AI Impact on UK Jobs: A New Era of Work
Ai impact uk jobs – AI Impact on UK Jobs: A New Era of Work – Artificial intelligence is rapidly changing the way we work, and the UK is no exception. From automating tasks to creating new industries, AI’s impact on the UK job market is undeniable.
While some jobs are at risk of being automated, others are being created, demanding new skills and knowledge. This dynamic landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for workers, businesses, and the UK economy as a whole.
AI’s Impact on the UK Job Market

Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various aspects of our lives, and the UK job market is no exception. While AI promises to create new opportunities and enhance productivity, it also raises concerns about potential job displacement. Understanding the impact of AI on the UK workforce is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike.
Industries Most Affected by AI
AI is expected to have a significant impact on several industries in the UK. These industries are characterized by tasks that can be automated or enhanced through AI, such as data analysis, customer service, and manufacturing.
- Financial Services:AI is already being used by financial institutions for tasks like fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service. This is leading to increased efficiency and cost savings, but also potentially displacing some traditional roles.
- Manufacturing:AI-powered robots and automation are transforming manufacturing processes, increasing production efficiency and reducing labor costs. This is leading to a shift towards more skilled and specialized roles, while some traditional manufacturing jobs may be lost.
- Healthcare:AI is being used in healthcare for tasks such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans. This is improving patient outcomes and reducing costs, but it also raises concerns about the potential displacement of healthcare professionals.
- Transportation:Autonomous vehicles and AI-powered logistics systems are expected to disrupt the transportation industry, potentially displacing truck drivers and other transportation workers. However, new opportunities are also emerging in the development and maintenance of these technologies.
- Retail:AI is being used in retail for tasks like inventory management, personalized recommendations, and customer service. This is leading to more efficient operations and improved customer experiences, but also potentially displacing some retail jobs.
Projected Job Losses and Gains
While AI is expected to lead to job losses in some sectors, it is also predicted to create new opportunities in other areas.
It’s fascinating to think about how AI will reshape the UK job market. While some roles will be automated, others will emerge, requiring new skills and adaptability. It’s a similar story with my own project, abm studio the kitchen progress , where I’m learning to juggle the practicalities of home renovation with the creative vision I have for the space.
Just like with AI, it’s about understanding the changes, adapting, and making the most of the opportunities that come with them.
The UK government’s “AI Sector Deal” estimates that AI could contribute £232 billion to the UK economy by 2035.
- Job Losses:A study by PwC predicts that up to 30% of UK jobs could be automated by the mid-2030s. However, the report also notes that these job losses will be offset by the creation of new jobs in areas like AI development, data science, and AI-related services.
- Job Gains:The UK government estimates that AI could create up to 1.3 million new jobs in the UK by 2030. These jobs will be in areas like AI development, data analysis, and AI-related services.
Jobs at Risk from AI Automation: Ai Impact Uk Jobs
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming various industries, including the UK job market. While AI offers numerous benefits, it also raises concerns about the potential displacement of workers in certain roles. This section will explore specific job roles in the UK that are most vulnerable to automation by AI and delve into the reasons behind their vulnerability.
Jobs at Risk from AI Automation
AI’s ability to perform tasks that were once considered exclusively human is driving the automation of various job roles. Here are some specific examples:
- Data Entry Clerks:AI-powered systems can efficiently process and input data, reducing the need for manual data entry. This automation can significantly impact data entry clerks, whose primary responsibility is to enter data into computer systems.
- Telemarketers:AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle customer interactions and inquiries, potentially replacing telemarketers who engage in outbound calls to promote products or services.
- Customer Service Representatives:AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are increasingly being deployed to handle customer inquiries and complaints, potentially reducing the need for human customer service representatives.
- Truck Drivers:The development of self-driving trucks is a significant threat to the trucking industry. AI-powered trucks can operate autonomously, potentially displacing human drivers.
- Factory Workers:AI-powered robots are becoming increasingly common in manufacturing settings, automating tasks such as assembly, welding, and painting. This automation can lead to job displacement for factory workers.
Reasons for Job Vulnerability
Several factors contribute to the vulnerability of these jobs to AI automation:
- Repetitive Tasks:Jobs involving repetitive tasks are particularly susceptible to automation. AI systems can easily learn and perform repetitive tasks with high accuracy and efficiency, surpassing human capabilities in speed and consistency.
- Data-Driven Processes:Jobs that rely heavily on data analysis and decision-making based on data patterns are vulnerable to AI automation. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data and identify patterns that humans may miss, leading to more informed and efficient decision-making.
- Rule-Based Operations:Jobs that follow a set of predefined rules and procedures are susceptible to AI automation. AI systems can be programmed to follow these rules and execute tasks consistently, reducing the need for human intervention.
Consequences for Workers
The automation of jobs by AI can have significant consequences for workers:
- Unemployment:As AI systems become more sophisticated, they are likely to displace workers in certain roles. This could lead to increased unemployment, particularly in industries heavily reliant on manual labor or repetitive tasks.
- Retraining Needs:Workers in roles vulnerable to automation will need to acquire new skills to remain competitive in the job market. This may require retraining or upskilling programs to adapt to the evolving demands of the workforce.
- Wage Stagnation:The availability of AI-powered automation can put downward pressure on wages for certain roles. As AI systems become more commonplace, employers may be able to reduce labor costs by automating tasks, potentially leading to wage stagnation or even wage reductions.
New Jobs Created by AI
While AI is automating certain tasks, it’s also creating new opportunities and roles in the UK. These roles often require specialized skills and knowledge related to AI development, data analysis, and ethical considerations.
AI Development Roles
AI development is a rapidly growing field, with demand for skilled professionals increasing. These roles involve designing, building, and maintaining AI systems.
- AI Engineers: These professionals develop, test, and deploy AI models and algorithms, often working with large datasets and complex software systems.
- Machine Learning Engineers: They focus on building and optimizing machine learning models, using techniques like deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.
- Data Scientists: Data scientists play a crucial role in preparing, analyzing, and interpreting data for AI development, using their expertise in statistics, programming, and data visualization.
AI Ethics and Governance
As AI systems become more sophisticated, the need for professionals who can ensure ethical and responsible AI development and deployment is growing.
- AI Ethics Specialists: These individuals analyze the ethical implications of AI systems, develop guidelines for responsible AI use, and ensure compliance with ethical standards.
- AI Governance Experts: They focus on creating frameworks and policies for managing and governing AI systems, addressing issues like data privacy, bias, and transparency.
AI-Driven Industries
AI is transforming various industries, creating new job roles and opportunities in sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
- Healthcare AI Specialists: These professionals use AI to analyze medical data, develop personalized treatment plans, and improve patient care. Roles include AI-powered diagnostic tools, robotic surgery assistants, and personalized medicine development.
- Financial AI Analysts: They utilize AI to analyze market trends, identify investment opportunities, and manage risk in financial institutions. Roles include fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and personalized financial advice.
- Manufacturing Automation Engineers: These engineers integrate AI into manufacturing processes, optimizing production lines, automating tasks, and improving efficiency. Roles include predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization.
Transitioning to AI-Related Roles
Individuals seeking to transition into AI-related roles can benefit from acquiring relevant skills and knowledge.
- Upskilling and Reskilling: Programs and courses are available to help workers develop skills in data science, machine learning, AI ethics, and programming.
- Networking and Mentorship: Connecting with professionals in the AI field can provide valuable insights and guidance on career paths and opportunities.
Government Policies and Initiatives
The UK government has recognized the potential of AI and its transformative impact on the economy and society. To navigate this technological revolution effectively, it has implemented a range of policies and initiatives aimed at promoting AI innovation while mitigating its potential risks, particularly in the realm of employment.
Current Policies and Initiatives
The UK government has established a comprehensive strategy for AI, encompassing various initiatives. These include:
- The AI Sector Deal: Launched in 2018, this deal Artikels the government’s commitment to supporting the development and adoption of AI in the UK. It aims to create a thriving AI ecosystem by fostering collaboration between academia, industry, and government. This includes funding research and development, supporting the growth of AI startups, and promoting the adoption of AI technologies across different sectors.
- The National AI Strategy: Published in 2021, this strategy sets out the government’s long-term vision for AI, emphasizing the importance of responsible and ethical development and deployment of AI technologies. It focuses on key areas such as skills development, data infrastructure, and ethical considerations.
This strategy also aims to position the UK as a global leader in AI research and innovation.
- The Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI): Established in 2018, the CDEI provides guidance and support to businesses and organizations on ethical and responsible AI development and use. It promotes best practices and facilitates dialogue on the societal implications of AI, including its impact on employment.
Skills Gap and Workforce Development
The rapid adoption of AI technologies in the UK is creating a significant skills gap in the workforce. While AI promises to create new jobs and enhance productivity, it also requires a workforce with specialized skills in data science, machine learning, and AI ethics.
Bridging this gap is crucial for the UK to remain competitive in the global economy and ensure a smooth transition to an AI-driven future.
Upskilling and Reskilling Programs
Upskilling and reskilling programs are essential for preparing workers for the changing job market. These programs can equip individuals with the necessary skills to adapt to new roles and remain competitive in the face of automation.
“Upskilling and reskilling programs are essential for ensuring that the UK workforce is equipped with the skills necessary to thrive in the digital economy.”
The potential impact of AI on UK jobs is a hot topic, and it’s one that keeps me up at night sometimes. I find it helps to unwind by crafting, and I recently discovered the beauty of frosted mason jar votives for adding a touch of elegance to my home.
They remind me that even in a world of rapid technological change, there’s still room for creativity and handmade beauty. And that, I think, is a valuable lesson as we navigate the future of work in the AI age.
UK Government
- Government-Funded Programs:The UK government offers various programs to support upskilling and reskilling initiatives, including the National Skills Fund, which provides funding for training and apprenticeships in digital skills.
- Industry-Led Initiatives:Companies are also taking the lead in upskilling their workforce. For example, Google’s Digital Skills for Everyone initiative provides free online courses in digital marketing, data analytics, and other in-demand skills.
- University Partnerships:Universities are partnering with industry to develop specialized programs in AI and data science, providing workers with the academic foundation needed to thrive in the field.
Training Programs and Initiatives
Here’s a table outlining specific training programs and initiatives available in the UK to address the skills gap:
| Program/Initiative | Description | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| National Skills Fund | Provides funding for training and apprenticeships in digital skills, including AI. | Individuals seeking to upskill or reskill in digital technologies. |
| Digital Skills for Everyone (Google) | Offers free online courses in digital marketing, data analytics, and other in-demand skills. | Individuals of all skill levels seeking to learn digital skills. |
| The Institute of Coding | A national network of universities and industry partners offering training in digital skills, including AI. | Individuals seeking to develop digital skills for careers in tech. |
| The Alan Turing Institute | Offers research and training programs in AI, data science, and related fields. | Researchers, students, and professionals seeking advanced training in AI. |
Social and Economic Implications
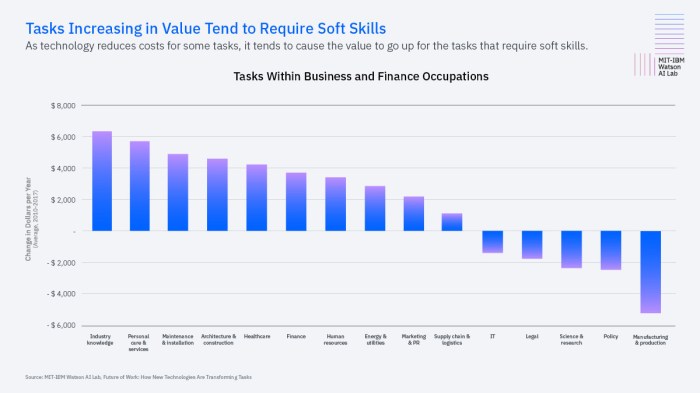
The potential social and economic implications of AI’s impact on the UK job market are multifaceted and far-reaching. AI’s ability to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and generate new products and services presents both opportunities and challenges for the UK economy and society.
Impact on Income Inequality and Social Mobility
The potential impact of AI on income inequality and social mobility is a complex issue. While AI can create new jobs and increase productivity, it also has the potential to exacerbate existing inequalities. Automation could displace workers in lower-skilled jobs, leading to increased unemployment and income disparities.
This could further widen the gap between the wealthy and the poor, potentially leading to social unrest and instability.
- Job Displacement:AI-driven automation could displace workers in sectors like manufacturing, transportation, and customer service, leading to higher unemployment rates, particularly among low-skilled workers.
- Wage Stagnation:As AI takes over routine tasks, wages for these jobs could stagnate or even decline, further widening the income gap.
- Skill Mismatch:The demand for new skills in AI-related fields could create a skills mismatch, making it difficult for displaced workers to find new employment opportunities.
On the other hand, AI could also create new job opportunities in fields like AI development, data science, and AI-related services. This could potentially lead to increased social mobility, as workers with the right skills could find high-paying jobs in these emerging fields.
“AI has the potential to create a more equitable society, but only if we invest in education and training to ensure that everyone has the opportunity to benefit from its advancements.” Dr. Kate Crawford, AI researcher and author
Impact on the UK Economy
AI has the potential to significantly impact the UK economy, leading to both benefits and challenges.
The AI revolution is undeniably impacting the UK job market, leading to both anxieties and exciting opportunities. It’s fascinating to see how individuals are adapting to this change, like Paula Passini, a UK-based entrepreneur featured in the inspiring article at home with paula passini.
Her story highlights the need for adaptability and creativity in a rapidly evolving world, skills that will be essential for navigating the AI-driven future of work.
- Productivity Growth:AI can automate tasks, improve efficiency, and increase productivity across various sectors, leading to economic growth and increased competitiveness.
- Innovation:AI can drive innovation by creating new products and services, leading to new industries and economic opportunities.
- Competitiveness:AI can help UK businesses stay competitive in the global market by improving efficiency and developing new products and services.
However, AI’s impact on the UK economy could also pose challenges.
- Job Losses:Automation could lead to job losses in sectors where AI can perform tasks more efficiently than humans.
- Economic Disruption:Rapid technological change can disrupt traditional industries and create uncertainty in the economy.
- Ethical Concerns:The use of AI raises ethical concerns regarding data privacy, bias, and the potential for job displacement.
AI and the Future of Work
AI is transforming the world of work, creating both opportunities and challenges. It is crucial to address the potential impact of AI on the UK job market to ensure a smooth transition to an AI-driven future.
- Investment in Education and Training:Governments and businesses must invest in education and training programs to equip workers with the skills needed for the AI-driven economy.
- Reskilling and Upskilling:Programs to reskill and upskill workers displaced by automation are essential to help them find new jobs in emerging fields.
- Social Safety Nets:Strong social safety nets are needed to support workers who lose their jobs due to automation.
- Ethical Guidelines:Ethical guidelines for the development and deployment of AI are crucial to mitigate potential risks and ensure that AI is used for the benefit of society.
“The future of work is not about replacing humans with machines. It’s about augmenting human capabilities with AI to create a more productive and fulfilling workplace.” Dr. Andrew Ng, AI expert and entrepreneur
Ethical Considerations
The rise of AI in the UK job market presents a complex ethical landscape. While AI offers potential for economic growth and efficiency, it also raises concerns about fairness, transparency, and the potential for negative societal impacts. This section explores these ethical considerations, focusing on the potential for bias in AI systems and the ethical implications of job displacement.
Bias and Discrimination in AI Systems
AI systems are trained on vast datasets, and if these datasets reflect existing societal biases, the resulting AI systems may perpetuate and even amplify these biases. For example, if a recruitment AI is trained on data from a company with a history of hiring primarily men, the AI may learn to discriminate against women, even if the company aims to be more inclusive.
- Algorithmic Bias:AI algorithms can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes. For example, facial recognition systems have been shown to be less accurate for people of color, potentially leading to unfair policing practices.
- Data Bias:The data used to train AI systems often reflects existing societal biases. For instance, if a job application AI is trained on data from a company with a predominantly white workforce, it may learn to favor white candidates, even if the company is committed to diversity.
- Feedback Loops:AI systems can create feedback loops where biased outputs reinforce existing biases. For example, if an AI-powered loan approval system disproportionately denies loans to people in certain neighborhoods, this could lead to a vicious cycle of economic disadvantage.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to ensure that AI systems are trained on diverse and representative datasets, and that they are regularly audited for bias. Developers should also implement mechanisms to allow for human oversight and intervention in cases where AI systems may be making discriminatory decisions.
Ethical Implications of Job Displacement
The potential for AI to automate jobs raises significant ethical concerns. While AI can create new jobs and improve productivity, it also risks displacing workers from their existing roles, leading to unemployment and economic hardship.
- Fair Transition:It is essential to ensure a fair transition for workers who are displaced by AI. This includes providing retraining and upskilling opportunities, as well as social safety nets to support workers during periods of unemployment.
- Transparency and Accountability:Decision-making processes related to AI-driven job displacement should be transparent and accountable. Workers should be informed about the rationale behind decisions that affect their employment, and have the opportunity to challenge unfair or discriminatory practices.
- Shared Benefits:The benefits of AI should be shared equitably across society. This includes ensuring that workers displaced by AI are not left behind, and that the economic gains from AI are used to invest in social programs and infrastructure that benefit all citizens.
“The ethical implications of AI are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful consideration and proactive measures to ensure a fair and equitable transition to a future shaped by AI.”
Case Studies and Examples
The impact of AI on the UK job market is not just a theoretical concept; it is being realized in real-world applications across various industries. Numerous companies are successfully using AI to improve efficiency, create new job opportunities, and drive innovation.
This section explores specific examples of AI implementation in the UK, analyzing its impact on different sectors and highlighting the challenges and successes of AI adoption.
AI’s Impact on Specific Industries, Ai impact uk jobs
The implementation of AI is transforming various sectors in the UK, bringing about significant changes in the way businesses operate and the nature of work. Here are some examples of AI’s impact on specific industries:
Retail
AI is revolutionizing the retail sector in the UK, from personalized shopping experiences to efficient supply chain management. AI-powered chatbots provide instant customer service, while predictive analytics helps retailers anticipate demand and optimize inventory.
- Ocado, a leading online grocery retailer, uses AI to predict customer demand, optimize warehouse operations, and personalize shopping recommendations.
- Marks & Spencer, a well-known British retailer, has implemented AI-powered systems to personalize customer interactions, improve inventory management, and optimize pricing strategies.
Healthcare
AI is playing a crucial role in improving healthcare outcomes and efficiency in the UK. AI-powered diagnostic tools assist doctors in identifying diseases earlier, while robotic surgery systems enhance precision and minimize risks.
- The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trustuses AI to analyze medical images and identify potential cancers, leading to earlier diagnoses and improved treatment outcomes.
- Babylon Health, a digital healthcare platform, leverages AI to provide virtual consultations, symptom assessments, and personalized health advice.
Manufacturing
AI is automating tasks, optimizing production processes, and improving quality control in the UK manufacturing sector. AI-powered robots perform repetitive tasks, while predictive maintenance systems minimize downtime and enhance efficiency.
- Rolls-Royce, a global aerospace and defense company, uses AI to optimize engine performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve aircraft safety.
- Jaguar Land Rover, a British luxury car manufacturer, has implemented AI-powered systems to enhance vehicle design, improve production processes, and personalize customer experiences.
Challenges and Successes of AI Implementation
While AI offers numerous opportunities for the UK economy, its implementation also presents challenges.
Challenges
- Data Privacy and Security:AI systems rely heavily on data, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Strict regulations and ethical considerations are essential to ensure responsible AI development and deployment.
- Skills Gap:The rapid adoption of AI creates a significant skills gap, requiring a workforce with specialized knowledge in AI, data science, and related fields. Investing in education and training programs is crucial to bridge this gap.
- Bias and Fairness:AI algorithms can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes. Addressing bias in AI systems is critical to ensure fairness and ethical use.
Successes
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency:AI has significantly improved productivity and efficiency in various industries, enabling businesses to optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
- New Job Creation:While AI automates some tasks, it also creates new job opportunities in areas such as AI development, data science, and AI ethics. Adapting to the changing job market and acquiring new skills is essential for individuals and businesses.
- Innovation and Growth:AI is driving innovation and growth in the UK economy, fostering the development of new products, services, and business models. Investing in AI research and development is crucial for maintaining the UK’s competitive edge.