.
- Regulatory Investigations and Fines: Data protection authorities, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), can investigate data breaches and impose substantial fines for non-compliance. These fines can be significant, reaching millions of dollars, depending on the severity of the breach and the applicable regulations.
- Criminal Charges: In some cases, data breaches can lead to criminal charges against IBM or its employees, particularly if the breach involves intentional or negligent conduct. These charges can range from data theft to violation of privacy laws, resulting in fines, imprisonment, or both.
Impact on IBM’s Business Operations and Compliance Efforts
Data breach regulations have a profound impact on IBM’s business operations and compliance efforts.
- Increased Compliance Costs: IBM must invest in robust data security measures, employee training programs, and compliance audits to comply with data protection regulations. These costs can be substantial, impacting IBM’s overall profitability.
- Reputational Damage: Data breaches can severely damage IBM’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and confidence. This reputational damage can impact IBM’s brand image, customer acquisition, and overall market value.
- Business Disruptions: Data breaches can disrupt IBM’s business operations, leading to downtime, data recovery efforts, and customer service disruptions. These disruptions can negatively impact IBM’s revenue and profitability.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Data protection authorities closely scrutinize organizations that experience data breaches, leading to increased regulatory oversight and potential enforcement actions.
Strategies for Mitigating IBM Data Breach Costs

Data breaches are a costly reality for businesses of all sizes, and IBM is no exception. The financial and reputational impact of a data breach can be devastating, making it crucial for organizations to implement robust security measures and develop comprehensive data breach response plans.
This section will explore strategies for mitigating the financial and reputational impact of data breaches, focusing on IBM’s existing security measures and data protection strategies.
IBM’s Existing Security Measures and Data Protection Strategies
IBM has a long history of investing in cybersecurity and data protection, recognizing the importance of safeguarding sensitive information. The company’s security measures are comprehensive and multi-layered, encompassing various technologies and practices designed to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber threats.
IBM’s security strategy is based on a framework of continuous improvement, with a focus on identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Threat Intelligence and Vulnerability Management:IBM employs advanced threat intelligence capabilities to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats. Its security researchers actively monitor the global threat landscape, analyzing malicious activity and identifying potential vulnerabilities in its systems and applications. This proactive approach allows IBM to implement timely security patches and updates, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Data Encryption and Access Control:Data encryption is a cornerstone of IBM’s data protection strategy. Sensitive data is encrypted both at rest and in transit, ensuring its confidentiality even if unauthorized access is gained. Additionally, IBM implements strict access controls, limiting access to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege.
This ensures that only authorized personnel can access the information they need to perform their job functions.
- Security Awareness Training:Human error is a significant factor in many data breaches. IBM invests heavily in security awareness training for its employees, equipping them with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other cyber threats.
By raising employee awareness, IBM reduces the likelihood of accidental or intentional data breaches.
- Incident Response and Recovery:IBM has established a robust incident response plan to handle data breaches and other security incidents. This plan includes clearly defined roles and responsibilities, procedures for identifying and containing breaches, and processes for recovering compromised systems and data. The company also conducts regular security drills to ensure that its incident response team is prepared to handle real-world incidents effectively.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Breach Prevention and Response Plan
While IBM has implemented robust security measures, it is essential to recognize that no system is completely immune to cyberattacks. To further minimize the risk of data breaches and mitigate their impact, a comprehensive plan should be developed that addresses prevention, detection, and response.
This plan should be tailored to IBM’s specific business needs and risk profile, incorporating best practices and industry standards.
- Regular Security Assessments:Conducting regular security assessments is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in IBM’s systems and applications. These assessments should be conducted by independent security experts and should cover all aspects of IBM’s IT infrastructure, including networks, servers, applications, and data storage.
The results of these assessments should be used to prioritize remediation efforts and ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):Implementing data loss prevention (DLP) technologies is essential for preventing sensitive data from leaving IBM’s control. DLP solutions can monitor network traffic, identify and block attempts to transfer sensitive data to unauthorized destinations, and provide real-time alerts of suspicious activity.
These technologies are particularly important for organizations that handle sensitive data, such as financial information, customer data, and intellectual property.
- Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication:Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) is crucial for securing access to IBM’s systems and applications. Strong password policies require users to create complex passwords that are difficult to guess, while MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication before granting access.
This combination significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Awareness Training and Phishing Simulations:Regular security awareness training is essential for educating employees about cyber threats and best practices for protecting sensitive information. Phishing simulations can help identify employees who are susceptible to phishing attacks and provide them with targeted training to improve their ability to recognize and avoid such attacks.
By investing in security awareness training and phishing simulations, IBM can reduce the likelihood of employees falling victim to social engineering attacks.
- Incident Response Plan and Testing:A well-defined incident response plan is essential for handling data breaches and other security incidents effectively. This plan should Artikel the roles and responsibilities of key personnel, procedures for identifying and containing breaches, and processes for recovering compromised systems and data.
Regular testing of the incident response plan is essential to ensure that it is up-to-date, effective, and that all personnel involved are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
- Data Backup and Recovery:Regular data backups are crucial for ensuring that IBM can recover lost or corrupted data in the event of a data breach or other disaster. These backups should be stored securely and regularly tested to ensure that they can be restored effectively.
A comprehensive data backup and recovery strategy is essential for minimizing the impact of data breaches and ensuring business continuity.
Best Practices for Mitigating the Financial and Reputational Impact of Data Breaches
| Best Practice | Description | Benefits ||—|—|—|| Proactive Security Measures| Implementing robust security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and vulnerability management, to prevent data breaches from occurring in the first place. | Reduces the likelihood of a data breach, minimizing financial and reputational damage.
|| Rapid Incident Response| Having a well-defined incident response plan and a dedicated team to handle security incidents promptly and effectively. | Minimizes the impact of a data breach by containing the damage and restoring systems and data quickly. || Effective Communication| Communicating transparently and promptly with affected parties, including customers, employees, and regulators, about the nature of the data breach and the steps being taken to mitigate its impact.
| Builds trust and confidence, minimizing reputational damage and potential legal liabilities. || Data Breach Insurance| Obtaining data breach insurance to cover the financial costs associated with a data breach, such as legal fees, regulatory fines, and customer notification expenses. | Provides financial protection, reducing the financial burden of a data breach.
|| Reputation Management| Developing a reputation management plan to mitigate the negative impact of a data breach on the company’s brand and reputation. | Helps restore public trust and confidence, minimizing long-term reputational damage. || Continuous Improvement| Regularly reviewing and improving security measures, incident response plans, and communication strategies based on lessons learned from past incidents.
| Enhances security posture, reduces the likelihood of future breaches, and improves the company’s ability to respond effectively. |
The Role of Technology in Reducing IBM Data Breach Costs
In the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, IBM must leverage advanced technologies to bolster its data protection capabilities and mitigate the financial impact of data breaches. By integrating innovative solutions into its cybersecurity strategy, IBM can significantly reduce its vulnerability to attacks, enhance its ability to detect and respond to incidents, and minimize the cost of recovery.
Advanced Security Technologies for Enhanced Data Protection
IBM can enhance its data protection by adopting a multi-layered approach that incorporates advanced security technologies. This includes:
- Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs):NGFWs go beyond traditional firewalls by incorporating intrusion prevention systems (IPS), application control, and deep packet inspection capabilities. They provide more comprehensive protection against advanced threats, such as zero-day exploits and malware.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR):EDR solutions monitor and analyze endpoint activity in real time, detecting and responding to malicious behavior. They provide a centralized platform for managing security events across the entire endpoint infrastructure.
- Data loss prevention (DLP):DLP technologies prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network. They monitor data movement and identify potential leaks, blocking unauthorized transfers and enforcing data security policies.
- Security information and event management (SIEM):SIEM platforms centralize security logs and events from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s security posture. They enable security analysts to detect anomalies, investigate security incidents, and respond effectively to threats.
- Threat intelligence platforms:These platforms collect and analyze threat data from various sources, providing insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities. They help organizations proactively identify and mitigate risks by staying ahead of attackers.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Data Breach Prevention and Detection
AI and ML can be powerful tools for enhancing IBM’s cybersecurity capabilities:
- Anomaly detection:AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify unusual patterns that may indicate malicious activity. This allows for the early detection of potential breaches before significant damage occurs.
- Threat prediction:By analyzing historical data and current threat trends, AI models can predict potential attacks and vulnerabilities. This enables organizations to proactively address risks and strengthen their defenses.
- Automated threat response:AI-powered systems can automate certain security tasks, such as incident response and remediation. This reduces the time and effort required to respond to threats, minimizing the impact of breaches.
- Adaptive security:AI can dynamically adjust security controls based on real-time threat intelligence. This allows for a more proactive and responsive security posture, adapting to evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Key Technologies for Improving Cybersecurity Posture and Reducing Data Breach Costs, Ibm data breach cost
IBM can adopt a range of technologies to enhance its cybersecurity posture and minimize the financial impact of data breaches:
- Zero-trust security:This approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default. It requires strict authentication and authorization processes, limiting access to sensitive data and systems only to authorized individuals.
- Cloud security posture management (CSPM):CSPM solutions monitor and manage security configurations in cloud environments. They help organizations ensure compliance with security policies and identify potential vulnerabilities in their cloud infrastructure.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR):SOAR platforms automate and orchestrate security workflows, streamlining incident response and reducing the time required to detect and remediate threats.
- Vulnerability management:Regularly scanning for and patching vulnerabilities is crucial for preventing attacks. Vulnerability management tools help organizations identify and prioritize vulnerabilities, ensuring timely remediation.
- Security awareness training:Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices is essential for preventing human error. Security awareness training helps employees understand common threats, recognize phishing attempts, and practice safe computing habits.







