New Endpoint Security Challenges: A Modern Landscape
New endpoint security challenges are taking center stage as the digital landscape evolves. The rise of cloud-native environments, the explosion of remote work, and the growing sophistication of cyberattacks have fundamentally changed the way we approach endpoint security. Gone are the days of simple antivirus solutions; today, organizations need a layered approach that incorporates advanced threat intelligence, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and robust user education programs.
This shift necessitates a deeper understanding of the evolving threat landscape and the adoption of modern security technologies. We’ll explore the specific challenges posed by cloud migration, remote work, and sophisticated attacks, and delve into the innovative solutions that are emerging to address them.
The Rise of Cloud-Native Environments

The shift towards cloud-native environments has fundamentally altered the endpoint security landscape, presenting new challenges and opportunities. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services and technologies, traditional endpoint security solutions designed for on-premises environments struggle to adapt to the dynamic and distributed nature of cloud deployments.
Impact of Cloud Migration on Endpoint Security Challenges
The migration to the cloud has significantly impacted endpoint security challenges. Traditional security models, often focused on perimeter defense, become less effective in a cloud-native environment where applications and data are dispersed across multiple cloud providers and geographically distributed. This shift introduces new vulnerabilities and necessitates a more comprehensive approach to endpoint security.
- Increased Attack Surface:Cloud migration expands the attack surface, as applications and data are exposed to the internet and potentially vulnerable to attacks from various sources.
- Dynamic Environments:Cloud-native environments are dynamic and constantly evolving, making it difficult to track and secure endpoints effectively. Ephemeral instances, containerized applications, and serverless functions create challenges for traditional endpoint security tools.
- Shared Responsibility Model:Cloud providers share responsibility for security with their customers. While cloud providers offer security services, organizations still need to implement robust endpoint security measures to protect their applications and data.
Serverless Computing and Containerization
Serverless computing and containerization have further transformed the endpoint security landscape. These technologies offer scalability, agility, and cost efficiency but also introduce new challenges for securing endpoints.
- Ephemeral Instances:Serverless functions and containerized applications are often ephemeral, existing for short durations, making it difficult to apply traditional endpoint security controls.
- Shared Resources:Containerized applications share resources, increasing the risk of vulnerabilities and potential attacks. A compromise in one container could potentially affect other containers on the same host.
- Supply Chain Security:The use of containers and serverless functions introduces new security risks related to the supply chain. Malicious code or vulnerabilities in container images or third-party libraries can compromise applications.
Securing Ephemeral and Dynamic Cloud Environments
Securing ephemeral and dynamic cloud environments requires a different approach to endpoint security. Traditional endpoint security solutions, often reliant on agents and signatures, may not be effective in these environments.
- Cloud-Native Security Tools:Organizations need to adopt cloud-native security tools that can adapt to the dynamic nature of cloud environments. These tools leverage cloud APIs and services to monitor and protect endpoints.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):Robust IAM policies are crucial for controlling access to cloud resources. Implementing least privilege access and multi-factor authentication can help mitigate unauthorized access.
- DevSecOps Practices:Integrating security into the development lifecycle (DevSecOps) is essential. This includes automated security testing, vulnerability scanning, and continuous monitoring to identify and remediate vulnerabilities early.
- Threat Intelligence and Monitoring:Organizations need to leverage threat intelligence feeds and continuous monitoring to detect and respond to threats in real-time. This includes monitoring cloud logs, security events, and network traffic.
The Explosion of Remote Work and BYOD

The rise of remote work and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies has fundamentally changed the endpoint security landscape. As more employees work from home or various locations using their personal devices, the attack surface for cybercriminals has expanded significantly.
This trend has introduced new challenges for organizations trying to protect their sensitive data and maintain business continuity.
With the rise of remote work and cloud adoption, new endpoint security challenges have emerged. Organizations need a robust solution to detect and respond to threats across diverse environments. CrowdStrike cloud threat hunting provides a powerful platform for proactive threat hunting and incident response, helping organizations stay ahead of evolving endpoint security threats.
Security Risks Associated with Remote Work and BYOD
The increased use of remote work and BYOD policies brings a host of security risks that organizations must address. These risks include:
- Increased Attack Surface:Remote work and BYOD policies expand the attack surface by introducing new endpoints and access points. This makes it more difficult to secure all devices and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Breaches:Employees working from home or using personal devices may be more likely to access sensitive data on unsecured networks or devices, increasing the risk of data breaches.
- Lack of Centralized Control:Organizations may struggle to maintain centralized control over endpoint security when employees are working remotely or using their own devices. This can lead to inconsistent security policies and vulnerabilities.
- Shadow IT:Employees may install unauthorized software or applications on their personal devices, which can introduce security risks and make it difficult for organizations to track and manage.
- Phishing Attacks:Remote workers are often targeted by phishing attacks, which can lead to malware infections and data breaches.
Managing and Securing Endpoints Accessed from Various Locations and Devices
Organizations need to implement robust security measures to manage and secure endpoints accessed from various locations and devices. This includes:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):EDR solutions provide real-time visibility into endpoint activity and can detect and respond to threats quickly.
- Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV):NGAV solutions go beyond traditional antivirus protection to detect and prevent zero-day threats and advanced malware.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Network Segmentation:Network segmentation helps to isolate sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):DLP solutions help to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, even if it is stored on a personal device.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE):SASE solutions provide secure access to applications and data from any location, regardless of the device or network.
Securing Personal Devices Used for Work Purposes, New endpoint security challenges
Organizations need to establish clear guidelines and policies for securing personal devices used for work purposes. These guidelines should include:
- Password Management:Employees should use strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication on all devices used for work.
- Software Updates:Employees should install all software updates promptly to patch vulnerabilities and protect against malware.
- Data Encryption:Employees should encrypt all sensitive data stored on their devices.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM):Organizations should use MDM solutions to manage and secure mobile devices used for work purposes.
- Security Awareness Training:Organizations should provide employees with regular security awareness training to educate them about the latest threats and best practices for protecting their devices.
The Growing Threat of Sophisticated Attacks
The landscape of cyber threats is constantly evolving, with attackers becoming increasingly sophisticated in their tactics and techniques. This has led to a significant rise in the number and complexity of attacks, making it more difficult for organizations to protect their data and systems.
Advanced Attack Vectors and Techniques
Cybercriminals are continuously developing new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. Some of the latest attack vectors and techniques include:
- Zero-day exploits:These are vulnerabilities that are unknown to software developers and vendors, making it difficult to patch them in a timely manner. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities before they are patched, giving them access to sensitive data and systems.
- Phishing attacks:Phishing attacks are a common way for attackers to gain access to sensitive information. These attacks typically involve sending emails or messages that appear to be from a legitimate source, but contain malicious links or attachments. Once clicked, these links or attachments can install malware or steal credentials.
Keeping up with new endpoint security challenges can feel like a constant uphill battle. You need to stay vigilant, constantly adapting your defenses to new threats. Sometimes, a little creative outlet can help you de-stress and refocus. Why not take a break and try a fun DIY project like making your own photo wall clock ?
Afterward, you’ll be refreshed and ready to tackle those endpoint security challenges with renewed energy.
- Ransomware:Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands payment for its decryption. This type of attack can be particularly devastating, as it can cripple businesses and organizations.
- Advanced persistent threats (APTs):APTs are highly sophisticated and targeted attacks that can go undetected for long periods. These attacks often involve multiple stages and techniques, and are designed to steal sensitive information or disrupt operations.
- Supply chain attacks:These attacks target software development or distribution chains to compromise software used by many organizations. Attackers can inject malware into the software supply chain, which can then be deployed to a large number of victims.
Challenges of Detecting and Preventing Zero-Day Exploits and Advanced Persistent Threats
Detecting and preventing zero-day exploits and APTs presents significant challenges for organizations. These attacks are often highly targeted and sophisticated, and they can exploit vulnerabilities that are unknown to security teams.
Navigating the ever-evolving landscape of endpoint security challenges can feel like trying to decipher a complex code. But sometimes, the best way to find clarity is to take a break and enjoy something refreshing, like a pineapple coconut daiquiri in a pineapple cup.
After a sip of that tropical delight, you’ll be ready to tackle those endpoint security challenges with a renewed sense of focus and energy.
- Rapidly evolving threats:The speed at which new threats emerge makes it difficult for organizations to keep up. Attackers are constantly developing new techniques and exploiting new vulnerabilities, making it a constant game of catch-up for security teams.
- Limited visibility:Many organizations lack the visibility needed to detect and prevent sophisticated attacks. Traditional security tools may not be able to identify these threats, especially if they are using novel techniques or exploiting unknown vulnerabilities.
- Lack of expertise:Not all organizations have the expertise needed to detect and respond to advanced threats. This can make it difficult to implement effective security measures and respond to incidents in a timely manner.
The Need for Advanced Threat Intelligence and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions
To effectively address the growing threat of sophisticated attacks, organizations need to invest in advanced threat intelligence and EDR solutions.
- Threat intelligence:Threat intelligence provides organizations with insights into the latest attack vectors, techniques, and actors. This information can be used to proactively identify and mitigate potential threats.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR):EDR solutions provide organizations with real-time visibility into the activities on their endpoints. This allows them to detect and respond to attacks in progress, even if they are using zero-day exploits or other sophisticated techniques. EDR solutions can also help organizations to identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
The Evolution of Endpoint Security Technologies: New Endpoint Security Challenges
The landscape of endpoint security has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving beyond traditional antivirus solutions to embrace a more comprehensive and proactive approach. This evolution has been driven by the changing nature of cyber threats, the increasing complexity of IT environments, and the rise of new technologies.
Traditional Antivirus Solutions vs. Modern Endpoint Security Platforms
Traditional antivirus solutions, while effective in detecting known malware signatures, have limitations in addressing the evolving threat landscape. Modern endpoint security platforms, on the other hand, offer a more comprehensive approach that goes beyond signature-based detection.
- Traditional Antivirus Solutions:
- Signature-based detection: Relies on identifying known malware signatures, making it vulnerable to zero-day attacks and polymorphic malware.
- Limited threat visibility: Offers a reactive approach, focusing on detection and remediation after an attack has occurred.
- Resource-intensive: Can consume significant system resources, impacting device performance.
- Modern Endpoint Security Platforms:
- Multi-layered protection: Combines multiple security technologies, including behavioral analysis, machine learning, and threat intelligence, to provide comprehensive protection.
- Proactive threat detection: Utilizes advanced techniques like behavioral analysis and threat hunting to identify and respond to emerging threats.
- Enhanced threat visibility: Provides real-time insights into endpoint activity, enabling security teams to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
- Lightweight and efficient: Designed to minimize impact on device performance, ensuring seamless user experience.
Benefits of a Layered Security Approach
Adopting a layered security approach that integrates multiple endpoint security technologies is crucial for effectively mitigating modern cyber threats.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide continuous monitoring and threat detection capabilities, enabling security teams to respond to incidents quickly and effectively.
- Real-time threat detection and response
- Advanced threat hunting and investigation capabilities
- Automated incident response and remediation
- Behavioral Analysis: Behavioral analysis techniques monitor endpoint activity for suspicious patterns, identifying anomalies that may indicate malicious activity.
- Detects zero-day attacks and unknown threats
- Provides insights into attacker behavior and tactics
- Reduces the risk of false positives
- Threat Hunting: Threat hunting involves proactively searching for malicious activity within the network and endpoints, uncovering hidden threats that may have evaded traditional security controls.
- Identifies advanced and persistent threats
- Proactive threat detection and mitigation
- Improves overall security posture
The Role of AI and ML in Endpoint Security
AI and ML are playing an increasingly important role in endpoint security, enabling organizations to enhance threat detection, response, and prevention capabilities.
- Threat Detection and Analysis: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from endpoints, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate malicious activity.
- Improved accuracy and speed of threat detection
- Reduced false positives and alert fatigue
- Enhanced threat intelligence and insights
- Automated Incident Response: AI-powered security solutions can automate incident response processes, enabling faster and more efficient remediation.
- Reduced time to detect and respond to threats
- Improved incident handling efficiency
- Minimized impact of security incidents
- Proactive Threat Prevention: AI and ML can be used to predict and prevent future attacks by analyzing historical data and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
- Enhanced security posture and threat prevention capabilities
- Reduced risk of successful attacks
- Proactive security measures to mitigate emerging threats
The Importance of User Education and Training
Endpoint security is a multifaceted challenge, but one of the most overlooked aspects is the human element. Even with the most sophisticated security technologies in place, a single user mistake can compromise an entire system. That’s why user education and training are crucial in mitigating endpoint security risks.
The Importance of User Awareness and Training in Mitigating Endpoint Security Risks
Effective user training is the cornerstone of a strong endpoint security strategy. By equipping users with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid potential threats, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to attacks.
A Comprehensive Training Program for Endpoint Security
A comprehensive training program should address the following key areas:
Phishing Scams
Phishing attacks are a common way for cybercriminals to gain access to sensitive information. Users should be trained to recognize phishing emails, websites, and other forms of communication that attempt to trick them into revealing personal or financial data.
- Educate users on common phishing tactics, such as spoofed emails, malicious links, and social engineering techniques.
- Train users to be suspicious of unsolicited emails, especially those that request personal information or ask them to click on suspicious links.
- Encourage users to report suspicious emails or websitesto the IT department.
Malware Threats
Malware can take many forms, including viruses, worms, and ransomware. Users should be trained to recognize and avoid malware threats, and to take appropriate steps to protect their devices.
- Explain the different types of malwareand their potential impact on devices and networks.
- Educate users on how to identify and avoid malicious websites, attachments, and downloads.
- Train users on how to use antivirus softwareand keep it up to date.
- Encourage users to report any suspicious activityto the IT department.
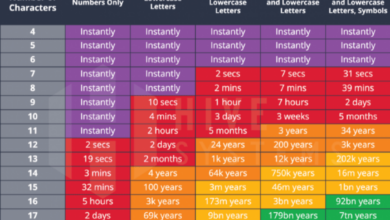
Secure Password Practices
Weak passwords are a major security vulnerability. Users should be trained to create strong passwords and to manage them securely.
- Explain the importance of using strong passwordsthat are at least 12 characters long and include a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Encourage users to use a password managerto store and manage their passwords securely.
- Train users to avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Educate users on the risks of sharing passwordswith others.
Real-World Scenarios Illustrating the Consequences of Neglecting Endpoint Security Best Practices
- A user clicks on a malicious link in a phishing email, allowing malware to infect their device and spread to the company network.
- An employee downloads a file from an untrusted source, unknowingly installing malware on their computer.
- A user uses a weak password for their work account, making it easy for hackers to gain access to sensitive data.
- An employee shares their login credentials with a colleague, creating a security risk for the entire organization.