What is Microsoft Dataverse: Your Centralized Data Hub
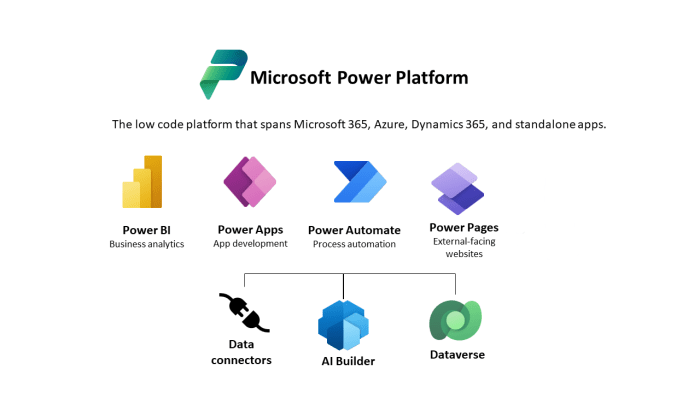
What is Microsoft Dataverse? It’s the heart of the Microsoft Power Platform, a robust and versatile platform that acts as a centralized data hub for all your business applications. Think of it as a single source of truth for your data, making it easily accessible and actionable across various Power Platform tools.
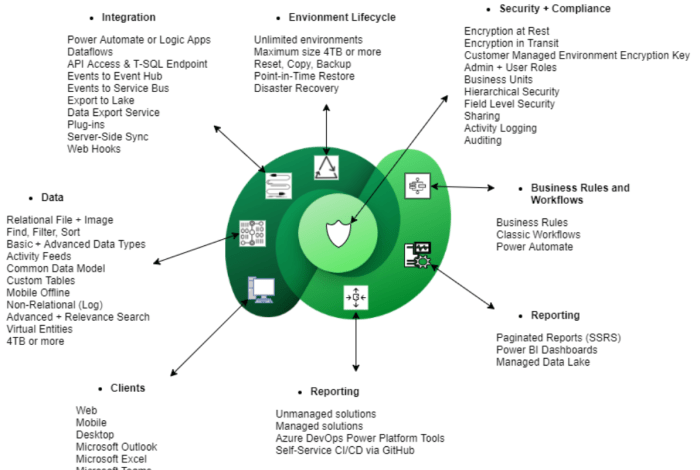
Dataverse offers a wide range of features, including secure data storage, robust governance, and seamless integration with other Microsoft Power Platform components like Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI. This powerful combination allows you to build custom applications, automate workflows, and gain insightful business intelligence, all within a unified ecosystem.
What is Microsoft Dataverse?
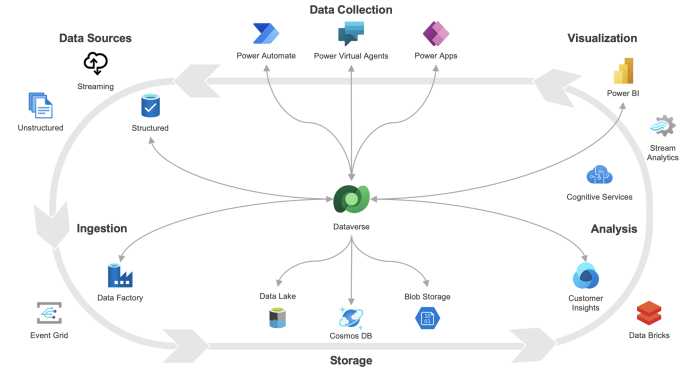
Dataverse is a centralized data platform that serves as the foundation for the Microsoft Power Platform. It’s a robust and scalable data store that empowers developers and business users to build and deploy powerful applications. Dataverse offers a secure and reliable environment for storing, managing, and accessing critical business data, fostering collaboration and driving better decision-making across organizations.
Dataverse’s Core Functionalities and Benefits
Dataverse provides a comprehensive set of features designed to streamline data management and enhance application development within the Power Platform ecosystem.
Microsoft Dataverse is a powerful platform for managing and storing data for your business applications. It’s like a central hub where all your information lives, making it easy to access and analyze. But, just like you might be tempted to buy those shiny new AirPods on Prime Day, it’s worth exploring alternative solutions before you commit.
This article provides some great insights into those alternatives. Ultimately, when it comes to data management, just like with your tech gadgets, finding the right fit for your needs is key, and Dataverse offers a robust solution for many businesses.
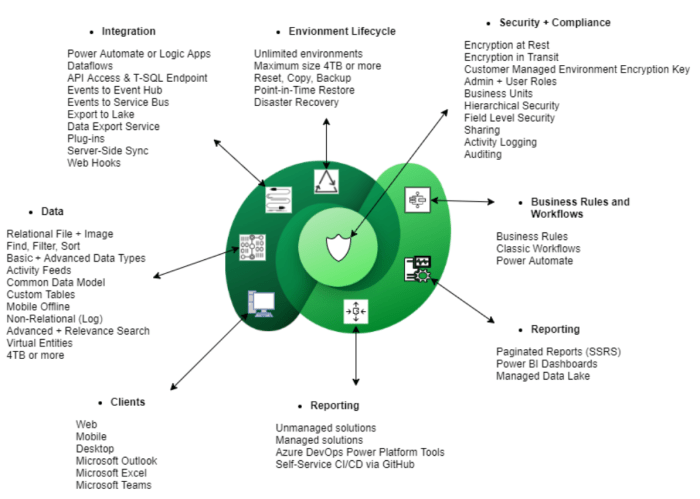
- Data Modeling and Storage:Dataverse allows users to create custom entities, define relationships between them, and store data in a structured and organized manner. It offers a rich set of data types, including text, numbers, dates, and relationships, enabling the creation of flexible and adaptable data models.
- Data Security and Governance:Dataverse prioritizes data security and governance, providing features such as role-based access control, data encryption, and audit trails. These measures ensure that data is protected from unauthorized access and that changes to data are tracked and documented.
- Data Integration and Extensibility:Dataverse seamlessly integrates with various data sources, including on-premises databases, cloud services, and external APIs. It supports data import and export capabilities, facilitating the flow of data between different systems. Additionally, Dataverse offers extensibility options, allowing developers to customize data behavior and extend its functionality.
- Business Logic and Automation:Dataverse enables the creation of business rules, workflows, and custom logic to automate processes and enforce business constraints. This functionality streamlines operations, reduces manual effort, and ensures consistency across data-driven processes.
Dataverse’s Relationship with Other Power Platform Components
Dataverse plays a central role in the Power Platform, serving as the data backbone for various components, including Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI.
- Power Apps:Dataverse acts as the primary data source for Power Apps, enabling developers to build custom applications that interact with business data stored within Dataverse. Power Apps leverages Dataverse’s data modeling capabilities, security features, and business logic to create dynamic and interactive applications.
Microsoft Dataverse is a powerful platform for managing and storing data, offering a flexible and scalable solution for businesses of all sizes. While Apple is facing a potential class action lawsuit over its iCloud storage limitations, raising concerns about user data control and access , Microsoft Dataverse provides a robust alternative, empowering users to manage their data with greater freedom and security.
- Power Automate:Power Automate relies on Dataverse to trigger and execute automated workflows based on changes in data. Dataverse’s events and triggers provide the foundation for creating automated processes that streamline workflows and enhance efficiency.
- Power BI:Power BI uses Dataverse as a data source for creating interactive dashboards and reports. Dataverse’s data insights and analytics capabilities empower businesses to gain valuable insights from their data and make informed decisions.
Key Features of Dataverse: What Is Microsoft Dataverse
Dataverse is the underlying data platform for Microsoft Power Platform, offering a robust set of features that simplify data management and empower users to build powerful applications. Let’s delve into some of the key features that make Dataverse a compelling choice for various business needs.
Data Storage Capabilities
Dataverse provides a structured and flexible environment for storing and managing data. It uses a relational database model, allowing users to organize data into tables, columns, and relationships.
Microsoft Dataverse is a powerful platform for storing and managing data, perfect for building custom business applications. It’s like a digital filing cabinet that can be accessed and updated from anywhere, but with much more functionality. Speaking of functionality, I recently took a huge leap in my photography skills after taking an online iPhone photography class and now I’m capturing stunning images.
Back to Dataverse, it’s a great tool for organizing and managing data related to any project, whether it’s photos, customer information, or anything else you need to keep track of.
- Tables:Tables represent entities or objects within your business domain. For example, you might have a table for “Customers,” “Products,” or “Orders.” Each table stores data related to a specific entity.
- Columns:Columns define the attributes or properties of each entity within a table. For instance, the “Customers” table might have columns for “Name,” “Email,” “Phone Number,” and “Address.”
- Relationships:Relationships define how different tables are connected. For example, a one-to-many relationship could exist between the “Customers” and “Orders” tables, where one customer can have multiple orders.
Data Security and Governance
Dataverse incorporates comprehensive security and governance features to protect your data and ensure its integrity.
- Role-Based Security:Dataverse allows you to define roles and assign them to users, granting them specific permissions to access and modify data. This ensures that only authorized individuals can interact with sensitive information.
- Data Encryption:Dataverse encrypts data at rest and in transit, safeguarding it from unauthorized access. This is essential for compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Data Retention Policies:You can configure retention policies to automatically manage data lifecycle, including deletion or archiving based on predefined rules. This helps maintain data quality and reduces storage costs.
- Auditing:Dataverse provides detailed auditing capabilities, allowing you to track changes made to data, including who made the changes and when. This helps with accountability and compliance.
Data Integration with External Systems
Dataverse seamlessly integrates with external systems, enabling you to leverage data from various sources and enrich your applications.
- Connectors:Dataverse offers a wide range of connectors that allow you to connect to popular cloud services, databases, and on-premises systems. These connectors facilitate data transfer and synchronization between Dataverse and external systems.
- APIs:Dataverse provides REST APIs that enable you to programmatically access and manipulate data. This flexibility allows you to build custom integrations and automate data workflows.
- Data Import/Export:You can import data from external sources into Dataverse and export data from Dataverse to other systems using various formats, such as CSV or Excel.
Dataverse and Development
Dataverse is a powerful platform for building and deploying applications, and its extensibility offers developers a wide range of options for customizing and enhancing its functionality. Let’s delve into the key aspects of Dataverse development and explore the best practices for creating robust and scalable applications.
Extending Dataverse Functionality
Dataverse provides a flexible framework for extending its core features. Developers can leverage several approaches to tailor Dataverse to specific business requirements.
- Custom Entities:Dataverse allows you to create custom entities to store unique data not covered by standard entities. These custom entities can have their own attributes, relationships, and business logic, enabling you to model complex business processes. For instance, you can create a custom entity for “Projects” with attributes like “Project Name,” “Start Date,” and “Project Manager,” along with relationships to other entities like “Tasks” or “Resources.”
- Custom Fields:You can add custom fields to existing Dataverse entities to capture additional information relevant to your business. For example, you might add a custom field “Project Status” to the “Project” entity to track the progress of each project.
- Plugins:Plugins are custom code components that execute during specific events within Dataverse, such as record creation, update, or deletion. They provide a powerful mechanism for extending Dataverse functionality and implementing custom business logic. Imagine a scenario where you want to automatically send an email notification when a new customer record is created.
You can achieve this by creating a plugin that triggers the email sending process upon record creation.
- Web API:Dataverse exposes a RESTful web API that allows you to interact with Dataverse data and perform operations programmatically. This API provides a flexible way to integrate Dataverse with external systems and build custom applications that interact with Dataverse data. For example, you can use the web API to retrieve customer data from Dataverse and display it in a web application.
- Power Automate:Power Automate is a low-code automation platform that integrates seamlessly with Dataverse. You can use Power Automate to create workflows that automate business processes, such as sending notifications, triggering approvals, or updating records in Dataverse. Imagine a scenario where you want to automatically create a task in Dataverse when a new opportunity is created.
You can achieve this by creating a Power Automate flow that triggers the task creation process upon opportunity creation.
Building Power Apps Solutions with Dataverse
Dataverse serves as the central data repository for Power Apps solutions, enabling developers to build powerful and data-driven applications.
- Data Source:Dataverse acts as the primary data source for Power Apps, providing a secure and scalable platform for storing and managing application data. Power Apps can access and manipulate Dataverse data through its built-in connectors, enabling seamless data integration.
- Business Logic:Dataverse allows developers to define business rules and logic within the platform, ensuring data integrity and consistency across Power Apps solutions. For example, you can set up business rules to validate data input, enforce data relationships, or trigger specific actions based on data changes.
- Security and Access Control:Dataverse provides robust security features, enabling developers to control access to data based on user roles and permissions. This ensures that only authorized users can access and modify sensitive information within Power Apps solutions.
Best Practices for Dataverse Development, What is microsoft dataverse
To ensure the successful development and management of applications on Dataverse, it’s essential to follow best practices:
- Design for Scalability:Consider the potential growth of your application and design your Dataverse entities and relationships to accommodate increasing data volumes and user activity. Optimize data models and use appropriate indexing strategies to improve query performance.
- Modularize Code:Break down complex logic into smaller, reusable components (e.g., plugins, custom actions) to enhance maintainability and reduce code duplication. This approach also simplifies troubleshooting and testing.
- Utilize Version Control:Implement a version control system (e.g., Git) to track changes to your Dataverse customizations and code. This allows you to roll back changes, collaborate with other developers, and maintain a history of development activities.
- Test Thoroughly:Conduct thorough testing of your Dataverse applications, covering various scenarios and user interactions. Use unit tests to validate individual components and integration tests to ensure seamless interactions between different parts of your application.
- Monitor Performance:Regularly monitor the performance of your Dataverse applications to identify bottlenecks and areas for optimization. Use Dataverse analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain insights into application usage.
Benefits of Using Dataverse
Dataverse offers a compelling solution for managing and leveraging data within the Microsoft ecosystem. Its robust features and integration with other Microsoft services provide numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes.
Data Management and Application Development
Dataverse streamlines data management and application development by providing a centralized platform for storing, managing, and accessing data.
- Unified Data Model:Dataverse employs a unified data model, ensuring consistency and standardization across applications and systems. This simplifies data integration and reduces the risk of inconsistencies.
- Data Security and Governance:Dataverse offers robust security features, including role-based access control, data encryption, and compliance with industry standards. This safeguards sensitive data and maintains regulatory compliance.
- Low-Code Development:Dataverse’s low-code development platform empowers citizen developers to build applications without extensive coding knowledge. This accelerates development cycles and allows businesses to quickly create custom solutions.
- Integration with Microsoft Services:Dataverse seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft services, including Power BI, Power Apps, and Azure, providing a comprehensive solution for data analysis, application development, and cloud infrastructure.
Comparison with Other Data Platforms
Dataverse stands out from other popular data platforms due to its unique strengths.
- Microsoft Ecosystem Integration:Dataverse’s deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, including Azure, Office 365, and Dynamics 365, provides a seamless and efficient experience for users familiar with these platforms.
- Low-Code Development Focus:Dataverse’s emphasis on low-code development makes it accessible to a wider range of users, including citizen developers, allowing for faster application development and deployment.
- Data Security and Compliance:Dataverse prioritizes data security and compliance, offering robust features that meet industry standards and regulations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Dataverse provides a cost-effective and scalable solution for data management and application development.
- Pay-as-you-go Model:Dataverse operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale their data storage and usage based on their needs. This reduces upfront costs and ensures that organizations only pay for what they use.
- Scalability and Performance:Dataverse is built on a scalable and robust cloud infrastructure, ensuring high performance and availability even as data volumes grow.