Tableau Business Analytics Platform: A Cheat Sheet
Tableau business analytics platform a cheat sheet – Tableau Business Analytics Platform: A Cheat Sheet is your guide to unlocking the power of data visualization and analysis. This comprehensive resource will walk you through the essential features, functionalities, and techniques that make Tableau a game-changer for businesses of all sizes.
Whether you’re a seasoned data analyst or just starting your journey with data exploration, this cheat sheet will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to harness the power of Tableau for impactful decision-making.
From understanding the basics of data connection and visualization to delving into advanced features like data blending and calculated fields, this cheat sheet will cover everything you need to know to get started and excel in your Tableau journey. We’ll explore the different chart types, learn how to create interactive dashboards and stories, and uncover the secrets of effective data analysis techniques.
Get ready to unlock the potential of your data with Tableau!
Introduction to Tableau
Tableau is a powerful and user-friendly business intelligence and data visualization platform that helps individuals and organizations gain insights from their data. It empowers users to create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations that effectively communicate complex data stories.Tableau’s intuitive interface and drag-and-drop functionality enable users with varying technical expertise to explore data, discover patterns, and share their findings with stakeholders.
Key Features and Functionalities
Tableau offers a comprehensive suite of features and functionalities that cater to various data analysis and visualization needs.
- Data Connectivity:Tableau connects to a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud applications, and more. This allows users to access and analyze data from various sources in a unified platform.
- Data Preparation and Transformation:Tableau provides data preparation tools that enable users to clean, shape, and transform data before visualization. This ensures data quality and consistency for accurate analysis.
- Visualizations and Charts:Tableau offers a vast library of visualization types, including charts, graphs, maps, and dashboards. Users can choose the most appropriate visualization to effectively communicate their data insights.
- Interactive Dashboards:Tableau’s interactive dashboards allow users to filter, drill down, and explore data in real-time. This empowers users to discover insights and answer questions on demand.
- Collaboration and Sharing:Tableau facilitates collaboration by enabling users to share dashboards, reports, and visualizations with colleagues and stakeholders. This promotes data-driven decision-making across the organization.
Benefits of Using Tableau
Tableau provides numerous benefits for organizations seeking to leverage data for better decision-making and insights.
- Improved Data Understanding:Tableau’s visualization capabilities enable users to easily understand complex data patterns and trends. This empowers them to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
- Faster Insights and Analysis:Tableau’s intuitive interface and drag-and-drop functionality allow users to quickly create visualizations and explore data without extensive coding or technical expertise. This accelerates the analysis process and enables faster decision-making.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:Tableau facilitates effective communication of data insights through interactive dashboards and reports. This promotes collaboration and data-driven decision-making across the organization.
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency:Tableau’s automated data preparation and visualization capabilities streamline the analysis process, freeing up time for users to focus on strategic tasks. This increases productivity and efficiency within the organization.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making:Tableau empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions based on real-time insights and trends. This leads to improved business outcomes and competitive advantage.
Getting Started with Tableau

Tableau is a powerful and intuitive data visualization tool that can help you turn raw data into insightful dashboards and interactive reports. This section guides you through the initial steps of setting up and using Tableau Desktop, enabling you to start exploring and analyzing your data.
Installing and Setting Up Tableau Desktop
The first step to using Tableau is installing the software. The installation process is straightforward and can be completed in a few simple steps:
- Download the Tableau Desktop installer from the official Tableau website. Select the appropriate version for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions. You might be asked to choose a destination folder and accept the license agreement.
- Once the installation is complete, launch Tableau Desktop. You will be prompted to activate your license, either through a trial period or by entering your license key.
After installing and activating Tableau, you are ready to connect to data sources and start creating visualizations.
Connecting to Data Sources
Tableau can connect to a wide range of data sources, including:
- Databases:Tableau supports connections to popular database management systems like SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. You can connect to databases using their respective drivers or by using Tableau’s built-in connectors.
- Spreadsheets:Tableau can directly connect to spreadsheets in Excel, Google Sheets, and other formats. You can import data from spreadsheets or connect to them live, allowing for dynamic updates.
- Cloud Services:Tableau can connect to various cloud-based data sources, including Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake. These connections enable you to analyze data stored in the cloud without having to download it locally.
- Text Files:Tableau can import data from various text file formats, such as CSV, TSV, and plain text files. This is useful for analyzing data that is not stored in a database or spreadsheet.
Connecting to a data source in Tableau is simple:
- Click on the “Connect” button in the Tableau Desktop interface.
- Select the data source type from the list. For example, choose “Microsoft Excel” to connect to an Excel file.
- Provide the necessary connection details, such as the file path or database credentials. You can also choose to connect to the data source live or import it into Tableau.
Importing and Preparing Data for Analysis
Once you have connected to your data source, Tableau will display a list of tables or sheets within that source. You can then select the specific data you want to analyze.
- Data Import:Importing data into Tableau allows you to work with a local copy of your data, which can be beneficial for performance and offline analysis. However, imported data is static and will not reflect any changes made to the original source.
To import data, simply drag the desired tables or sheets from the “Data Source” pane to the “Sheet” area.
- Live Connections:Live connections allow you to analyze data directly from the original source. This ensures that your analysis reflects the most up-to-date data. However, live connections can be slower than importing data, especially if the data source is large or remote.
- Data Cleaning and Preparation:Before you start analyzing data, it’s important to clean and prepare it. This may involve removing duplicates, handling missing values, formatting data types, and creating new calculated fields. Tableau provides tools to help you with these tasks, including data blending, filters, and calculations.
“Clean data is the foundation of any successful data analysis. Spend time preparing your data to ensure accurate and insightful results.”
Data Visualization Techniques
Data visualization is the process of presenting data in a graphical format to make it easier to understand and interpret. It’s a powerful tool for communicating insights and making data-driven decisions. Tableau, a leading business analytics platform, provides a wide range of tools and features for creating impactful visualizations.
Types of Charts in Tableau
Tableau offers a variety of chart types, each suited for different types of data and analytical goals.
- Bar Charts:Ideal for comparing discrete categories. They represent data as bars, with the height or length of each bar proportional to the value it represents. For example, a bar chart can be used to compare sales figures across different product categories or regions.
- Line Charts:Used to visualize trends over time. They connect data points with lines, showing how a value changes over a specific period. For instance, a line chart can depict the growth of website traffic or the fluctuation of stock prices over months.
- Scatter Plots:Show the relationship between two continuous variables. Each data point is represented by a dot, and the position of the dot on the chart indicates its value on both axes. Scatter plots can reveal correlations or patterns between variables, like the relationship between advertising spending and sales revenue.
- Maps:Used to visualize geographical data. Tableau allows you to create interactive maps, where you can color-code regions based on specific metrics, such as population density, sales figures, or crime rates. This helps to identify geographical patterns and trends.
- Pie Charts:Display proportions or percentages of a whole. Each slice of the pie represents a different category, and the size of each slice is proportional to its percentage of the whole. Pie charts are useful for showing the composition of a dataset, like the distribution of customer demographics.
Principles of Effective Data Visualization
Effective data visualization goes beyond simply presenting data in a graphical format. It’s about creating clear, concise, and accurate visualizations that convey insights effectively.
- Clarity:Visualizations should be easy to understand and interpret, avoiding clutter or unnecessary complexity. This involves using appropriate chart types, clear labels, and a consistent color scheme.
- Conciseness:Visualizations should focus on conveying the key insights without overwhelming the viewer with unnecessary information. This means avoiding too many data points, unnecessary details, or overly complex charts.
- Accuracy:Visualizations should accurately represent the data and avoid misleading interpretations. This requires careful selection of data, appropriate scaling, and accurate labeling.
Creating Interactive Dashboards and Stories
Tableau allows you to create interactive dashboards and stories that bring your data to life.
Tableau’s a powerful tool for data visualization, but it can feel overwhelming at first. That’s where a cheat sheet comes in handy! It’s like having a quick reference guide to help you navigate the platform and understand its various features.
Speaking of nostalgia, did you know that the cult classic early 2000s game Habbo Hotel is back and you can play it on your modern Mac for free right now ? It’s like stepping back in time! Anyway, back to Tableau…
A cheat sheet can really help you unlock its full potential and create stunning data visualizations that tell a story.
Dashboards
Dashboards are collections of visualizations that provide a comprehensive overview of key metrics and insights. They allow users to explore data interactively, filtering and drilling down into specific areas of interest.
- Dynamic Filters:Users can interact with dashboards by applying filters to the data, allowing them to focus on specific segments or time periods. For example, a dashboard showing sales figures could allow users to filter data by product category, region, or date.
- Interactive Elements:Dashboards can include interactive elements like tooltips, drill-down capabilities, and parameter controls, enabling users to explore data in detail and gain deeper insights.
Stories
Tableau Stories are sequential narratives that guide viewers through a series of visualizations, telling a compelling story about the data.
- Narrative Structure:Stories are organized into a series of slides, each containing a visualization and accompanying text. This structure helps to guide the viewer through the data, highlighting key insights and supporting the narrative.
- Data-Driven Storytelling:Stories allow you to present data in a way that engages the audience and helps them understand the underlying trends and patterns. This can be used to communicate complex insights, support decision-making, or persuade stakeholders.
Data Analysis with Tableau
Tableau empowers you to go beyond simple data visualization and delve into the intricacies of your data, uncovering valuable insights and trends. By leveraging Tableau’s intuitive interface and powerful analytical capabilities, you can unlock the full potential of your data and make informed decisions.
Filtering and Sorting Data
Filtering and sorting are fundamental data analysis techniques that help you focus on specific subsets of your data, enabling you to identify patterns and trends more effectively.
- Filtering:Tableau provides various filtering options, including:
- Quick Filters:Drag a field onto the filter shelf to create quick filters that allow you to easily select specific values.
- Advanced Filters:Use the “Edit Filter” option to define complex filtering criteria using logical operators (AND, OR, NOT) and comparison operators (=, !=, >, =, <=).
- Top N:Display the top or bottom N values of a field based on a specified measure.
- Sorting:Tableau allows you to sort data based on various criteria, including:
- Ascending or Descending Order:Sort data in ascending or descending order based on a field.
- Custom Sort:Define a custom sort order for a field by manually specifying the desired sequence.
Data Aggregation
Aggregation allows you to summarize data and gain insights into the overall trends and patterns within your dataset.
- Common Aggregation Functions:Tableau provides a wide range of aggregation functions, including:
- SUM:Calculates the total sum of a numeric field.
- AVG:Calculates the average value of a numeric field.
- MIN:Finds the minimum value of a numeric field.
- MAX:Finds the maximum value of a numeric field.
- COUNT:Counts the number of distinct values in a field.
- Aggregation Levels:You can control the level of aggregation by specifying the dimensions you want to group your data by. For example, you can aggregate sales data by region, product category, or time period.
Using Tableau’s Built-in Functions and Calculations
Tableau’s built-in functions and calculations extend your analytical capabilities, allowing you to perform complex calculations and derive new insights from your data.
- Mathematical Functions:Perform mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation.
- Date and Time Functions:Extract information from date and time fields, such as day, month, year, hour, and minute.
- String Functions:Manipulate text data, such as finding substrings, replacing characters, and converting case.
- Logical Functions:Evaluate conditions and return Boolean values (TRUE or FALSE), enabling you to filter data based on specific criteria.
- Custom Calculations:Create your own custom calculations using Tableau’s formula editor to derive new metrics and insights.
For example, you can create a calculation to calculate the percentage of sales growth over a specific period: `(SUM(Sales)- SUM(Sales LAST YEAR)) / SUM(Sales LAST YEAR)`.
Tableau for Business Intelligence
Tableau is a powerful data visualization and analytics platform that empowers businesses to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions. Its user-friendly interface and robust features make it a valuable tool for business intelligence (BI) purposes, enabling organizations to effectively track performance, identify trends, and optimize operations.
Reporting and Data Exploration
Tableau excels at creating interactive reports and dashboards that provide a comprehensive overview of business performance. Users can easily connect to various data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and cloud services, and visualize data in a variety of formats, such as charts, graphs, maps, and tables.
This allows for dynamic exploration of data, enabling users to drill down into specific areas of interest and uncover hidden patterns.
Forecasting and Trend Analysis
Tableau’s forecasting capabilities enable organizations to predict future trends and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging statistical models and historical data, users can generate accurate forecasts for key metrics such as sales, revenue, and customer churn. These insights are crucial for planning, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making.
Creating Interactive Dashboards
Dashboards are central to Tableau’s BI capabilities, providing a centralized view of key performance indicators (KPIs) and other critical business metrics. Users can create customized dashboards that display data in an easily digestible format, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp the overall health of the business.
Interactive features like filters, drill-downs, and parameter controls allow for dynamic analysis and exploration of data within the dashboard.
Examples of Tableau Use Cases
Tableau is widely used across industries, empowering organizations to make data-driven decisions and gain a competitive edge.
- Retail:Retailers use Tableau to analyze sales trends, customer behavior, and inventory levels, enabling them to optimize pricing strategies, improve customer experience, and manage supply chain efficiently.
- Healthcare:Healthcare providers utilize Tableau to track patient outcomes, analyze medical records, and identify potential health risks. This allows them to improve patient care, optimize resource allocation, and develop personalized treatment plans.
- Finance:Financial institutions leverage Tableau to analyze market trends, assess investment opportunities, and manage risk. This helps them make informed investment decisions, identify potential fraud, and improve compliance.
- Manufacturing:Manufacturers use Tableau to monitor production processes, track quality control metrics, and identify areas for improvement. This enables them to optimize production efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality.
Tableau Server and Sharing
Tableau Server plays a crucial role in enabling collaboration and sharing of Tableau visualizations within organizations. It acts as a central hub for managing, publishing, and distributing interactive dashboards and reports to various stakeholders.
Deployment Options for Tableau Server
There are two primary deployment options for Tableau Server: on-premises and cloud-based.
Tableau’s a powerful tool for visualizing data, but even with its intuitive interface, a cheat sheet can be a lifesaver for those new to the platform. It’s interesting how Apple’s venturing into architectural design, like with their rumored project building a modern-day pyramid in Malaysia.
Maybe they’ll even incorporate some data visualization elements into the design, which would be a perfect opportunity to put those Tableau skills to use!
- On-premises Deployment:In this option, Tableau Server is installed and managed within the organization’s own data center or infrastructure. This provides greater control over the server environment and data security, but requires significant investment in hardware, software, and IT resources for maintenance and administration.
So you’ve got your Tableau cheat sheet ready, you’re feeling confident about analyzing your data, but what about security? If you’re traveling and accessing sensitive information, a good VPN is a must. I recommend checking out best vpn for travel to keep your data safe.
Once you’ve got your VPN sorted, you can dive back into your Tableau cheat sheet and conquer those data visualizations!
- Cloud-based Deployment:Tableau Server can also be deployed on cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness as the cloud provider manages the infrastructure and resources. It also allows for easier access and collaboration for users across different locations.
Publishing and Sharing Tableau Dashboards and Reports, Tableau business analytics platform a cheat sheet
Once visualizations are created in Tableau Desktop, they can be published to Tableau Server for wider distribution and collaboration.
- Publishing to Tableau Server:Tableau Desktop provides a seamless interface for publishing workbooks containing dashboards and reports to Tableau Server. Users can specify access permissions and manage the visibility of published content.
- Sharing with Stakeholders:Tableau Server offers various mechanisms for sharing published content with stakeholders. These include:
- Direct Links:Users can generate unique links to specific dashboards or reports, which can be shared via email, messaging apps, or embedded in websites.
- Project Sites:Tableau Server allows for creating project sites, which act as centralized repositories for related dashboards and reports. Users can organize and categorize content within these sites for easier navigation and discovery.
- Subscriptions:Tableau Server enables users to set up subscriptions, which automatically deliver dashboards or reports to designated recipients on a regular schedule, such as daily, weekly, or monthly.
- Embed Functionality:Tableau Server allows for embedding interactive dashboards and reports into web pages or applications, providing a seamless integration with other business tools and platforms.
Advanced Tableau Features
Tableau is a powerful data visualization and analysis tool, offering a range of features to help users extract meaningful insights from their data. While the basic features of Tableau are easy to learn and use, advanced features enable users to perform complex analysis and create sophisticated visualizations.
This section explores some of the advanced features of Tableau that can significantly enhance your data analysis capabilities.
Data Blending
Data blending allows you to combine data from multiple data sources into a single visualization. This is particularly useful when your data is spread across different tables or databases. For example, you might want to blend sales data from a CRM system with customer demographics from a separate database.
- Primary Data Source:This is the main data source that defines the structure of the blended view. It typically contains the primary dimensions and measures for your analysis.
- Secondary Data Source:This data source is connected to the primary data source using a common field. The secondary data source can be used to add additional dimensions or measures to the visualization.
- Join Type:Tableau offers various join types, including inner join, left join, right join, and full join. The join type determines which data points are included in the blended view.
For example, you could blend sales data with customer demographics to analyze sales performance by customer age group.
Calculated Fields
Calculated fields allow you to create new fields based on existing data. This is useful for performing calculations, creating custom metrics, and transforming data. You can use a variety of functions and operators to create calculated fields, including:
- Mathematical Operators:+, -, -, /, %
- Logical Operators:AND, OR, NOT
- String Functions:LEFT, RIGHT, LEN, UPPER, LOWER
- Date Functions:DATE, YEAR, MONTH, DAY
For example, you could create a calculated field called “Profit Margin” by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the sales revenue.
Parameters
Parameters are variables that can be used to control the behavior of a visualization. This allows you to create interactive dashboards that users can customize to suit their needs. For example, you could create a parameter to allow users to select a specific date range for their analysis.
- Parameter Type:Parameters can be of various types, including numeric, string, boolean, and date.
- Parameter Values:You can define a set of values for the parameter, or allow users to enter their own values.
- Using Parameters in Calculations:Parameters can be used in calculated fields to dynamically change the calculations based on the selected parameter value.
For example, you could create a parameter to filter sales data by region. Users could then select a specific region from a dropdown list, and the visualization would update to show the sales data for that region.
Custom Visualizations and Extensions
Tableau’s API allows you to create custom visualizations and extensions that can be used to extend the functionality of Tableau. This provides a high level of flexibility and allows you to create visualizations that are tailored to your specific needs.
- Tableau JavaScript API:This API allows you to create custom visualizations using JavaScript. You can create interactive visualizations that respond to user interactions and data changes.
- Tableau Extensions API:This API allows you to create extensions that add new functionality to Tableau. This could include features like custom data connectors, custom filters, or custom actions.
For example, you could create a custom visualization to display a map with interactive markers that show the location of different sales offices.
Performance Optimization and Scalability
As your data volume grows, it’s important to optimize Tableau’s performance and scalability to ensure that your dashboards load quickly and efficiently.
- Data Extraction:Extract your data into a Tableau data extract (.tde or .hyper) to improve performance. Extracts are smaller and faster to query than live connections.
- Data Aggregation:Aggregate your data before loading it into Tableau. This reduces the amount of data that Tableau needs to process.
- Tableau Server Optimization:Optimize Tableau Server by configuring settings such as data source caching, background refresh, and user permissions.
For example, you could extract your sales data into a .hyper file and aggregate it by region to improve the performance of a dashboard that shows sales performance by region.
Tableau Resources and Community
The Tableau platform is rich with resources and a vibrant community to support your learning journey and ongoing use of the software. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, there are ample opportunities to enhance your skills and connect with fellow data enthusiasts.
Official Tableau Resources
Tableau provides a comprehensive suite of official resources to aid your learning and exploration.
- Tableau Help:The official documentation is an invaluable resource for in-depth explanations of features, functionalities, and best practices. It offers step-by-step guides, troubleshooting tips, and detailed explanations of concepts.
- Tableau Desktop Training:Tableau offers a structured training program for Desktop users, covering fundamental concepts and advanced techniques. This program includes video tutorials, interactive exercises, and downloadable resources.
- Tableau Public:A free platform for creating and sharing interactive visualizations, Tableau Public allows you to showcase your work, connect with others, and learn from the diverse projects available in the community.
- Tableau Community Forums:Engage with a vast network of Tableau users through the active community forums. You can ask questions, seek advice, share your experiences, and learn from others’ insights.
- Tableau Blogs and Webinars:Tableau regularly publishes blog posts and hosts webinars featuring industry experts, product updates, and insightful case studies.
The Tableau Community
The Tableau community is a dynamic and supportive network of users, developers, and data enthusiasts. This community fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and professional development.
- Tableau User Groups:Local user groups provide opportunities for in-person networking, knowledge sharing, and skill development. These groups host regular meetings, workshops, and presentations, allowing you to connect with fellow Tableau users in your area.
- Tableau Conference:The annual Tableau Conference brings together thousands of Tableau users from around the world for a week of learning, networking, and inspiration. The conference features keynote speeches, breakout sessions, workshops, and hands-on training.
- Online Communities:Online platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter serve as hubs for connecting with Tableau users, sharing insights, and engaging in discussions. These platforms provide a space for exchanging ideas, asking questions, and staying up-to-date with the latest trends in data visualization.
Real-World Applications of Tableau
Tableau’s versatility and user-friendliness have led to its adoption across various industries, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights from their data.
- Sales and Marketing:Tableau helps businesses track sales performance, analyze customer behavior, and optimize marketing campaigns. By visualizing data on customer demographics, product trends, and campaign effectiveness, businesses can make informed decisions to drive revenue growth.
- Finance and Accounting:Tableau assists financial professionals in analyzing financial data, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), and identifying trends and anomalies. It facilitates budgeting, forecasting, and risk management, providing a comprehensive view of financial health.
- Healthcare:Tableau enables healthcare organizations to analyze patient data, track disease trends, and improve patient outcomes. By visualizing data on patient demographics, treatment effectiveness, and resource allocation, healthcare providers can make informed decisions to enhance patient care.
- Education:Tableau helps educational institutions analyze student performance, track enrollment trends, and optimize resource allocation. By visualizing data on student demographics, academic progress, and program effectiveness, educators can make informed decisions to improve educational outcomes.
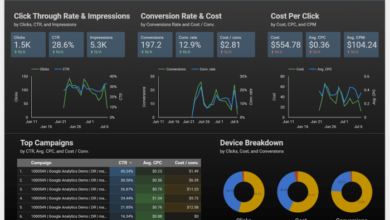
Examples of Tableau Dashboards: Tableau Business Analytics Platform A Cheat Sheet

Tableau dashboards are powerful visual representations of data that can be used to communicate insights, track progress, and make better decisions. They can be customized to meet the specific needs of any business or organization.This section provides several examples of Tableau dashboards, showcasing their versatility and effectiveness in various domains.
These examples demonstrate how Tableau can be used to visualize data, uncover trends, and support decision-making across different industries.
Examples of Tableau Dashboards
| Dashboard | Description | Visual Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Sales Performance Dashboard | This dashboard displays key sales metrics such as revenue, sales by region, and top-performing products. It provides a comprehensive overview of sales performance and helps identify areas for improvement. | The dashboard displays a bar chart showing sales revenue by region, a pie chart showing sales by product category, and a line chart showing sales trends over time. It also includes a table listing the top-performing sales representatives. |
| Customer Churn Dashboard | This dashboard helps businesses understand why customers are leaving and identify potential churn risks. It analyzes customer data to identify factors that contribute to churn and provides insights into customer behavior. | The dashboard includes a heatmap showing churn rates by customer segment, a scatter plot showing the relationship between customer satisfaction and churn, and a table listing customers at risk of churning. |
| Marketing Campaign Performance Dashboard | This dashboard tracks the performance of marketing campaigns across different channels. It provides insights into campaign effectiveness, audience engagement, and return on investment. | The dashboard displays a bar chart showing campaign reach and engagement metrics, a pie chart showing the distribution of campaign spend across channels, and a line chart showing campaign performance over time. |
| Financial Performance Dashboard | This dashboard provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance. It displays key financial metrics such as revenue, expenses, profit, and cash flow. | The dashboard includes a bar chart showing revenue and expenses over time, a line chart showing profit trends, and a table listing key financial ratios. |
Real-World Use Cases
Tableau’s versatility makes it a valuable tool across various industries, enabling organizations to leverage data for informed decision-making and improved business outcomes.
Finance
Financial institutions rely on Tableau to analyze market trends, track investment performance, manage risk, and detect fraud.
- Investment Analysis:Tableau helps investment firms analyze market data, identify investment opportunities, and track portfolio performance. For example, a hedge fund might use Tableau to visualize historical stock prices, market sentiment indicators, and economic data to identify potential investment targets.
- Risk Management:Tableau is used to monitor financial risk by analyzing data from various sources, such as credit reports, market data, and internal systems. This helps financial institutions identify potential risks early and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
- Fraud Detection:Tableau can be used to analyze transaction data and identify unusual patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity. This helps financial institutions prevent financial losses and protect their customers.