Zero Trust Security Tips: Protecting Your Digital Assets
Zero Trust security tips are essential in today’s digital landscape, where threats are constantly evolving. The traditional perimeter-based security model is no longer sufficient to protect sensitive data and applications. Zero Trust, on the other hand, assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict verification and authorization before access is granted.
This shift in security paradigm is crucial for organizations of all sizes to effectively mitigate cyber risks.
Implementing Zero Trust principles can seem daunting at first, but it’s a journey worth undertaking. By embracing a Zero Trust approach, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture and safeguard their digital assets from malicious actors. This blog post will delve into the key aspects of Zero Trust security, providing practical tips and strategies to help you implement this robust security framework.
Understanding Zero Trust Security
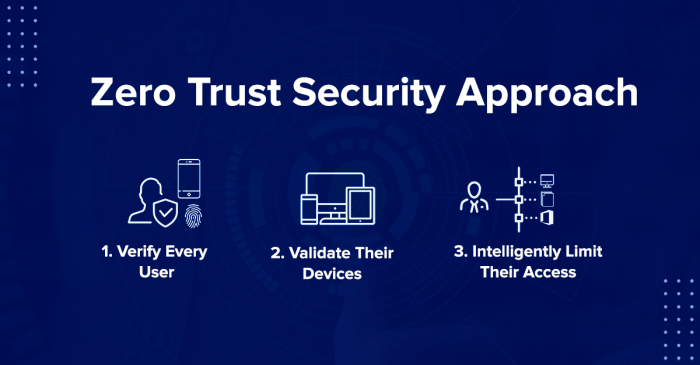
Zero Trust security is a modern approach to cybersecurity that assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, regardless of its location or whether it is on the internal network. This approach is a departure from traditional security models that relied on perimeter security and assumed that anything inside the network was safe.
Zero trust security is all about assuming no user or device is inherently trustworthy, so you need to verify everything. This means implementing strong authentication, granular access controls, and robust monitoring. And just like you need to carefully manage access to your network, you also need to be mindful of how you align content right left word in your website design to prevent potential security vulnerabilities.
By taking a proactive approach to security, you can better protect your organization from cyberattacks.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
The core principles of Zero Trust security are:
- Verify explicitly:Every user, device, and application must be authenticated and authorized before being granted access to resources.
- Least privilege:Users and devices should only be granted access to the resources they need to perform their jobs, and no more.
- Assume breach:Security systems should be designed to detect and respond to attacks, even if they occur inside the network.
- Continuously monitor and enforce:Security systems should constantly monitor for suspicious activity and enforce security policies in real time.
Zero Trust vs. Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models rely on a perimeter-based approach, where a firewall protects the network from external threats. This approach assumes that everything inside the network is safe and trusted. However, this approach is vulnerable to attacks that bypass the perimeter or exploit vulnerabilities within the network.Zero Trust security, on the other hand, assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default.
Zero trust security tips are more crucial than ever in today’s data-driven world. With the rise of AI and machine learning, the potential for data breaches is growing, especially with the integration of Google’s generative AI chatbots into business operations.
It’s important to remember that even with the potential benefits of using google generative ai chatbots company data , we must remain vigilant about data security. Implementing robust zero trust principles can help safeguard sensitive information and mitigate risks associated with these powerful technologies.
This approach requires verifying the identity and authorization of every user and device before granting access to resources. This approach is more secure because it does not rely on the assumption that anything inside the network is safe.
Benefits of Implementing a Zero Trust Framework
Implementing a Zero Trust framework offers several benefits, including:
- Improved security:Zero Trust security helps to prevent data breaches by assuming that no user or device can be trusted by default. This approach makes it more difficult for attackers to gain access to sensitive data.
- Reduced risk:By verifying the identity and authorization of every user and device, Zero Trust security reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Increased compliance:Zero Trust security can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- Enhanced productivity:By providing users with access only to the resources they need, Zero Trust security can help to improve productivity and reduce downtime.
Implementing Zero Trust Security Measures

Implementing Zero Trust security is not a one-time action but a continuous process that requires careful planning, design, and ongoing management. It involves a shift in security mindset, moving away from perimeter-based security to a more granular, identity-centric approach.
Best Practices for Implementing Zero Trust
To successfully implement Zero Trust, organizations need to adopt a set of best practices that guide their approach.
- Start with a clear understanding of your assets and data:Before implementing any security measures, it’s essential to know what you’re protecting. This includes identifying your critical assets, their value, and the data they contain.
- Define your Zero Trust strategy:A clear strategy is essential for guiding your implementation efforts. This strategy should Artikel your goals, principles, and the specific controls you’ll use to achieve your Zero Trust objectives.
- Implement strong identity and access management (IAM):IAM is the foundation of Zero Trust. This includes using multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users, including administrators, and implementing least privilege access controls.
- Utilize microsegmentation:This involves segmenting your network into smaller, isolated zones, limiting access to only authorized users and applications.
- Continuously monitor and adapt:Zero Trust is a dynamic approach that requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation. Regularly review your security posture and make adjustments as needed.
Zero Trust Architecture Design
Designing a Zero Trust architecture involves considering the various components and how they interact.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM):This component is at the core of Zero Trust, responsible for verifying user identities and granting access based on pre-defined policies.
- Network Segmentation:This involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit lateral movement and prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Protection:Data encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions are crucial for protecting sensitive information.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):This component collects and analyzes security events to identify threats and anomalies.
- Threat Intelligence:Integrating threat intelligence feeds helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and adapt their security posture accordingly.
Role of Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM plays a pivotal role in Zero Trust security by establishing a robust system for verifying user identities and granting access based on pre-defined policies.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA):MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code.
- Least Privilege Access Controls:This principle ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to perform their job duties.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):This approach assigns access permissions based on the user’s role within the organization.
- Single Sign-On (SSO):SSO allows users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without having to re-enter their credentials.
Securing Network Access
In a Zero Trust model, network access control is paramount. This involves rigorously verifying and controlling access to sensitive resources, regardless of user location or device.
Common Vulnerabilities Associated with Network Access Control
Network access control vulnerabilities arise from weak security measures, misconfigurations, and outdated practices.
- Lack of Strong Authentication:Using weak passwords or relying solely on usernames for authentication can lead to unauthorized access.
- Unsecured Remote Access:Unsecured remote access protocols like Telnet or FTP expose networks to potential attacks.
- Insufficient Device Security:Unpatched devices, including personal laptops or mobile devices, can act as entry points for attackers.
- Misconfigured Firewall Rules:Incorrectly configured firewalls can allow unauthorized access to sensitive resources.
- Lack of Network Segmentation:Failing to segment networks into smaller, isolated zones can allow attackers to move laterally and access sensitive data.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Methods
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Password-Based MFA:This involves entering a password and a one-time code generated by an authenticator app or hardware token.
- Biometric MFA:This uses unique biological characteristics like fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or iris scanning for authentication.
- Hardware Token MFA:This method utilizes physical tokens that generate unique codes for authentication.
- SMS/Email-Based MFA:This involves receiving a one-time code via SMS or email for verification.
Network Segmentation
Network segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated zones based on security requirements. This restricts lateral movement within the network, making it harder for attackers to spread across the environment.
- Micro-Segmentation:This approach segments network traffic at a very granular level, often down to individual applications or devices.
- Zone-Based Segmentation:This method groups resources based on their security sensitivity, creating distinct zones with specific access rules.
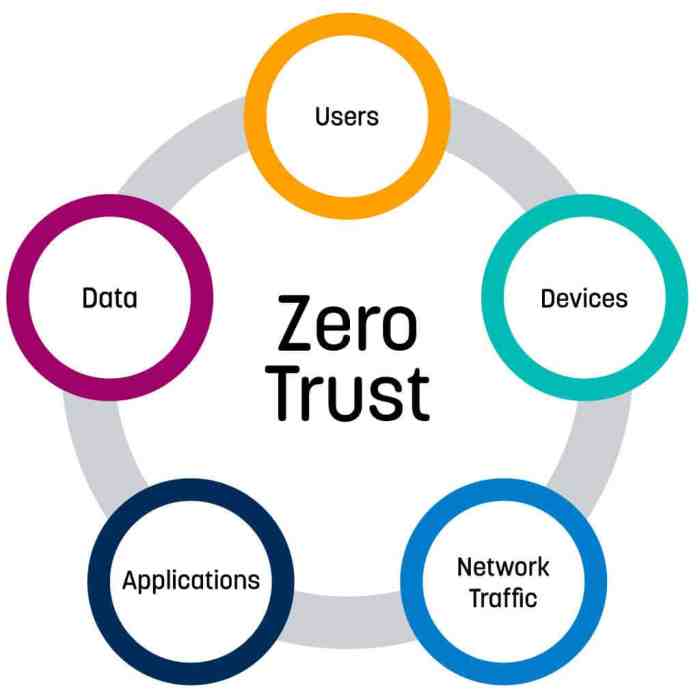
Protecting Data and Applications: Zero Trust Security Tips
In a Zero Trust environment, data and applications are the most valuable assets. The principle of “never trust, always verify” applies to these assets, requiring stringent security measures to protect them from unauthorized access and malicious activities. Data encryption and access controls are crucial for safeguarding data, while securing cloud applications and services is essential for maintaining the integrity and availability of applications.
Zero trust security is all about assuming no one can be trusted, and that includes your own devices. It’s about creating a secure perimeter around your data, no matter where it’s accessed. This is why I agree with the Rivian CEO’s decision to not adopt CarPlay , which could introduce security vulnerabilities.
By controlling the software environment, Rivian can better ensure the safety of their drivers and their data. Zero trust security isn’t just about locking things down, it’s about creating a more secure and reliable system.
Implementing micro-segmentation within a Zero Trust framework provides granular control over network traffic and enhances the overall security posture.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure that transforms data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals. In a Zero Trust environment, data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information both at rest and in transit.
Access controls, on the other hand, determine who can access specific data and applications, limiting access based on roles, permissions, and other factors. Implementing robust access controls is crucial for enforcing the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks.
Securing Cloud Applications and Services
Cloud applications and services are increasingly becoming the target of cyberattacks. Adopting a Zero Trust approach for cloud security is paramount for mitigating these risks. Cloud security measures should include strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, regular security assessments, and the use of cloud security tools and services.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, before granting access to cloud applications.
- Utilize Cloud Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):SIEM tools aggregate and analyze security data from various cloud sources, providing valuable insights into potential threats and security breaches.
- Implement Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB):CASBs act as a security gateway between users and cloud applications, enforcing security policies and controlling data access.
Implementing Micro-segmentation
Micro-segmentation is a security strategy that divides a network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the impact of security breaches. In a Zero Trust environment, micro-segmentation provides granular control over network traffic, ensuring that only authorized communication is allowed.
- Identify Critical Assets:Start by identifying the most sensitive data and applications within your network.
- Define Security Zones:Create distinct security zones based on the sensitivity of assets, separating critical resources from less sensitive ones.
- Implement Network Segmentation Tools:Utilize network segmentation tools to enforce micro-segmentation policies, restricting communication between different zones.
- Continuously Monitor and Adjust:Regularly monitor network traffic and adjust micro-segmentation policies as needed to ensure the effectiveness of the security strategy.
Zero Trust and Endpoint Security
Endpoint security plays a crucial role in a Zero Trust model by ensuring that all devices accessing the network, regardless of their location, are secure and trusted. This approach treats every device as a potential threat, regardless of its location or user identity.
Endpoint Security Measures
Endpoint security measures are critical in a Zero Trust environment. They help protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access and malicious activities.A comprehensive list of endpoint security measures includes:
- Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software:This software helps protect endpoints from viruses, malware, and other threats. It scans files and programs for malicious code and prevents them from running on the device.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities. They monitor endpoint activity, detect suspicious behavior, and automatically respond to threats.
- Firewall:A firewall acts as a barrier between the endpoint and the network, blocking unauthorized access and preventing malicious traffic from entering the device.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):DLP solutions help prevent sensitive data from leaving the endpoint without authorization. They monitor data transfer activities and block attempts to send confidential information to unauthorized destinations.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS):IDPS solutions monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block suspicious connections. They can detect and prevent attacks that target endpoints.
- Vulnerability Scanning:Vulnerability scanning tools identify security weaknesses in endpoints and software applications. This allows organizations to patch vulnerabilities and prevent attackers from exploiting them.
- Endpoint Encryption:Endpoint encryption encrypts data stored on the device, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. This helps protect sensitive information even if the device is lost or stolen.
- Hardening:Hardening involves configuring endpoints to minimize security risks. This includes disabling unnecessary services, removing unneeded software, and strengthening password policies.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, to access the endpoint. This makes it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- User Education:Educating users about security best practices is essential for endpoint security. Users should be trained to recognize phishing attempts, avoid downloading suspicious files, and use strong passwords.
Managing and Securing Remote Workers in a Zero Trust Environment
Managing and securing remote workers in a Zero Trust environment requires a robust approach that addresses the unique challenges of remote work.Here are some key strategies:
- Enforce Strong Endpoint Security:Ensure that all remote worker endpoints meet the organization’s security standards. This includes implementing all the endpoint security measures mentioned earlier.
- Implement Secure Remote Access:Use secure VPNs or other remote access solutions that encrypt all data traffic and authenticate users before granting access to the network.
- Use a Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Solution:ZTNA solutions provide secure access to applications and data based on user identity and device context, regardless of location. This allows organizations to control access to resources even when employees are working from home or other remote locations.
- Regularly Monitor and Audit Endpoint Activity:Monitor endpoint activity for suspicious behavior and conduct regular security audits to ensure that all devices meet security standards.
- Provide Security Training for Remote Workers:Train remote workers on security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and reporting suspicious activity.
- Use a Secure Communication Platform:Implement a secure communication platform for remote workers to communicate with each other and with the organization. This platform should provide end-to-end encryption to protect sensitive information.
Monitoring and Incident Response
In a Zero Trust environment, where every access is treated as potentially malicious, continuous monitoring and threat detection are paramount. This section delves into the significance of these practices and explores best practices for incident response within a Zero Trust framework.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection, Zero trust security tips
Continuous monitoring and threat detection are crucial for identifying and responding to security incidents in a timely manner. They involve the ongoing collection and analysis of security data to identify anomalies, suspicious activities, and potential threats. This data can include network traffic, user activity, system logs, and security alerts.
- Real-time Threat Detection:Zero Trust requires real-time threat detection to quickly identify and mitigate security risks. Advanced threat detection technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, can analyze security data in real time to detect anomalies and suspicious patterns.
- Anomaly Detection:Monitoring for deviations from established baselines helps identify unusual activity that might indicate a security breach. This can involve analyzing network traffic patterns, user behavior, and system performance metrics.
- Vulnerability Management:Regularly scanning for and patching vulnerabilities is crucial for preventing attackers from exploiting weaknesses in systems and applications.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):SIEM solutions aggregate and analyze security data from various sources, providing a centralized view of security events and facilitating incident response.
Incident Response Best Practices
Effective incident response within a Zero Trust framework requires a well-defined plan and coordinated actions. The following best practices can enhance the effectiveness of incident response:
- Rapid Detection and Containment:Zero Trust principles emphasize quick detection and containment of security incidents. Automated detection systems and response mechanisms are essential for limiting the impact of attacks.
- Incident Response Team:A dedicated incident response team with expertise in security incident handling is critical for coordinating and executing response actions.
- Incident Response Plan:A documented incident response plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and escalation procedures.
- Regular Testing and Drills:Regularly testing and simulating security incidents helps ensure the effectiveness of the incident response plan and the team’s ability to respond effectively.
- Post-Incident Analysis:After an incident, a thorough post-incident analysis is essential to identify the root cause, learn from the experience, and improve security measures.
SIEM Solutions Comparison
SIEM solutions play a critical role in Zero Trust by centralizing security data and providing real-time threat detection and incident response capabilities. Here is a comparison of some popular SIEM solutions:
| SIEM Solution | Key Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Splunk | Real-time threat detection, machine learning, log correlation, incident response automation | Powerful analytics, extensive data sources, flexible deployment options | Complex to configure, can be expensive, requires skilled personnel |
| IBM QRadar | Threat intelligence, vulnerability management, security orchestration, automation | Comprehensive security capabilities, good integration with other IBM products | Can be expensive, requires specialized training, may have a steep learning curve |
| AlienVault OSSIM | Open-source SIEM, log management, vulnerability assessment, intrusion detection | Cost-effective, flexible, customizable | May require more technical expertise, limited support options |
| LogRhythm | Real-time threat detection, security analytics, incident response, automation | User-friendly interface, comprehensive reporting, strong security capabilities | Can be expensive, requires dedicated hardware, may have a steep learning curve |
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing Zero Trust can bring significant security benefits, but it also presents several challenges that organizations must address. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful adoption and achieving the desired outcomes.
Impact on User Experience
The shift to a Zero Trust model can potentially impact user experience, particularly if not implemented thoughtfully.
- Increased Authentication Requirements:Zero Trust mandates frequent authentication, which can be perceived as inconvenient by users. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can enhance security but may also lead to increased login times and complexity.
- Access Restrictions:Users may experience delays or difficulties accessing resources due to strict access controls. This can hinder productivity if not managed effectively.
- User Education and Training:Users need to be educated on Zero Trust principles and the importance of security measures. Lack of proper training can lead to user frustration and resistance to the new security framework.
Automation and AI in Zero Trust
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) play crucial roles in facilitating Zero Trust implementation and management.
- Automated Policy Enforcement:AI can analyze user behavior and network traffic patterns to automatically adjust security policies, adapting to evolving threats and ensuring continuous security.
- Threat Detection and Response:AI-powered systems can detect suspicious activities and anomalies, providing real-time threat detection and response capabilities. This can significantly reduce the time to identify and mitigate security breaches.
- Security Orchestration and Automation (SOAR):SOAR platforms leverage AI and automation to streamline security operations, automating tasks like incident response, threat intelligence gathering, and vulnerability management.
Common Challenges
Adopting Zero Trust security presents several common challenges that organizations must overcome:
- Legacy Infrastructure:Organizations with legacy systems may face difficulties in integrating Zero Trust principles into existing infrastructure. This can require significant investments in upgrading or replacing outdated systems.
- Complexity and Management:Implementing Zero Trust requires complex configuration and management, which can be challenging for IT teams with limited expertise.
- Cost:Implementing Zero Trust can be costly, requiring investments in new technologies, software, and skilled personnel.
- Cultural Change:Shifting from a perimeter-based security model to Zero Trust requires a cultural shift within the organization. This involves changing user behavior, security practices, and IT processes.