Types of CRM Software: A Guide to Choosing the Right One
Types of CRM software are essential for businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises. CRM, which stands for Customer Relationship Management, helps you manage your customer interactions and data in a centralized system. It allows you to track leads, nurture prospects, manage sales, and provide excellent customer service, all while improving your overall business efficiency.
But with so many different types of CRM software available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your needs. This guide will explore the various types of CRM software, their advantages and disadvantages, and key features to consider.
Introduction to CRM Software: Types Of Crm Software
CRM software, or Customer Relationship Management software, is a tool designed to manage and improve customer interactions and relationships. It encompasses various functionalities that help businesses understand their customers better, track their interactions, and ultimately, boost sales and customer loyalty.The implementation of CRM software offers numerous benefits for businesses of all sizes.
By centralizing customer data and interactions, CRM systems streamline processes, enhance communication, and provide valuable insights for informed decision-making.
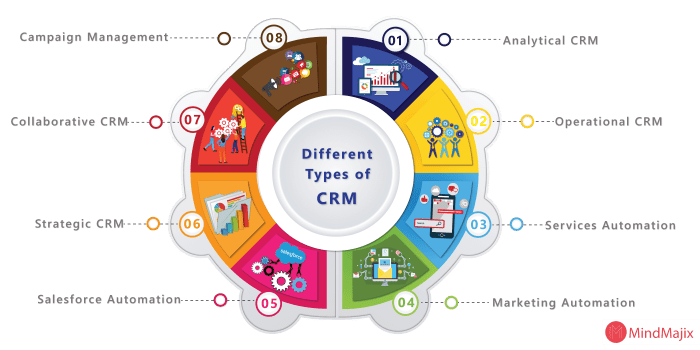
Core Functionalities of CRM Software
CRM systems typically include a range of core functionalities that work together to achieve these goals. These functionalities can be categorized into various modules, each focusing on a specific aspect of customer management. The core functionalities of CRM software can be categorized into the following modules:
- Sales Management:This module helps manage the sales pipeline, track leads, and manage opportunities. It allows businesses to automate sales processes, track sales performance, and forecast future sales.
- Marketing Automation:This module helps automate marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, social media marketing, and lead nurturing. It allows businesses to segment their customer base, personalize marketing messages, and track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Customer Service:This module helps manage customer support requests, track issues, and provide resolutions. It allows businesses to offer a consistent and efficient customer service experience, improve response times, and track customer satisfaction.
- Analytics and Reporting:This module provides insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. It allows businesses to identify trends, make data-driven decisions, and optimize their CRM strategy.
Types of CRM Software
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for any business, regardless of size. But with so many options available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. To help you navigate this landscape, we’ll explore the various types of CRM software, their features, and their strengths and weaknesses.
Types of CRM Software
CRM software comes in many forms, each designed to cater to specific needs and business models. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
| Type of CRM | Description | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Premise CRM | Software installed and managed on a company’s own servers, providing complete control over data and security. | Customization, high security, offline access | SAP CRM, Oracle Siebel, Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
| Cloud-Based CRM | Software hosted on a third-party provider’s servers, accessible via the internet. | Scalability, affordability, easy deployment | Salesforce, Zoho CRM, HubSpot CRM |
| Open Source CRM | Software with publicly available source code, allowing customization and modification. | Flexibility, cost-effectiveness, community support | SugarCRM, vtiger CRM, Dolibarr ERP/CRM |
| Industry-Specific CRM | Software tailored to the specific needs of a particular industry, such as healthcare, finance, or retail. | Specialized features, industry-specific insights, regulatory compliance | Salesforce Health Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Retail, Zoho CRM for Real Estate |
| Small Business CRM | Software designed for small businesses with limited resources and simple requirements. | User-friendliness, affordability, basic features | Pipedrive, Freshsales, Insightly |
| Enterprise CRM | Software for large businesses with complex needs and high volumes of data. | Advanced features, scalability, integration capabilities | SAP CRM, Oracle Siebel, Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
Let’s delve deeper into each type:
On-Premise CRM
On-premise CRM is a traditional approach where the software is installed and managed on a company’s own servers. This provides complete control over data security and customization, but it also requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT personnel.
- Advantages:
- High level of control over data and security.
- Customization options to meet specific business needs.
- Offline access for employees.
- Disadvantages:
- High upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT personnel.
- Maintenance and updates require technical expertise.
- Limited scalability and flexibility.
- Examples:
- SAP CRM
- Oracle Siebel
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
Cloud-Based CRM
Cloud-based CRM, also known as Software as a Service (SaaS), is hosted on a third-party provider’s servers and accessed via the internet. This eliminates the need for on-premise infrastructure and allows for easy scalability and accessibility.
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs compared to on-premise solutions.
- Scalability to accommodate growing businesses.
- Easy deployment and access from any device with an internet connection.
- Regular updates and maintenance handled by the provider.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited customization options compared to on-premise solutions.
- Dependence on internet connectivity.
- Security concerns, as data is stored on third-party servers.
- Examples:
- Salesforce
- Zoho CRM
- HubSpot CRM
Open Source CRM
Open source CRM software has publicly available source code, allowing users to customize and modify it to meet their specific needs. This provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness, as there are no licensing fees.
- Advantages:
- Flexibility and customization options.
- Cost-effectiveness, as there are no licensing fees.
- Access to a large community of developers and users for support.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires technical expertise to install, configure, and maintain.
- Limited support and documentation compared to commercial CRM solutions.
- Security vulnerabilities may arise due to the open-source nature.
- Examples:
- SugarCRM
- vtiger CRM
- Dolibarr ERP/CRM
Industry-Specific CRM
Industry-specific CRM software is tailored to the unique needs of a particular industry, such as healthcare, finance, or retail. This provides specialized features, industry-specific insights, and compliance with regulations.
- Advantages:
- Specialized features and functionalities relevant to the industry.
- Industry-specific insights and data analysis.
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher costs compared to general CRM solutions.
- Limited flexibility and customization options.
- Dependence on the specific industry’s requirements.
- Examples:
- Salesforce Health Cloud
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Retail
- Zoho CRM for Real Estate
Small Business CRM
Small business CRM software is designed for businesses with limited resources and simple requirements. It typically offers user-friendly interfaces, affordable pricing, and basic features for managing customer interactions.
- Advantages:
- User-friendly interface and easy to use.
- Affordable pricing for small businesses.
- Basic features for managing customer interactions.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited features and functionalities compared to enterprise solutions.
- Scalability may be a concern as the business grows.
- May not be suitable for businesses with complex requirements.
- Examples:
- Pipedrive
- Freshsales
- Insightly
Enterprise CRM
Enterprise CRM software is designed for large businesses with complex needs and high volumes of data. It offers advanced features, scalability, integration capabilities, and comprehensive reporting functionalities.
- Advantages:
- Advanced features and functionalities for managing complex business processes.
- Scalability to handle high volumes of data and users.
- Integration capabilities with other enterprise systems.
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics.
- Disadvantages:
- High upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Requires technical expertise to implement and manage.
- May be overwhelming for businesses with simpler needs.
- Examples:
- SAP CRM
- Oracle Siebel
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
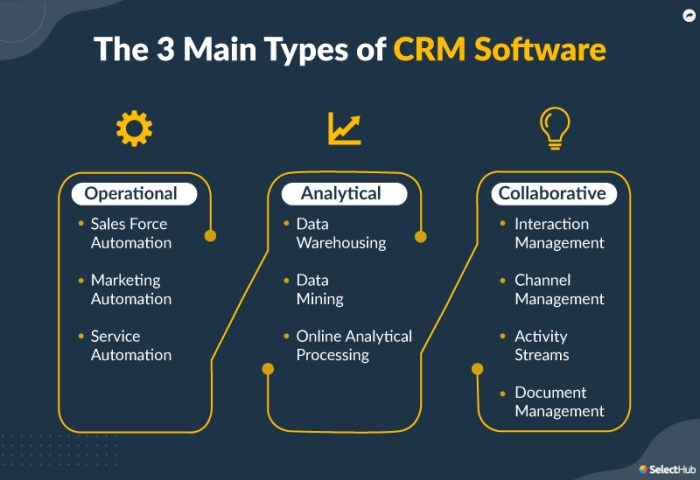
Key Features of CRM Software
CRM software is designed to streamline and optimize interactions with customers across various stages of the customer lifecycle. At the heart of every CRM system is the ability to manage customer data effectively.
Contact Management
Effective contact management is essential for building strong customer relationships. CRM systems provide a centralized database for storing and organizing customer information.
- Centralized Customer Database:CRM systems act as a single source of truth for all customer-related data, including contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and preferences. This eliminates the need for multiple spreadsheets or databases and ensures data consistency.
- Detailed Customer Profiles:CRM systems allow you to create comprehensive customer profiles by capturing a wide range of information, including demographics, interests, purchase behavior, and interactions with your business. This detailed understanding enables personalized communication and targeted marketing efforts.
- Segmentation and Targeting:CRM systems empower you to segment your customer base based on various criteria, such as demographics, purchase history, or engagement levels. This segmentation allows you to tailor marketing campaigns and communication to specific customer groups, improving effectiveness and ROI.
Sales Automation
Sales automation features streamline sales processes, improve efficiency, and boost productivity.
- Lead Management:CRM systems automate the lead capture and qualification process. They track lead sources, assign leads to sales representatives, and nurture leads through automated email campaigns and personalized follow-ups.
- Opportunity Tracking:CRM systems provide a clear view of sales opportunities, allowing you to track progress, identify potential roadblocks, and prioritize deals. Features like opportunity stages, probability estimates, and activity tracking help sales teams stay organized and on top of their sales pipeline.
- Forecasting:CRM systems enable accurate sales forecasting by analyzing historical data and current trends. This helps businesses predict future sales performance, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions about sales strategies.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation features automate repetitive tasks, personalize customer interactions, and measure marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Email Marketing:CRM systems integrate with email marketing platforms to automate email campaigns, segment audiences, personalize content, and track email performance. They enable sending targeted emails based on customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history.
- Social Media Integration:CRM systems can connect with social media platforms to monitor brand mentions, engage with customers, and track social media campaigns. This integration allows businesses to leverage social media for customer service, lead generation, and brand building.
- Campaign Management:CRM systems help manage marketing campaigns from planning to execution and analysis. They provide tools for creating and scheduling campaigns, tracking campaign performance, and optimizing campaign strategies based on data insights.
Customer Service
Customer service features enhance customer support, improve response times, and increase customer satisfaction.
- Ticketing Systems:CRM systems include ticketing systems that allow customers to submit support requests and track their progress. This centralized system ensures that all customer inquiries are addressed promptly and efficiently.
- Live Chat:Live chat features enable real-time communication with customers on your website. This provides immediate assistance, resolves queries quickly, and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Knowledge Bases:CRM systems often include knowledge bases or help centers where customers can find answers to frequently asked questions. This self-service option reduces support inquiries and empowers customers to find solutions independently.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics features provide valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Dashboards:CRM systems offer customizable dashboards that display key performance indicators (KPIs) and provide a high-level overview of business operations. This visual representation of data helps identify trends, track progress, and make informed decisions.
- Performance Tracking:CRM systems track various metrics, such as sales conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and customer lifetime value. This data helps businesses measure the effectiveness of their sales and marketing efforts and identify areas for improvement.
- Data Visualization:CRM systems provide tools for visualizing data through charts, graphs, and reports. This makes complex data easier to understand and interpret, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Integration
CRM systems can integrate with other software applications to enhance functionality and streamline workflows.
- E-commerce Platforms:Integration with e-commerce platforms allows businesses to track customer purchases, manage orders, and provide personalized recommendations based on purchase history.
- Marketing Automation Platforms:Integration with marketing automation platforms enables automated email campaigns, lead nurturing, and targeted marketing based on customer data stored in the CRM system.
- Accounting Software:Integration with accounting software simplifies financial management by syncing customer data, invoices, and payments. This ensures accurate financial reporting and streamlines billing processes.
Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility features enable CRM data management on the go, improving flexibility and productivity.
Choosing the right CRM software can be overwhelming, with options ranging from cloud-based solutions to on-premise systems. But beyond the technical aspects, it’s also crucial to consider how you’ll integrate it into your daily workflow. For example, if you’re a busy professional, this handy Apple Siri cheat sheet for business might be a game-changer, allowing you to manage your CRM tasks with voice commands.
Ultimately, the best CRM software is the one that seamlessly fits your existing processes and enhances your productivity.
- Mobile Apps:CRM systems often offer mobile apps that provide access to core features, such as contact management, opportunity tracking, and customer communication. This allows sales representatives and customer service agents to manage CRM data from their smartphones or tablets.
- Offline Access:Mobile apps may offer offline access to CRM data, enabling users to access and update information even without an internet connection. This ensures data availability and continuity during travel or in areas with limited connectivity.
- Push Notifications:Mobile apps can send push notifications to alert users about important events, such as new leads, customer inquiries, or upcoming deadlines. This ensures timely responses and prevents missed opportunities.
Choosing the Right CRM Software
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for any business looking to streamline operations, improve customer relationships, and drive growth. With a vast array of options available, it’s essential to carefully evaluate your needs and consider various factors to make an informed decision.
Business Needs
Determining your specific business needs is the first step in choosing the right CRM software. Consider the following questions: * What are your primary goals for using a CRM?Are you aiming to improve customer service, automate marketing campaigns, manage sales pipelines, or track customer interactions?
- What are your current pain points?Identify areas where your business struggles with customer management, data organization, or communication.
- What are your specific industry requirements?Different industries have unique needs and regulatory requirements that may influence your CRM choice.
- What is the size of your team and customer base?The size of your organization will determine the features and scalability required.
Budget
Budget considerations are crucial when selecting a CRM. Pricing models vary significantly, so it’s important to understand the cost structure and potential long-term expenses. * Free vs. Paid:Free CRM options are available for small businesses with limited needs, while paid versions offer more advanced features and support.
Subscription Models
Most CRM software providers offer subscription-based pricing models, with monthly or annual fees.
Per-User Pricing
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for any business, and there are many different types to consider. From cloud-based solutions to on-premise installations, the options are plentiful. But even with the right CRM, sometimes you need to personalize your work environment.
If you’re using Microsoft Office, customize color microsoft office can help create a more visually appealing and productive space. This can help you stay focused on your CRM tasks and make your day more enjoyable.
Some CRMs charge per user, making them more expensive for larger teams.
Additional Costs
Factor in potential costs for customization, integration, training, and support.
Scalability
Choosing a CRM that can scale with your business is essential for long-term success. Consider the following:* Growth Potential:Can the CRM handle an increase in customer volume, data storage, and user accounts?
Flexibility
Does the CRM allow for customization and integration as your business evolves?
Future Needs
Think about your anticipated future needs and ensure the CRM can accommodate them.
Ease of Use
User-friendliness is paramount for CRM adoption. A complex and difficult-to-use system will lead to low adoption rates and wasted resources. * Intuitive Interface:The CRM should have a clear and intuitive interface that is easy to navigate and understand.
Training and Support
Look for vendors that provide comprehensive training and support resources to help users get up to speed quickly.
Mobile Accessibility
Consider the availability of a mobile app for accessing the CRM on the go.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is essential for resolving issues and ensuring a smooth CRM implementation. * Response Time:Assess the vendor’s response time to support requests and their availability.
Knowledge Base
Look for vendors with a comprehensive knowledge base and online resources to help users find answers quickly.
Live Chat and Phone Support
Consider vendors that offer live chat or phone support for immediate assistance.
Choosing the right CRM software can be a real head-scratcher, especially when you’re considering factors like scalability, integrations, and AI capabilities. Speaking of AI, the new Intel Lunar Lake NPU is a game-changer for AI-powered applications, and it’s definitely something to keep in mind when evaluating CRM options.
Ultimately, the best CRM is the one that aligns with your specific business needs and goals, and that’s something you should consider carefully before making a decision.
Integration
CRM integration with other business systems is crucial for seamless data flow and improved efficiency. * Existing Systems:Determine which systems your CRM needs to integrate with, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
API Availability
Look for CRMs with robust application programming interfaces (APIs) that enable integration with other systems.
Third-Party Integrations
Explore the availability of pre-built integrations with popular third-party applications.
Implementation and Adoption of CRM Software
Implementing and adopting a CRM system is a crucial step in leveraging its benefits. It involves a structured approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximize user adoption.
Planning and Preparation, Types of crm software
A well-defined plan is essential for successful CRM implementation. It involves:
- Defining Goals and Objectives:Clearly outlining the desired outcomes from the CRM system, such as improved customer satisfaction, increased sales, or enhanced marketing effectiveness.
- Identifying Stakeholders:Recognizing all individuals or teams who will be impacted by the CRM system, including sales, marketing, customer service, and IT departments.
- Project Scope and Timeline:Defining the specific features and functionalities to be implemented, along with a realistic timeline for each stage.
- Resource Allocation:Determining the required resources, including personnel, budget, and technology, to support the implementation process.
- Communication Plan:Establishing clear communication channels to keep all stakeholders informed throughout the implementation journey.
Data Migration
Moving existing customer data from legacy systems to the CRM is a critical step. It requires careful planning and execution to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
- Data Mapping:Identifying and matching data fields from the old system to the CRM’s structure. This ensures consistency and eliminates duplication.
- Data Cleaning and Validation:Addressing inconsistencies, errors, or missing data before migration. This enhances data quality and improves the reliability of CRM insights.
- Data Transfer Method:Choosing an appropriate method for transferring data, such as manual entry, file transfer, or API integration. The choice depends on the data volume and complexity.
- Data Backup and Recovery:Creating backups of existing data before migration to ensure data recovery in case of any issues. This safeguards against data loss during the transfer process.
Training and User Adoption
Effective training and user adoption are essential for maximizing the value of a CRM system. This involves:
- Comprehensive Training Programs:Developing training programs that cover all aspects of the CRM system, including functionalities, best practices, and troubleshooting tips.
- Interactive Training Sessions:Providing hands-on training sessions that allow users to practice using the CRM system in a simulated environment.
- User Guides and Documentation:Creating user-friendly guides and documentation that provide detailed information about the CRM system and its features.
- Ongoing Support and Assistance:Offering ongoing support and assistance to users through help desks, FAQs, or dedicated support teams.
- Incentivize and Reward:Recognizing and rewarding users for their adoption and effective use of the CRM system. This promotes positive engagement and encourages continuous usage.
Customization and Configuration
Customizing the CRM system to meet specific business requirements is essential for maximizing its effectiveness. This involves:
- Workflow Automation:Configuring automated workflows to streamline processes, such as lead qualification, opportunity management, and customer support.
- Reporting and Analytics:Customizing reports and dashboards to provide insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) and track progress towards business goals.
- Integration with Other Systems:Connecting the CRM system with other business applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, or social media tools.
- User Interface and Branding:Customizing the user interface to align with the company’s branding and provide a familiar experience for users.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Regular maintenance and support are crucial for ensuring the CRM system remains up-to-date, secure, and performs optimally. This includes:
- Software Updates and Patches:Applying regular software updates and patches to address security vulnerabilities and improve system performance.
- Data Backup and Recovery:Implementing regular data backups and recovery procedures to safeguard against data loss or corruption.
- Technical Support:Providing technical support to users who encounter issues or require assistance with the CRM system.
- Performance Monitoring:Monitoring the performance of the CRM system to identify any bottlenecks or issues that need to be addressed.
Benefits of Using CRM Software
CRM software has become an indispensable tool for businesses of all sizes, offering a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline operations, enhance customer interactions, and ultimately drive growth. By leveraging CRM software, organizations can unlock a wide range of benefits that positively impact various aspects of their business, from sales and marketing to customer service and data management.
Improved Customer Relationships
At the heart of any successful business lies strong customer relationships. CRM software plays a pivotal role in fostering these connections by providing a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, preferences, and data.
- Personalized Communication:CRM systems enable businesses to personalize their communication with customers by leveraging data about their preferences, purchase history, and interactions. This personalized approach fosters a sense of value and strengthens customer relationships.
- Targeted Marketing:CRM software empowers businesses to segment their customer base based on various criteria, allowing them to tailor marketing campaigns and offers to specific customer groups. This targeted approach increases the effectiveness of marketing efforts and resonates better with individual customers.
- Proactive Engagement:By analyzing customer data, CRM systems can identify opportunities for proactive engagement. Businesses can leverage this insight to reach out to customers with relevant offers, support, or updates, demonstrating a genuine interest in their well-being and enhancing the customer experience.
Increased Sales and Revenue
CRM software directly contributes to increased sales and revenue by providing businesses with valuable insights into customer behavior, enabling them to optimize their sales strategies and drive conversions.
- Lead Management:CRM systems streamline the lead management process, helping businesses track, qualify, and nurture leads effectively. By automating tasks and providing a centralized view of lead interactions, CRM software ensures that no potential opportunity is missed.
- Sales Forecasting:CRM systems provide powerful analytical tools that enable businesses to forecast sales accurately. By analyzing historical data and current trends, businesses can make informed decisions about resource allocation, inventory management, and sales targets.
- Cross-Selling and Up-Selling:CRM software empowers businesses to identify opportunities for cross-selling and up-selling by analyzing customer purchase history and preferences. By recommending complementary products or services, businesses can increase customer lifetime value and drive additional revenue.
Enhanced Customer Service
Exceptional customer service is a cornerstone of any successful business, and CRM software plays a crucial role in delivering a seamless and positive experience for customers.
- Faster Response Times:CRM systems provide a centralized platform for managing customer inquiries, allowing businesses to respond to requests promptly and efficiently. This reduces wait times and improves customer satisfaction.
- Personalized Support:By leveraging customer data, CRM software enables businesses to provide personalized support tailored to individual needs and preferences. This demonstrates a genuine understanding of customer requirements and fosters stronger relationships.
- Improved Issue Resolution:CRM systems facilitate efficient issue resolution by providing a comprehensive history of customer interactions, allowing support agents to quickly access relevant information and resolve issues effectively. This reduces the time and effort required to address customer concerns and enhances their overall experience.
Better Data Management
CRM software is a powerful tool for centralizing and managing customer data effectively, providing businesses with a single source of truth for all customer-related information.
- Centralized Database:CRM systems consolidate customer data from various sources into a single, centralized database, eliminating data silos and ensuring consistency across the organization.
- Data Insights:CRM software provides advanced analytical tools that enable businesses to extract valuable insights from customer data. By analyzing trends, patterns, and customer behavior, businesses can make data-driven decisions that improve their operations and enhance customer engagement.
- Data Security:CRM systems prioritize data security by implementing robust access controls and encryption protocols. This protects sensitive customer information from unauthorized access and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
Improved Marketing Effectiveness
CRM software empowers businesses to create more targeted and effective marketing campaigns by leveraging customer data and insights to personalize messaging and optimize campaign delivery.
- Targeted Campaigns:CRM systems enable businesses to segment their customer base based on various criteria, allowing them to tailor marketing campaigns and offers to specific customer groups. This targeted approach increases the effectiveness of marketing efforts and resonates better with individual customers.
- Automated Marketing:CRM software automates repetitive marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, social media updates, and lead nurturing, freeing up marketing teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Campaign Performance Tracking:CRM systems provide comprehensive tracking and analytics for marketing campaigns, allowing businesses to measure the effectiveness of their efforts and identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach ensures that marketing investments are optimized for maximum return.
Increased Productivity and Efficiency
CRM software streamlines business processes, automates tasks, and provides a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, ultimately leading to increased productivity and efficiency across the organization.
- Task Automation:CRM systems automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry, lead assignment, and email follow-ups, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value activities. This improves overall efficiency and productivity.
- Workflow Management:CRM software provides tools for managing workflows and processes, ensuring that tasks are completed in a timely and efficient manner. This eliminates bottlenecks and improves the overall flow of information within the organization.
- Improved Collaboration:CRM systems facilitate collaboration among teams by providing a centralized platform for sharing information, tracking progress, and managing tasks. This improves communication and coordination, leading to greater efficiency and productivity.