VMware ESXi, Ransomware, and Cicada3301: A Cyber Threat Analysis
VMware ESXi ransomware Cicada3301 – the very mention of these words sends shivers down the spines of IT professionals. The rise of ransomware attacks targeting VMware ESXi environments has become a serious concern, and the mysterious cyber group Cicada3301 adds another layer of intrigue to this already complex issue.
While the exact nature of Cicada3301 remains shrouded in mystery, their alleged involvement in ransomware attacks targeting ESXi systems has sparked a wave of concern and investigations. This blog delves into the heart of this cyber threat, exploring the vulnerabilities, attack methods, and defense strategies necessary to combat this growing menace.
The core functionality of VMware ESXi revolves around virtualization, enabling organizations to consolidate multiple physical servers into a single, centralized platform. This powerful technology streamlines server management, optimizes resource utilization, and enhances scalability. However, the very features that make ESXi so valuable also make it a tempting target for attackers.
Ransomware groups, like Cicada3301, exploit vulnerabilities within ESXi to gain unauthorized access, encrypt critical data, and hold organizations hostage for ransom. The impact of such attacks can be devastating, disrupting operations, causing financial losses, and compromising sensitive information. Understanding the intricacies of this threat, from the vulnerabilities exploited to the tactics employed by attackers, is crucial for developing effective defense strategies.
VMware ESXi: Vmware Esxi Ransomware Cicada3301
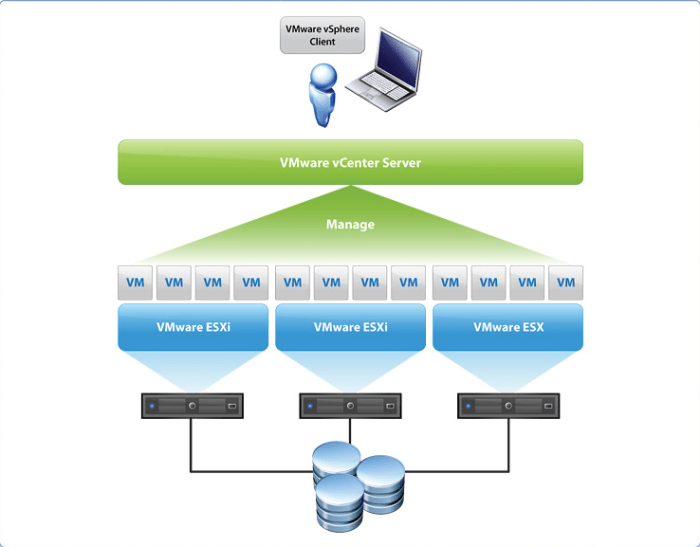
VMware ESXi is a powerful hypervisor that forms the foundation of modern data centers and cloud environments. It plays a pivotal role in server virtualization, enabling organizations to consolidate physical servers into virtual machines (VMs) and manage them efficiently.
Core Functionalities of VMware ESXi
ESXi acts as a thin layer of software that sits directly on top of the physical hardware, providing a platform for running virtual machines. It handles the core functions of managing resources, such as CPU, memory, storage, and networking, allowing multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical server.
The recent wave of ransomware attacks targeting VMware ESXi servers, attributed to the mysterious group Cicada3301, is a stark reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape. This incident highlights the need for robust security measures, especially as reports like akamai report lockbit cl0p expand ransomware efforts indicate that ransomware groups like LockBit and Cl0p are constantly refining their tactics and expanding their operations.
Understanding the motivations and methods behind these attacks is crucial to proactively defend against them, especially as the targeting of critical infrastructure and essential services becomes increasingly prevalent.
This virtualization capability brings significant benefits, including increased server utilization, reduced hardware costs, and improved agility in deploying and managing applications.
Key Features and Benefits of VMware ESXi
ESXi offers a range of features that contribute to its effectiveness and popularity in IT infrastructure:
- Virtual Machine Management:ESXi provides tools for creating, configuring, and managing virtual machines, allowing for easy deployment and scaling of workloads.
- Resource Allocation:ESXi enables precise allocation of resources to virtual machines, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization.
- High Availability:Features like vMotion and Fault Tolerance allow for seamless migration of virtual machines between hosts, ensuring continuous availability and minimizing downtime.
- Storage Management:ESXi supports various storage technologies, including SANs, NAS, and local storage, providing flexibility and scalability for data storage.
- Networking:ESXi offers advanced networking capabilities, including virtual switches and VLANs, enabling efficient network management and connectivity for virtual machines.
- Security:ESXi includes robust security features, such as access control, encryption, and anti-malware protection, to safeguard virtual environments from threats.
Examples of ESXi Use Cases
Organizations across various industries leverage ESXi for a wide range of applications and workloads:
- Server Consolidation:By virtualizing servers, organizations can reduce the number of physical servers needed, lowering hardware costs and simplifying management.
- Cloud Infrastructure:ESXi is a key component of private and hybrid cloud deployments, enabling organizations to build flexible and scalable cloud environments.
- Desktop Virtualization:ESXi can be used to host virtual desktops, allowing users to access their desktops from any device, improving mobility and flexibility.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC):ESXi is used in HPC environments to run demanding applications, such as scientific simulations and financial modeling.
- DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):ESXi provides a platform for deploying and managing development and testing environments, enabling faster software delivery cycles.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks have become an increasingly prevalent and devastating threat to organizations of all sizes, particularly those reliant on critical infrastructure. These attacks leverage malicious software to encrypt sensitive data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. The consequences of such attacks can be catastrophic, leading to significant financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
Impact on Critical Infrastructure
Ransomware attacks pose a significant threat to critical infrastructure, which encompasses essential services like power grids, water treatment plants, healthcare facilities, and transportation networks. The disruption of these services can have far-reaching consequences, affecting public safety, economic stability, and national security.
“Ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure can have a ripple effect, impacting not only the targeted organization but also its customers, suppliers, and the broader community.”
Common Tactics Employed by Ransomware Attackers
Ransomware attackers employ a variety of tactics to infiltrate and compromise their targets. These tactics often involve exploiting vulnerabilities in software, networks, and user behavior.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
Ransomware attackers actively seek out and exploit vulnerabilities in software and operating systems. These vulnerabilities can be present in applications, operating systems, or network devices. Once exploited, attackers can gain unauthorized access to systems and deploy ransomware.
Data Encryption
The primary objective of ransomware attacks is to encrypt sensitive data, making it inaccessible to the victim. This encryption is typically achieved using strong cryptographic algorithms, making it difficult or impossible to decrypt the data without the attacker’s decryption key.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Ransomware attackers often employ phishing and social engineering tactics to trick users into downloading malicious software or revealing sensitive information. These tactics can involve sending emails with malicious attachments, creating fake websites, or using social media platforms to spread malware.
High-Profile Ransomware Attacks Targeting VMware ESXi Environments
Several high-profile ransomware attacks have targeted VMware ESXi environments, highlighting the vulnerability of these systems to malicious actors.
- The REvil Ransomware Attack on Kaseya:In July 2021, the REvil ransomware group launched a large-scale attack targeting Kaseya, a software company that provides IT management solutions to thousands of organizations worldwide. The attack exploited a vulnerability in Kaseya’s VSA software, which is used to manage VMware ESXi servers.
This attack resulted in the disruption of services for hundreds of organizations, including grocery stores, schools, and gas stations.
- The Conti Ransomware Attack on the Colonial Pipeline:In May 2021, the Conti ransomware group targeted the Colonial Pipeline, a major oil pipeline in the United States. The attack led to a shutdown of the pipeline, causing fuel shortages and panic buying across the East Coast. While the attack did not directly target VMware ESXi environments, it demonstrated the potential impact of ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure.
The recent VMware ESXi ransomware attacks attributed to Cicada3301 have highlighted the importance of robust security measures, especially in critical infrastructure environments. While the attackers leveraged vulnerabilities to gain access, understanding how to navigate and manage systems effectively is crucial.
Learning how to use the command line interface in Microsoft systems, as detailed in this article , can empower you to proactively monitor and secure your infrastructure, potentially mitigating the risk of such attacks.
Cicada3301
Cicada3301 is a mysterious online entity that has been active since 2012. Its enigmatic nature, characterized by intricate puzzles and cryptic messages, has sparked widespread interest and speculation about its origins, purpose, and motivations.
Cicada3301’s Online Presence and Activities
Cicada3301’s online presence is primarily characterized by its use of puzzles and challenges. These puzzles, often presented as digital scavenger hunts, require participants to solve complex riddles, decrypt encrypted messages, and decipher hidden clues. The puzzles typically involve a variety of disciplines, including cryptography, computer programming, and digital forensics.
The group’s activities often involve recruiting individuals with specialized skills, seemingly for unknown purposes. The recruitment process is selective and often involves solving intricate puzzles and completing challenging tasks.
Alleged Connection to Ransomware Attacks and Potential Motivations, Vmware esxi ransomware cicada3301
While Cicada3301’s exact motivations remain unclear, there have been allegations linking the group to ransomware attacks. The group’s advanced technical capabilities and its recruitment of individuals with expertise in cryptography and security suggest a potential link to cybercrime. However, there is no concrete evidence to directly connect Cicada3301 to specific ransomware attacks.Some speculate that the group’s activities may be related to intelligence gathering, social engineering, or the development of advanced cyberweapons.
Others believe that Cicada3301 is a purely intellectual challenge, with no malicious intent.
Links to VMware ESXi Attacks
There is no publicly available evidence to suggest a direct link between Cicada3301 and the recent ransomware attacks targeting VMware ESXi environments. The attacks, attributed to various ransomware groups, exploit vulnerabilities in ESXi servers to gain access and encrypt data.
While Cicada3301’s expertise in cryptography and its recruitment practices might suggest a potential role in such attacks, there is no concrete evidence to support this connection.
Vulnerabilities and Exploitation
The recent wave of ransomware attacks targeting VMware ESXi servers has highlighted critical vulnerabilities within the platform, exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access and compromise sensitive data. Understanding these vulnerabilities and the methods used by attackers is crucial for mitigating future threats and strengthening the security posture of ESXi environments.
Vulnerabilities Exploited by Ransomware Attackers
These vulnerabilities have been exploited by ransomware attackers, enabling them to gain unauthorized access to ESXi systems and deploy malicious payloads:
- OpenSSH Authentication Bypass:This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms in OpenSSH, a widely used remote access protocol, by exploiting weaknesses in the implementation of the ‘PermitRootLogin’ setting. By exploiting this vulnerability, attackers can gain root access to ESXi systems without requiring valid credentials.
The recent wave of ransomware attacks targeting VMware ESXi servers, linked to the mysterious Cicada3301 group, highlights the urgent need for robust security solutions. While investigating these attacks, I stumbled upon the Microsoft Security Copilot Experience Center , which offers a promising approach to proactive threat detection and response.
This innovative platform leverages AI and automation to streamline security tasks, potentially providing a valuable tool in the fight against sophisticated threats like those targeting VMware ESXi systems.
- VMware vCenter Server Proxy Service:This vulnerability, affecting older versions of VMware vCenter Server, allows attackers to exploit a remote code execution (RCE) flaw in the vCenter Server Proxy Service. By sending specially crafted HTTP requests to the proxy service, attackers can execute arbitrary code on the ESXi host, enabling them to install malware and gain control of the system.
- VMware ESXi Guest Operating System (OS) File Access:This vulnerability allows attackers to gain access to files within guest operating systems running on ESXi hosts. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability to steal sensitive data, deploy ransomware, or compromise other systems within the virtualized environment.
Methods Used by Attackers to Gain Unauthorized Access
Attackers employ various methods to exploit these vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to ESXi systems:
- Brute-force Attacks:Attackers use automated scripts to try various combinations of usernames and passwords, attempting to guess valid credentials. This method is effective against systems with weak or easily guessable passwords.
- Phishing and Social Engineering:Attackers send malicious emails or messages, disguised as legitimate communications, to trick users into revealing their credentials or downloading malware. This technique leverages human error and trust to gain access to systems.
- Exploiting Publicly Known Vulnerabilities:Attackers leverage publicly available information about vulnerabilities to exploit known weaknesses in ESXi systems. They often use automated tools and scripts to scan for vulnerable systems and launch attacks.
- Scanning for Open Ports and Services:Attackers scan networks for open ports and services, identifying potential entry points into ESXi systems. They may use tools like Nmap to scan for vulnerable services and exploit any weaknesses they discover.
Impact of Exploited Vulnerabilities
The exploitation of these vulnerabilities can have severe consequences for organizations, including:
- Data Breaches:Attackers can access and steal sensitive data stored on ESXi hosts, including customer information, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Ransomware Infections:Attackers can deploy ransomware, encrypting critical data and demanding payment for its decryption. This can cripple business operations and result in significant financial losses.
- System Disruptions:Attackers can disrupt or disable ESXi hosts, leading to downtime and loss of productivity. This can affect critical services and applications, impacting business operations.
- Reputation Damage:Data breaches and ransomware attacks can damage an organization’s reputation, erode customer trust, and lead to legal and regulatory scrutiny.
Defense Strategies
Ransomware attacks on VMware ESXi servers pose a significant threat to organizations, disrupting operations and potentially leading to data loss. However, by implementing a comprehensive security strategy, organizations can significantly mitigate the risk of such attacks. This strategy should encompass proactive measures, such as regular patching, strict access control, and robust data backups, alongside the deployment of specialized security tools.
Best Practices for Securing VMware ESXi Environments
To effectively protect your VMware ESXi environments against ransomware attacks, follow these best practices:
- Patch Regularly:Keep your ESXi hosts, vCenter Server, and other related software up to date with the latest security patches. This addresses vulnerabilities that ransomware attackers exploit.
- Implement Strong Passwords:Use complex and unique passwords for all administrative accounts, including root and vCenter Server accounts. Avoid using default passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):Implement 2FA for all administrative accounts to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Restrict Network Access:Limit network access to ESXi hosts and vCenter Server to authorized users and systems only. This reduces the attack surface.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity:Regularly monitor system logs and network traffic for any unusual activity that could indicate a ransomware attack.
- Implement Security Best Practices:Adhere to security best practices for managing virtualized environments, including proper user account management, regular security audits, and the principle of least privilege.
Comprehensive Security Strategy
A comprehensive security strategy for protecting VMware ESXi environments should include the following key elements:
- Patch Management:Establish a robust patch management process to ensure that all ESXi hosts, vCenter Server, and other related software are patched promptly and consistently. This includes testing patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to production.
- Access Control:Implement strict access control measures to limit access to ESXi hosts and vCenter Server to authorized personnel. This can be achieved through role-based access control (RBAC), where users are granted specific permissions based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Data Backups:Regularly back up all critical data and ensure that backups are stored in a secure, off-site location. This allows for data recovery in the event of a ransomware attack.
- Security Monitoring:Implement security monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity and potential threats. These tools can monitor system logs, network traffic, and other relevant data for anomalies.
- Security Awareness Training:Provide regular security awareness training to all users to educate them about ransomware threats and best practices for preventing attacks. This includes training on identifying phishing emails, recognizing suspicious links, and practicing safe browsing habits.
Security Tools and Technologies
| Security Tool/Technology | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| VMware vCenter Server | Centralized management console for VMware ESXi environments, providing comprehensive visibility and control over virtual machines, hosts, and resources. | Improved visibility and control over ESXi environments, facilitating proactive security management and incident response. |
| Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | A security tool that monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and alerts administrators to potential threats. | Early warning system for detecting malicious activity, enabling timely intervention and mitigating potential damage. |
| Network Segmentation | Dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to restrict the spread of malware and limit the impact of security breaches. | Reduced attack surface by isolating sensitive systems and preventing lateral movement of attackers. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | A security measure that requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, to access systems. | Stronger security posture by making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to systems. |
| Anti-Malware Software | Software designed to detect and remove malware, including ransomware, from systems. | Protection against known ransomware threats, reducing the risk of infection and data loss. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Software that monitors data movement and prevents sensitive information from leaving the organization’s network without authorization. | Protection against data exfiltration and ransomware attacks that target sensitive data. |
Recovery and Remediation
Recovering from a ransomware attack targeting VMware ESXi requires a systematic approach that combines data restoration, system remediation, and incident response procedures. This section Artikels the crucial steps involved in restoring data from backups, remediating infected systems, and managing the aftermath of such an attack.
Data Restoration
Restoring data from backups is the cornerstone of recovering from a ransomware attack. It’s essential to have a robust backup strategy in place, ensuring that backups are regularly created, stored off-site, and regularly tested for their integrity and recoverability.
- Verify Backup Integrity:Before attempting to restore data, it’s crucial to verify the integrity of the backups. This involves ensuring that the backups are complete, up-to-date, and not corrupted. Utilize checksums or other validation methods to confirm the authenticity of the backup data.
- Select the Appropriate Backup:Identify the most recent backup that predates the ransomware attack. This ensures that the restored data is free from any malicious modifications introduced by the ransomware.
- Restore Data to a Clean Environment:Restore the backed-up data to a clean, isolated environment, preferably a different physical or virtual machine. This minimizes the risk of re-infection during the restoration process.
- Test Restored Data:After restoring the data, thoroughly test its functionality to ensure that it’s operational and free from any residual malware. This step is crucial to confirm that the restored data is usable and that the ransomware has been successfully removed.
System Remediation
Remediating infected systems involves eliminating the ransomware, restoring system configurations, and implementing security measures to prevent future attacks.
- Isolate Infected Systems:Disconnect infected systems from the network to prevent the spread of the ransomware to other systems. This isolation step is crucial in containing the attack and preventing further damage.
- Remove Ransomware:Identify and remove the ransomware from the infected systems. This may involve using antivirus software, specialized ransomware removal tools, or manual removal techniques.
- Restore System Configuration:Restore the system configuration to a known good state. This may involve reinstalling the operating system, restoring system files from backups, or using system restore points.
- Update Security Software:Update antivirus and endpoint security software to the latest versions. This ensures that the system is protected against the latest ransomware threats and vulnerabilities.
- Patch Vulnerabilities:Patch all known vulnerabilities in the operating system, applications, and other software components. This includes applying security updates and patches released by vendors to address known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by ransomware.
Incident Response Procedures
Responding to a ransomware attack requires a coordinated effort involving various stakeholders. Effective communication and collaboration are essential for a successful incident response.
- Activate Incident Response Plan:Trigger the organization’s incident response plan, which Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. This plan should include clear roles and responsibilities for different teams and individuals involved in the response.
- Gather Evidence:Collect evidence of the ransomware attack, including system logs, network traffic data, and other relevant information. This evidence is crucial for forensic analysis and determining the extent of the attack.
- Communicate with Stakeholders:Communicate the incident to relevant stakeholders, including management, IT staff, legal counsel, and other affected parties. Provide timely updates on the incident response progress, the impact of the attack, and any potential risks.
- Report the Incident:Report the incident to law enforcement agencies and relevant authorities. This is essential for tracking ransomware activity, identifying attackers, and potentially recovering stolen data.
The Future of ESXi Security
The recent wave of ransomware attacks targeting VMware ESXi servers highlights the urgent need for a proactive approach to security. While organizations have focused on patching vulnerabilities and implementing defensive measures, the evolving threat landscape necessitates a shift towards anticipating and mitigating future attacks.
Emerging Security Trends and Threats
The security landscape is constantly evolving, and ESXi environments are not immune to new threats. Here are some emerging trends and threats that could impact ESXi security in the future:
- Sophisticated Attack Techniques:Ransomware actors are constantly developing more sophisticated attack techniques, such as zero-day exploits and supply chain attacks. These techniques can bypass traditional security measures and exploit vulnerabilities that have not yet been identified or patched.
- AI-Powered Attacks:The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in cyberattacks is becoming increasingly common. AI-powered tools can automate the process of identifying vulnerabilities, exploiting them, and spreading malware. This can make it more difficult to detect and respond to attacks.
- Increased Use of Cloud Services:Organizations are increasingly migrating their workloads to the cloud. While this can offer benefits in terms of scalability and cost savings, it also introduces new security challenges. Attackers can target cloud-based services and compromise ESXi servers connected to these services.
- The Rise of IoT Devices:The growing number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices presents new attack vectors. Attackers can compromise IoT devices and use them as stepping stones to gain access to ESXi servers.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Attack Vectors
Organizations need to proactively identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors in their ESXi environments. These include:
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities:ESXi servers are regularly updated with security patches. However, organizations may not be aware of all vulnerabilities or may not apply patches in a timely manner. This can leave their servers exposed to attack.
- Misconfigured Security Settings:Incorrectly configured security settings can create vulnerabilities. For example, weak passwords, open ports, and lack of proper access control can make it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access to ESXi servers.
- Lack of Monitoring and Logging:Organizations need to monitor their ESXi environments for suspicious activity. Proper logging can help identify and investigate attacks. However, many organizations lack adequate monitoring and logging capabilities.
- Third-Party Software Vulnerabilities:ESXi servers often rely on third-party software, such as drivers, agents, and plugins. These software components can have vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Proactive Security Measures
To stay ahead of the curve and ensure the long-term security of their ESXi environments, organizations should implement the following proactive security measures:
- Implement a Robust Patching Strategy:Organizations should develop a comprehensive patching strategy that includes regular updates and the prompt application of security patches. This should involve a clear process for evaluating, testing, and deploying patches, and should be prioritized based on the severity of the vulnerability.
- Secure Configuration and Hardening:Organizations should implement best practices for securing ESXi servers, including the use of strong passwords, access control policies, and network segmentation. They should also configure ESXi servers to minimize the attack surface by disabling unnecessary services and protocols.
- Enable Logging and Monitoring:Organizations should enable detailed logging on ESXi servers and implement centralized logging and monitoring solutions. This will allow them to track activity, identify anomalies, and detect attacks early on.
- Utilize Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):SIEM solutions can help organizations correlate security events across their IT infrastructure, including ESXi servers. This can provide valuable insights into potential threats and help them respond to incidents more effectively.
- Implement a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of authentication. This makes it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to ESXi servers.
- Regularly Conduct Security Audits:Organizations should regularly conduct security audits to assess their ESXi environments for vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. These audits should be conducted by qualified security professionals and should cover all aspects of the ESXi infrastructure, including physical security, network security, and application security.
- Implement Security Awareness Training:Organizations should provide security awareness training to all employees who have access to ESXi servers. This training should cover best practices for password management, recognizing phishing attacks, and reporting suspicious activity.