Endpoint Security Tools Report: A Comprehensive Guide
Endpoint security tools report is a must-read for anyone concerned about safeguarding their digital assets. In today’s interconnected world, endpoint devices are the front line of defense against cyberattacks. From laptops and smartphones to servers and IoT devices, these endpoints are constantly under threat from malware, ransomware, and other sophisticated attacks.
This report delves into the ever-evolving landscape of endpoint security tools, exploring their features, benefits, and deployment strategies. We’ll discuss the key trends shaping the market, the leading players, and the critical factors to consider when choosing the right tools for your organization.
Key Features of Endpoint Security Tools
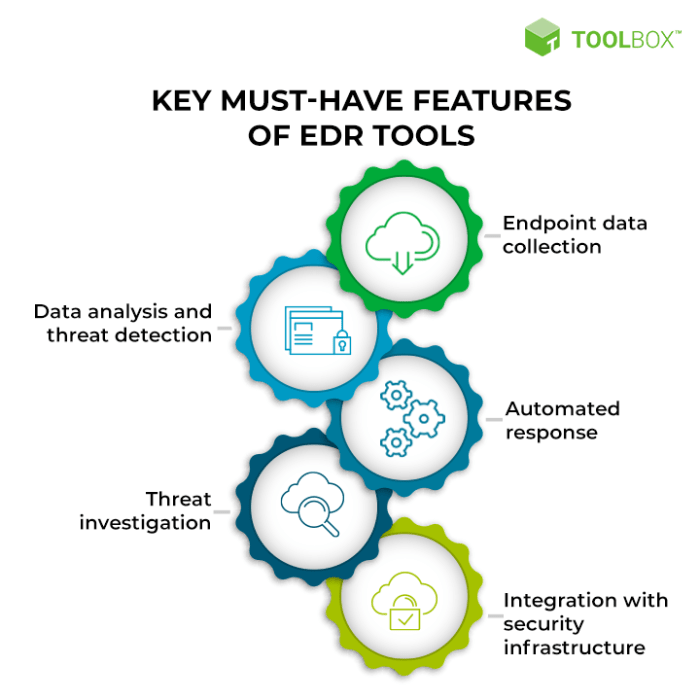
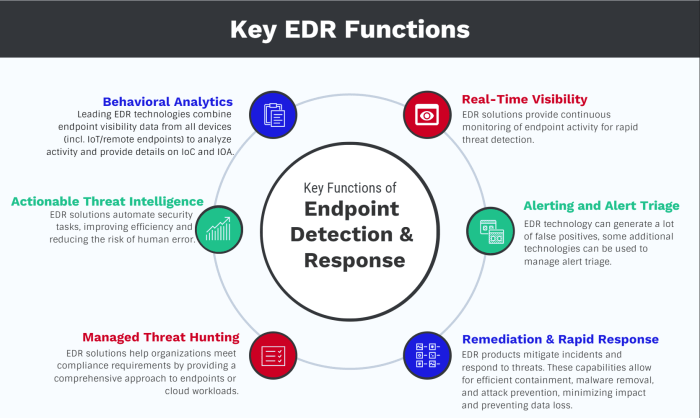
Endpoint security tools are essential for safeguarding modern businesses against the ever-evolving threat landscape. These tools offer a comprehensive approach to protecting devices, data, and users from various cyberattacks.
After spending all day poring over the latest endpoint security tools report, I was craving something indulgent. I’m talking about a dish that screams “reward” – like lobster baked macaroni cheese. It’s the perfect way to unwind after navigating the complexities of endpoint security, which, let’s face it, can be a real mind-bender sometimes.
Now, back to the report – I need to figure out how to best implement these new security measures.
Real-Time Threat Detection and Response
Real-time threat detection and response are crucial components of modern endpoint security tools. These features enable rapid identification and mitigation of threats, minimizing the impact on business operations.
The latest endpoint security tools report highlights the growing importance of robust protection against cyber threats. While the report focuses on traditional security measures, it’s interesting to see how Apple’s Craig Federighi views the future of computing, taking a swipe at AI-powered PCs in a recent interview, saying, “I guessed we missed the boat” apple exec craig federighi takes swipe at ai pcs i guessed we missed the boat.
This highlights the ongoing debate about the role of AI in security, and whether it can truly replace traditional methods. Ultimately, the report emphasizes the need for a comprehensive approach to endpoint security, incorporating both traditional and emerging technologies.
- Continuous Monitoring:Endpoint security tools continuously monitor device activity for suspicious behavior, such as unusual file access patterns, network connections, or software installations.
- Threat Intelligence Integration:By leveraging threat intelligence feeds, these tools can identify and prioritize known threats, enabling faster response times.
- Automated Response:Advanced endpoint security solutions can automatically take action to contain threats, such as quarantining infected files, blocking malicious websites, or isolating compromised devices.
Endpoint Security Protection Against Malware, Ransomware, and Other Threats
Endpoint security tools play a critical role in protecting against a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, and data breaches.
I’m deep in the trenches of my endpoint security tools report, trying to make sense of all the data. It’s a bit like trying to figure out how to sew a lace panel onto a denim shirt, which, by the way, I’m totally doing right now! I found a great tutorial for a diy denim lace shirt that I’m following, and it’s actually pretty similar to how I’m approaching this report.
You need a good plan, the right tools, and a bit of creativity. Once I’m done with this report, I’m definitely going to try out that lace shirt project.
- Malware Detection and Prevention:These tools use various techniques, such as signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and machine learning, to identify and prevent malware from infiltrating devices.
- Ransomware Protection:Advanced endpoint security solutions offer specific ransomware protection features, such as file encryption monitoring, suspicious process blocking, and rollback capabilities to restore data from backups.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):Endpoint security tools can help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, blocking unauthorized data transfers and enforcing data access policies.
Integration with Other Security Solutions
Modern endpoint security tools are designed to integrate seamlessly with other security solutions, creating a holistic security posture.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):Integration with SIEM systems enables centralized logging and analysis of security events, providing comprehensive visibility across the organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Cloud Security Platforms:Endpoint security tools can integrate with cloud security platforms to extend protection to devices accessing cloud services and applications.
- Network Security Solutions:Integration with network security solutions allows for coordinated threat detection and response, enabling a more comprehensive approach to security.
Benefits of Implementing Endpoint Security Tools

In today’s digital landscape, organizations face an ever-growing threat from cyberattacks. Endpoint security tools are crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring business continuity. By implementing robust endpoint security solutions, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, mitigate risks, and improve their overall security posture.
Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
Endpoint security tools play a vital role in reducing the risk of data breaches. They provide a multi-layered approach to protect sensitive data by preventing unauthorized access, malware infections, and data exfiltration.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):DLP solutions monitor and control data transfers, preventing sensitive information from leaving the organization’s network without authorization. This is particularly crucial for organizations dealing with confidential customer data, financial records, or intellectual property.
- Anti-Malware and Anti-Virus Protection:Endpoint security tools include advanced anti-malware and anti-virus engines that detect and remove known and unknown threats. They constantly update their threat signatures to stay ahead of evolving malware and protect against zero-day attacks.
- Firewall Protection:Endpoint firewalls act as a barrier between the device and the internet, blocking unauthorized connections and preventing malicious traffic from entering the network. This helps prevent malware infections and data breaches.
Improved Incident Response Times
Endpoint security tools can significantly improve incident response times by providing real-time visibility into security events and automating key tasks. This allows security teams to quickly identify and address threats before they can cause significant damage.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting:Endpoint security solutions provide continuous monitoring of devices for suspicious activities and security events. They generate alerts in real-time, allowing security teams to respond quickly to potential threats.
- Automated Incident Response:Some endpoint security tools offer automated incident response capabilities, enabling the system to automatically quarantine infected devices, block malicious connections, and initiate remediation actions. This reduces the time it takes to contain threats and minimizes potential damage.
- Forensics and Investigation:Endpoint security tools can capture and store logs of system activities, providing valuable data for incident investigations. This information helps security teams understand the nature of the attack, identify the source, and take appropriate actions to prevent future incidents.
Cost-Effectiveness, Endpoint security tools report
While implementing endpoint security tools involves an initial investment, they are ultimately cost-effective in the long run. They help organizations avoid the significant financial losses associated with data breaches, downtime, and reputational damage.
“The cost of a data breach can be staggering, with the average cost reaching millions of dollars. Endpoint security tools can help organizations avoid these costs by preventing breaches and minimizing the impact of incidents.”
- Reduced Downtime:By preventing malware infections and security breaches, endpoint security tools help minimize downtime and ensure business continuity. This translates into significant cost savings by avoiding lost productivity and revenue.
- Improved Compliance:Many industries have strict regulations regarding data security and privacy. Endpoint security tools help organizations comply with these regulations by providing the necessary security controls and reporting capabilities. This reduces the risk of fines and legal penalties.
- Reduced Insurance Premiums:Organizations with strong endpoint security measures in place may qualify for lower insurance premiums, as they are considered less risky. This can result in significant cost savings over time.
Choosing the Right Endpoint Security Tools: Endpoint Security Tools Report
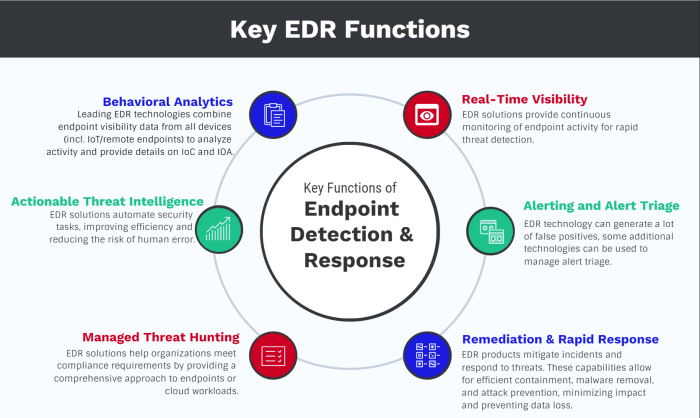
The process of selecting the ideal endpoint security tools for your organization is critical for ensuring robust protection against cyber threats. A well-chosen solution will provide comprehensive security, minimize disruptions, and align with your specific needs and budget.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Endpoint Security Tools
When choosing endpoint security tools, several crucial factors must be considered to ensure a successful implementation.
- Type of Threats:Analyze the specific threats your organization faces, such as malware, phishing, ransomware, or data breaches. Choose tools that effectively address these threats.
- Operating Systems and Devices:Ensure compatibility with the operating systems and devices used within your organization. The tool should seamlessly integrate with Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android platforms.
- Deployment Model:Consider whether a cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid deployment model best suits your infrastructure and security needs. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and ease of management, while on-premises options provide greater control and customization.
- Management Console:A user-friendly and intuitive management console simplifies administration and allows for efficient monitoring and configuration. The console should provide clear insights into security events and alerts.
- Scalability:Select a solution that can scale with your organization’s growth. The tool should be able to handle increasing numbers of endpoints and data volumes without compromising performance.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Ensure compatibility with existing security systems, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and security information and event management (SIEM) platforms. This enables seamless data sharing and threat correlation.
- Reporting and Analytics:The solution should provide comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities to track security events, identify trends, and generate insights for improving security posture.
- Cost and Licensing:Consider the cost of the solution, including licensing fees, maintenance, and support. Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) and compare it with the value it provides.
Comparing Different Endpoint Security Tools
The market offers a diverse range of endpoint security tools, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Features:Compare the features offered by different tools, including antivirus and anti-malware protection, endpoint detection and response (EDR), data loss prevention (DLP), and vulnerability management.
- Pricing:Analyze the pricing models, such as subscription-based, per-device, or per-user pricing. Consider the cost of the solution in relation to its features and value proposition.
- Compatibility:Ensure compatibility with your organization’s existing infrastructure, operating systems, and devices. Check for support for various operating systems and device types.
Aligning Endpoint Security Tools with Organizational Needs
It is crucial to align endpoint security tools with the specific needs and requirements of your organization.
- Industry Regulations:Consider compliance with industry regulations, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR, which may dictate specific security requirements.
- Security Posture:Evaluate your current security posture and identify areas for improvement. The chosen solution should address vulnerabilities and enhance overall security.
- User Experience:Ensure that the solution is user-friendly and does not hinder productivity. Minimal user intervention and easy integration with existing workflows are crucial.
- Support and Training:Consider the availability of technical support and training resources to ensure effective implementation and ongoing management of the solution.
Comparison Table of Endpoint Security Tools
| Feature | Tool 1 | Tool 2 | Tool 3 ||—|—|—|—|| Antivirus and Anti-malware Protection | Excellent | Good | Fair || Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Advanced | Basic | None || Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Comprehensive | Limited | None || Vulnerability Management | Integrated | Separate Tool | None || Cloud-Based Deployment | Yes | Yes | No || On-premises Deployment | Yes | Yes | Yes || Hybrid Deployment | Yes | Yes | No || Management Console | User-friendly | Basic | Clunky || Reporting and Analytics | Advanced | Basic | Limited || Pricing | Subscription-based | Per-device | Per-user || Compatibility | Windows, macOS, Linux | Windows, macOS | Windows only || Support | Excellent | Good | Fair || Training | Comprehensive | Basic | None |







