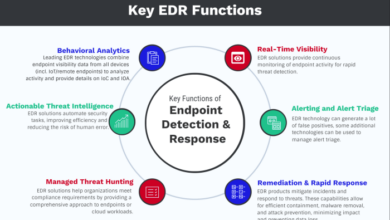
Prepare for the Security Skills Shortage
Prepare security skills shortage – Prepare for the Security Skills Shortage: It’s a topic that’s become increasingly urgent as the digital world evolves at breakneck speed. Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, and businesses are struggling to find qualified cybersecurity professionals to protect their systems and data.
This skills gap isn’t just a problem for large corporations – it affects every organization, from small businesses to government agencies.
The consequences of this shortage are dire. Without skilled cybersecurity professionals, organizations are vulnerable to breaches, data theft, and financial losses. The lack of expertise can also lead to poor security practices, leaving businesses exposed to even greater risks.
It’s a situation that demands attention and action.
The Growing Cybersecurity Skills Gap

The cybersecurity skills gap is a global issue, with a significant shortage of qualified professionals to combat the ever-growing threat of cyberattacks. This gap is widening, leaving organizations vulnerable to breaches and data theft.
Factors Contributing to the Skills Shortage
Several factors contribute to the widening cybersecurity skills gap. These include rapid technological advancements, the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, and the lack of skilled professionals.
Preparing for the security skills shortage is a critical task, requiring a multi-faceted approach. It’s easy to get caught up in the excitement of Prime Day deals, like those tempting AirPods offers. But remember, investing in your future is just as important.
Take a look at these alternative ways to spend your money: sure you could buy some airpods this prime day but what about these alternatives. By prioritizing skills development, you can equip yourself to tackle the growing demand for cybersecurity professionals and build a fulfilling career in this dynamic field.
Rapid Technological Advancements
The rapid pace of technological advancements in cybersecurity has created a demand for specialized skills that are difficult to acquire. New technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), introduce new vulnerabilities and require professionals with specific expertise.
Preparing for the security skills shortage is like running a business – you need to understand the bottom line. In this case, the bottom line is the security of your organization, and that means understanding the difference between gross profit vs net profit in terms of your security investments.
Gross profit represents the direct costs of securing your systems, while net profit considers all the indirect costs, like lost productivity due to breaches. By understanding these financial realities, you can make smarter decisions about allocating resources to build a robust security posture.
Increasing Sophistication of Cyber Threats
Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their attacks, using advanced techniques and tools to bypass traditional security measures. This necessitates professionals with advanced skills in threat intelligence, incident response, and security analysis.
Preparing for the security skills shortage requires a multi-faceted approach. One way to make the field more appealing to potential candidates is to personalize the experience. For example, you can customize color Microsoft Office to create a more engaging and visually appealing environment for employees, especially those working in cybersecurity, which can be a demanding field.
This small change can go a long way in boosting morale and attracting talent to a field that is vital for our digital future.
Lack of Skilled Professionals
The shortage of skilled professionals is exacerbated by a lack of qualified candidates entering the cybersecurity workforce. This can be attributed to factors such as a lack of awareness about cybersecurity careers, limited educational opportunities, and a perception that cybersecurity is a difficult field to enter.
Statistics and Data Illustrating the Severity of the Problem
- A 2022 study by (ISC)² found a global cybersecurity workforce shortage of 3.4 million professionals.
- The same study projected that the global cybersecurity workforce shortage will reach 3.5 million by 2025.
- A 2023 report by Cybersecurity Ventures estimated that the global cost of cybercrime will reach $10.5 trillion by 2025.
Strategies for Addressing the Shortage: Prepare Security Skills Shortage
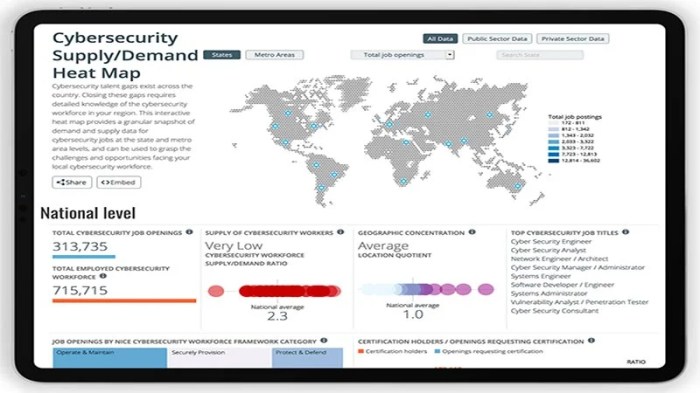
The cybersecurity skills gap is a pressing issue, demanding innovative solutions to ensure a robust digital landscape. Addressing this shortage requires a multifaceted approach, involving collaboration between governments, educational institutions, businesses, and individuals.
Strategies to Address the Cybersecurity Skills Gap
A comprehensive approach to address the cybersecurity skills gap involves various strategies, each contributing to the overall solution. The table below Artikels these strategies, their benefits, and potential challenges:
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upskilling and Reskilling Programs | Training existing professionals in cybersecurity skills or transitioning them from other fields. | Leverages existing workforce, provides immediate impact, cost-effective compared to hiring new talent. | Requires effective training programs, may not be suitable for all professionals, time commitment for training. |
| Education and Training Initiatives | Developing comprehensive cybersecurity curricula in schools, colleges, and universities. | Creates a pipeline of skilled professionals, fosters interest in cybersecurity from a young age, promotes diverse talent pool. | Requires investment in infrastructure, curriculum development, and qualified instructors, takes time to see results. |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Collaboration between governments and private companies to fund training programs, research, and development. | Leverages resources and expertise from both sectors, fosters innovation, promotes industry standards. | Requires coordination and communication between different stakeholders, potential conflicts of interest. |
| Cybersecurity Awareness Campaigns | Raising public awareness about cybersecurity threats and best practices. | Empowers individuals to protect themselves and their data, reduces the impact of attacks, creates a more secure digital environment. | Reaching a diverse audience, measuring effectiveness, overcoming skepticism and apathy. |
| Mentorship and Networking Programs | Connecting experienced professionals with aspiring cybersecurity professionals to provide guidance and support. | Provides practical experience, fosters career development, builds a strong cybersecurity community. | Requires commitment from mentors, finding suitable matches, managing expectations. |
Upskilling and Reskilling Programs
Upskilling and reskilling programs play a crucial role in addressing the cybersecurity skills gap. By providing training and certifications to existing professionals, organizations can quickly fill critical roles. For example, individuals with backgrounds in IT can be trained in cybersecurity principles, network security, and incident response.
This approach allows companies to leverage their existing workforce and avoid the costs associated with hiring new talent.
Education and Training Initiatives
Education and training initiatives are essential for creating a sustainable pipeline of skilled cybersecurity professionals. This involves developing comprehensive curricula at all levels of education, from high school to university. These programs should focus on both theoretical concepts and practical skills, preparing students for real-world challenges.
Integrating cybersecurity education into existing STEM programs can attract a wider range of students and foster a more diverse talent pool.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships are crucial for driving innovation and addressing the cybersecurity skills gap. Governments can provide funding for research, development, and training programs, while private companies can contribute expertise and resources. This collaboration can lead to the development of new technologies, improved cybersecurity practices, and a more secure digital landscape.
For example, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has partnered with industry leaders to develop cybersecurity frameworks and best practices.
Cybersecurity Awareness Campaigns
Cybersecurity awareness campaigns are essential for empowering individuals to protect themselves and their data. These campaigns can educate the public about common threats, best practices for online security, and the importance of reporting suspicious activity. By raising awareness, organizations can reduce the impact of attacks and create a more secure digital environment.
Mentorship and Networking Programs, Prepare security skills shortage
Mentorship and networking programs can provide aspiring cybersecurity professionals with guidance, support, and practical experience. Experienced professionals can share their knowledge, insights, and career paths, helping mentees develop their skills and navigate the industry. These programs can also foster a strong cybersecurity community, connecting professionals across different organizations and fostering collaboration.
Building a Cybersecurity Workforce

The global cybersecurity skills shortage is a critical issue, demanding a proactive approach to building a robust and skilled cybersecurity workforce. This involves understanding the essential skills and qualifications required for cybersecurity professionals, exploring available resources and programs for aspiring professionals, and implementing effective strategies for attracting and retaining talent within organizations.
Essential Skills and Qualifications for Cybersecurity Professionals
To thrive in the dynamic field of cybersecurity, professionals need a comprehensive skillset encompassing technical expertise, analytical capabilities, and a deep understanding of security principles.
- Technical Skills:Proficiency in various cybersecurity tools and technologies is crucial. This includes network security, operating systems, cryptography, incident response, and penetration testing.
- Analytical Skills:Cybersecurity professionals need strong analytical skills to identify, analyze, and respond to security threats. They must be able to interpret data, draw conclusions, and develop effective solutions.
- Communication Skills:Effective communication is essential for conveying security risks, implementing policies, and collaborating with colleagues and stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving Skills:Cybersecurity professionals must be adept at identifying and resolving complex security issues, often under pressure.
- Ethical Hacking:Understanding ethical hacking techniques allows cybersecurity professionals to identify vulnerabilities in systems and develop mitigation strategies.
Resources and Programs for Cybersecurity Professionals
A multitude of resources and programs are available to individuals seeking to enter or advance their careers in cybersecurity.
- Educational Programs:Universities and colleges offer a range of cybersecurity-related degrees, including Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Doctoral programs. These programs provide a comprehensive foundation in cybersecurity principles, technologies, and practices.
- Professional Certifications:Industry-recognized certifications, such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), and CompTIA Security+, validate cybersecurity knowledge and skills.
- Online Courses and Bootcamps:Online learning platforms and cybersecurity bootcamps offer flexible and accessible training options for individuals seeking to acquire specific cybersecurity skills.
- Cybersecurity Training Programs:Government agencies and private organizations offer specialized cybersecurity training programs, including those focused on specific areas like incident response, penetration testing, and digital forensics.
- Mentorship and Networking:Mentorship programs and cybersecurity networking events provide valuable opportunities for aspiring professionals to learn from experienced professionals and build their professional network.
Attracting and Retaining Cybersecurity Talent
Organizations face a competitive landscape in attracting and retaining top cybersecurity talent.
- Competitive Compensation and Benefits:Offering competitive salaries, comprehensive benefits packages, and opportunities for professional development is essential for attracting and retaining skilled cybersecurity professionals.
- Flexible Work Arrangements:Flexibility in work arrangements, such as remote work options and flexible schedules, can enhance employee satisfaction and attract a wider pool of talent.
- Career Advancement Opportunities:Providing opportunities for career growth, including leadership roles, specialized training, and mentorship programs, can motivate employees and foster long-term commitment.
- Positive Work Environment:Cultivating a positive and supportive work environment, characterized by open communication, collaboration, and recognition, can enhance employee morale and retention.
- Focus on Diversity and Inclusion:Creating a diverse and inclusive workplace fosters innovation and attracts a wider range of perspectives and talent.