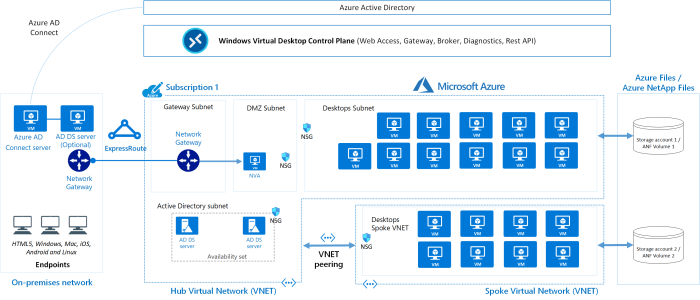
Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop: A Cheat Sheet
Microsoft azure virtual desktop a cheat sheet – Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop: A Cheat Sheet is your guide to navigating the world of cloud-based desktop virtualization. Imagine a scenario where your employees can access their work desktops from anywhere, on any device, with seamless performance and robust security.
This is the power of Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD), a powerful tool that’s revolutionizing the way organizations work.
This cheat sheet will walk you through the fundamentals of AVD, from deployment and configuration to user experience and management. We’ll explore its key benefits, including cost optimization, enhanced security, and improved user productivity. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just starting your journey with AVD, this guide provides a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions and unleash the full potential of this transformative technology.
Introduction to Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop
Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) is a cloud-based desktop and app virtualization service that enables organizations to deliver Windows desktops and applications to users on any device, anywhere, and at any time. It offers a secure and scalable solution for managing and delivering virtual desktops, eliminating the need for traditional on-premises infrastructure.AVD empowers organizations to enhance productivity, streamline IT operations, and improve security by providing a modern, flexible, and cost-effective approach to desktop virtualization.
Key Benefits of Azure Virtual Desktop
The advantages of using AVD are numerous and can significantly benefit organizations of all sizes.
- Simplified Management:AVD simplifies desktop management by centralizing the administration of virtual desktops and applications in the cloud. This reduces the burden on IT teams and enables them to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security:AVD provides a secure environment for accessing and managing virtual desktops, reducing the risk of data breaches and malware infections. The service integrates with Azure Active Directory for identity and access management, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- Improved User Experience:AVD offers a seamless user experience, enabling users to access their desktops and applications from any device with a reliable internet connection. This flexibility allows users to work from anywhere, anytime, improving productivity and collaboration.
- Cost Savings:AVD can significantly reduce the cost of managing and deploying desktops by eliminating the need for expensive hardware, software licenses, and on-premises infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go pricing model allows organizations to scale their desktop environment up or down based on their needs, further reducing costs.
While you’re brushing up on your Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop skills, it’s worth remembering that even the most advanced tech isn’t immune to vulnerabilities. A recent report on a new Apple Silicon security flaw reminds us that security is an ongoing concern.
So, while your Azure Virtual Desktop cheat sheet will help you master the platform, don’t forget to keep your systems updated and your security practices strong.
- Increased Scalability:AVD is highly scalable and can accommodate the changing needs of organizations. Organizations can easily add or remove users and desktops as required, ensuring that they have the resources they need to meet their business demands.
Components of Azure Virtual Desktop
AVD consists of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive desktop virtualization solution.
- Host Pools:A host pool is a collection of virtual machines (VMs) that host the virtual desktops. Each host pool can be configured with different settings, such as the operating system, memory, and storage capacity. This allows organizations to tailor their virtual desktops to meet the specific needs of different user groups.
- Desktop Applications:AVD allows organizations to deploy and manage desktop applications that can be accessed by users on their virtual desktops. This enables organizations to provide users with the specific tools and software they need to perform their jobs effectively.
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD):Azure AD provides identity and access management for AVD, ensuring that only authorized users can access the virtual desktops and applications. Organizations can leverage their existing Azure AD infrastructure to manage user accounts and permissions for AVD.
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM):ARM is used to deploy and manage the resources required for AVD, including host pools, virtual machines, and network resources. This provides a consistent and automated approach to managing the AVD environment.
AVD Deployment and Configuration
Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) provides a flexible and scalable solution for delivering virtual desktops and applications to users. Deploying and configuring AVD involves various steps and considerations, depending on your specific requirements and infrastructure.
A Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop cheat sheet can be a lifesaver when you’re navigating the complexities of managing virtual desktops. But sometimes, you need to go beyond the GUI and dive into the nitty-gritty details using the command line.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive guide on how to leverage the power of the command line interface in Microsoft environments, check out this article on using command line interface microsoft. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can easily incorporate command line techniques into your Azure Virtual Desktop workflow for enhanced efficiency and control.
AVD Deployment Models
There are different deployment models for AVD, each offering distinct advantages and catering to different needs. The choice of deployment model depends on factors such as the size of your organization, security requirements, and budget.
- Host Pools: Host pools are the fundamental building blocks of AVD. They represent a collection of virtual machines (VMs) that host user sessions. Host pools can be deployed in different ways, depending on your requirements. For example, you can choose to deploy a single host pool with multiple VMs or multiple host pools with a single VM each.
- Session Hosts: Session hosts are the VMs that run the user sessions. They can be deployed in different sizes and configurations, depending on the requirements of your applications. For example, you can use a smaller VM for users who need to access only basic applications or a larger VM for users who need to run demanding applications.
- Azure Resource Groups: Resource groups are logical containers for your AVD resources, such as host pools, session hosts, and network resources. They provide a way to manage your AVD environment efficiently and securely.
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): Azure AD is used for authentication and authorization in AVD. It provides a centralized way to manage user identities and access permissions.
Setting Up an AVD Environment
Setting up an AVD environment involves several steps, including:
- Create an Azure subscription: If you don’t have an Azure subscription, you need to create one.
- Create a resource group: Create a resource group to contain your AVD resources.
- Create a host pool: Create a host pool to host your user sessions.
- Create session hosts: Create VMs that will host the user sessions.
- Configure network connectivity: Ensure that your users can connect to the AVD environment.
- Deploy applications: Install the applications that your users need to access.
- Configure user accounts: Create user accounts and assign them to the appropriate host pools.
- Test and deploy: Test your AVD environment and then deploy it to your users.
Configuring AVD to Meet Specific Requirements
AVD provides a wide range of configuration options to meet specific requirements. Some of the key configuration options include:
- Session Host Size and Configuration: Choose the appropriate VM size and configuration for your session hosts, depending on the performance requirements of your applications.
- User Profile Management: Configure user profile management to ensure that users have the correct settings and applications available when they log in.
- Security: Implement security measures to protect your AVD environment from unauthorized access. This includes configuring network security, user authentication, and data encryption.
- Monitoring and Logging: Configure monitoring and logging to track the health and performance of your AVD environment. This can help you identify and resolve issues quickly.
Comparing AVD Deployment Models
The following table compares the different deployment models for AVD:
| Deployment Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop Virtualization | Users access virtual desktops hosted in the cloud. | Scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness. | Requires a stable internet connection. |
| Application Virtualization | Users access virtual applications hosted in the cloud. | Simplified application management, reduced IT overhead. | Limited support for legacy applications. |
AVD User Experience and Management
The user experience of Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) is designed to be seamless and secure. Users can access their virtual desktops from various devices, including personal computers, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This section explores the user experience, management aspects, security features, and steps for accessing AVD desktops.
User Access and Interaction
Users can access their AVD desktops through the Azure Virtual Desktop client, a downloadable application available for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. The client connects to the AVD environment and provides a familiar desktop experience. Users can interact with the virtual desktop just like they would with a physical computer, accessing applications, files, and network resources.
Managing AVD User Profiles and Settings
AVD offers flexible options for managing user profiles and settings. Users can choose to use their local profiles, which are stored on the client device, or their roaming profiles, which are stored in the cloud. Roaming profiles ensure that users’ settings and data are synchronized across all their devices, enhancing user experience and productivity.
Security Features and Considerations
AVD incorporates robust security features to protect user data and applications. These features include multi-factor authentication (MFA), conditional access policies, and device compliance checks. AVD also leverages Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for identity and access management, providing a centralized and secure authentication system.
Accessing an AVD Desktop
To access an AVD desktop, follow these steps:
- Download and install the Azure Virtual Desktop client from the Microsoft website.
- Open the Azure Virtual Desktop client and sign in using your Azure AD credentials.
- Select the desired virtual desktop from the list of available desktops.
- The virtual desktop will launch in a new window, providing access to your applications and data.
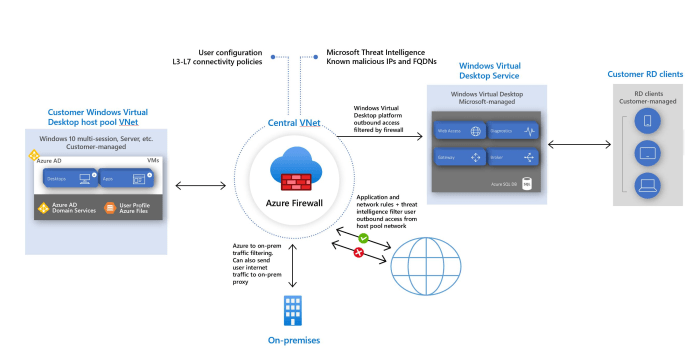
AVD Integration and Customization
Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) offers a robust platform for delivering virtual desktops and applications, but its true potential lies in its seamless integration with other Azure services and the flexibility for customization. This section explores how AVD can be integrated with various Azure services, how to tailor AVD desktops with specific applications and configurations, and how to effectively manage and update AVD images.
Integration with Azure Services
AVD seamlessly integrates with several Azure services, expanding its capabilities and enhancing its overall functionality. These integrations enable businesses to leverage the power of Azure’s comprehensive ecosystem to streamline operations, enhance security, and optimize performance.
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): AVD leverages Azure AD for user authentication and authorization, providing centralized identity management and simplifying user access control. This integration ensures secure and controlled access to virtual desktops, aligning with modern security best practices.
- Azure Storage: AVD utilizes Azure Storage to store and manage virtual machine images, user profiles, and other essential data. Azure Storage offers scalability, high availability, and cost-effective storage solutions, ensuring reliable and efficient data management for AVD deployments.
- Azure Monitor: AVD integrates with Azure Monitor to collect and analyze performance data, providing valuable insights into the health and performance of virtual desktops and applications. This integration enables proactive monitoring, early detection of issues, and efficient troubleshooting.
- Azure Log Analytics: AVD leverages Azure Log Analytics to centralize and analyze log data from various components, providing a comprehensive view of system events, user activity, and potential security threats. This integration enables proactive threat detection, security auditing, and incident response.
- Azure Networking: AVD integrates with Azure Networking services, such as virtual networks (VNets), network security groups (NSGs), and load balancers, to establish secure and efficient network connectivity for virtual desktops. This integration enables fine-grained network control, secure communication, and optimal performance.
Customizing AVD Desktops
Tailoring AVD desktops to meet specific user requirements and business needs is essential for maximizing productivity and user satisfaction. AVD offers flexible customization options, allowing administrators to configure desktops with specific applications, settings, and configurations.
- Application Deployment: AVD allows administrators to deploy applications to virtual desktops using various methods, including MSI packages, scripts, and Azure Marketplace applications. This flexibility enables organizations to provide users with the necessary software tools for their specific tasks.
- Desktop Configuration: AVD enables administrators to customize desktop settings, such as wallpaper, themes, and taskbar configuration, to enhance the user experience and ensure consistency across the organization. These customizations can reflect company branding, improve usability, and create a more personalized environment for users.
A Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop cheat sheet is a handy resource for anyone working with this technology. It can help you quickly access key information about the service, including its features, deployment options, and security considerations. It’s important to remember that even with robust technology like Azure Virtual Desktop, security remains crucial.
To protect your environment, it’s essential to understand how social engineering attacks work, and a great place to start is by reading about the 6 persuasion tactics used in social engineering attacks. By understanding these tactics, you can better protect your organization from falling victim to these attacks and keep your Azure Virtual Desktop environment secure.
- User Profile Management: AVD supports user profile management, allowing administrators to control user settings, applications, and data access on virtual desktops. This ensures that users have access to their preferred settings and applications while maintaining a secure and consistent environment.
Managing and Updating AVD Images
Maintaining the security and functionality of AVD deployments requires effective image management and regular updates. AVD provides tools and processes for managing and updating AVD images, ensuring that desktops are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and software versions.
- Image Creation and Management: AVD allows administrators to create and manage custom AVD images using tools like Azure Disk Image (ADI) or the AVD Image Management service. These tools enable administrators to create base images, customize them with specific applications and configurations, and deploy them to virtual desktops.
- Image Updates and Patching: AVD facilitates regular image updates and patching to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and ensure compatibility with the latest software versions. Administrators can schedule automatic updates or manually apply patches to AVD images, maintaining a secure and reliable environment.
- Image Versioning and Rollback: AVD supports image versioning, allowing administrators to track changes and roll back to previous versions if necessary. This feature ensures that updates do not disrupt user operations and provides a safety net in case of unexpected issues.
Integration with AVD: Benefits
| Integration | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) | Centralized identity management, simplified user access control, enhanced security |
| Azure Storage | Scalable and cost-effective storage for virtual machine images, user profiles, and data, ensuring high availability and reliability |
| Azure Monitor | Proactive monitoring, performance insights, early detection of issues, efficient troubleshooting |
| Azure Log Analytics | Centralized log management, security auditing, threat detection, incident response |
| Azure Networking | Secure and efficient network connectivity, fine-grained network control, optimal performance |
AVD Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Keeping an eye on your AVD environment is crucial for ensuring smooth user experiences and efficient resource utilization. Monitoring AVD performance and identifying potential issues early can prevent service disruptions and help you optimize your deployment.
Monitoring AVD Performance and Resource Utilization
You can leverage various tools and methods to monitor the health and performance of your AVD environment. This involves tracking key metrics related to resource utilization, user experience, and system health.
- Azure Monitor:Azure Monitor provides comprehensive monitoring capabilities for Azure resources, including AVD. You can configure alerts based on predefined thresholds for critical metrics. It also offers powerful dashboards for visualizing performance trends and identifying potential issues.
- Azure Log Analytics:This service allows you to collect and analyze log data from your AVD environment, including session logs, performance counters, and error messages. This data can help you diagnose performance bottlenecks and identify root causes of issues.
- Performance Counters:Windows Performance Monitor (Perfmon) provides access to a wide range of performance counters that can be used to monitor AVD components, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, and network bandwidth. These counters can be used to identify resource contention and performance bottlenecks.
- User Experience Monitoring:Tools like Azure Application Insights can be used to monitor the user experience of AVD sessions. This includes tracking metrics like session latency, connection quality, and application responsiveness. By analyzing user experience data, you can identify issues that affect user productivity and satisfaction.
Common AVD Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques
Understanding common AVD issues and the corresponding troubleshooting techniques is essential for resolving performance problems and ensuring a stable environment.
- Slow Session Startup:This can be caused by factors like network latency, insufficient resources allocated to the host pool, or slow application loading times. To troubleshoot, check network connectivity, review resource allocation, and analyze application performance.
- Session Disconnections:Frequent session disconnections can be caused by network connectivity issues, resource exhaustion, or unstable host pool configuration. To troubleshoot, check network connectivity, review resource allocation, and examine host pool settings.
- Application Performance Issues:Slow application performance can be caused by resource constraints, network latency, or application configuration issues. To troubleshoot, review resource allocation, analyze network traffic, and examine application settings.
- User Authentication Problems:Users may experience authentication issues due to incorrect credentials, network connectivity problems, or Active Directory configuration issues. To troubleshoot, verify user credentials, check network connectivity, and review Active Directory configuration.
Best Practices for Optimizing AVD Performance
Implementing best practices can significantly improve AVD performance and user experience.
- Optimize Network Connectivity:Ensure a reliable and high-bandwidth network connection between users and the AVD environment. Consider using a dedicated network for AVD traffic and optimize network settings to reduce latency.
- Allocate Sufficient Resources:Ensure adequate resources are allocated to host pools, including CPU, memory, and storage. Overprovisioning resources can help prevent performance bottlenecks during peak usage periods.
- Optimize Application Performance:Ensure that applications running on AVD are optimized for performance. This may involve adjusting application settings, reducing resource consumption, or optimizing application code.
- Regularly Monitor and Analyze:Regularly monitor AVD performance metrics and analyze trends to identify potential issues early. This proactive approach can help prevent performance degradation and ensure a stable environment.
- Implement Security Best Practices:Secure your AVD environment by implementing appropriate security measures, including access control, encryption, and regular security updates.
AVD Monitoring Metrics
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| CPU Utilization | Percentage of CPU resources used by AVD host pools. |
| Memory Usage | Amount of memory consumed by AVD host pools. |
| Disk I/O | Rate of disk read and write operations performed by AVD host pools. |
| Network Bandwidth | Amount of network bandwidth consumed by AVD sessions. |
| Session Latency | Time taken for a user’s request to reach the AVD session and receive a response. |
| Session Connection Quality | Quality of the network connection between users and AVD sessions. |
| Application Responsiveness | Time taken for applications to respond to user interactions. |
AVD Cost Optimization and Scaling
Optimizing AVD costs and scaling resources effectively are crucial for ensuring efficient and cost-effective deployment. Understanding AVD pricing, implementing cost-saving strategies, and scaling resources based on demand are essential for managing your AVD environment efficiently.
AVD Cost Optimization Strategies
Implementing cost optimization strategies can significantly reduce your AVD expenses.
- Rightsizing AVD Resources:Select the appropriate VM size based on the workload requirements. Overprovisioning can lead to unnecessary costs. Using smaller VMs for less demanding workloads can reduce costs without compromising performance.
- Optimize Session Host Utilization:Utilize session hosts efficiently by ensuring they are not idle for extended periods. Implementing features like session timeouts and user disconnection policies can optimize resource utilization.
- Leverage Spot Instances:Consider using spot instances for non-critical workloads. Spot instances offer significant cost savings, but availability is not guaranteed. You can configure your environment to gracefully handle potential disruptions.
- Utilize Reserved Instances:If you have predictable workloads, consider using reserved instances. Reserved instances provide discounted pricing for a committed period, offering substantial cost savings.
- Enable Auto-Scaling:Implement auto-scaling rules to automatically adjust the number of session hosts based on user demand. This ensures optimal resource allocation and prevents overprovisioning or underprovisioning.
AVD Resource Scaling, Microsoft azure virtual desktop a cheat sheet
Scaling AVD resources based on demand is essential for maintaining optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Manual Scaling:Manually adjust the number of session hosts based on observed user activity. This approach provides granular control but requires constant monitoring and manual intervention.
- Automatic Scaling:Configure auto-scaling rules to automatically adjust the number of session hosts based on predefined metrics like CPU utilization or session count. This approach provides dynamic scaling, adapting to fluctuations in user demand.
- Scaling based on Time of Day:Implement scaling schedules based on anticipated user activity patterns. For example, you can scale up resources during peak hours and scale down during off-peak hours.
AVD Pricing and Cost Considerations
Understanding AVD pricing is essential for making informed cost optimization decisions.
- Session Host Costs:Costs are based on the VM size and the operating system used. Consider using smaller VMs for less demanding workloads to reduce costs.
- Storage Costs:Costs are based on the storage type and capacity used. Optimize storage usage by utilizing appropriate storage tiers for different data types.
- Network Costs:Costs are based on data transfer volume and network bandwidth usage. Optimize network usage by implementing appropriate network configurations and minimizing unnecessary data transfers.
- Licensing Costs:Costs are based on the number of users and the chosen license type. Consider using appropriate license models based on user needs and usage patterns.
AVD Scaling Options Comparison
| Scaling Option | Advantages | Disadvantages ||—|—|—|| Manual Scaling | Granular control over resource allocation | Requires constant monitoring and manual intervention || Automatic Scaling | Dynamic scaling based on demand | Requires careful configuration and monitoring || Time-Based Scaling | Predictable resource allocation based on usage patterns | Requires careful planning and configuration |
AVD Use Cases and Best Practices: Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop A Cheat Sheet
Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) is a powerful cloud-based desktop virtualization service that offers a range of benefits for organizations of all sizes. AVD enables organizations to deliver secure, scalable, and cost-effective virtual desktops to users across various devices and locations.
This section explores real-world examples of how AVD is used in different industries, provides a list of best practices for implementing and managing AVD, and discusses the potential challenges and limitations of AVD.
Real-World AVD Use Cases
AVD offers a versatile solution for various business needs, and its application extends across different industries. Here are some examples:
- Financial Services:AVD enables financial institutions to provide secure access to sensitive data and applications for employees working remotely or from branch offices. It ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and safeguards against data breaches.
- Healthcare:Healthcare organizations can use AVD to deliver secure access to patient records, medical imaging systems, and other critical applications for doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. AVD’s centralized management capabilities enhance security and streamline compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Education:Educational institutions can leverage AVD to provide students with access to specialized software and resources, regardless of their location or device. AVD simplifies the management of student desktops and ensures a consistent learning environment.
- Manufacturing:Manufacturing companies can use AVD to provide factory floor workers with access to critical applications and data, enabling them to perform tasks efficiently and securely. AVD also facilitates remote access for engineers and technicians who need to monitor and troubleshoot equipment.
Best Practices for AVD Implementation and Management
Implementing and managing AVD effectively requires adhering to best practices to ensure optimal performance, security, and scalability.
- Plan for scalability and performance:Determine the expected number of users and their resource requirements to ensure AVD can handle the workload efficiently. Consider using autoscaling features to automatically adjust resources based on demand.
- Implement strong security measures:Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA), network segmentation, and other security best practices to protect AVD environments from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Regularly update AVD components and operating systems to mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Optimize user experience:Configure AVD to provide a smooth and responsive user experience by optimizing network connectivity, resource allocation, and application performance. Leverage features like session shadowing and remote assistance to enhance user support.
- Monitor and troubleshoot proactively:Regularly monitor AVD performance, user activity, and security logs to identify potential issues early on. Utilize AVD monitoring tools and dashboards to gain insights and troubleshoot problems effectively.
- Implement cost optimization strategies:Optimize resource allocation, leverage spot instances for cost-effective scaling, and consider using Azure Reserved Instances to reduce overall AVD costs.
Challenges and Limitations of AVD
While AVD offers numerous advantages, it also comes with certain challenges and limitations that organizations should consider.
- Network connectivity:AVD requires a reliable and high-bandwidth network connection for optimal performance. Network latency can impact user experience, especially for applications that require real-time interaction.
- Resource allocation:Determining the appropriate resource allocation for each user can be challenging, especially when dealing with diverse workloads and application requirements. Over-provisioning resources can lead to unnecessary costs, while under-provisioning can affect performance.
- Complexity of management:Managing AVD environments can be complex, requiring expertise in cloud infrastructure, virtualization technologies, and security best practices.
- Integration with existing systems:Integrating AVD with existing on-premises systems and applications can require careful planning and configuration.


