Hybrid Cloud: The Smart Persons Guide
Hybrid cloud the smart persons guide – Hybrid Cloud: The Smart Person’s Guide is your roadmap to navigating the complex world of cloud computing. It’s a journey that takes you beyond the traditional confines of on-premises infrastructure and into the dynamic realm of cloud services. We’ll explore the advantages of combining the best of both worlds, uncovering the benefits and challenges of this innovative approach.
Imagine a scenario where your business can seamlessly scale resources on demand, harnessing the power of public cloud for peak performance while keeping sensitive data secure within your own data centers. This is the promise of hybrid cloud, a flexible and cost-effective solution that empowers organizations to adapt and thrive in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid cloud computing is a blend of public and private cloud services, allowing businesses to leverage the best of both worlds. It offers flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness while maintaining control over sensitive data and applications.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud Environment
A hybrid cloud environment consists of various components that work together to provide a seamless and integrated cloud experience.
- Public Cloud:This refers to cloud services provided by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Public clouds offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, scalability, and a wide range of services.
- Private Cloud:This is a cloud infrastructure owned and managed by an organization within its own data center or through a colocation provider. Private clouds offer greater control, security, and compliance but require significant upfront investment.
- Connectivity:Secure and reliable connectivity between the public and private cloud components is crucial for data transfer, application access, and seamless integration.
- Management Tools:These tools help manage and orchestrate resources across both public and private cloud environments, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Common Hybrid Cloud Use Cases
Hybrid cloud offers a flexible solution for various business needs. Here are some common use cases:
- Disaster Recovery:Organizations can leverage public cloud services for disaster recovery, ensuring business continuity in case of a local outage or disaster.
- Bursting:When experiencing peak demand, organizations can use public cloud resources to handle the surge in traffic, while maintaining core operations on their private cloud.
- Data Analytics:Organizations can leverage public cloud platforms for data storage and processing, while keeping sensitive data within their private cloud.
- DevOps:Hybrid cloud environments provide a flexible platform for development and deployment, allowing organizations to leverage both public and private cloud resources for agile development and testing.
Why Choose Hybrid Cloud?
The decision to adopt a hybrid cloud strategy is often driven by a desire to reap the benefits of both public and private cloud environments. This approach offers a balance of control, flexibility, and cost efficiency, allowing organizations to tailor their cloud deployments to meet specific needs.
Flexibility and Scalability
Hybrid cloud provides organizations with the flexibility to choose the best environment for each workload. For example, applications requiring high security or low latency can be hosted on-premises, while applications with fluctuating demand can be deployed to the public cloud for scalability.
This approach allows for dynamic resource allocation, ensuring that resources are only used when needed, reducing costs and optimizing performance.
Cost Optimization
Hybrid cloud allows organizations to optimize costs by leveraging the most cost-effective cloud solution for each workload. On-premises infrastructure can be used for workloads with consistent demand, while public cloud can be used for workloads with fluctuating demand, resulting in significant cost savings.
Navigating the complex world of hybrid cloud can feel like trying to decipher a secret recipe. But just like a refreshing dragon fruit limeade cocktail balances sweet and tart flavors, a well-designed hybrid cloud strategy blends the best of public and private clouds, delivering the agility and cost-effectiveness you need to thrive in today’s digital landscape.
Organizations can also leverage cloud services like serverless computing to further optimize costs by only paying for the resources used.
Hybrid cloud is all about finding the right balance between flexibility and control, and that’s a constant conversation in the boardroom. It’s interesting to see how companies like Euro Manganese are navigating this, as evidenced by the recent appointment of Ms.
Ludivine Wouters as non-executive director, as reported by ExploreInsights. This kind of leadership change can signal a shift in priorities, which could impact their approach to cloud infrastructure and ultimately, their journey towards hybrid cloud optimization.
Disaster Recovery
Hybrid cloud provides a robust disaster recovery solution by allowing organizations to replicate critical applications and data to the public cloud. This ensures that in the event of a disaster, organizations can quickly restore their operations with minimal downtime. The public cloud’s high availability and scalability also provide a reliable platform for disaster recovery, ensuring business continuity.
Real-World Examples
Several organizations have successfully implemented hybrid cloud strategies to achieve significant benefits. For example, financial institutions often use hybrid cloud to host critical applications on-premises while leveraging public cloud for data analytics and other non-critical workloads. Similarly, retail companies use hybrid cloud to host their e-commerce platforms on-premises while leveraging public cloud for peak demand management.
Comparison with Traditional On-premises and Public Cloud Deployments
| Feature | On-premises | Public Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | High | Low | Medium |
| Flexibility | Low | High | High |
| Scalability | Low | High | High |
| Cost | High (upfront investment) | Low (pay-as-you-go) | Medium (combination of both) |
| Security | High (controlled environment) | Medium (shared infrastructure) | High (can leverage security features of both) |
Hybrid cloud offers a balance between the control and security of on-premises deployments and the flexibility and scalability of public cloud deployments. It provides organizations with the best of both worlds, allowing them to tailor their cloud deployments to meet specific needs and achieve optimal outcomes.
Key Considerations for Hybrid Cloud Adoption
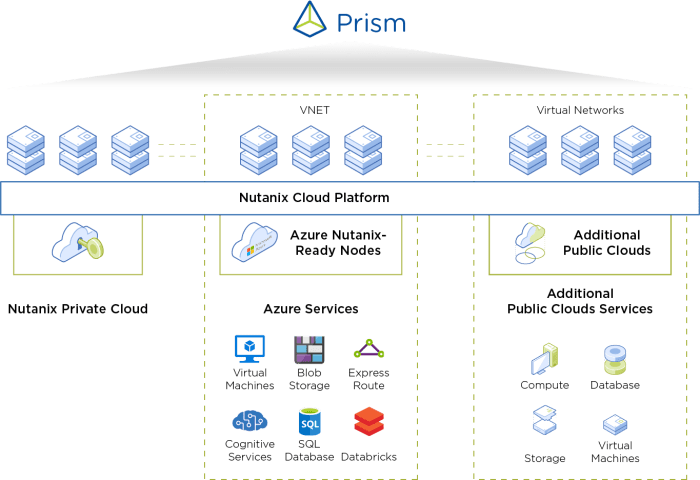
Embarking on a hybrid cloud journey requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. It’s not just about technology; it’s about aligning your cloud strategy with your business objectives, addressing potential challenges, and ensuring a secure and efficient environment.
Technical Considerations
Technical aspects play a crucial role in the success of your hybrid cloud adoption. Understanding the technical intricacies is essential for seamless integration and optimal performance.
- Network Connectivity:A robust and secure network connection is paramount for data transfer between your on-premises infrastructure and the cloud. Consider latency, bandwidth requirements, and network security protocols to ensure smooth communication and data integrity.
- Data Management:Data movement, storage, and access across different environments require careful planning. You need to establish clear data governance policies, define data migration strategies, and ensure consistent data backup and recovery processes.
- Application Compatibility:Not all applications are created equal. Evaluate your applications’ compatibility with cloud environments, and identify potential modifications or re-architecting required for seamless integration.
- Security Integration:Maintaining consistent security across your hybrid environment is crucial. Implement robust security measures, including access control, encryption, and threat detection, to safeguard your data and applications.
Organizational Considerations
The success of your hybrid cloud implementation goes beyond technical aspects. It requires a holistic approach that involves organizational alignment and resource management.
- Skills and Expertise:Adopting a hybrid cloud strategy necessitates a workforce with the necessary skills and expertise to manage both on-premises and cloud environments. Consider training and upskilling your team to ensure they are equipped to handle the complexities of a hybrid infrastructure.
- Governance and Compliance:Establish clear governance policies and procedures to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices. This includes data security, privacy, and disaster recovery protocols.
- Cost Management:Hybrid cloud deployments offer flexibility but require careful cost management. Develop a comprehensive cost model that considers infrastructure, software licenses, operational expenses, and cloud service consumption.
- Change Management:Implementing a hybrid cloud strategy involves significant changes to your IT infrastructure and processes. Ensure you have a well-defined change management process to minimize disruption and ensure smooth transition.
Security Implications
Security is paramount in a hybrid cloud environment, where data resides across multiple locations and access points.
Hybrid cloud is all about flexibility and control, right? You get to choose the best solution for each workload, whether it’s on-premises, in the cloud, or a mix of both. It’s like having the freedom to create a unique look for your wardrobe, maybe with a hand-stamped DIY pony print dress for a fun, personal touch.
Just like a hybrid cloud strategy allows you to tailor your IT infrastructure to meet your specific needs, a DIY dress lets you express your individual style. So, when it comes to your cloud journey, remember that hybrid cloud is the smart way to go, offering the best of both worlds!
- Data Encryption:Encrypt data both at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Implement encryption mechanisms at various layers, including data storage, network communication, and application level.
- Identity and Access Management:Establish robust identity and access management (IAM) policies to control user access to your hybrid cloud resources. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to enhance security.
- Threat Detection and Response:Implement security monitoring and threat detection tools to identify and respond to potential security incidents. Leverage security information and event management (SIEM) solutions to correlate events and provide comprehensive visibility.
- Vulnerability Management:Regularly scan your hybrid cloud environment for vulnerabilities and implement patches promptly to mitigate security risks. Use automated vulnerability scanning tools to ensure continuous monitoring and proactive security.
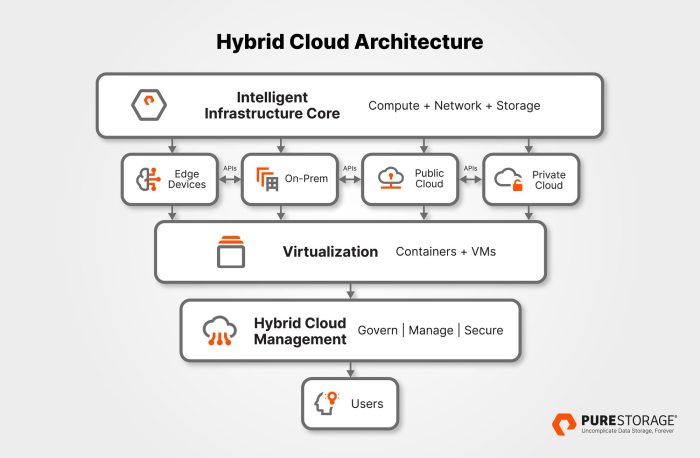
Architecting a Hybrid Cloud Solution
A hybrid cloud architecture combines the strengths of both on-premises and cloud environments, offering flexibility and scalability. It involves integrating your existing infrastructure with public cloud services, allowing you to leverage the best of both worlds.
Designing a Hybrid Cloud Architecture
Designing a hybrid cloud architecture requires careful consideration of your specific needs and requirements. A typical architecture might include:
- On-premises infrastructure:This can include your existing servers, storage, and network equipment. It’s ideal for applications requiring low latency, high security, or sensitive data that needs to remain on-premises.
- Public cloud services:This can include services like compute, storage, and databases from providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. It’s beneficial for applications that require scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Connectivity:A secure and reliable connection between your on-premises infrastructure and the public cloud is crucial. This can be achieved through dedicated connections, VPNs, or other secure networking technologies.
- Management tools:Managing a hybrid cloud environment requires tools that can orchestrate resources across both on-premises and cloud environments. These tools provide centralized control and visibility across your entire infrastructure.
- Security:Ensuring security in a hybrid cloud environment is paramount. This involves implementing appropriate security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access management policies, across both on-premises and cloud environments.
Deploying a Hybrid Cloud Solution
Deploying a hybrid cloud solution involves a series of steps:
- Define your requirements:Clearly identify your business needs, application requirements, and desired outcomes for your hybrid cloud environment.
- Choose your cloud providers:Select public cloud providers that align with your requirements and offer the services you need.
- Assess your existing infrastructure:Determine which components of your on-premises infrastructure can be integrated with the public cloud.
- Design your architecture:Develop a detailed architecture diagram that Artikels the interaction between your on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services.
- Configure networking:Establish secure and reliable connections between your on-premises infrastructure and the public cloud.
- Deploy and configure services:Deploy and configure the necessary public cloud services and integrate them with your on-premises infrastructure.
- Implement security measures:Ensure robust security measures are in place across both on-premises and cloud environments.
- Test and optimize:Thoroughly test your hybrid cloud environment to ensure performance, reliability, and security.
Managing and Monitoring a Hybrid Cloud Environment
Managing and monitoring a hybrid cloud environment requires a holistic approach:
- Centralized management:Utilize tools that provide centralized control and visibility across your entire infrastructure, including on-premises and cloud resources.
- Automated processes:Automate tasks like provisioning, scaling, and patching to improve efficiency and reduce manual errors.
- Performance monitoring:Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance.
- Security monitoring:Continuously monitor your environment for security threats and vulnerabilities.
- Cost optimization:Track and analyze your cloud spending to identify opportunities for cost savings.
Hybrid Cloud Services and Technologies
Hybrid cloud environments leverage a blend of public and private cloud resources, offering flexibility and scalability. This approach allows organizations to choose the best platform for different workloads, optimizing costs and performance. To fully understand hybrid cloud, it’s crucial to explore the services and technologies that underpin this architecture.
Popular Hybrid Cloud Services
Hybrid cloud services encompass a range of offerings, each catering to specific needs and use cases. These services can be broadly categorized into Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- IaaS:IaaS providers offer virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These services enable organizations to build and manage their own infrastructure within the cloud.
- PaaS:PaaS providers offer a platform for developing and deploying applications, providing tools and services like databases, middleware, and runtime environments. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, and Google App Engine. PaaS simplifies application development and management, reducing the burden on developers.
- SaaS:SaaS providers offer fully managed applications accessible over the internet. Examples include Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Dropbox. SaaS solutions eliminate the need for on-premises software installation and maintenance, making them ideal for collaborative work and data management.
Key Technologies in Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud environments rely on several key technologies to enable seamless integration and management of resources across public and private clouds.
- Virtualization:Virtualization is a core technology that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server. This technology enables efficient resource utilization and flexibility in allocating resources to different workloads.
- Containerization:Containerization packages applications and their dependencies into portable units, enabling consistent deployment across different environments. Popular containerization technologies include Docker and Kubernetes.
- Orchestration Tools:Orchestration tools automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Kubernetes is a widely used orchestration platform, providing features like self-healing, load balancing, and service discovery.
Comparing Hybrid Cloud Providers
Several major cloud providers offer hybrid cloud solutions, each with unique features and capabilities.
| Provider | Key Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | Extensive IaaS and PaaS offerings, strong security features, global infrastructure | Comprehensive service portfolio, robust ecosystem, high availability | Complex pricing structure, potential vendor lock-in |
| Microsoft Azure | Hybrid connectivity options, strong integration with Microsoft products, enterprise-grade security | Strong enterprise focus, good integration with on-premises systems, competitive pricing | Limited open-source support compared to AWS |
| Google Cloud Platform | Advanced analytics and AI capabilities, strong developer tools, global infrastructure | Innovative technologies, strong focus on data and AI, competitive pricing | Smaller ecosystem compared to AWS and Azure |
Hybrid Cloud Use Cases in Different Industries: Hybrid Cloud The Smart Persons Guide
Hybrid cloud adoption is not just a trend, it’s a strategic necessity for businesses across industries. It allows organizations to leverage the best of both worlds: the agility and scalability of the public cloud and the security and control of on-premises infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud in Financial Services
The financial services industry is heavily regulated and requires a high level of security and compliance. Hybrid cloud offers a solution by allowing financial institutions to store sensitive data on-premises while leveraging public cloud services for non-critical workloads.
- Data Analytics and Risk Management:Banks can use public cloud services to analyze large datasets, identify trends, and assess risk, while keeping sensitive customer data on-premises.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:Financial institutions can use hybrid cloud to ensure business continuity by replicating critical data and applications to the public cloud in case of a disaster.
- Regulatory Compliance:Hybrid cloud enables financial institutions to meet regulatory requirements by providing a secure and compliant environment for data storage and processing.
Hybrid Cloud in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is facing increasing pressure to reduce costs, improve patient care, and comply with regulations. Hybrid cloud provides a flexible and scalable platform for healthcare providers to meet these challenges.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR):Healthcare providers can use hybrid cloud to store and manage EHRs securely on-premises while leveraging public cloud services for data analytics and patient engagement.
- Telemedicine:Hybrid cloud enables healthcare providers to offer telemedicine services, connecting patients with doctors remotely via video conferencing and other tools.
- Research and Development:Hybrid cloud can be used to support research and development activities in the healthcare industry, such as drug discovery and clinical trials.
Hybrid Cloud in Retail
Retailers are facing increasing competition from online retailers and are looking for ways to improve their customer experience and operational efficiency. Hybrid cloud can help retailers achieve these goals.
- E-commerce:Retailers can use public cloud services to scale their e-commerce platforms during peak seasons, while keeping their core systems on-premises.
- Inventory Management:Retailers can use hybrid cloud to optimize their inventory management processes, leveraging data analytics and machine learning to predict demand and reduce stockouts.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Hybrid cloud can be used to enhance CRM systems, providing retailers with a 360-degree view of their customers and enabling personalized marketing campaigns.
The Future of Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting business needs. As we look ahead, several trends and technologies are poised to shape the future of hybrid cloud computing, presenting both opportunities and challenges for organizations.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
The future of hybrid cloud will be influenced by emerging trends and technologies, including:
- Edge Computing:The rise of edge computing, where data processing and storage occur closer to the source of data, will significantly impact hybrid cloud deployments. Edge computing will enable organizations to leverage hybrid cloud solutions for real-time applications and low-latency requirements, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
- Serverless Computing:Serverless computing, where developers only pay for the resources they use, is gaining traction. This trend will further empower organizations to leverage hybrid cloud solutions for greater agility and cost optimization. Serverless functions can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, providing flexibility and scalability for hybrid cloud environments.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML are rapidly transforming businesses across industries. Hybrid cloud platforms are well-suited to support AI/ML workloads, offering the necessary computing power, storage capacity, and data analytics capabilities.
- Cloud-Native Technologies:Cloud-native technologies, such as containers and microservices, are designed for cloud environments and offer enhanced portability and scalability. Organizations can leverage these technologies to build and deploy applications seamlessly across hybrid cloud environments.
Challenges and Opportunities
The adoption of hybrid cloud presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Security:Ensuring data security across multiple environments is a critical challenge for organizations adopting hybrid cloud. Organizations need to implement robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and threat detection, to protect sensitive data in hybrid cloud deployments.
- Management Complexity:Managing hybrid cloud environments can be complex, requiring expertise in both on-premises and cloud technologies. Organizations need to adopt tools and strategies for effective management and orchestration of hybrid cloud resources.
- Cost Optimization:Optimizing costs across multiple environments can be challenging. Organizations need to carefully analyze their usage patterns and leverage cost-effective solutions to manage their hybrid cloud spending.
- Data Migration:Migrating data and applications to the cloud can be a complex process. Organizations need to plan and execute data migration strategies carefully, considering data volume, security, and application dependencies.
Predictions for the Role of Hybrid Cloud, Hybrid cloud the smart persons guide
The role of hybrid cloud in the evolving digital landscape is expected to continue to grow:
- Increased Adoption:Hybrid cloud adoption is expected to accelerate as organizations recognize the benefits of flexibility, scalability, and cost optimization.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies:Hybrid cloud platforms will be increasingly integrated with emerging technologies, such as edge computing, serverless computing, and AI/ML, enabling organizations to leverage these technologies more effectively.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance:Hybrid cloud providers will continue to invest in security and compliance features, providing organizations with greater confidence in protecting their data and meeting regulatory requirements.
- Greater Focus on Automation:Automation will play a crucial role in managing and optimizing hybrid cloud environments. Organizations will adopt tools and technologies to automate tasks such as provisioning, monitoring, and security.