EU AI Act Draft Law: Shaping the Future of Artificial Intelligence
EU AI Act draft law is a landmark piece of legislation aiming to regulate the development and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) systems within the European Union. It seeks to establish a framework that promotes responsible AI innovation while safeguarding fundamental rights and ethical considerations.
The Act classifies AI systems into different risk categories, with varying requirements based on their potential impact. High-risk AI systems, such as those used in healthcare or transportation, are subject to stringent regulations, including risk assessments, transparency, and human oversight.
The goal is to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed in a safe, ethical, and transparent manner, fostering trust and confidence in their use.
Overview of the EU AI Act Draft Law
The EU AI Act Draft Law is a landmark piece of legislation aimed at regulating the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems within the European Union. Its primary objective is to ensure that AI systems are developed and used in a safe, ethical, and trustworthy manner, while fostering innovation and economic growth.The Act seeks to establish a comprehensive legal framework for AI, addressing concerns related to potential risks and promoting responsible AI practices.
It Artikels a risk-based approach to regulation, categorizing AI systems based on the level of risk they pose to individuals and society.
The EU AI Act draft law is a hot topic, raising concerns about the ethical implications of artificial intelligence. While I ponder the complexities of AI regulation, I’m finding solace in the vibrant world of fashion, particularly Etro’s best summer looks, fresh and fashionable styles.
The bold prints and luxurious fabrics are a welcome distraction from the sometimes-dry legal discussions surrounding AI. Ultimately, I believe finding a balance between innovation and ethical considerations is crucial for the future of AI, just as finding the right balance between trends and personal style is key to a successful wardrobe.
Scope of the Act
The EU AI Act Draft Law applies to a wide range of AI systems, including those based on machine learning, deep learning, expert systems, and other techniques. However, it explicitly excludes certain AI systems from its scope, such as those used for purely scientific research or those solely developed and used by individuals for personal purposes.The Act focuses on regulating AI systems that have the potential to impact individuals’ fundamental rights and freedoms.
It aims to address risks related to discrimination, bias, privacy violations, manipulation, and safety.
Risk Categories
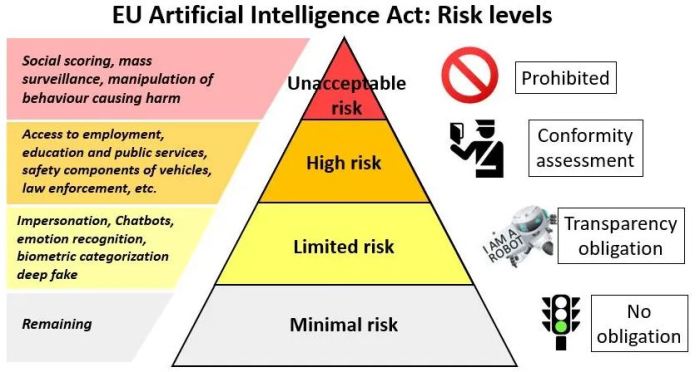
The EU AI Act Draft Law defines four risk categories for AI systems:
- Unacceptable Risk: AI systems deemed to pose an unacceptable risk to safety, health, or fundamental rights are prohibited. Examples include AI systems that manipulate human behavior or exploit vulnerabilities of specific groups.
- High Risk: AI systems that pose a high risk to safety, health, or fundamental rights are subject to stringent requirements. These systems must undergo a conformity assessment process to ensure they meet specific standards and are designed and developed in accordance with ethical principles.
Examples include AI systems used in critical infrastructure, healthcare, or law enforcement.
- Limited Risk: AI systems that pose a limited risk are subject to less stringent requirements. They are encouraged to follow ethical guidelines and ensure transparency and accountability. Examples include AI systems used in customer service or marketing.
- Minimal Risk: AI systems that pose minimal risk are largely unregulated. They are subject to general requirements related to transparency and information provision. Examples include AI systems used for simple tasks like spam filtering or fraud detection.
Key Provisions and Requirements

The EU AI Act draft law establishes a comprehensive regulatory framework for AI systems, aiming to ensure their safe, ethical, and responsible development and deployment. The Act categorizes AI systems into different risk levels, with the most stringent requirements imposed on high-risk systems.
This section delves into the key provisions and requirements of the EU AI Act, particularly focusing on high-risk AI systems.
Requirements for High-Risk AI Systems
The EU AI Act identifies specific requirements for high-risk AI systems, ensuring they meet stringent standards of safety, transparency, and accountability. These requirements are designed to minimize potential risks and promote trust in the use of AI.
| Requirement | Description | Example | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Assessment and Mitigation Measures | Developers and deployers of high-risk AI systems are obligated to conduct thorough risk assessments, identifying and evaluating potential risks associated with their systems. They must implement appropriate mitigation measures to address these risks, ensuring the systems operate safely and ethically. | A risk assessment for a high-risk AI system used in healthcare might identify potential risks of biased diagnoses or inaccurate treatment recommendations. Mitigation measures could include using diverse datasets, implementing robust testing protocols, and providing clear explanations for decisions made by the AI system. | This requirement ensures that potential risks are proactively identified and addressed, promoting responsible development and deployment of high-risk AI systems. |
| Data Governance and Quality Control | The Act mandates stringent data governance practices for high-risk AI systems, ensuring the quality, reliability, and integrity of the data used to train and operate these systems. This includes requirements for data provenance, data security, and data quality checks. | For a high-risk AI system used in autonomous vehicles, the Act would require robust data governance practices, ensuring the data used to train the system is accurate, diverse, and free from biases. This would involve measures like data validation, data annotation, and data quality control. | Strong data governance practices are crucial for ensuring the accuracy, fairness, and reliability of high-risk AI systems, minimizing the potential for biased or inaccurate outcomes. |
| Transparency and Explainability | High-risk AI systems must be designed and developed to provide clear and understandable explanations for their decisions. This requirement aims to enhance transparency and accountability, allowing users to understand how the system reaches its conclusions. | An AI system used for credit scoring should provide transparent explanations for its decisions, allowing users to understand why they were granted or denied credit. This could involve providing insights into the factors considered by the AI system, such as credit history, income, and debt-to-income ratio. | Transparency and explainability are essential for building trust in AI systems, enabling users to understand the basis for their decisions and fostering accountability. |
| Human Oversight and Control | The Act emphasizes the importance of human oversight and control over high-risk AI systems. This includes requirements for human intervention in critical situations, ensuring that AI systems do not operate autonomously in situations where human judgment is necessary. | For a high-risk AI system used in autonomous vehicles, human oversight would be crucial in situations where the system encounters unexpected or complex scenarios. This could involve mechanisms for human intervention, such as remote control or the ability to override the system’s decisions. | Human oversight and control are essential for mitigating potential risks and ensuring the safety and ethical operation of high-risk AI systems. |
Obligations for Developers and Deployers of High-Risk AI Systems
Developers and deployers of high-risk AI systems are subject to specific obligations under the EU AI Act, ensuring responsible development, deployment, and ongoing management of these systems.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation Measures:Developers and deployers must conduct thorough risk assessments to identify and evaluate potential risks associated with their high-risk AI systems. They must implement appropriate mitigation measures to address these risks, ensuring the systems operate safely and ethically. This includes measures such as data quality control, bias mitigation, and robust testing protocols.
- Data Governance and Quality Control:Developers and deployers are responsible for ensuring the quality, reliability, and integrity of the data used to train and operate their high-risk AI systems. This involves implementing robust data governance practices, including data provenance, data security, and data quality checks.
They must ensure that the data is relevant, accurate, and representative, minimizing the risk of biased or inaccurate outcomes.
- Transparency and Explainability:Developers and deployers must design and develop their high-risk AI systems to provide clear and understandable explanations for their decisions. This ensures transparency and accountability, allowing users to understand how the system reaches its conclusions. This could involve providing insights into the factors considered by the AI system, the data used for training, and the logic behind its decisions.
- Human Oversight and Control:The Act emphasizes the importance of human oversight and control over high-risk AI systems. Developers and deployers must ensure that human operators are involved in critical situations, ensuring that AI systems do not operate autonomously in situations where human judgment is necessary.
This could involve mechanisms for human intervention, such as remote control or the ability to override the system’s decisions.
- Conformity Assessment and Certification:Developers and deployers must undergo conformity assessment and certification processes to demonstrate that their high-risk AI systems comply with the requirements of the EU AI Act. This involves independent assessments by accredited bodies, ensuring that the systems meet the required standards of safety, transparency, and accountability.
Certification provides assurance to users and stakeholders that the AI systems have been rigorously evaluated and meet the necessary standards.
Provisions for AI Systems Deemed Unacceptable Risk
The EU AI Act identifies certain applications of AI as posing unacceptable risks and prohibits their development and deployment. These prohibitions aim to protect fundamental rights and prevent potential harms associated with these applications.
The EU AI Act draft law is a crucial step towards ensuring ethical and responsible development of artificial intelligence. It tackles issues like transparency, accountability, and bias in AI systems. This approach to AI regulation resonates with the urgent need for robust safeguards in the rapidly evolving metaverse, as highlighted in this insightful article on the metaverse needs aggressive regulation.
Just as the EU AI Act aims to mitigate potential harms from AI, a comprehensive regulatory framework for the metaverse is essential to prevent exploitation, privacy violations, and other negative consequences.
- Prohibited Applications:The Act prohibits the development and deployment of AI systems that are deemed to pose unacceptable risks, such as systems that manipulate or exploit vulnerable individuals, or systems that violate fundamental rights. These applications are considered inherently harmful and are deemed incompatible with the principles of ethical and responsible AI.
- Justification:The Act provides justification for these prohibitions, highlighting the potential harms associated with these applications. This justification is based on ethical considerations, human rights principles, and the need to protect vulnerable individuals from exploitation and manipulation. The Act emphasizes the importance of safeguarding fundamental rights and preventing the misuse of AI technologies.
- Potential Sanctions for Non-Compliance:The Act Artikels potential sanctions for non-compliance with its provisions, including fines and other penalties. These sanctions aim to deter developers and deployers from developing or deploying AI systems that violate the Act’s requirements. The Act seeks to create a strong deterrent effect, encouraging compliance and promoting responsible AI development and deployment.
Impact on Businesses and Industries
The EU AI Act is poised to have a profound impact on businesses across various sectors, prompting them to adapt their operations and strategies to comply with the new regulations. While the Act aims to foster responsible AI development and deployment, it also presents challenges and opportunities for businesses.
Impact on Healthcare
The healthcare industry stands to benefit significantly from AI, with applications ranging from disease diagnosis and treatment planning to drug discovery and personalized medicine. However, the EU AI Act imposes specific requirements for high-risk AI systems used in healthcare, such as those involved in medical diagnosis or treatment.
These requirements include ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and transparency of AI systems, as well as establishing robust risk management and data governance frameworks.
The Act emphasizes the need for transparency and accountability in AI systems used in healthcare, requiring developers to provide clear explanations for the AI’s decisions and to ensure that users understand the limitations of the technology.
The EU AI Act draft law is a complex piece of legislation, aiming to regulate the development and deployment of artificial intelligence. It’s a fascinating topic, and one that makes me think about how we interact with technology on a daily basis.
It’s a bit like the elsies fashion challenge three months in – a challenge that’s pushing the boundaries of creativity and sustainability. Just like the fashion challenge, the EU AI Act is trying to shape the future of a rapidly evolving field, and it’s going to be interesting to see how it all unfolds.
Impact on Finance
The financial sector is already heavily reliant on AI for tasks such as fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading. The EU AI Act will likely impact the financial industry by requiring financial institutions to comply with specific regulations for high-risk AI systems used in financial services.
This could include ensuring the fairness and transparency of AI algorithms, as well as implementing robust risk management and data security measures.
The Act’s focus on fairness and transparency in AI algorithms will likely lead to greater scrutiny of AI-powered financial services, such as loan applications and investment recommendations, to ensure that they do not discriminate against certain groups of customers.
Impact on Transportation
The transportation industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by AI, with applications in autonomous vehicles, traffic management, and logistics. The EU AI Act will have a significant impact on the development and deployment of AI in transportation, requiring developers to meet specific safety and security standards for high-risk AI systems.
The Act’s emphasis on safety and security will likely lead to increased testing and validation of AI-powered autonomous vehicles, ensuring that they meet rigorous safety standards before they are deployed on public roads.
Impact on Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry is increasingly adopting AI for tasks such as predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. The EU AI Act will likely impact the manufacturing sector by requiring companies to comply with specific regulations for high-risk AI systems used in industrial settings.
This could include ensuring the safety and reliability of AI systems, as well as implementing robust risk management and data governance frameworks.
The Act’s focus on safety and reliability will likely lead to increased scrutiny of AI systems used in manufacturing, ensuring that they do not pose risks to workers or the environment.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
The EU AI Act, with its comprehensive approach to regulating AI, grapples with the multifaceted ethical and societal implications of this transformative technology. It aims to ensure that AI development and deployment are aligned with human values, safeguarding fundamental rights and fostering a fair and equitable society.
Bias and Discrimination in AI Systems, Eu ai act draft law
The Act recognizes the potential for AI systems to perpetuate and even amplify existing societal biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes. It addresses this by imposing obligations on developers to mitigate bias throughout the AI lifecycle. This includes:
- Data quality and diversity:Developers must ensure that the training data used for AI systems is representative and free from biases, minimizing the risk of biased outcomes.
- Transparency and explainability:The Act promotes transparency by requiring developers to explain the decision-making processes of their AI systems, enabling users to understand and challenge potentially discriminatory outcomes.
- Risk assessment and mitigation:Developers must assess the potential risks of bias and discrimination associated with their AI systems and implement appropriate mitigation measures.
For example, the Act emphasizes the importance of diverse and representative data sets in the development of facial recognition systems, which have been shown to exhibit racial bias in the past.
Privacy and Data Protection Concerns
The EU AI Act acknowledges the significant privacy and data protection implications of AI systems, particularly those that process personal data. It builds upon the existing GDPR framework to provide further safeguards:
- Data minimization:AI systems should only process the minimum amount of data necessary for their intended purpose, limiting the potential for misuse or breaches.
- Data access and control:Individuals should have access to and control over their personal data processed by AI systems, enabling them to exercise their right to erasure or rectification.
- Privacy by design and default:AI systems should be designed and developed with privacy considerations at the forefront, ensuring that data protection is embedded in their architecture.
The Act also emphasizes the importance of secure data storage and processing practices, minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Comparison with Other AI Regulations
The EU AI Act stands out as a comprehensive regulatory framework for AI, but it is not the only attempt to govern this rapidly evolving technology. Several other jurisdictions have implemented or proposed AI regulations, each with its own approach and priorities.
Comparing these frameworks can shed light on the global landscape of AI regulation and potential areas for harmonization.
Risk-Based Approach and Categorization
Different regulatory frameworks employ distinct risk-based approaches to AI regulation. The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems into four risk levels: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal risk. The US AI Risk Management Framework adopts a broader approach, focusing on managing risks across the AI lifecycle, while the UK AI Regulation emphasizes the importance of responsible innovation.
The Chinese AI Governance Principles focus on promoting ethical AI development and application.
- The EU AI Act: Prohibits AI systems deemed unacceptable, such as those used for social scoring or real-time facial recognition in public spaces. High-risk AI systems, including those used in critical infrastructure, healthcare, and law enforcement, are subject to stringent requirements, including conformity assessments and risk management.
Limited-risk AI systems, such as chatbots, are subject to transparency obligations, while minimal-risk AI systems face minimal regulatory scrutiny.
- The US AI Risk Management Framework: Focuses on managing risks throughout the AI lifecycle, including design, development, deployment, and use. It encourages organizations to adopt risk management practices, such as identifying and assessing risks, implementing controls, and monitoring outcomes.
However, it lacks specific regulatory requirements for different risk categories.
- The UK AI Regulation: Emphasizes responsible innovation and encourages organizations to adopt ethical principles and best practices for AI development and deployment. It also Artikels regulatory principles for AI systems that pose risks to public safety, security, or human rights.
- The Chinese AI Governance Principles: Promote the development and application of ethical AI, emphasizing principles such as fairness, transparency, accountability, and human control. The principles aim to guide the development and use of AI in accordance with ethical and societal values.
Future Implications and Challenges
The EU AI Act, with its far-reaching scope and ambitious goals, is poised to have a profound impact on the future of AI development and deployment. It represents a significant step towards establishing a global framework for responsible AI governance, shaping the trajectory of AI innovation and its societal implications.
Fostering Innovation and Responsible AI Practices
The EU AI Act aims to foster innovation by creating a predictable and trustworthy environment for AI development and deployment. By establishing clear guidelines and standards, it aims to reduce uncertainty and encourage businesses to invest in AI technologies. The Act also emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations, ensuring that AI systems are developed and used in a responsible manner.
Shaping Global Standards for AI Governance
The EU AI Act is expected to have a significant influence on the development of global standards for AI governance. As a leading player in the global technology landscape, the EU’s regulatory framework is likely to be adopted or adapted by other countries and regions.
This could lead to the emergence of a more harmonized approach to AI governance, reducing fragmentation and promoting international cooperation.
Influencing the Development of AI Technologies
The EU AI Act is likely to influence the development of AI technologies themselves. By requiring developers to consider ethical and societal implications, the Act could encourage the development of AI systems that are more transparent, accountable, and aligned with human values.
It could also lead to the development of new tools and technologies that support responsible AI development and deployment.
Defining and Measuring AI Risk
One of the key challenges in implementing the EU AI Act is defining and measuring AI risk. The Act categorizes AI systems based on their potential risk levels, ranging from unacceptable to minimal. However, there is no single, universally accepted definition of AI risk, and different stakeholders may have varying perspectives.
Developing clear and objective criteria for assessing AI risk is crucial for ensuring effective enforcement of the Act.
Ensuring Effective Oversight and Enforcement
The EU AI Act establishes a complex regulatory framework involving multiple stakeholders, including national authorities, industry actors, and civil society organizations. Ensuring effective oversight and enforcement requires close collaboration between these stakeholders and the development of clear procedures for monitoring and addressing potential violations.
Balancing Innovation with Ethical Considerations
The EU AI Act seeks to strike a balance between fostering innovation and addressing ethical concerns. This balance is not always easy to achieve, as stringent regulations could stifle innovation, while lax regulations could lead to unintended negative consequences. Finding the right balance will require ongoing dialogue and collaboration between policymakers, industry actors, and researchers.