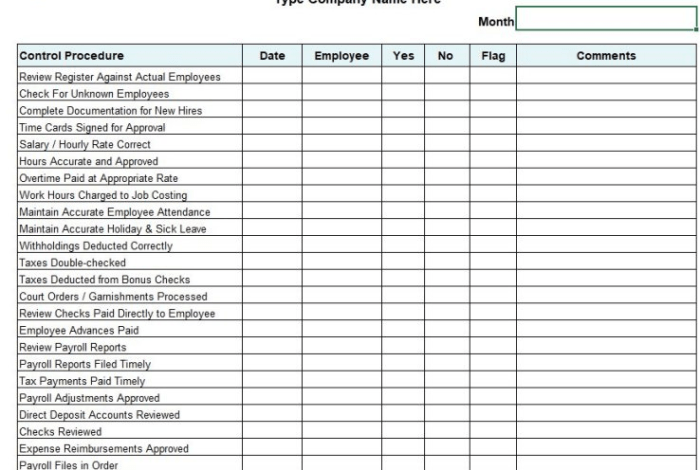
First Payroll Run Checklist: A Guide for New Businesses
First payroll run checklist – The first payroll run is a significant milestone for any new business. It’s the moment when you transition from planning to execution, ensuring your employees are paid accurately and on time. This checklist will guide you through the essential steps, from setting up payroll software to managing tax deductions and ensuring compliance.
Navigating the intricacies of payroll can feel overwhelming, but with a structured approach and a clear understanding of the process, you can ensure a smooth and successful first payroll run. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key steps, from collecting employee information to processing payments and staying compliant with regulations.
Pre-Payroll Setup
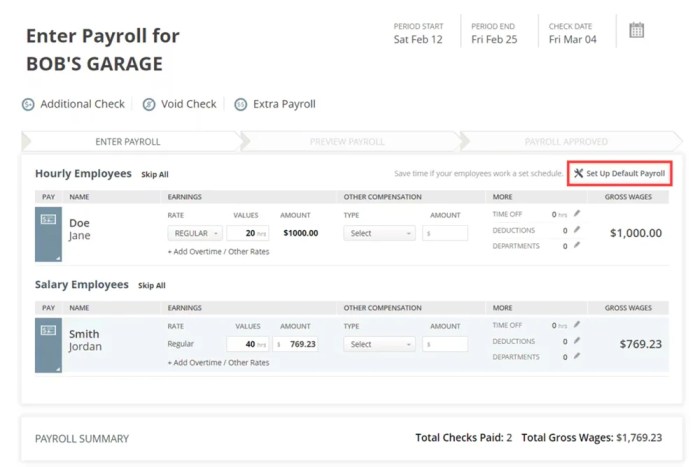
The first payroll run is a crucial milestone for any business. A smooth and accurate process requires meticulous planning and preparation. Establishing a clear payroll schedule is essential for consistent and timely payments to your employees. This schedule will serve as a roadmap for all future payroll cycles, ensuring predictable and reliable payment distribution.
Getting your first payroll run right is crucial for any business. It involves ensuring accurate employee data, setting up deductions correctly, and filing the necessary taxes. While navigating this process, remember that investing in your financial knowledge is equally important.
The tykr stock screener top tools training bundle offers valuable insights and tools to help you make informed financial decisions. Once you’ve mastered the payroll process, consider exploring these resources to enhance your overall financial literacy and grow your business effectively.
Essential Documents for Payroll
Having all the necessary documents in order before your first payroll run is critical for a successful process. These documents provide the foundational information required for calculating wages, deductions, and taxes.
- Employee Information: Gather essential details about each employee, including their name, address, Social Security number, date of birth, and employment start date. This information is vital for accurate payroll calculations and tax reporting.
- Tax Forms: Obtain and review the relevant tax forms from your employees, such as W-4 (Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate) and I-9 (Employment Eligibility Verification). These forms determine the amount of federal and state income tax to withhold from employee paychecks.
- Bank Details: Collect bank account information from your employees, including their bank name, account number, and routing number. This information is necessary for direct deposit payments.
Setting Up Payroll Software or Systems
Selecting and setting up the right payroll software or system is essential for managing payroll efficiently.
- Choose Payroll Software: Research and select payroll software that meets your business needs and budget. Consider features like tax compliance, direct deposit capabilities, reporting tools, and integration with other business systems.
- Set Up Employee Profiles: Create employee profiles in the payroll system, entering their personal information, tax details, and bank account information accurately.
- Configure Payroll Settings: Configure payroll settings, such as pay frequency, tax rates, and deductions. Ensure these settings are accurate and compliant with local and federal regulations.
- Test Payroll System: Before processing your first payroll run, test the system with sample data to ensure accuracy and functionality. This step helps identify any potential errors or issues before processing actual payroll data.
Data Entry Accuracy and Verification
Accurate data entry is critical for ensuring accurate payroll calculations and avoiding costly errors.
- Double-Check Data: Always double-check all entered data, including employee information, hours worked, and tax details. This step helps prevent mistakes and ensures the accuracy of payroll calculations.
- Utilize Data Validation Tools: Employ data validation tools within your payroll software to ensure data accuracy and consistency. These tools can help identify potential errors and inconsistencies in data entry.
- Regular Data Audits: Conduct regular data audits to verify the accuracy and completeness of payroll data. This process helps identify any discrepancies or errors that may have occurred.
Employee Data Collection
Accurate and complete employee data is crucial for payroll processing. It ensures timely and accurate payment of wages and benefits, as well as compliance with tax and labor regulations.
Getting your first payroll run right is crucial, but it’s also a great opportunity to celebrate! After all, you’re officially a business owner! And just like you deserve a comfortable spot to relax after a long day, your furry friend deserves the same.
Check out the Sadie Bed how to make a modern pet bed for some DIY inspiration. Once you’ve got your payroll process nailed down and your pet is snuggled in their new bed, you can focus on the exciting growth of your business.
Employee Data Table
This table Artikels the necessary employee information for payroll processing.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Employee’s full legal name |
| Address | Employee’s current residential address |
| Social Security Number | Employee’s unique identification number for tax purposes |
| Pay Rate | Employee’s hourly or salary rate |
| Date of Birth | Employee’s birthdate |
| Tax Withholding Information | Employee’s tax withholding preferences, including federal, state, and local taxes |
| Direct Deposit Information | Employee’s bank account details for direct deposit of wages |
| Emergency Contact Information | Contact information for a person to be reached in case of emergency |
Verifying Employee Information
Verifying employee information for accuracy is essential to avoid errors in payroll processing. This can be done by:
- Comparing informationprovided by the employee with existing records, such as government-issued identification documents or previous employment records.
- Cross-referencinginformation with other sources, such as the Social Security Administration’s website or the employee’s bank statements.
- Requesting employeesto review and confirm their information before payroll processing.
Collecting New Hire Information
The process for collecting and documenting new hire information is crucial for accurate payroll processing.
- Complete a new hire formthat includes all necessary employee information, such as name, address, Social Security number, and pay rate.
- Verify the employee’s identityusing government-issued identification documents, such as a driver’s license or passport.
- Obtain the employee’s tax withholding information, including their W-4 form and any other relevant tax documents.
- Set up direct depositfor the employee’s wages, if desired.
- Maintain a secure and organized systemfor storing employee information.
Managing Employee Changes
Managing employee changes, such as salary adjustments or address updates, requires careful attention to detail.
- Implement a systemfor tracking employee changes, such as a spreadsheet or a dedicated software program.
- Notify employeesof any changes to their payroll information, such as salary adjustments or tax withholding changes.
- Document all changesto employee information, including the date of the change, the reason for the change, and the person who made the change.
- Review employee informationregularly to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Tax and Deduction Setup
Setting up taxes and deductions correctly is crucial for accurate payroll processing and compliance with tax regulations. This involves understanding the various types of taxes and deductions, configuring withholding settings in your payroll software, and ensuring that all deductions are calculated and processed correctly.
Types of Taxes and Deductions
Taxes and deductions are essential components of payroll processing. They are typically categorized into two main types:
- Federal Taxes:These are taxes levied by the federal government on employee income. They include:
- Income Tax:A percentage of an employee’s income is withheld for federal income tax purposes. The amount withheld depends on factors such as the employee’s filing status, income level, and the number of dependents they claim.
- Social Security Tax:This tax funds Social Security benefits, which provide retirement, disability, and survivor benefits to eligible individuals. Both the employer and employee contribute to Social Security tax.
- Medicare Tax:This tax funds Medicare, a health insurance program for people over 65 and individuals with disabilities. Like Social Security tax, both the employer and employee contribute to Medicare tax.
- State and Local Taxes:Depending on the state and local jurisdiction, employees may be subject to additional taxes. These include:
- State Income Tax:Most states have income taxes, which are calculated and withheld based on the employee’s income and state tax laws.
- Local Income Tax:Some cities and counties have local income taxes, which are levied on top of state income tax.
- Unemployment Tax:This tax is paid by employers to fund unemployment benefits for eligible individuals who lose their jobs.
Configuring Tax Withholding Settings
Payroll software allows you to configure tax withholding settings for each employee. This involves setting up the employee’s tax information, including their filing status, dependents, and any other relevant tax information.
- Employee Information:The payroll system should capture essential employee information, such as their Social Security number, address, and date of birth, to correctly identify and classify them for tax purposes.
- Tax Forms:Employees are typically required to complete Form W-4, Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate, to inform their employer about their withholding preferences. The system should allow you to input the information from Form W-4 to calculate federal income tax withholding accurately.
- State and Local Tax Forms:Similar to federal income tax, employees may need to complete state and local tax forms to provide their tax information. The payroll system should have the functionality to capture this information and calculate state and local taxes.
Common Payroll Deductions
In addition to taxes, employers often deduct various items from employee paychecks. These deductions can be categorized as follows:
| Deduction Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Health Insurance | This covers premiums for health insurance plans, including medical, dental, and vision coverage. |
| Retirement Contributions | These are contributions made by employees to retirement plans, such as 401(k) or 403(b) plans. |
| Union Dues | If employees belong to a union, their dues are deducted from their paychecks. |
| Child Support | Court-ordered child support payments can be deducted from paychecks. |
| Garnishment | This is a legal process where a portion of an employee’s wages is deducted to pay off a debt, such as unpaid taxes or student loans. |
| Other Deductions | This category includes deductions for items like charitable contributions, flexible spending accounts, and life insurance premiums. |
Best Practices for Calculating and Processing Taxes and Deductions
To ensure accurate payroll processing, follow these best practices:
- Regularly Update Tax Information:Employees’ tax situations can change throughout the year. It’s crucial to update their withholding information in the payroll system promptly to ensure accurate tax calculations.
- Verify Deduction Amounts:Before processing payroll, double-check that all deduction amounts are accurate and that the correct deductions are being applied to each employee’s paycheck.
- Stay Informed About Tax Laws:Tax laws are constantly changing. Staying informed about the latest tax regulations and updates is crucial for accurate payroll processing.
- Utilize Payroll Software:Payroll software can help automate tax and deduction calculations, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
- Maintain Records:Keep accurate records of all tax and deduction calculations. This will help you track employee earnings and withholdings and ensure compliance with tax reporting requirements.
Payroll Processing

The payroll processing stage involves calculating employee earnings, deductions, and net pay, and generating paychecks or direct deposits. This step also includes generating and submitting payroll reports to relevant authorities, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Generating Paychecks
This involves calculating the gross pay, deductions, and net pay for each employee.
Gross pay represents the total earnings before any deductions.
Deductions include taxes, insurance premiums, retirement contributions, and other withholdings.
Running your first payroll is a big deal, and it’s essential to have a solid checklist to ensure everything goes smoothly. From setting up employee information to understanding tax deductions, there are many details to consider. And if you’re looking to streamline your accounting processes even further, you might want to check out introducing the Floqast accounting transformation platform bringing AI power to accounting automation.
This platform can help automate tasks, improve accuracy, and free up your time to focus on more strategic initiatives. Once your payroll is up and running, you can explore how Floqast can help you manage other critical accounting processes, making your life easier and more efficient.
Net pay is the amount of money an employee receives after all deductions have been taken out.
The following steps Artikel the process of generating paychecks:
- Collect time and attendance data:This includes hours worked, overtime, and any other relevant information.
- Calculate gross pay:Multiply the employee’s hourly rate by the number of hours worked.
- Calculate deductions:Apply the appropriate tax rates and deduction amounts based on the employee’s information and relevant laws.
- Calculate net pay:Subtract deductions from gross pay.
- Generate paychecks or direct deposits:Issue paychecks or initiate direct deposits to employee bank accounts.
Generating Payroll Reports
Payroll reports provide a summary of payroll information, including earnings, deductions, and taxes withheld. They are essential for compliance and tax reporting purposes.
- Payroll register:This report lists each employee’s earnings, deductions, and net pay for a specific pay period.
- Tax reports:These reports summarize the taxes withheld from employees’ paychecks and are filed with relevant tax authorities.
- Wage and tax statements:These statements provide employees with a summary of their earnings and taxes withheld for the year.
Maintaining Accurate Payroll Records
Maintaining accurate payroll records is crucial for compliance and auditing purposes.
- Employee information:This includes names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and other relevant details.
- Earnings and deductions:This includes information on hourly rates, overtime pay, taxes withheld, and other deductions.
- Payroll reports:These reports should be kept organized and easily accessible for future reference.
Handling Payroll Discrepancies
Payroll discrepancies can occur due to errors in timekeeping, calculations, or data entry.
- Identify the discrepancy:Determine the nature of the error and the affected employees.
- Investigate the cause:Review payroll records, timekeeping data, and other relevant information to identify the root cause of the discrepancy.
- Correct the error:Make the necessary adjustments to payroll records and issue any required corrections.
- Communicate with employees:Inform affected employees about the discrepancy and any necessary corrections.
Post-Payroll Procedures
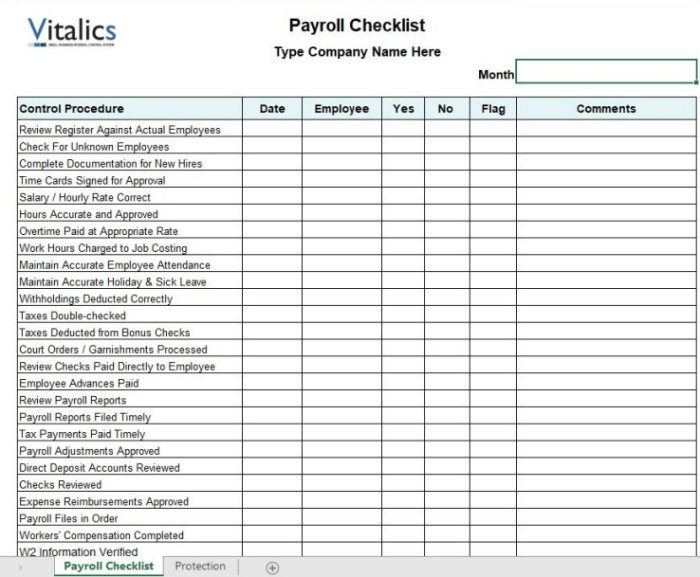
Once you’ve successfully processed payroll, it’s time to move on to the post-payroll procedures, which ensure accuracy, compliance, and proper record-keeping. These procedures are essential for maintaining a smooth and efficient payroll process.
Distributing Paychecks or Making Direct Deposits
This step involves getting the paychecks into the hands of your employees or ensuring direct deposits are made into their bank accounts.
- Prepare Paychecks:After payroll processing, print paychecks or generate electronic pay stubs for employees who receive paper checks. Verify that the details on each paycheck are accurate, including employee name, pay period, gross pay, deductions, and net pay.
- Direct Deposit Processing:For employees who receive direct deposits, ensure that their bank account information is accurate and up-to-date. Initiate the electronic transfer of funds to their designated accounts. Confirm that the correct amount is deposited into each employee’s account.
- Distribution:Deliver paychecks to employees who receive paper checks. You can distribute them in person, by mail, or through a secure online portal. For direct deposits, confirm that funds have been credited to employees’ accounts.
Reconciling Payroll Data with Bank Statements
Reconciling your payroll data with your bank statements is crucial for ensuring that all payroll transactions are accurate and accounted for.
- Compare Transactions:Match the payroll data, such as the total amount of payroll expenses, with the corresponding entries on your bank statement. Ensure that all payroll transactions are reflected in both your payroll records and your bank statement.
- Investigate Discrepancies:If you find discrepancies between your payroll data and bank statement, investigate the reason for the difference. Common causes of discrepancies include incorrect entries, missing transactions, or unauthorized payments. Correct any errors and document the resolution process.
- Regular Reconciliation:Reconcile your payroll data with your bank statement regularly, ideally on a monthly basis. This practice helps you catch errors early on and prevent financial losses.
Archiving Payroll Records and Ensuring Data Security
Maintaining accurate and secure payroll records is crucial for compliance and historical reference.
- Record Retention:Establish a clear record retention policy for payroll documents, including paychecks, pay stubs, tax forms, and other related documents. The specific retention period will vary depending on your location and applicable regulations.
- Data Security:Implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive payroll information from unauthorized access. Use strong passwords, secure storage systems, and encryption techniques to safeguard employee data.
- Secure Storage:Store payroll records in a secure location, either physically or digitally. Use secure file-sharing systems or cloud storage solutions with strong security protocols.
Managing Payroll Compliance and Staying Updated on Regulatory Changes
Staying up-to-date on payroll regulations is essential for avoiding penalties and ensuring compliance.
- Tax Compliance:Ensure that all payroll taxes are calculated and paid correctly and on time. Stay informed about any changes in tax laws and regulations.
- Wage and Hour Laws:Comply with all federal, state, and local wage and hour laws, including minimum wage requirements, overtime rules, and record-keeping regulations.
- Stay Informed:Subscribe to relevant industry publications, attend webinars, and consult with payroll professionals to stay abreast of changes in payroll regulations.
Payroll Software and Tools
Payroll software and tools are essential for businesses of all sizes to streamline payroll processing, ensure accuracy, and comply with tax regulations. Choosing the right payroll software can significantly impact efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall payroll management.
Comparing Payroll Software Options
Payroll software options vary in features, pricing, and target audience. Understanding the different types of software available is crucial for making an informed decision.
- Cloud-based payroll software: This type of software is hosted online and accessible from any device with an internet connection. Cloud-based payroll solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and automatic updates. Popular examples include QuickBooks Online Payroll, Gusto, and Paychex Flex.
- On-premise payroll software: On-premise software is installed and operated on a company’s own servers. This option provides greater control over data security but requires more upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Examples include ADP Workforce Now and Oracle PeopleSoft.
- Hybrid payroll software: Hybrid payroll software combines elements of cloud-based and on-premise solutions. This approach offers flexibility and control while minimizing the need for significant IT infrastructure.
Features and Functionalities of Popular Payroll Software
Popular payroll software solutions offer a wide range of features designed to simplify payroll processing and enhance efficiency.
- Payroll processing: Software automates payroll calculations, including gross pay, deductions, and net pay, ensuring accuracy and reducing manual errors. Features like time and attendance tracking, leave management, and direct deposit integration streamline payroll processing.
- Tax calculations: Payroll software automatically calculates and files federal, state, and local taxes, ensuring compliance with ever-changing tax laws. Some software solutions even offer tax planning tools and insights.
- Reporting and analytics: Comprehensive reporting features allow businesses to track payroll costs, identify trends, and generate insights for decision-making. Reports may include payroll summaries, tax forms, employee earnings statements, and more.
- Integration with other systems: Many payroll software solutions integrate with other business applications, such as accounting software, HR systems, and time tracking software. This integration eliminates data entry duplication and streamlines workflows.
Pros and Cons of Using Payroll Software
| Feature | Payroll Software | Manual Payroll Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Higher accuracy due to automation and built-in calculations | Prone to errors due to manual calculations and data entry |
| Efficiency | Streamlined processes and automated tasks save time and effort | Time-consuming and labor-intensive, requiring significant manual effort |
| Compliance | Ensures compliance with tax laws and regulations through automated calculations and filings | Requires extensive knowledge of tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance |
| Cost | Recurring subscription fees or one-time purchase costs | Potentially lower initial costs but may require additional resources for payroll management |
| Scalability | Easily scales to accommodate growing businesses and changing payroll needs | May require significant adjustments to handle increased payroll volume |
Choosing the Right Payroll Software
Selecting the right payroll software depends on various factors, including business size, industry, budget, and specific needs.
- Business size and industry: Small businesses may opt for affordable cloud-based solutions, while larger enterprises may require more robust on-premise software. Industry-specific needs, such as union compliance or specific tax requirements, should also be considered.
- Budget: Payroll software options vary in pricing, ranging from free or low-cost plans to more expensive enterprise solutions. Consider the features and functionality offered at different price points to find the best value for your business.
- Features and functionality: Evaluate the features and functionality offered by different software solutions to ensure they meet your specific needs. Consider factors like time and attendance tracking, leave management, tax calculations, reporting, and integrations with other systems.
- Customer support: Choose a software provider with excellent customer support, including phone, email, and live chat options. Reliable support ensures timely assistance with any technical issues or questions.
Payroll Compliance: First Payroll Run Checklist
Payroll compliance is a critical aspect of running a successful business. It involves adhering to a complex web of federal, state, and local laws and regulations that govern how you pay your employees. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in significant financial penalties, legal issues, and damage to your company’s reputation.
Federal, State, and Local Payroll Laws
Understanding the specific laws that apply to your business is crucial. Federal laws establish minimum wage requirements, overtime regulations, and tax withholding rules. State laws may have their own minimum wage standards, unemployment insurance requirements, and other specific regulations. Local laws might include additional requirements for sick leave or paid time off.
Complying with Labor Laws, First payroll run checklist
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) is a federal law that sets minimum wage and overtime standards for most workers in the United States. It also establishes child labor laws. It’s essential to understand the FLSA’s requirements, such as the minimum wage, overtime pay, and exemptions for certain types of employees.
State laws may have their own minimum wage and overtime regulations, which can be more stringent than federal laws.
Payroll Tax Returns and Reporting
Payroll taxes are collected from employees’ wages and paid to the government. These taxes include Social Security, Medicare, federal income tax, and state and local income taxes. Employers are responsible for withholding these taxes from employee paychecks and filing regular tax returns with the appropriate government agencies.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires employers to file Form 941, Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return, to report and pay federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes withheld from employee wages.
Best Practices for Payroll Compliance
Maintaining payroll compliance is an ongoing process. Here are some best practices to help you avoid potential penalties:
- Stay Updated on Legal Changes:Payroll laws are constantly evolving. Regularly review updates to ensure your processes remain compliant.
- Use Reliable Payroll Software:Payroll software can help automate tax calculations, generate accurate paychecks, and simplify compliance tasks.
- Maintain Accurate Records:Keep detailed records of employee information, pay rates, deductions, and tax withholdings. These records should be easily accessible and organized.
- Seek Professional Advice:If you’re unsure about payroll compliance requirements, consult with a payroll specialist or an accountant. They can provide guidance and help you navigate the complexities of payroll laws.






