Tech Leaders Align IT & Business Strategies: Driving Success
Tech leaders align it business strategies – a concept that’s crucial for any organization seeking to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving landscape. In this digital age, technology is no longer a mere support function; it’s the very backbone of innovation and growth.
The success of any business hinges on the seamless integration of IT and business goals, ensuring that technology fuels the company’s strategic direction.
Misalignment between IT and business objectives can lead to costly inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and even competitive disadvantage. Conversely, companies that prioritize aligning their IT strategies with their business goals often achieve significant competitive advantage. They can leverage technology to drive innovation, enhance customer experiences, and optimize operations for maximum efficiency.
The Importance of Alignment
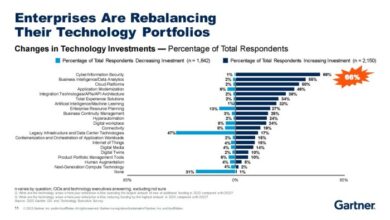
In the dynamic world of business, aligning IT and business strategies is not just a good practice; it’s a critical factor for organizational success. This alignment ensures that IT investments directly support business goals, leading to enhanced efficiency, innovation, and ultimately, a competitive edge.
The Consequences of Misalignment
When IT and business strategies are misaligned, organizations face several challenges that can hinder their growth and profitability. The lack of a shared vision can lead to wasted resources, inefficient processes, and a failure to capitalize on emerging technologies. For instance, if a company invests heavily in cloud computing without considering its impact on existing business processes, it may face integration challenges, increased costs, and reduced productivity.
Just like tech leaders need to align their IT strategies with business goals for optimal performance, a delicious dessert like a peaches whiskey ice cream float requires a perfect balance of sweet, creamy, and boozy flavors. By blending these elements, you create a truly satisfying experience, just as tech leaders strive to create seamless and efficient workflows within their organizations.
Examples of Successful Alignment
Several companies have demonstrated the benefits of strong IT-business alignment. Amazon, for example, has achieved remarkable success by prioritizing customer experience and leveraging technology to enhance its e-commerce platform. Its investment in cloud computing, data analytics, and machine learning has enabled it to personalize customer interactions, optimize logistics, and offer a seamless shopping experience.
Similarly, Netflix has revolutionized the entertainment industry by aligning its IT strategy with its business objective of providing on-demand streaming services. By investing in a robust streaming infrastructure and data-driven content recommendations, Netflix has captured a significant market share and become a global leader in entertainment.
Key Drivers of Alignment
The need for IT-business alignment is driven by a confluence of factors that underscore the critical role technology plays in achieving business objectives. This alignment ensures that IT investments directly support strategic goals, fostering innovation and agility in today’s dynamic business landscape.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The emergence of transformative technologies like AI, cloud computing, and big data has significantly impacted the need for IT-business alignment. These technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for organizations to gain a competitive edge, but their successful implementation hinges on a deep understanding of business needs and objectives.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered solutions, from chatbots to predictive analytics, are rapidly changing how businesses operate. To leverage AI effectively, organizations need to identify specific business problems that AI can address and align IT resources accordingly. For example, a retail company might use AI to personalize customer experiences, while a manufacturing company might use it to optimize production processes.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud adoption has accelerated the shift towards agile and scalable IT infrastructure. Businesses are increasingly relying on cloud-based services to access computing power, storage, and software on demand. This shift necessitates aligning IT strategies with cloud adoption, considering factors like data security, compliance, and cost optimization.
- Big Data: The exponential growth of data has created a need for robust data management and analytics capabilities. Organizations need to align IT investments with data storage, processing, and analysis solutions to extract meaningful insights from big data. This can involve developing data governance policies, implementing data warehousing solutions, and investing in data science expertise.
The Changing Nature of Business
The business landscape is constantly evolving, driven by factors like globalization, digital transformation, and customer expectations. These changes demand agility and adaptability from organizations, making IT alignment even more crucial.
- Globalization: Businesses are increasingly operating in global markets, requiring IT systems that can handle diverse languages, currencies, and regulations. IT alignment should ensure that technology supports international expansion and cross-border operations.
- Digital Transformation: Businesses are embracing digital technologies to improve customer experiences, streamline operations, and create new revenue streams. IT alignment is essential to support this transformation, ensuring that technology enables innovation and digital initiatives. For example, a traditional brick-and-mortar retailer might need to align IT resources with the development of an e-commerce platform.
- Customer Expectations: Customers today expect seamless, personalized experiences across all channels. IT alignment is crucial to ensure that technology meets these expectations, providing access to information, products, and services in a convenient and engaging manner.
Strategies for Achieving Alignment

Now that we understand the importance of aligning IT and business strategies and the key drivers that contribute to this alignment, let’s explore practical strategies to make it a reality. This section will delve into best practices, frameworks, and methodologies for fostering a shared vision and understanding between IT and business leaders.
Tech leaders are constantly looking for ways to streamline operations and enhance user experiences, and this quest for innovation often leads to surprising partnerships. For example, the integration of gesture control technology into wearable devices, like the Apple Watch band that allows for hands-free gesture controls , exemplifies how tech leaders are embracing new functionalities to align their business strategies with user needs.
Best Practices for Aligning IT and Business Strategies
Achieving alignment between IT and business strategies requires a proactive approach. Here are some best practices to guide your efforts:
- Establish a Shared Vision and Language:Both IT and business leaders must agree on a common vision for the organization’s future. This vision should be translated into a shared language that everyone understands, ensuring everyone is working towards the same goals.
- Develop a Collaborative Framework:Create a collaborative framework that encourages regular communication and interaction between IT and business teams. This could involve joint planning sessions, cross-functional teams, and shared decision-making processes.
- Focus on Business Outcomes:IT projects and initiatives should be aligned with specific business outcomes. Instead of focusing solely on technology, prioritize the impact of technology on achieving business goals.
- Embrace Agile and Iterative Approaches:Adopt agile and iterative methodologies to adapt to changing business needs. This allows for continuous feedback and adjustments to ensure IT strategies remain aligned with evolving business priorities.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration:Cultivate a culture of collaboration and mutual understanding between IT and business teams. This can be achieved through cross-training, joint projects, and social events that encourage interaction and knowledge sharing.
Framework for Establishing a Shared Vision and Understanding
A structured framework can help guide the alignment process. Consider these key elements:
- Executive Sponsorship:Strong executive sponsorship is crucial for driving alignment. Leaders from both IT and business should champion the initiative and provide the necessary resources and support.
- Strategic Planning Alignment:IT and business strategies should be developed and reviewed together. This ensures that IT investments and initiatives are aligned with the organization’s overall strategic goals.
- Regular Communication and Feedback:Establish regular communication channels between IT and business leaders to share progress, discuss challenges, and provide feedback. This can include joint meetings, presentations, and reports.
- Performance Measurement and Tracking:Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure the impact of IT investments on business outcomes. Regularly track and monitor these metrics to assess alignment and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement:Alignment is an ongoing process. Regularly review and adjust strategies and practices to ensure they remain relevant and effective in meeting changing business needs.
Alignment Methodologies
Various methodologies can be employed to achieve alignment. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific context and organizational needs.
| Methodology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) | Provides a comprehensive framework for IT service management, promoting best practices and standardization. | Can be complex and require significant effort to implement. May not be suitable for all organizations. |
| TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) | Offers a structured approach to enterprise architecture, enabling alignment between IT and business goals. | Can be complex and require specialized expertise. May not be suitable for small or agile organizations. |
| Agile Project Management | Promotes iterative development and collaboration, allowing for flexibility and adaptability to changing business needs. | May require a shift in organizational culture and mindset. Can be challenging to implement for complex projects. |
| Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | Focuses on streamlining and improving business processes, potentially leading to significant efficiency gains. | Can be disruptive and require significant investment. May require extensive organizational change. |
| Lean Management | Emphasizes efficiency and waste reduction, promoting alignment by focusing on value creation for the customer. | May require a change in organizational culture and mindset. Can be challenging to implement in complex organizations. |
Roles and Responsibilities
Successfully aligning IT and business strategies requires a clear understanding of roles and responsibilities. Both IT and business leaders play crucial roles in this process, and their collaborative efforts are essential for achieving successful outcomes.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
Effective alignment demands a clear division of roles and responsibilities between IT and business leaders. While the specific responsibilities may vary based on the organization’s structure and industry, here’s a general overview:
IT Leaders
- Understanding Business Needs:IT leaders must actively engage with business stakeholders to understand their strategic goals, pain points, and technology requirements.
- Translating Business Needs into Technology Solutions:IT leaders are responsible for translating business requirements into feasible and effective technology solutions. This involves selecting the right technologies, developing implementation plans, and ensuring alignment with overall business objectives.
- Developing and Managing IT Infrastructure:IT leaders oversee the development, maintenance, and security of IT infrastructure, ensuring it supports the business’s current and future needs.
- Managing IT Budget and Resources:IT leaders are responsible for managing IT budgets, allocating resources effectively, and ensuring the efficient use of IT investments.
- Building and Leading High-Performing IT Teams:IT leaders play a crucial role in attracting, developing, and motivating skilled IT professionals to deliver on the organization’s technology strategy.
Business Leaders
- Defining Business Strategies and Objectives:Business leaders are responsible for setting the overall business strategy, defining key performance indicators (KPIs), and establishing clear objectives for the organization.
- Communicating Business Requirements to IT:Business leaders must effectively communicate their needs and expectations to IT, providing clear and concise descriptions of their requirements and desired outcomes.
- Prioritizing IT Investments:Business leaders play a vital role in prioritizing IT investments, ensuring they align with the organization’s strategic goals and financial constraints.
- Championing IT Initiatives:Business leaders must champion IT initiatives within the organization, fostering a culture of collaboration and understanding between IT and business teams.
- Ensuring Business Processes are Optimized:Business leaders are responsible for ensuring that business processes are optimized and streamlined, leveraging technology to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Importance of Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration between IT and business teams are fundamental to achieving successful alignment.
“The most important factor in successful IT-business alignment is open and honest communication between IT and business leaders.”
[Source
Gartner]
Here’s why communication and collaboration are essential:
- Bridging the Gap:Communication helps bridge the gap between IT and business, ensuring both teams understand each other’s perspectives, challenges, and goals.
- Shared Understanding:Open communication fosters a shared understanding of business needs and technology capabilities, leading to more effective solutions and decision-making.
- Faster Problem Solving:Collaboration enables faster problem-solving by facilitating the exchange of ideas, insights, and expertise between IT and business teams.
- Increased Efficiency:Effective communication and collaboration streamline processes, reduce redundancies, and improve overall efficiency.
- Improved Decision Making:When IT and business teams work together, they can make more informed and strategic decisions, leading to better outcomes for the organization.
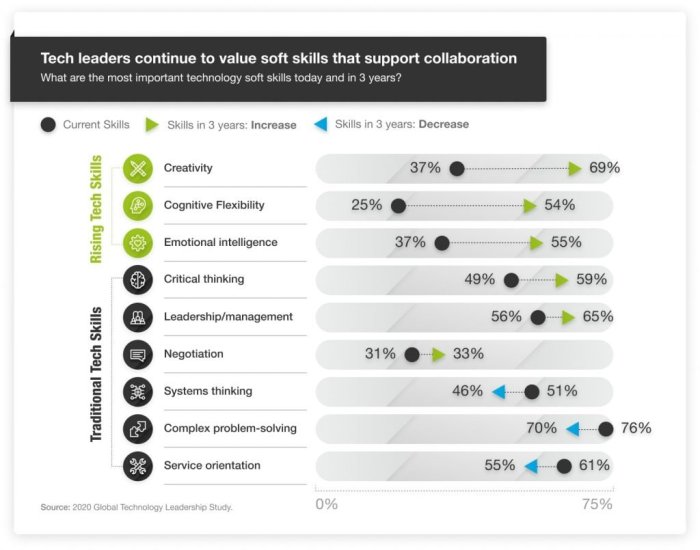
Key Skills and Competencies
Effective IT-business alignment requires a set of key skills and competencies from both IT and business leaders.
Tech leaders are increasingly recognizing the importance of aligning IT strategies with business goals, and this includes prioritizing the well-being of their workforce. This is especially crucial for cybersecurity analysts, who face constant pressure and stress. Understanding the mental health challenges of these professionals, such as burnout and anxiety, is vital.
Organizations can support their cybersecurity teams by fostering a healthy work environment and providing resources like access to mental health professionals. Mental health cybersecurity analysts are more likely to be engaged and effective, contributing to a more secure and resilient organization.
IT Leaders
| Skill/Competency | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Acumen | Understanding of business principles, market dynamics, and financial concepts. |
| Communication Skills | Ability to effectively communicate technical information to non-technical audiences. |
| Relationship Building | Ability to build strong relationships with business stakeholders, fostering trust and collaboration. |
| Problem-Solving Skills | Ability to identify and solve complex technical and business challenges. |
| Strategic Thinking | Ability to think strategically, aligning IT plans with the organization’s overall business objectives. |
Business Leaders
| Skill/Competency | Description |
|---|---|
| Technology Awareness | Understanding of current and emerging technologies, their potential impact on the business, and their role in achieving strategic goals. |
| Data Literacy | Ability to understand and interpret data, making informed decisions based on data insights. |
| Process Optimization | Ability to identify and improve business processes, leveraging technology to enhance efficiency. |
| Change Management | Ability to effectively manage organizational change, ensuring smooth adoption of new technologies and processes. |
| Collaboration Skills | Ability to work effectively with IT teams, fostering a culture of partnership and mutual understanding. |
Measuring Alignment Success: Tech Leaders Align It Business Strategies
While aligning IT and business strategies is crucial, it’s equally important to measure the effectiveness of this alignment. This ensures that the efforts are truly delivering value and driving desired outcomes. Measuring alignment success requires a clear understanding of key metrics, tracking mechanisms, and the challenges associated with quantifying progress.
Key Metrics for Measuring Alignment Effectiveness, Tech leaders align it business strategies
The effectiveness of IT-business alignment can be measured using a range of metrics, each providing insights into different aspects of the alignment process. These metrics can be broadly categorized into three areas:
- Business Performance Metrics: These metrics directly reflect the impact of IT on business goals. Examples include:
- Revenue growth
- Customer satisfaction
- Market share
- Profitability
- Time-to-market
- IT Performance Metrics: These metrics focus on the efficiency and effectiveness of IT operations and their alignment with business needs. Examples include:
- IT service availability
- IT cost optimization
- IT project success rate
- IT infrastructure utilization
- IT security incidents
- Alignment Process Metrics: These metrics measure the effectiveness of the alignment process itself, focusing on collaboration, communication, and feedback loops. Examples include:
- Number of joint IT-business initiatives
- Frequency of IT-business meetings
- IT-business communication channels
- Feedback on IT-business collaboration
- Alignment score based on surveys or assessments
Tracking and Measuring Alignment Progress
Tracking and measuring alignment progress involves implementing systems and processes to collect data on the chosen metrics and analyze the results. Some common methods include:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Companies can define specific KPIs related to IT-business alignment, such as IT project success rate, customer satisfaction with IT services, or the percentage of IT initiatives aligned with business priorities. Tracking these KPIs over time provides insights into progress and areas for improvement.
- Dashboards and Reporting: Interactive dashboards can be used to visualize key metrics, providing real-time insights into alignment progress. These dashboards can also be used to track trends, identify potential issues, and support decision-making. Regular reporting can further highlight key findings and areas for focus.
- Surveys and Feedback Mechanisms: Regular surveys can be conducted among IT and business stakeholders to gather feedback on the effectiveness of alignment efforts. These surveys can assess collaboration, communication, and the perceived impact of IT on business goals. Feedback mechanisms can be integrated into project management systems or used as part of regular performance reviews.
Challenges Associated with Quantifying Alignment Success
While measuring alignment success is crucial, it presents several challenges:
- Defining Measurable Metrics: Selecting the right metrics for measuring alignment success can be challenging. Metrics should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). It’s important to avoid metrics that are too generic or difficult to quantify.
- Data Availability and Accuracy: Accurate and reliable data is essential for meaningful measurement. Companies need to ensure data is collected consistently, accurately, and from relevant sources. Data silos and inconsistencies can make it difficult to get a clear picture of alignment progress.
- Attribution Challenges: Attributing business success to IT alignment can be complex. Many factors contribute to business performance, and it’s challenging to isolate the impact of IT alignment alone. This requires careful analysis and consideration of other contributing factors.
- Subjectivity and Perception: Alignment success can be influenced by subjective perceptions and opinions. Different stakeholders may have varying views on what constitutes successful alignment. This can lead to inconsistencies in measurement and interpretation.
Future Trends in IT-Business Alignment
The landscape of IT-business alignment is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting business priorities. Emerging trends are reshaping how organizations approach this crucial relationship, demanding a more dynamic and collaborative approach.
Agile Methodologies and DevOps
Agile methodologies and DevOps have emerged as critical drivers of IT-business alignment, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and rapid response to changing market demands. Agile principles promote iterative development and close collaboration between IT and business teams, enabling faster delivery of value and enhanced responsiveness.
DevOps, on the other hand, emphasizes automation and integration across the entire software development lifecycle, breaking down silos and streamlining workflows.
“Agile and DevOps are not just about technology; they are about creating a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.”
Impact of Digital Transformation on Alignment Strategies
Digital transformation is fundamentally changing the way businesses operate, requiring a complete overhaul of IT-business alignment strategies. Organizations are increasingly adopting cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, necessitating a more flexible and scalable IT infrastructure. Digital transformation also demands a shift in mindset, encouraging businesses to embrace innovation and experiment with new technologies.
This requires a strong partnership between IT and business leaders to identify opportunities, manage risks, and drive digital initiatives.
Preparing for the Future of IT-Business Alignment
To thrive in the evolving digital landscape, organizations must proactively prepare for the future of IT-business alignment. This includes:
- Embracing a Data-Driven Approach:Data analytics plays a crucial role in optimizing IT investments and driving business outcomes. Organizations should leverage data insights to understand user behavior, identify opportunities, and measure the impact of IT initiatives.
- Developing a Culture of Innovation:A culture that embraces experimentation and continuous improvement is essential for staying ahead of the curve. Organizations should encourage their IT and business teams to explore new technologies and solutions, fostering a spirit of innovation.
- Investing in Talent and Skills:The future of IT-business alignment hinges on having the right talent and skills. Organizations should invest in training and development programs to equip their workforce with the necessary knowledge and expertise to navigate the complexities of digital transformation.