Managing Payroll for Small Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Managing payroll for small business can seem daunting, but it’s a crucial aspect of running a successful company. From understanding basic payroll components to choosing the right system and navigating compliance, there’s a lot to learn. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to confidently manage payroll, ensuring your employees are paid accurately and on time while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
We’ll delve into the fundamentals of payroll, exploring wages, taxes, deductions, and benefits. We’ll also examine the legal landscape, outlining key regulations and requirements you need to be aware of. This comprehensive guide will cover everything from choosing the right payroll software to processing payments, managing taxes, and ensuring compliance.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to navigate the intricacies of payroll and set your small business up for success.
Understanding Payroll Basics for Small Businesses
Payroll is a critical aspect of running any business, especially for small business owners who often wear multiple hats. It involves more than just cutting checks to employees; it encompasses a complex web of regulations, calculations, and record-keeping. Understanding the fundamentals of payroll can help you avoid costly mistakes, ensure compliance with the law, and maintain a positive relationship with your employees.
Components of Payroll
Payroll involves several key components that must be calculated and processed accurately. These include:
- Wages:This refers to the total amount of money earned by an employee for their work, including their regular salary, overtime pay, and any bonuses or commissions.
- Taxes:Employers are required to withhold certain taxes from employee wages and pay them to the government on their behalf. These taxes include federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax.
- Deductions:Employees may choose to have certain amounts deducted from their paychecks, such as contributions to retirement plans, health insurance premiums, and payments for other benefits.
- Benefits:Some employers offer benefits to their employees, such as health insurance, paid time off, and disability insurance. These benefits can be a significant expense for businesses, but they can also be a valuable way to attract and retain employees.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Payroll in the United States is subject to a complex web of federal, state, and local laws and regulations. Understanding these requirements is crucial for small business owners to avoid penalties and ensure compliance. Here are some key areas to consider:
- Federal Tax Laws:The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets the rules for federal income tax withholding, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax.
- State and Local Tax Laws:Each state and locality may have its own tax laws that apply to payroll, including income tax, unemployment insurance, and disability insurance.
- Labor Laws:The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets the minimum wage, overtime pay rules, and child labor standards.
- Employee Benefits Laws:Federal and state laws regulate employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
Common Payroll Terms and Definitions
Understanding common payroll terms is essential for navigating the complexities of payroll. Here are some key definitions:
- Gross Pay:The total amount of money an employee earns before any deductions are taken out.
- Net Pay:The amount of money an employee receives after all deductions are taken out of their gross pay.
- Payroll Taxes:Taxes withheld from employee wages and paid to the government by the employer.
- Payroll Deductions:Amounts deducted from an employee’s paycheck for things like taxes, retirement contributions, and insurance premiums.
- Pay Period:The time frame for which an employee is paid. This can be weekly, bi-weekly, semi-monthly, or monthly.
Processing Payroll Payments
Getting your employees paid on time and accurately is crucial for maintaining a positive work environment and avoiding potential legal issues. There are several methods available for processing payroll payments, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Payroll Payment Methods
Payroll payments can be made through different methods, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages:
- Direct Deposit:Direct deposit is the most common method for payroll payments. It involves transferring funds directly into an employee’s bank account. This method is convenient, secure, and eliminates the need for physical checks.
- Paper Checks:Paper checks are a traditional method of payroll payment. They are still used by some businesses, especially for employees who do not have bank accounts. However, paper checks are more susceptible to loss, theft, and fraud.
- Mobile Payments:Mobile payments are becoming increasingly popular as a payroll payment method. This method allows employees to receive their pay directly into their mobile wallets. It offers convenience and flexibility but may not be available for all employees.
The Importance of Timely and Accurate Payroll Processing
Timely and accurate payroll processing is critical for maintaining employee satisfaction and avoiding legal penalties.
- Employee Satisfaction:Employees expect to receive their pay on time and accurately. Late or incorrect payments can lead to frustration, decreased morale, and potential turnover.
- Legal Compliance:Payroll regulations are complex and vary by jurisdiction. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, penalties, and legal action.
Step-by-Step Guide for Processing Payroll Payments
The following steps Artikel a typical payroll processing workflow:
- Gather Employee Information:Collect all necessary information about your employees, including their names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and bank account details.
- Calculate Gross Pay:Determine each employee’s gross pay based on their hourly rate, salary, or other compensation arrangements.
- Calculate Deductions:Calculate all applicable deductions from gross pay, such as federal and state income taxes, Social Security, Medicare, health insurance premiums, and retirement contributions.
- Calculate Net Pay:Subtract total deductions from gross pay to determine each employee’s net pay.
- Process Payments:Make payroll payments using your chosen method, whether it’s direct deposit, paper checks, or mobile payments.
- Generate Payroll Reports:Generate and maintain detailed payroll records for each pay period. This documentation is essential for tax purposes and compliance.
Reporting and Filing Payroll Taxes
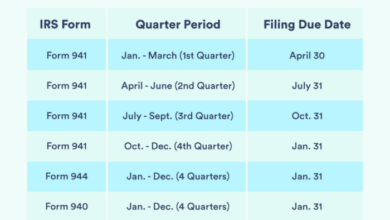
Payroll taxes are a significant responsibility for any small business owner. They are a complex system of federal, state, and local taxes that you are required to withhold from your employees’ paychecks and pay to the government. Understanding and fulfilling these obligations is crucial to avoiding penalties and ensuring your business operates smoothly.
Payroll Tax Forms, Managing payroll for small business
Payroll tax forms are the documents you use to report and pay payroll taxes to the IRS and your state tax agency. The specific forms you need will depend on the type of business you run, the location of your business, and the type of employees you have.
- Form 941, Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return:This form is used to report and pay federal income tax withholding, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax. You must file this form quarterly, even if you have no employees.
- Form 940, Employer’s Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return:This form is used to report and pay the federal unemployment tax. You must file this form annually.
- Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement:This form is used to report the wages and taxes withheld from each employee’s pay. You must provide this form to your employees by January 31st of each year.
- Form W-3, Transmittal of Wage and Tax Statements:This form is used to summarize the information reported on Form W-2. You must file this form with the IRS by January 31st of each year.
Payroll Tax Filing Deadlines
The deadlines for filing payroll tax returns and making payments vary depending on the form. Here are some general deadlines to keep in mind:
- Form 941:You must file Form 941 quarterly, typically on the last day of the month following the end of the quarter (April 15th, July 15th, October 15th, and January 15th).
- Form 940:You must file Form 940 annually, typically by January 31st.
- Form W-2 and Form W-3:You must file these forms with the IRS by January 31st of each year.
Consequences of Failing to File or Pay Payroll Taxes on Time
Failing to file or pay payroll taxes on time can result in significant penalties. These penalties can include:
- Late filing penalties:The IRS charges a penalty for late filing, typically 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
- Late payment penalties:The IRS charges a penalty for late payment, typically 0.5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that the payment is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
- Interest charges:The IRS also charges interest on unpaid taxes, which is calculated based on the current interest rate.
- Criminal penalties:In some cases, failing to file or pay payroll taxes on time can result in criminal penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
Payroll Compliance and Best Practices: Managing Payroll For Small Business
Payroll compliance is crucial for any small business. Failing to comply with payroll laws can lead to hefty fines, penalties, and even legal action. Understanding and adhering to payroll regulations is essential for smooth operations and a positive working environment.
Common Payroll Compliance Issues
Small businesses may face various compliance challenges, including:
- Wage and Hour Laws:The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) mandates minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping requirements. Businesses must accurately track employee hours, calculate overtime pay, and maintain proper records. Incorrectly classifying employees as exempt or non-exempt can lead to violations.
Managing payroll for a small business can be a real headache, especially when it comes to keeping track of all the deductions and taxes. It’s like trying to align content right and left in a word document – you’ve got to make sure everything lines up perfectly or you’ll end up with a mess.
Thankfully, there are tools and resources available to help streamline the process, like online payroll software, which can make managing payroll a breeze.
- Discrimination:Equal pay laws prohibit wage discrimination based on gender, race, religion, or other protected characteristics. Businesses must ensure equal pay for equal work, regardless of an employee’s background.
- Data Privacy:Employee data, including payroll information, is subject to strict privacy regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Businesses must implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive information.
Best Practices for Payroll Compliance
To mitigate risks and ensure compliance, consider these best practices:
- Stay Updated on Laws:Payroll regulations are constantly evolving. Businesses should regularly review and update their policies to reflect current legislation.
- Classify Employees Correctly:Accurate employee classification is crucial for determining wage and hour requirements. Consult with an HR professional or legal expert to ensure proper classification.
- Implement Robust Recordkeeping:Maintain comprehensive payroll records, including time sheets, pay stubs, and tax forms. These records should be easily accessible and organized for audits.
- Utilize Payroll Software:Payroll software automates many tasks, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with regulations. Choose a reputable software provider with features that meet your specific needs.
- Seek Professional Advice:Consult with a payroll specialist or accountant to navigate complex payroll regulations and ensure compliance.
Payroll Compliance Checklist
This checklist can help minimize payroll risks and ensure accurate recordkeeping:
- Review and Update Payroll Policies:Ensure your policies reflect current laws and regulations.
- Verify Employee Classifications:Confirm that employees are properly classified as exempt or non-exempt.
- Implement Time Tracking Systems:Use accurate time tracking methods to ensure accurate calculation of hours worked.
- Maintain Payroll Records:Keep comprehensive payroll records, including time sheets, pay stubs, and tax forms.
- Regularly Review Payroll Data:Periodically review payroll data for errors or inconsistencies.
- Conduct Internal Audits:Perform regular internal audits to identify any compliance issues.
- Train Employees on Payroll Policies:Ensure employees understand payroll policies and their responsibilities.
- Consult with Experts:Seek guidance from payroll specialists or accountants for complex issues.
Common Payroll Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Payroll is the lifeblood of any business, and ensuring its accuracy is crucial for smooth operations and financial stability. Small businesses, in particular, often face challenges in managing payroll effectively, leading to potential errors that can have serious consequences.
Understanding common payroll mistakes and implementing preventive measures is essential for maintaining compliance, minimizing financial penalties, and fostering positive employee relations.
Incorrect Tax Calculations
Incorrect tax calculations can result in significant financial penalties and legal complications. It is essential to stay updated on federal, state, and local tax laws and regulations, which are subject to change.
- Using outdated tax tables:Tax rates and withholding requirements are updated regularly. Using outdated tax tables can lead to inaccurate withholdings, resulting in underpayment or overpayment of taxes. To ensure accuracy, always use the most recent tax tables provided by the IRS or your state’s tax agency.
- Misclassifying employees:Misclassifying employees as independent contractors can lead to significant penalties. The IRS has strict guidelines for determining employee status. Factors such as control over work, the nature of the relationship, and the degree of independence are considered.
- Incorrectly calculating deductions:Deductions for taxes, health insurance, retirement contributions, and other benefits must be calculated accurately. Errors in these calculations can result in underpayment or overpayment of deductions, impacting employee pay and tax obligations.
To avoid these mistakes, consider using payroll software that automatically updates tax tables and calculates deductions accurately. Regularly review payroll reports and consult with a tax professional for guidance on complex tax matters.
Late Payments
Late payroll payments can damage employee morale, lead to legal issues, and attract penalties from tax agencies. Timely payment is crucial for maintaining a positive work environment and avoiding financial repercussions.
- Failure to meet deadlines:Payroll deadlines vary depending on the jurisdiction. Failing to meet these deadlines can result in late payment penalties. Establish a system for tracking payroll deadlines and ensure timely processing of payments.
- Incorrectly calculating payment dates:Payroll payment dates should be calculated accurately, taking into account weekends and holidays. Errors in calculating payment dates can lead to late payments and employee dissatisfaction.
- Technical glitches:Technical issues with payroll software or payment systems can cause delays in processing payments. Ensure your systems are reliable and have backup plans in place to minimize disruptions.
To prevent late payments, automate payroll processes as much as possible, set reminders for deadlines, and have a contingency plan in place for unexpected issues. Consider using a payroll service provider that specializes in ensuring timely payments.
Data Entry Errors
Data entry errors are common in payroll processing and can have far-reaching consequences. Even seemingly minor mistakes can lead to incorrect paychecks, tax filings, and other financial discrepancies.
- Incorrect employee information:Incorrect employee names, Social Security numbers, addresses, or bank account details can result in paychecks being sent to the wrong person or deposited into the wrong account. Double-check all employee information before processing payroll.
- Incorrect hours worked:Inaccurate time tracking can lead to incorrect calculations of wages and overtime pay. Implement a reliable time tracking system and review time sheets carefully.
- Incorrect rates of pay:Ensure that all employees are paid at their correct rates, including hourly rates, overtime rates, and bonuses. Regularly review pay rates to ensure accuracy.
To minimize data entry errors, use a payroll software that includes data validation features. Train employees on proper data entry procedures and implement a system for reviewing payroll data before processing.
Other Common Payroll Mistakes
Other common payroll mistakes include:
- Failing to track employee benefits:Employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement contributions, and paid time off should be tracked accurately and included in payroll calculations.
- Not keeping adequate records:Maintain complete and accurate payroll records, including time sheets, pay stubs, and tax forms. These records are essential for audits, compliance, and dispute resolution.
- Not staying current with payroll regulations:Payroll laws and regulations are constantly changing. Stay informed about updates and consult with a tax professional for guidance.
Technology and Payroll Automation
In today’s digital age, technology has revolutionized many aspects of business operations, and payroll is no exception. Automating payroll processes can significantly benefit small businesses by streamlining tasks, reducing errors, and saving valuable time and resources.
Benefits of Payroll Automation
Automating payroll processes offers numerous advantages for small businesses.
- Improved Accuracy:Manual payroll calculations are prone to errors, leading to potential financial losses and compliance issues. Payroll automation software eliminates manual calculations and ensures accurate payroll processing, reducing the risk of mistakes.
- Increased Efficiency:Automating payroll tasks frees up time for business owners and HR professionals to focus on other critical aspects of their business. It eliminates repetitive tasks and streamlines the entire payroll process, increasing efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Compliance:Payroll regulations are complex and constantly evolving. Payroll automation software helps businesses stay compliant with federal, state, and local tax laws by providing automated tax calculations, withholding, and reporting features. It also ensures timely and accurate filing of payroll taxes, minimizing the risk of penalties.
- Reduced Costs:Payroll automation software can help businesses save money by reducing the need for manual labor, minimizing errors, and streamlining processes. It also eliminates the need for specialized payroll software or outsourcing, further reducing costs.
Payroll Automation Tools and Software
Various payroll automation tools and software are available for small businesses, catering to different needs and budgets.
- Cloud-Based Payroll Software:These platforms offer a comprehensive suite of payroll features, including time tracking, expense management, payroll processing, and tax filing, accessible from any device with an internet connection. Examples include Gusto, Paychex Flex, and QuickBooks Payroll.
- Time Tracking Software:These tools help businesses track employee hours worked, overtime, and breaks, ensuring accurate timekeeping and payroll calculations. Examples include Toggl Track, Clockify, and Timely.
- Expense Management Software:These platforms streamline the process of tracking and reimbursing employee expenses, integrating with payroll systems for seamless expense management. Examples include Expensify, Zoho Expense, and Divvy.
How Technology Improves Payroll Accuracy, Efficiency, and Compliance
Technology plays a crucial role in improving payroll accuracy, efficiency, and compliance:
- Real-Time Data:Payroll automation software provides real-time access to payroll data, enabling businesses to track employee hours, deductions, and payments in real time. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
- Automated Calculations:Payroll automation software automatically calculates payroll taxes, deductions, and net pay, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of manual errors. It also simplifies compliance by automatically calculating and filing payroll taxes.
- Integration with Other Systems:Payroll automation software integrates with other business systems, such as HR systems, time tracking software, and accounting software, streamlining data flow and reducing manual data entry. This improves efficiency and reduces the risk of errors.
- Automated Reporting:Payroll automation software generates comprehensive payroll reports, including pay stubs, tax forms, and compliance reports. This provides valuable insights into payroll data and simplifies compliance reporting.