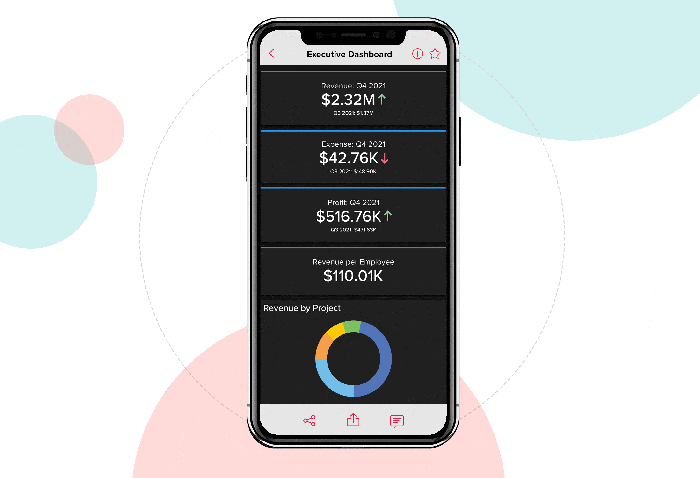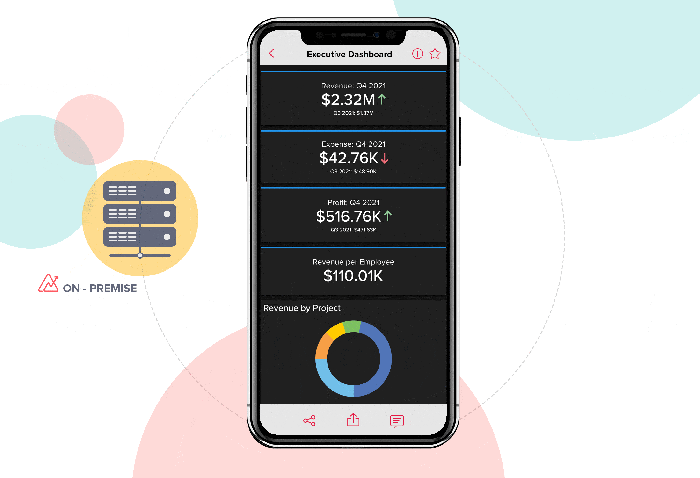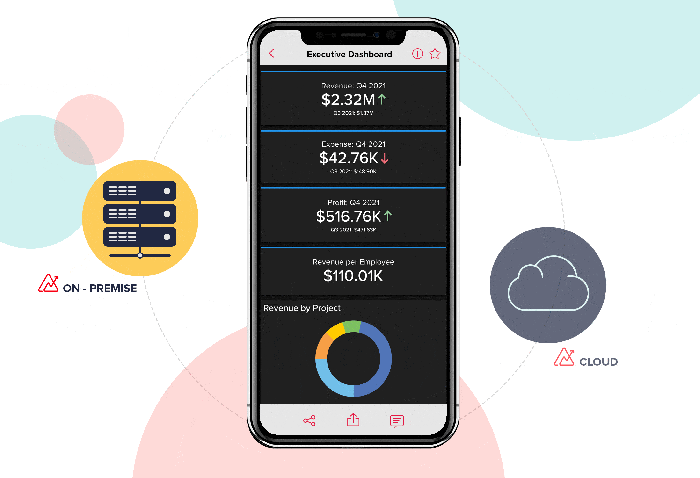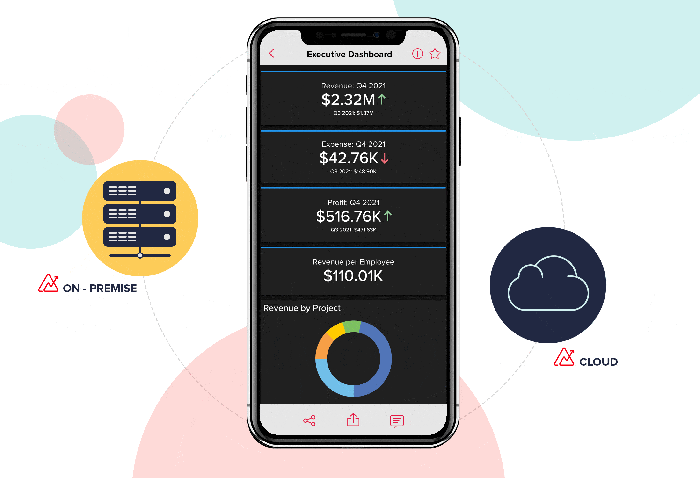
Unlocking Business Insights: Best Predictive Analytics Tools
Best predictive analytics tools – In today’s data-driven world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to gain a competitive edge. Predictive analytics tools have emerged as indispensable allies, empowering organizations to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. These tools leverage advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data, identify patterns, and predict future trends.
The power of predictive analytics extends across industries, from healthcare and finance to retail and marketing. By analyzing patient records, financial transactions, and customer behavior, businesses can anticipate future events, optimize operations, and personalize experiences. Whether it’s predicting customer churn, identifying fraudulent activities, or forecasting sales trends, predictive analytics offers a powerful arsenal for navigating the complexities of the modern business landscape.
Introduction
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool that leverages data to anticipate future outcomes and trends. In today’s data-driven world, where businesses are constantly striving to make informed decisions, predictive analytics has become an indispensable asset. It empowers organizations to gain insights from historical data, identify patterns, and make predictions about future events.Predictive analytics is essential because it helps businesses:
Benefits of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics offers a multitude of benefits, enabling businesses to:
- Improve decision-making:By analyzing historical data and identifying trends, predictive analytics provides data-driven insights that support better decision-making across various business functions.
- Optimize operations:Businesses can optimize their operations by identifying bottlenecks, predicting demand fluctuations, and optimizing resource allocation based on predictive analytics insights.
- Enhance customer experiences:Predictive analytics can personalize customer interactions, recommend relevant products or services, and anticipate customer needs, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
- Reduce risks and mitigate losses:By predicting potential risks and identifying early warning signs, businesses can proactively take steps to mitigate losses and minimize potential damage.
- Gain a competitive advantage:Businesses that leverage predictive analytics can gain a competitive edge by making faster and more accurate decisions, anticipating market shifts, and optimizing their strategies.
Industries Where Predictive Analytics is Used
Predictive analytics is widely adopted across diverse industries, including:
- Finance:Financial institutions use predictive analytics for fraud detection, risk assessment, customer churn prediction, and investment strategies.
- Healthcare:Healthcare providers leverage predictive analytics for disease prediction, patient risk assessment, treatment optimization, and resource allocation.
- Retail:Retailers utilize predictive analytics for demand forecasting, inventory management, personalized recommendations, and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Manufacturing:Manufacturers use predictive analytics for production planning, quality control, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization.
- Marketing:Marketers employ predictive analytics for customer segmentation, campaign optimization, lead scoring, and churn prediction.
Essential Features of Predictive Analytics Tools

Predictive analytics tools are software applications designed to analyze historical data and identify patterns to forecast future trends and outcomes. They leverage statistical algorithms, machine learning techniques, and data visualization tools to extract insights from data and support informed decision-making.
Essential Features of Predictive Analytics Tools
These tools offer a wide range of functionalities, allowing users to perform various tasks related to data analysis, modeling, and prediction.
Core Functionalities
- Data Collection and Integration:Predictive analytics tools need to gather data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, APIs, and cloud storage. The ability to integrate data from diverse sources is crucial for building comprehensive models.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:Raw data often contains inconsistencies, missing values, and outliers. Tools should provide features to clean and prepare data for analysis by handling missing values, removing duplicates, and transforming data into a suitable format.
- Data Exploration and Visualization:Understanding the underlying patterns in data is essential for building accurate models. Tools should offer features for data exploration, including data visualization techniques like charts, graphs, and dashboards, to gain insights from the data.
- Model Building and Selection:Predictive analytics tools provide various algorithms for building predictive models, including linear regression, logistic regression, decision trees, and neural networks. The ability to select the appropriate algorithm based on the nature of the data and the problem being solved is crucial.
- Model Evaluation and Validation:After building a model, it is essential to evaluate its performance and ensure it generalizes well to unseen data. Tools should provide metrics for evaluating model accuracy, such as R-squared, AUC, and F1 score. Cross-validation techniques can be used to assess the model’s ability to generalize.
- Model Deployment and Monitoring:Once a model is validated, it needs to be deployed for real-time predictions. Tools should offer features for deploying models as APIs or web services. Monitoring the performance of deployed models over time is crucial to ensure they remain accurate and effective.
Feature Importance
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection and Integration | Ability to gather data from diverse sources and integrate it for analysis. | High. Comprehensive data is essential for building accurate models. |
| Data Cleaning and Preprocessing | Features for handling missing values, removing duplicates, and transforming data into a suitable format. | High. Clean and preprocessed data is crucial for accurate model building. |
| Data Exploration and Visualization | Tools for understanding data patterns through visualization techniques. | High. Data exploration helps identify relationships and patterns for model building. |
| Model Building and Selection | Variety of algorithms for building predictive models, allowing selection based on the problem and data. | High. The choice of algorithm significantly impacts model performance. |
| Model Evaluation and Validation | Metrics and techniques for assessing model accuracy and generalizability. | High. Model evaluation ensures the model’s performance and reliability. |
| Model Deployment and Monitoring | Features for deploying models and monitoring their performance over time. | High. Deployment allows real-time predictions, while monitoring ensures model accuracy. |
Real-World Examples
- Customer churn prediction:A telecommunications company can use predictive analytics to identify customers at risk of churn based on their usage patterns, billing history, and demographics. The tool can analyze historical data and build a model to predict which customers are likely to churn, allowing the company to take proactive steps to retain them.
- Fraud detection:Financial institutions can use predictive analytics to detect fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns in transaction data. The tool can identify anomalies and suspicious activities, helping prevent financial losses.
- Inventory management:Retailers can use predictive analytics to optimize their inventory levels by forecasting demand based on historical sales data, seasonal trends, and external factors. The tool can help them avoid stockouts and overstocking, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Choosing the best predictive analytics tools can feel like sifting through a mountain of data. But just like organizing your iPhone photo library, a little bit of effort goes a long way. If you’re struggling with a cluttered photo library and want to take control of your digital memories, check out this helpful shortcut: is your iphone photo library cluttered and taking up storage this shortcut will help you take control of your images and declutter your digital memories for good.
Once you’ve streamlined your photos, you can apply the same principles of organization and clarity to choosing the right predictive analytics tools for your needs.
- Healthcare risk assessment:Hospitals can use predictive analytics to identify patients at risk of developing certain conditions based on their medical history, lifestyle factors, and genetic data. This allows for early intervention and personalized care, improving patient outcomes.
Types of Predictive Analytics Tools

Predictive analytics tools are categorized based on their functionalities, offering a diverse range of solutions for various business needs. Understanding these categories helps in selecting the most suitable tool for specific tasks and data analysis requirements.
Statistical Analysis Tools
Statistical analysis tools are essential for exploring data patterns, identifying trends, and drawing inferences. They provide a solid foundation for understanding data and making informed decisions.Statistical analysis tools excel in handling structured data, enabling users to perform various statistical tests, such as hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and correlation analysis.
These tools are often used for:
- Market research:Analyzing customer demographics, purchase patterns, and market trends to identify opportunities and optimize marketing strategies.
- Financial analysis:Evaluating financial performance, predicting stock prices, and assessing investment risks.
- Quality control:Identifying defects, analyzing production processes, and improving product quality.
Statistical analysis tools often come with user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible to users with varying levels of statistical expertise. However, their capabilities might be limited in handling complex data structures or unstructured data, requiring specialized tools for advanced analysis.
Choosing the best predictive analytics tools depends heavily on your specific needs and the data you’re working with. For a deeper understanding of the skills required to utilize these tools effectively, check out this data modeler job description to see the kind of expertise needed to build predictive models.
Ultimately, the best tools are those that empower you to gain actionable insights from your data and make informed decisions.
Machine Learning Tools
Machine learning tools empower organizations to build predictive models that learn from data and make predictions about future outcomes. These tools are particularly effective in handling large datasets and complex relationships, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights and automate decision-making processes.Machine learning tools are categorized into various algorithms, each with unique strengths and weaknesses.
Choosing the right predictive analytics tool can be a game-changer for your business, and it’s important to consider factors like your budget, data volume, and specific needs. While you’re weighing those options, why not treat yourself to a new pair of AirPods?
Check out these are the cheapest AirPods you can buy this Amazon Prime Day to boost your productivity while you’re exploring the world of predictive analytics. After all, a clear head and a little motivation can go a long way when making critical business decisions.
Some common algorithms include:
- Supervised learning:Training models on labeled data to predict future outcomes based on specific inputs. Examples include regression models for predicting continuous values and classification models for categorizing data points.
- Unsupervised learning:Discovering hidden patterns and structures in unlabeled data. Examples include clustering algorithms for grouping similar data points and dimensionality reduction techniques for simplifying data representations.
- Reinforcement learning:Training agents to learn from interactions with their environment and optimize their actions based on rewards and penalties. This is often used in robotics, game development, and autonomous systems.
Machine learning tools can be applied in various industries, including:
- Healthcare:Predicting patient outcomes, identifying potential diseases, and personalizing treatment plans.
- Finance:Detecting fraudulent transactions, predicting market volatility, and personalizing financial advice.
- E-commerce:Recommending products, personalizing marketing campaigns, and optimizing pricing strategies.
While machine learning tools offer powerful capabilities, they require specialized skills and knowledge to implement and maintain effectively. The complexity of these tools can also present challenges in terms of data preparation, model training, and interpretation.
Data Visualization Tools
Data visualization tools play a crucial role in presenting complex data in a clear and understandable way. They allow users to explore data patterns, identify trends, and communicate insights effectively.Data visualization tools offer various chart types and interactive features, enabling users to create compelling visualizations that highlight key findings and facilitate decision-making.
Common visualization techniques include:
- Scatter plots:Visualizing relationships between two variables, revealing trends and correlations.
- Bar charts:Comparing categorical data, highlighting differences and trends across categories.
- Line charts:Tracking data changes over time, revealing patterns and trends in time series data.
- Heatmaps:Visualizing data distributions across multiple dimensions, highlighting areas of high and low values.
Data visualization tools are valuable for:
- Reporting:Presenting key findings and insights to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner.
- Exploration:Discovering hidden patterns and trends in data, leading to new insights and discoveries.
- Communication:Effectively communicating data-driven insights to different audiences, including technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Data visualization tools are generally user-friendly and accessible to users with varying technical skills. However, the effectiveness of visualization depends on the data quality and the ability to choose appropriate chart types and design elements.
Key Considerations for Choosing Predictive Analytics Tools: Best Predictive Analytics Tools

Selecting the right predictive analytics tool is crucial for leveraging the power of data to make informed decisions and achieve business objectives. There are many factors to consider, each with its own importance and influence on the effectiveness of the chosen tool.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Predictive Analytics Tools
Choosing the right predictive analytics tool involves careful consideration of several factors. These factors encompass technical aspects, usability, scalability, and integration capabilities, ensuring a seamless and effective implementation that aligns with your specific needs and goals.
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handling and Processing Capabilities | The tool should be able to handle the volume, variety, and velocity of your data, including structured and unstructured data. It should also offer efficient data processing and transformation capabilities. | High |
| Predictive Modeling and Algorithm Support | The tool should offer a wide range of predictive modeling algorithms, including regression, classification, clustering, and time series analysis. It should also provide features for model building, training, and evaluation. | High |
| Visualization and Reporting Features | The tool should offer robust visualization capabilities to present insights from data in a clear and understandable way. It should also provide reporting features to communicate results to stakeholders. | Medium |
| Usability and User Interface | The tool should have a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and understand, even for users with limited technical expertise. | Medium |
| Scalability and Performance | The tool should be able to handle increasing data volumes and complex models without compromising performance. It should also be scalable to accommodate future growth. | High |
| Integration with Existing Systems | The tool should integrate seamlessly with your existing data sources, business intelligence platforms, and other applications. | Medium |
| Security and Compliance | The tool should meet your security and compliance requirements, including data privacy regulations. | High |
| Support and Documentation | The vendor should provide adequate support and documentation to help you use the tool effectively. | Medium |
| Cost and Return on Investment (ROI) | The tool should offer a reasonable price point and a clear path to ROI, demonstrating the value it brings to your business. | High |
Popular Predictive Analytics Tools
Predictive analytics tools are essential for businesses looking to gain insights from their data and make better decisions. These tools can be used to predict future outcomes, identify trends, and optimize processes. There are a variety of predictive analytics tools available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
This section explores some of the most popular tools and their key features.
Popular Predictive Analytics Tools
Predictive analytics tools are a diverse group, catering to different needs and skill levels. Understanding their key features, pricing, and target audience can help you choose the right tool for your business.
| Tool Name | Key Features | Pricing Model | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAS | Comprehensive analytics platform, offering advanced statistical modeling, machine learning, and data visualization. | Subscription-based, with various pricing tiers based on features and user count. | Large enterprises, researchers, and data scientists. |
| IBM SPSS Modeler | User-friendly interface for building predictive models, with a focus on data mining and statistical analysis. | Subscription-based, with different pricing plans based on features and user count. | Data analysts, business analysts, and researchers. |
| RapidMiner | Open-source and commercial predictive analytics platform, offering a wide range of algorithms and visualization tools. | Open-source version is free, while the commercial version offers advanced features and support. | Data scientists, researchers, and students. |
| Alteryx | Drag-and-drop interface for building predictive models, suitable for both technical and non-technical users. | Subscription-based, with different pricing plans based on features and user count. | Business analysts, data analysts, and data scientists. |
| Tableau | Data visualization and analysis platform, offering features for building interactive dashboards and exploring data. | Subscription-based, with different pricing plans based on features and user count. | Business analysts, data analysts, and marketing professionals. |
| Microsoft Azure Machine Learning | Cloud-based machine learning platform, offering a wide range of algorithms and tools for building and deploying predictive models. | Pay-as-you-go pricing based on usage. | Data scientists, developers, and businesses of all sizes. |
| Amazon Machine Learning | Cloud-based machine learning platform, offering tools for building and deploying predictive models. | Pay-as-you-go pricing based on usage. | Data scientists, developers, and businesses of all sizes. |
| Google Cloud AI Platform | Cloud-based machine learning platform, offering a wide range of tools for building and deploying predictive models. | Pay-as-you-go pricing based on usage. | Data scientists, developers, and businesses of all sizes. |
Best Practices for Using Predictive Analytics Tools
Predictive analytics tools are powerful instruments for gaining insights and making data-driven decisions. However, their effectiveness hinges on how they are implemented and utilized. This section explores best practices for maximizing the value of predictive analytics tools, ensuring accurate predictions, and fostering actionable insights.
Data Preparation and Quality, Best predictive analytics tools
Preparing and ensuring the quality of data is paramount to accurate predictions. Data quality directly influences the accuracy of predictive models.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing:Removing inconsistencies, errors, and redundancies is crucial. This involves handling missing values, addressing outliers, and standardizing data formats. For instance, ensuring consistent date formats, eliminating duplicate entries, and handling missing values through imputation or removal can significantly enhance data quality.
- Feature Engineering:Transforming raw data into meaningful features that capture relevant patterns and relationships is essential. For example, creating new features by combining existing ones or using domain knowledge to extract relevant features can improve model performance.
- Data Validation and Verification:Regularly verifying the accuracy and completeness of data is crucial to maintain model reliability. This can involve comparing data sources, conducting data audits, and implementing data quality checks.
Model Selection and Training
Selecting the right predictive model and training it effectively are key to generating accurate predictions.
- Model Selection:Choosing the appropriate model depends on the specific problem, data characteristics, and desired outcomes. For instance, linear regression is suitable for predicting continuous variables, while logistic regression is better for binary classification. Evaluating various models based on metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall can help in choosing the best option.
- Model Training and Tuning:Training the model on a representative dataset is crucial for its performance. Tuning model parameters to optimize performance on a validation dataset can further enhance accuracy. Cross-validation techniques, such as k-fold cross-validation, help ensure that the model generalizes well to unseen data.
- Model Evaluation:Assessing the model’s performance using appropriate metrics is essential to understand its effectiveness. Common metrics include accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and AUC (Area Under the Curve). It’s important to select metrics that align with the specific business objectives.
For example, if identifying false positives is critical, precision is a more relevant metric than accuracy.
Deployment and Monitoring
Deploying the model and continuously monitoring its performance are crucial for maintaining its effectiveness.
- Model Deployment:Deploying the trained model into a production environment enables real-time predictions and actionable insights. This may involve integrating the model into existing systems or building new applications.
- Model Monitoring:Regularly monitoring the model’s performance after deployment is essential to ensure its continued accuracy and effectiveness. This involves tracking key metrics, analyzing prediction errors, and identifying potential issues. For example, monitoring the model’s accuracy over time and identifying any significant changes can help in detecting data drift or model degradation.
- Model Retraining:As data evolves, models may become outdated and require retraining. This involves updating the model with new data and ensuring its continued performance. Periodic retraining can help maintain the model’s relevance and accuracy in a dynamic environment.
Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are vital for translating insights into actionable decisions.
- Communicating Insights:Clearly communicating the model’s predictions and insights to stakeholders is crucial for driving action. This involves using visualizations, dashboards, and reports to present the information effectively.
- Stakeholder Engagement:Engaging with stakeholders throughout the process is essential to ensure that the model addresses their needs and aligns with business objectives. This includes soliciting feedback, clarifying assumptions, and ensuring understanding of the model’s limitations.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing:Collaborating with data scientists, business analysts, and domain experts can enhance the model’s effectiveness. Sharing knowledge and best practices can lead to improved model development and deployment.
Future Trends in Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data technologies. These advancements are leading to new possibilities and shaping the future of predictive analytics.
AI-Powered Tools and Advanced Algorithms
The integration of AI into predictive analytics tools is revolutionizing the field. AI-powered tools can automate tasks, improve model accuracy, and unlock new insights. For example, natural language processing (NLP) algorithms can analyze unstructured data like customer reviews and social media posts, providing valuable insights into customer sentiment and behavior.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning algorithms, inspired by the structure of the human brain, are particularly effective in handling complex data patterns. They are being used in areas like fraud detection, risk assessment, and medical diagnostics.
- Reinforcement Learning: This type of ML allows algorithms to learn through trial and error, optimizing their performance based on feedback. It is finding applications in areas like personalized recommendations, autonomous vehicles, and robotics.
Potential Future Applications of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is poised to transform various industries, with applications extending beyond traditional areas like marketing and finance.
- Healthcare: Predictive analytics can be used to identify patients at risk of developing chronic diseases, optimize treatment plans, and predict hospital readmissions.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance can help companies anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
- Education: Predictive analytics can personalize learning experiences, identify students at risk of dropping out, and optimize resource allocation.
Impact of Trends on the Field
These trends are transforming the field of predictive analytics in several ways:
- Increased Automation: AI-powered tools are automating many tasks, freeing up data scientists to focus on higher-level activities like model development and interpretation.
- Improved Accuracy and Insights: Advanced algorithms and increased data availability are leading to more accurate predictions and deeper insights.
- Wider Adoption: The increasing accessibility and affordability of predictive analytics tools are driving wider adoption across industries.