VMware NSX: The Smart Persons Guide
Vmware nsx the smart persons guide – VMware NSX: The Smart Person’s Guide is your gateway to mastering network virtualization and security in modern data centers. Forget the days of complex, inflexible networks; NSX brings a wave of agility and control, transforming how you manage your infrastructure.
Imagine a world where your network adapts to your needs, where security is woven into the fabric of your infrastructure, and where you can effortlessly scale to meet the demands of your business.
This guide will take you on a journey through the core concepts of NSX, its deployment, configuration, and the powerful features it offers. We’ll explore how NSX empowers you to implement micro-segmentation, enforce granular security policies, and leverage advanced networking services like load balancing and VPNs.
Get ready to dive deep into the world of NSX, where you’ll discover how this revolutionary technology can unlock the full potential of your data center.
Introduction to VMware NSX
VMware NSX is a software-defined networking (SDN) solution that allows organizations to virtualize their network infrastructure. It provides a centralized platform for managing and automating network services, including routing, switching, firewalling, and load balancing. NSX enables organizations to build highly flexible and agile data centers that can adapt quickly to changing business needs.
It also helps to improve security by isolating workloads and enforcing granular access controls.
Key Components of VMware NSX
VMware NSX consists of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive SDN solution. These components include:
- NSX Manager: The central management and control plane for NSX. It provides a single point of administration for all NSX components and services.
- NSX Controller: The distributed control plane that manages the virtual network topology and enforces network policies.
- NSX Edge: A virtualized network appliance that provides network services such as routing, firewalling, and load balancing.
Benefits of Using VMware NSX
VMware NSX offers several benefits for organizations looking to modernize their data center network infrastructure. These benefits include:
- Improved Agility and Flexibility: NSX enables organizations to provision and configure network services quickly and easily, allowing them to adapt to changing business needs.
- Enhanced Security: NSX provides granular security controls that can be applied to individual workloads, isolating them from each other and preventing unauthorized access.
- Reduced Costs: NSX can help organizations reduce their network infrastructure costs by eliminating the need for dedicated hardware and simplifying network management.
- Increased Automation: NSX automates many network tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
How VMware NSX Works, Vmware nsx the smart persons guide
VMware NSX works by creating a virtual network overlay on top of the physical network infrastructure. This overlay network is managed and controlled by the NSX Manager and Controller. The NSX Edge appliances provide network services to the virtual network, such as routing, firewalling, and load balancing.
VMware NSX allows organizations to create a virtual network that is independent of the underlying physical network. This allows for greater flexibility and agility, as the virtual network can be easily reconfigured without impacting the physical network.
VMware NSX is a powerful tool for network virtualization, and understanding its intricacies can be a game-changer for anyone working in the IT field. While mastering NSX might seem daunting, the right resources can make the journey much smoother. For instance, if you’re interested in the data modeling aspect of NSX, a great place to start is by checking out a data modeler job description to understand the specific skills and knowledge required for this role.
This can provide valuable insights into the kind of data modeling challenges you might encounter when working with NSX.
Use Cases for VMware NSX
VMware NSX can be used in a variety of use cases, including:
- Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC): NSX is a key component of a software-defined data center, providing the networking foundation for a virtualized and automated infrastructure.
- Cloud Migration: NSX can be used to simplify the migration of workloads to the cloud, providing consistent networking and security across on-premises and cloud environments.
- Microservices Architecture: NSX provides the necessary networking and security capabilities to support microservices-based applications, enabling organizations to deploy and manage microservices at scale.
- Network Security: NSX provides advanced security features, such as micro-segmentation, that can be used to isolate workloads and prevent unauthorized access.
Understanding NSX Concepts
VMware NSX is a revolutionary technology that fundamentally changes how we design, deploy, and manage networks. It’s built upon the core principles of network virtualization, software-defined networking (SDN), and network functions virtualization (NFV), empowering organizations to achieve unprecedented agility, scalability, and security in their IT environments.
Network Virtualization
Network virtualization is the key to unlocking the power of NSX. It enables the abstraction of physical network components, such as switches, routers, and firewalls, into software-defined counterparts. This allows for the creation of virtual networks that are independent of the underlying physical infrastructure.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN is the foundation upon which network virtualization thrives. It separates the control plane from the data plane, allowing for centralized management and automation of network functions. In the context of NSX, the control plane resides in the NSX Manager, which orchestrates and configures the virtual network.
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)
NFV further enhances the capabilities of NSX by virtualizing network functions, such as firewalls, load balancers, and VPNs. This allows organizations to deploy these functions as virtual machines (VMs) or containers, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware appliances.
Traditional Networking vs. NSX-based Networking
- Traditional networkingrelies on physical hardware and a complex, manual configuration process. This can lead to limitations in scalability, agility, and security.
- NSX-based networkingutilizes software-defined components and a centralized management approach. This allows for dynamic network provisioning, automation, and granular security policies.
Advantages of NSX
- Agility and Scalability: NSX enables rapid deployment and scaling of virtual networks, allowing organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs.
- Automation: NSX automates many network tasks, reducing manual errors and freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security: NSX offers robust security features, including micro-segmentation, which isolates applications and data from unauthorized access.
- Cost Savings: NSX eliminates the need for expensive hardware appliances, leading to significant cost reductions.
Micro-segmentation with NSX
Micro-segmentation is a key security strategy enabled by NSX. It involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting communication between applications and data based on predefined policies. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the impact of security breaches.
Security Enhancement with NSX
NSX provides a comprehensive suite of security features, including:
- Distributed Firewall: NSX offers a distributed firewall that enforces security policies at the hypervisor level, providing granular control over network traffic.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: NSX integrates with intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to detect and block malicious activity.
- Advanced Threat Protection: NSX supports advanced threat protection solutions, such as sandboxing and malware analysis, to identify and neutralize sophisticated threats.
Example of NSX Micro-segmentation
Imagine a scenario where a company has a web application running on a virtual machine. With NSX, the IT team can create a micro-segment for this application, restricting access only to authorized users and services. This ensures that even if the web server is compromised, the attacker cannot access other critical systems or data.
NSX Deployment and Configuration
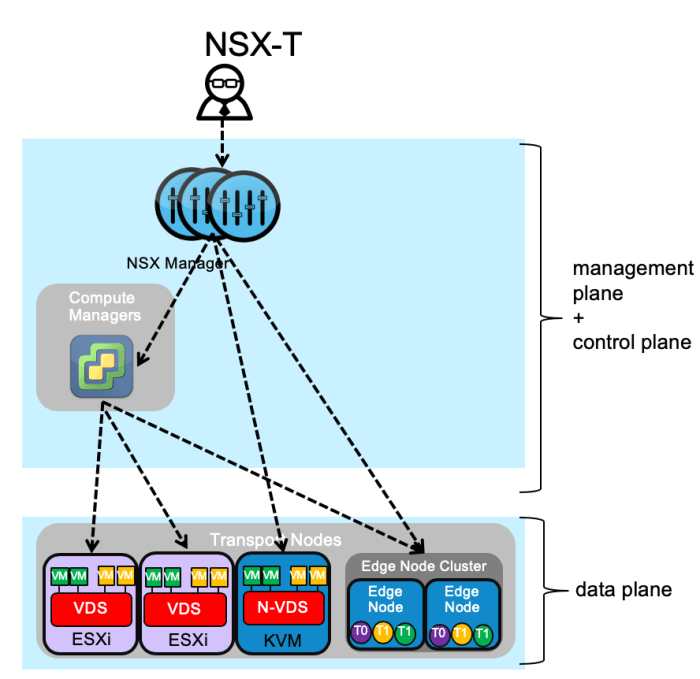
Deploying and configuring VMware NSX involves understanding its deployment models and the key steps required to set up the NSX environment. NSX offers two main deployment models: vSphere Integrated NSX and NSX-T Data Center, each with its own advantages and use cases.
This section delves into the deployment process, focusing on the essential steps and configuration elements of NSX.
NSX Deployment Models
NSX offers two primary deployment models, each tailored to different environments and needs:
- vSphere Integrated NSX: Designed for environments already using VMware vSphere, this model integrates NSX functionality directly into the vSphere environment. It leverages existing vCenter Server and ESXi hosts for management and deployment, offering a seamless integration with vSphere features and tools.
vSphere Integrated NSX is ideal for organizations seeking a streamlined approach to deploying NSX in vSphere-based data centers.
- NSX-T Data Center: This model provides a more independent and flexible deployment option, allowing NSX to be deployed on various platforms, including bare metal servers and public cloud environments. NSX-T Data Center utilizes its own management plane, separate from vCenter Server, enabling deployment on non-vSphere platforms.
It’s well-suited for organizations seeking a more flexible and scalable solution, capable of integrating with diverse infrastructure environments.
Deploying and Configuring NSX
Deploying NSX involves several steps, including setting up the NSX Manager and controllers, configuring logical switches and routers, and integrating with the underlying physical network.
Setting Up the NSX Manager and Controllers
The NSX Manager is the central control point for NSX, managing the entire NSX environment. The NSX controllers, on the other hand, handle the distributed routing and firewalling functions. Setting up the NSX Manager and controllers is a crucial step in deploying NSX.
- Install the NSX Manager: The NSX Manager is a virtual appliance that acts as the central brain of NSX. It handles configuration, monitoring, and management of the entire NSX environment. Installing the NSX Manager involves deploying the virtual appliance on a suitable host, configuring its network settings, and providing necessary credentials.
- Deploy the NSX Controllers: NSX controllers are also virtual appliances responsible for distributed routing and firewalling. They work in conjunction with the NSX Manager to enforce security policies and manage network traffic flow. The number of NSX controllers required depends on the scale and complexity of the NSX environment.
Configuring Logical Switches and Routers
NSX employs logical switches and routers to create and manage virtual networks. These components provide the foundation for network segmentation and isolation within the virtualized environment.
- Logical Switches: Logical switches represent the virtual network segments within the NSX environment. They are responsible for connecting virtual machines to the NSX network. Each logical switch can be configured with specific security policies, VLAN settings, and other attributes to meet specific network requirements.
- Logical Routers: Logical routers enable communication between different logical networks. They provide routing functionality within the NSX environment, allowing virtual machines on different logical switches to communicate with each other. Logical routers can be configured with static routes, BGP, and other routing protocols to manage network traffic flow.
Integrating with the Physical Network
NSX requires integration with the underlying physical network to function effectively. This involves configuring the physical switches and routers to support NSX traffic and ensure seamless communication between the physical and virtual environments.
- Physical Switch Configuration: Physical switches must be configured to support NSX traffic, including VLAN tagging and trunk ports. This ensures that NSX traffic can flow correctly between the physical and virtual environments.
- Physical Router Configuration: Physical routers may need to be configured to support NSX traffic, including static routes and routing protocols. This enables communication between the NSX environment and external networks.
NSX Security Features
VMware NSX offers a comprehensive suite of security features that enhance the security posture of virtualized environments. These features provide granular control over network traffic, enforce strict security policies, and protect against various threats. This section delves into the key security features of NSX, including micro-segmentation, firewalling, and intrusion detection and prevention.
VMware NSX is a game-changer for network virtualization, and understanding its intricacies can make a huge difference in your IT strategy. It’s not just about managing virtual machines; it’s about creating a flexible and secure network infrastructure. While you’re diving into the world of NSX, take a moment to check out this article on Apple Intelligence 5 AI-powered things you should do immediately , which explores how AI is transforming the way we interact with technology.
You’ll be surprised how these two seemingly different topics can actually complement each other, and how AI can help you optimize your NSX deployment even further.
Micro-segmentation
Micro-segmentation is a critical security strategy that divides a network into smaller, isolated segments based on specific criteria. This approach reduces the attack surface by limiting the communication between virtual machines and applications, preventing lateral movement of attackers within the network.
NSX enables micro-segmentation by creating logical security zones, also known as security groups, which define the communication rules between virtual machines and applications.
- Policy-Based Segmentation:NSX allows administrators to define security policies based on various criteria, such as application type, operating system, or security posture. These policies determine which virtual machines and applications are allowed to communicate with each other.
- Dynamic Segmentation:NSX can dynamically adjust security policies based on real-time changes in the environment, such as the creation or deletion of virtual machines or applications. This ensures that security policies remain relevant and effective.
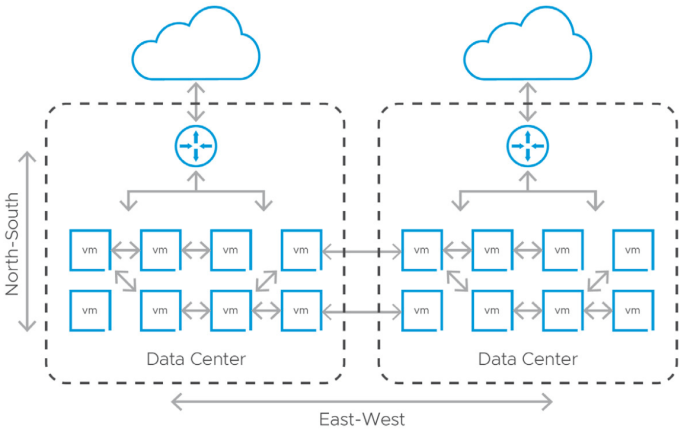
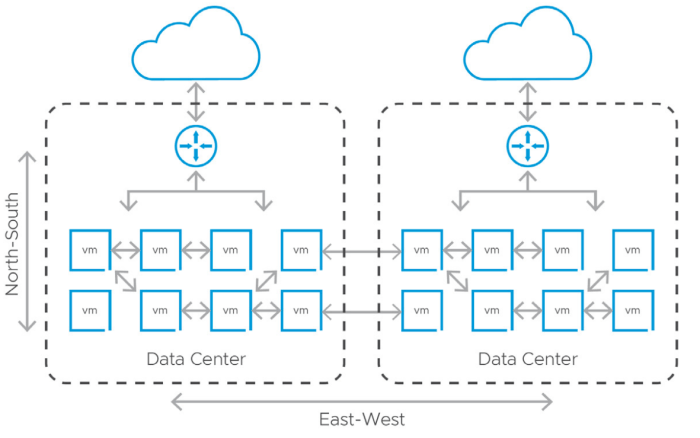
- East-West Traffic Control:Micro-segmentation in NSX focuses on controlling traffic within the data center, known as east-west traffic. This allows for granular control over communication between virtual machines and applications, enhancing security and reducing the risk of lateral movement.
Firewalling
NSX provides distributed firewalling capabilities, enabling the enforcement of security policies at the virtual machine and application level. This approach eliminates the need for traditional, centralized firewalls, simplifying security management and improving performance.
- Distributed Firewall:NSX integrates a distributed firewall into the hypervisor, allowing for fine-grained control over network traffic at the virtual machine level. This approach eliminates the performance bottlenecks associated with traditional, centralized firewalls.
- Application-Aware Firewalling:NSX can identify and control traffic based on applications, allowing administrators to create specific firewall rules for different applications. This ensures that only authorized traffic is allowed to access sensitive applications.
- Security Policy Enforcement:NSX enforces security policies defined by administrators, blocking unauthorized traffic and preventing malicious activities. This helps to protect virtualized environments from various threats.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
NSX integrates with industry-leading intrusion detection and prevention (IDS/IPS) solutions, enhancing security by detecting and preventing malicious activity. This integration allows for the detection and blocking of known attacks, protecting virtualized environments from various threats.
- Real-Time Threat Detection:NSX’s IDS/IPS capabilities monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and activities, alerting administrators to potential threats in real-time. This allows for prompt response to security incidents.
- Attack Prevention:NSX’s IPS features can block malicious traffic and prevent known attacks from compromising virtualized environments. This helps to protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access.
- Integration with Existing Solutions:NSX seamlessly integrates with popular IDS/IPS solutions, leveraging existing investments and expertise. This allows for a smooth transition to a more secure virtualized environment.
NSX Networking Services: Vmware Nsx The Smart Persons Guide
VMware NSX offers a comprehensive suite of networking services that enhance network performance, security, and manageability. These services extend beyond basic connectivity, providing advanced capabilities like load balancing, VPN, and network address translation (NAT).
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and optimal resource utilization. This approach prevents server overload, improves performance, and enhances application responsiveness. NSX offers two primary load balancing methods:
- Layer 4 Load Balancing: This method balances traffic based on destination port and IP address, effectively distributing traffic across multiple servers based on these criteria.
- Layer 7 Load Balancing: This method balances traffic based on application-level data, such as HTTP headers, allowing for more granular control and intelligent traffic distribution. This approach is particularly beneficial for web applications with diverse traffic patterns and requirements.
NSX load balancing services can be configured through the NSX Manager interface, enabling administrators to define load balancing rules, monitor traffic distribution, and manage virtual servers.
VPN
NSX provides robust VPN capabilities, enabling secure communication between virtual machines and external networks. These capabilities are crucial for establishing secure connections for remote access, data transfer, and inter-site communication. NSX supports two primary VPN types:
- Site-to-Site VPN: This type establishes a secure connection between two NSX environments, allowing for seamless communication between virtual machines in different locations. This is ideal for connecting geographically dispersed data centers or branch offices.
- Client-to-Site VPN: This type allows remote users to connect securely to virtual machines within the NSX environment. This is particularly useful for providing remote access to applications or data residing within the virtualized infrastructure.
NSX VPN configurations are managed through the NSX Manager interface, allowing administrators to define VPN tunnels, configure security policies, and monitor VPN traffic.
VMware NSX is a powerful tool for network virtualization, but it can be overwhelming to learn. That’s why I’m working on a “Smart Person’s Guide” to NSX, breaking down the complexities into digestible chunks. It’s a little like how Apple accidentally revealed a new version of the Beats Solo headphones in the latest iOS update – a sneak peek into the future! I’m hoping my NSX guide will be just as helpful, providing a sneak peek into the world of network virtualization and making it easier to understand.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT allows virtual machines to communicate with external networks using a different IP address than their internal IP address. This is particularly useful for:
- Private Network Connectivity: NAT enables virtual machines on a private network to access public networks without exposing their internal IP addresses to the internet, enhancing security.
- IP Address Conservation: NAT allows organizations to use a smaller pool of public IP addresses for their virtual machines, maximizing IP address utilization and reducing costs.
- Network Segmentation: NAT can be used to create isolated network segments within the NSX environment, further enhancing security and simplifying network management.
NSX NAT configurations are managed through the NSX Manager interface, enabling administrators to define NAT rules, manage translation pools, and monitor NAT traffic.
NSX Integration with Other Technologies
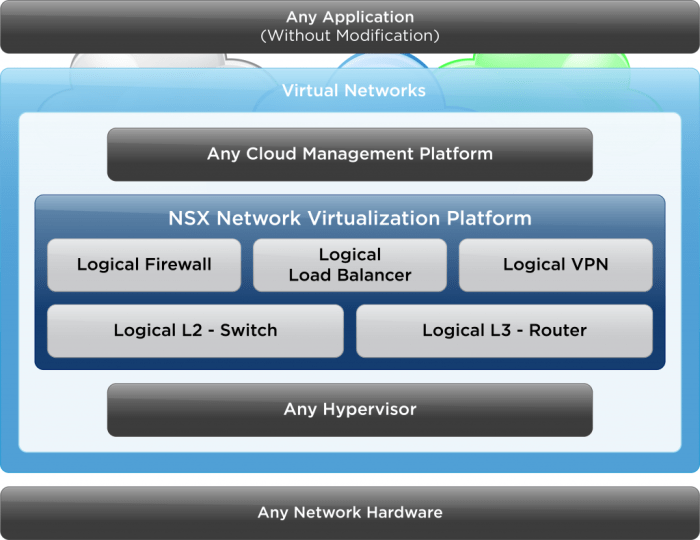
VMware NSX is designed to seamlessly integrate with other VMware technologies and cloud platforms, offering a comprehensive solution for managing and securing virtualized and cloud-native environments. This integration enhances operational efficiency, simplifies management, and fosters a more secure and flexible infrastructure.
Integration with vSphere and vCenter Server
NSX leverages the existing vSphere infrastructure, including vCenter Server, for centralized management and control. This integration provides a unified platform for managing both physical and virtual network resources.
- Simplified Management:NSX integrates with vCenter Server, providing a single console for managing both physical and virtual networks. This eliminates the need for separate management tools and simplifies network administration.
- Automated Deployment and Configuration:NSX can be deployed and configured through vCenter Server, automating tasks like network provisioning and policy enforcement. This reduces manual intervention and ensures consistency across the infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security:NSX leverages vCenter Server’s security features, such as role-based access control, to enforce granular security policies on network resources.
Integration with Cloud Platforms
NSX extends its capabilities to cloud platforms, enabling organizations to manage and secure their hybrid cloud environments.
- Hybrid Cloud Management:NSX provides consistent network and security policies across on-premises and cloud environments, simplifying management and ensuring seamless connectivity between different platforms.
- Cloud-Native Security:NSX offers micro-segmentation capabilities for cloud-native applications, providing granular security controls and protecting workloads running on cloud platforms.
- Multi-Cloud Support:NSX supports various cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, allowing organizations to manage their network and security policies across multiple cloud providers.
NSX in Hybrid Cloud Environments
NSX enables organizations to build and manage hybrid cloud environments by providing a consistent network and security framework across on-premises and cloud platforms.
- Application Mobility:NSX facilitates the migration of applications between on-premises and cloud environments without requiring significant network reconfiguration. This enables organizations to optimize application deployment based on cost and performance requirements.
- Disaster Recovery:NSX supports disaster recovery scenarios by enabling the replication of network and security policies to cloud environments. This ensures business continuity and reduces downtime in case of an outage.
- Cloud Bursting:NSX allows organizations to leverage cloud resources for peak demand, providing a scalable and cost-effective solution for handling temporary spikes in traffic.
NSX Use Cases and Best Practices
VMware NSX, a powerful network virtualization platform, offers a wide range of use cases that can significantly enhance data center operations, streamline cloud migration, and bolster security posture. This section delves into common NSX use cases, Artikels best practices for designing, implementing, and managing NSX environments, and provides guidance on troubleshooting common issues.
Data Center Modernization
Modernizing legacy data centers often involves transitioning from physical networking to software-defined networking (SDN). NSX facilitates this transition by enabling the creation of virtual networks that are independent of the underlying physical infrastructure. This allows for greater flexibility, agility, and automation in network management.
- Simplified Network Management:NSX centralizes network management, enabling administrators to configure and manage virtual networks from a single console. This simplifies operations and reduces the need for manual intervention.
- Increased Network Agility:NSX allows for rapid provisioning and reconfiguration of virtual networks, enabling organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs. This agility is crucial in today’s dynamic IT environments.
- Enhanced Security:NSX provides robust security features, such as micro-segmentation, which helps isolate applications and data within the virtual network, enhancing security posture and reducing the attack surface.
Cloud Migration
NSX plays a vital role in cloud migration strategies, enabling seamless migration of applications and workloads to public or private cloud environments.
- Consistent Networking:NSX ensures consistent network policies and configurations across on-premises and cloud environments, simplifying the migration process and ensuring smooth operation of applications in the cloud.
- Hybrid Cloud Connectivity:NSX facilitates secure and reliable connectivity between on-premises and cloud environments, enabling organizations to leverage the benefits of both worlds while maintaining a unified network architecture.
- Simplified Cloud Management:NSX extends network management capabilities to cloud environments, enabling administrators to manage both on-premises and cloud networks from a single console, improving efficiency and reducing complexity.
Security Enhancements
NSX’s security features are critical for bolstering data center security, protecting sensitive data, and mitigating cyber threats.
- Micro-segmentation:NSX enables micro-segmentation, which isolates applications and data within the virtual network, restricting communication between different components and reducing the attack surface. This granular security approach significantly enhances data center security.
- Network Firewall:NSX includes a built-in network firewall that provides stateful inspection of network traffic, blocking unauthorized access and protecting against malicious attacks. This firewall can be configured to enforce granular security policies based on specific requirements.
- Distributed Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDS/IPS):NSX integrates with distributed intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to detect and prevent malicious activity within the virtual network. This proactive security approach helps identify and neutralize threats before they can cause significant damage.
Best Practices for NSX
Implementing and managing NSX effectively requires adherence to best practices that ensure optimal performance, security, and scalability.
- Proper Planning and Design:Before deploying NSX, it is crucial to carefully plan and design the network architecture, considering factors such as network segmentation, security requirements, and scalability needs. A well-defined design ensures smooth implementation and avoids potential issues down the line.
- Thorough Testing:Thorough testing is essential before deploying NSX in a production environment. This includes testing network connectivity, security policies, and performance under various load conditions. Testing helps identify and resolve potential issues before they impact production systems.
- Regular Monitoring and Maintenance:Continuous monitoring and maintenance are critical for ensuring the optimal performance and security of NSX environments. This includes monitoring network traffic, performance metrics, and security events to identify and address potential issues promptly. Regular software updates and security patches are also essential for maintaining the integrity and security of the NSX platform.
Troubleshooting Common NSX Issues
Troubleshooting NSX issues can be challenging, but following a systematic approach can help identify and resolve problems effectively.
- Review Logs:NSX generates extensive logs that provide valuable information about system events, errors, and performance metrics. Analyzing these logs can often provide clues about the root cause of an issue.
- Check Network Connectivity:Network connectivity issues are a common source of problems in NSX environments. Ensure that all components are properly connected and that network communication is functioning as expected.
- Verify Configuration:Double-check the configuration of NSX components, including virtual networks, security policies, and routing rules. Incorrect configurations can lead to various issues, including connectivity problems and security vulnerabilities.
- Consult Documentation and Support Resources:VMware provides extensive documentation and support resources for NSX, including online guides, forums, and technical support. Consult these resources for troubleshooting tips, best practices, and solutions to common problems.
NSX Future and Trends
VMware NSX, the leading network virtualization platform, continues to evolve, driven by the relentless pace of technological advancements and the ever-changing demands of modern IT environments. The future of NSX is intertwined with the emergence of new technologies and the evolving needs of businesses.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on NSX
The convergence of 5G, edge computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to significantly impact the role of NSX in the future.
- 5G and Edge Computing:The widespread adoption of 5G will create a distributed edge computing environment, where applications and data are processed closer to users. This will necessitate a more distributed and agile network infrastructure. NSX will play a crucial role in enabling this distributed network by providing consistent security and policy enforcement across the edge.
- AI and Automation:AI and machine learning (ML) are transforming network operations. NSX will leverage AI and ML to automate network tasks, improve performance, and enhance security. AI-powered network analytics can help identify and remediate security threats proactively, while automated policy enforcement can streamline network management.
NSX Evolution to Address Future Challenges
NSX is evolving to address the challenges posed by the changing IT landscape.
- Multi-Cloud Support:Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. NSX is extending its capabilities to provide consistent network virtualization and security across multiple cloud environments, including public clouds like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Microservices and Containerization:The rise of microservices and containerized applications requires a network that can support dynamic and ephemeral workloads.
NSX is enhancing its support for containerized environments, providing networking and security for containers running on Kubernetes and other platforms.
- Zero Trust Security:The traditional perimeter-based security model is becoming increasingly ineffective. NSX is embracing zero trust security principles, where trust is assumed to be zero, and all users and devices are authenticated and authorized before accessing resources.
This approach helps to mitigate the risks of data breaches and insider threats.