What Is Return on Investment (ROI)?
What is return on investment, you ask? It’s a fundamental concept that every investor, business owner, and even individual should grasp. It’s the ultimate measure of how well your investments are performing, providing a clear picture of the financial gains you’re reaping compared to your initial outlay.
Imagine you invest $100 in a project and it brings in $120 in profits. Your ROI is 20%, signifying a healthy return. But ROI isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the efficiency and effectiveness of your investments.
Whether you’re buying stocks, launching a marketing campaign, or simply putting money into your savings account, knowing your ROI helps you make informed decisions and maximize your financial potential.
Definition of Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI) is a fundamental metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. It measures the efficiency of an investment by comparing the gain from the investment to the cost of the investment. This metric is crucial for making informed financial decisions, allowing individuals and businesses to assess the potential returns on their investments and allocate resources effectively.
Calculating ROI
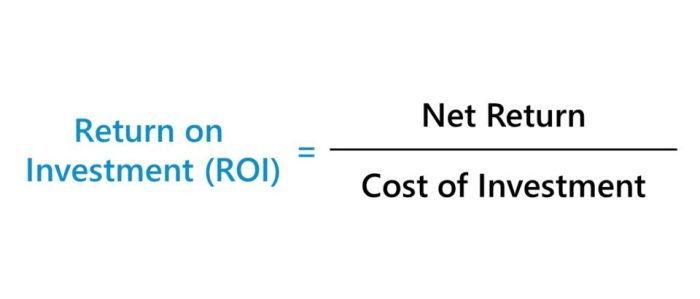
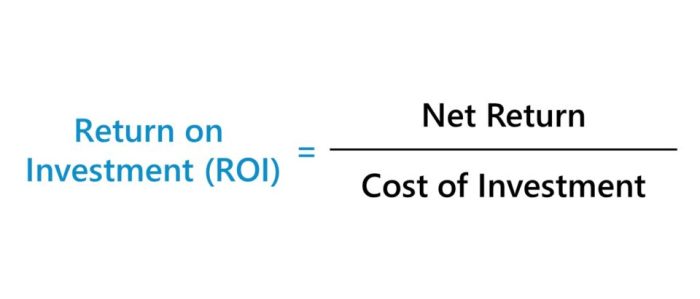
The formula for calculating ROI is straightforward:
ROI = (Gain from Investment
Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment
This formula helps break down the calculation into its essential components:
- Gain from Investment:This refers to the total amount of money earned from the investment, including any profits, dividends, or interest received. For example, if you invested $100 in a stock and it grew to $120, your gain would be $20.
- Cost of Investment:This represents the initial amount of money invested, including any associated expenses, such as transaction fees or brokerage commissions. For example, if you purchased a stock for $100 and paid a $5 transaction fee, your total cost of investment would be $105.
The result of the ROI calculation is expressed as a percentage, indicating the return generated for every dollar invested. For example, an ROI of 20% signifies that for every $1 invested, you earned $0.20 in return.
Real-World Applications of ROI
ROI is a versatile metric used across various industries to assess the effectiveness of investments. Some examples include:
- Marketing Campaigns:Businesses use ROI to determine the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns by comparing the cost of the campaign to the revenue generated from it. For example, a company might invest $10,000 in a social media campaign and generate $20,000 in sales.
This would result in an ROI of 100% ( ($20,000 – $10,000) / $10,000).
- Real Estate Investments:Investors use ROI to evaluate the profitability of real estate investments by considering the purchase price, renovation costs, rental income, and potential appreciation. For example, an investor might purchase a property for $200,000, spend $50,000 on renovations, and generate $2,000 in monthly rental income.
This would result in an annual ROI of 10% ( ($24,000 – $250,000) / $250,000).
- Project Management:Companies use ROI to assess the profitability of new projects by considering the project costs, expected revenue, and potential benefits. For example, a company might invest $500,000 in developing a new software product that is expected to generate $1 million in revenue.
This would result in an ROI of 100% ( ($1,000,000 – $500,000) / $500,000).
Calculating ROI
Now that we understand what ROI is, let’s delve into how to calculate it. This process is fairly straightforward, involving a simple formula and a few key inputs.
Calculating ROI
The fundamental formula for calculating ROI is:
ROI = (Gain from Investment
Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment
Let’s break down this formula with a hypothetical scenario.Imagine you invest $1,000 in a stock, and after a year, the stock’s value increases to $1,
200. Here’s how you would calculate the ROI
Gain from Investment
Return on investment (ROI) is often measured in dollars and cents, but when it comes to family, the most valuable returns are immeasurable. If you’re considering adoption, I encourage you to read my advice to families considering adoption , as it delves into the emotional and personal aspects of this journey.
While the financial investment may be significant, the return on investment in love, joy, and family is truly priceless.
$1,200 (current value)$1,000 (initial investment) = $200
Cost of Investment
$1,000
-
ROI
($200 / $1,000)
- 100 = 20%
This means your investment generated a 20% return.To further illustrate the calculation of ROI for different investment types, let’s consider the following table:
| Investment Type | Investment Amount | Returns | ROI Calculation | ROI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | $500,000 | $550,000 | ($550,000
|
10% |
| Business Venture | $10,000 | $15,000 | ($15,000
|
50% |
| Savings Account | $5,000 | $5,100 | ($5,100
|
2% |
As you can see, the ROI varies significantly depending on the investment type and its performance. This highlights the importance of understanding and comparing ROI across different investment options to make informed financial decisions.
ROI in Different Contexts
While ROI is a universal concept, its application and interpretation vary significantly across different investment scenarios. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Stock Market Investments
The ROI in stock market investments is calculated by considering the total return generated from the investment, including capital appreciation and dividends, and dividing it by the initial investment cost.
Return on investment (ROI) is a key metric for businesses, but it can also apply to personal choices. For example, investing in beautiful, high-quality home decor can be a great ROI, as it brings joy and value to your space.
If you’re looking for a stunning collection that embodies both beauty and quality, be sure to shop the new Copper Coast collection at Waterford. These pieces are not just décor; they are investments in your well-being and the lasting beauty of your home, which is a kind of ROI that’s priceless.
- Capital Appreciation:The increase in the stock’s value over time.
- Dividends:Periodic payments made by companies to their shareholders.
ROI = (Total Return
Return on investment (ROI) is a crucial metric for businesses, measuring the efficiency of investments. It’s interesting to see how board changes can impact a company’s ROI. For example, euro manganese announces appointment of ms ludivine wouters as non executive director gregory martyr steps down from the board , which could lead to a shift in strategy and potentially influence their overall ROI.
Ultimately, understanding ROI helps businesses make informed decisions about resource allocation and maximize their profitability.
Initial Investment) / Initial Investment
Key factors influencing stock market ROI include:
- Company Performance:Strong financial performance, market share growth, and innovative product development can lead to higher stock prices and dividends.
- Market Conditions:Economic growth, interest rates, and investor sentiment can impact the overall stock market and influence individual stock prices.
- Risk Tolerance:Investors with higher risk tolerance may choose to invest in more volatile stocks, which have the potential for higher returns but also higher risks.
The limitations of ROI calculations in the stock market include:
- Time Horizon:ROI calculations can be influenced by the investment timeframe. Short-term fluctuations in stock prices can make ROI appear volatile, while long-term investments tend to provide a more stable and accurate representation of returns.
- Past Performance:Past stock performance is not necessarily indicative of future returns. Market conditions and company performance can change, making historical ROI data less reliable as a predictor of future returns.
Using ROI for Decision-Making: What Is Return On Investment
ROI is a powerful tool for making informed investment decisions. It helps you compare different investment opportunities, understand the potential return on your investment, and prioritize projects based on their profitability.
Prioritizing Investment Opportunities
ROI can be used to prioritize investment opportunities by ranking them based on their expected return. This allows you to allocate your resources to the most promising projects and maximize your overall return. For example, if you have a limited budget and two investment options, one with an expected ROI of 20% and another with an ROI of 10%, you would likely prioritize the investment with the higher ROI.
This is because the investment with the higher ROI is expected to generate a greater return on your investment.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Investing Based Solely on ROI
While ROI is a valuable metric for evaluating investment opportunities, it’s important to consider both the benefits and drawbacks of relying solely on ROI for decision-making.
- Benefits
- Provides a standardized way to compare different investments.
- Helps identify the most profitable investment opportunities.
- Can be used to track the performance of investments over time.
- Drawbacks
- Doesn’t account for all factors that may influence investment decisions, such as risk, time horizon, and personal preferences.
- Can be misleading if not used in conjunction with other metrics.
- May not accurately reflect the true value of long-term investments.
Integrating ROI into Financial Planning Strategies
ROI can be integrated into broader financial planning strategies by using it to evaluate different investment options, set financial goals, and track progress towards those goals. For example, you can use ROI to determine the best mix of investments for your portfolio, based on your risk tolerance and time horizon.
You can also use ROI to track the performance of your investments and make adjustments to your portfolio as needed.
ROI is a valuable tool for making informed investment decisions, but it’s not a magic bullet. It’s important to consider all factors that may influence your investment decisions and use ROI in conjunction with other metrics to make the best possible choices.
Beyond ROI
While ROI is a powerful metric for evaluating investments, it’s essential to remember that it provides only a partial picture. A singular focus on ROI can sometimes lead to overlooking crucial aspects of an investment’s value. Therefore, it’s vital to consider other metrics that offer a more comprehensive perspective.
These complementary metrics can help you make informed decisions, ensuring that you’re not sacrificing long-term benefits for short-term gains.
Understanding Different Investment Metrics
The limitations of ROI become apparent when we consider its inability to capture the full scope of an investment’s impact. For instance, ROI might not accurately reflect the value of investments in areas like employee training, brand building, or research and development.
These investments, while not immediately yielding tangible returns, contribute significantly to long-term success.To overcome this limitation, we can employ a range of complementary metrics that offer a more holistic view of investment performance.
Return on Equity (ROE)
Return on Equity (ROE) measures a company’s profitability relative to its shareholder equity. It indicates how effectively a company is using its equity to generate profits.
ROE = Net Income / Shareholder Equity
ROE is a valuable metric for investors seeking to assess a company’s financial health and its ability to generate returns for shareholders. A higher ROE generally signifies better profitability and efficiency in utilizing equity.
Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Assets (ROA) assesses a company’s profitability in relation to its total assets. It reflects how effectively a company uses its assets to generate earnings.
ROA = Net Income / Total Assets
ROA is a crucial metric for analyzing a company’s operational efficiency and its ability to generate profits from its assets. A higher ROA indicates better asset utilization and stronger profitability.
Payback Period, What is return on investment
The payback period is the time it takes for an investment to generate enough cash flow to recover its initial cost.
Payback Period = Initial Investment / Annual Cash Flow
This metric is particularly relevant for businesses seeking to quickly recoup their investments. It helps in evaluating the time horizon for realizing returns and assessing the financial viability of projects.
Net Present Value (NPV)
Net Present Value (NPV) considers the time value of money, discounting future cash flows to their present value. It reflects the overall profitability of an investment, taking into account the cost of capital and the timing of cash flows.
NPV = Present Value of Future Cash Flows
Initial Investment
NPV is a powerful metric for evaluating long-term investments, as it accounts for the opportunity cost of capital and the potential for inflation.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is the discount rate that makes the NPV of an investment equal to zero. It represents the effective rate of return generated by an investment.
IRR = Discount Rate that makes NPV = 0
IRR is a valuable metric for comparing different investment opportunities, as it provides a standardized measure of profitability that considers the time value of money.
Qualitative Factors
While quantitative metrics like ROI, ROE, and NPV provide valuable insights into investment performance, it’s crucial to consider qualitative factors as well. These factors can significantly influence the success of an investment and should be carefully evaluated alongside quantitative data.
Market Analysis
Understanding the market dynamics and the competitive landscape is essential for evaluating the potential success of an investment. Factors like market size, growth potential, and the presence of competitors can influence the profitability and sustainability of an investment.
Team and Management
The quality of the team and the leadership driving the investment is a crucial determinant of its success. Experienced and capable management can significantly enhance the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk assessment is vital to understand the potential downsides of an investment. Identifying and evaluating potential risks, such as regulatory changes, technological disruptions, or economic downturns, can help mitigate potential losses and ensure a more informed decision-making process.
Sustainability
In today’s world, it’s crucial to consider the environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects of investments. Sustainability considerations can influence the long-term value of an investment and align with growing investor preferences for responsible investing.
Conclusion
Beyond ROI, a comprehensive approach to investment evaluation requires considering a range of complementary metrics and qualitative factors. By taking into account both quantitative and qualitative aspects, investors can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they are not sacrificing long-term value for short-term gains.