Global Cyber Attacks Double: QBEs Role in Defense
Global cyber attacks double qbe – Global cyber attacks double: QBE’s role in defense sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The world is increasingly reliant on technology, making us more vulnerable than ever to cyber threats.
In recent years, cyber attacks have become more frequent and sophisticated, with attackers targeting individuals, businesses, and even governments. The impact of these attacks can be devastating, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even national security breaches.
This alarming trend has prompted a search for new and innovative ways to combat cyber threats, and one promising solution is Query by Example (QBE).
QBE is a powerful tool that can be used to identify and analyze malicious patterns in data. It allows security analysts to create examples of known threats and then use these examples to search for similar patterns in real-time data streams.
This approach can help to detect threats that might otherwise go unnoticed, giving organizations a much-needed edge in the fight against cybercrime.
The Rise of Global Cyber Attacks: Global Cyber Attacks Double Qbe
The digital landscape is facing a growing threat: cyberattacks. In recent years, these attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and frequent, posing a significant risk to individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. This alarming trend has sparked global concern, as the potential consequences of successful cyberattacks can be devastating.
The Frequency and Impact of Cyber Attacks
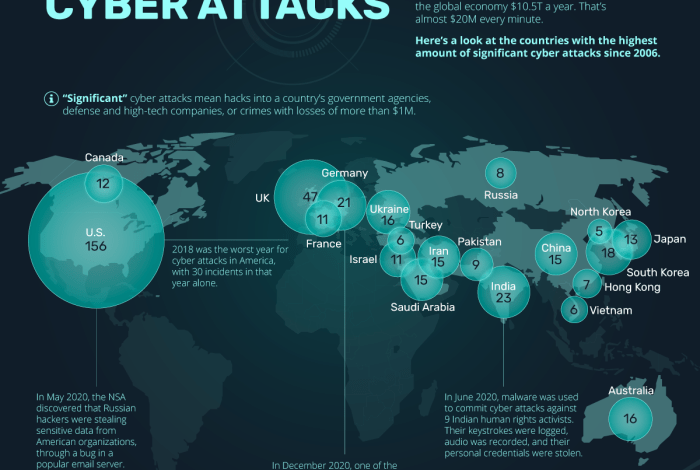
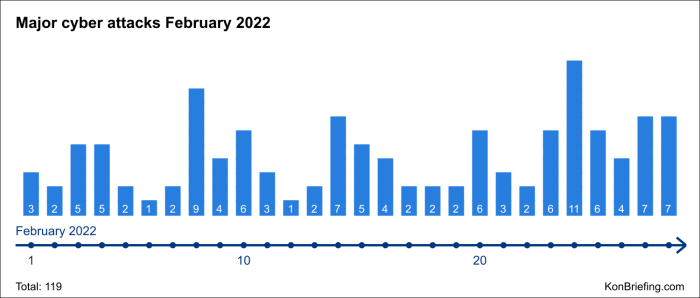
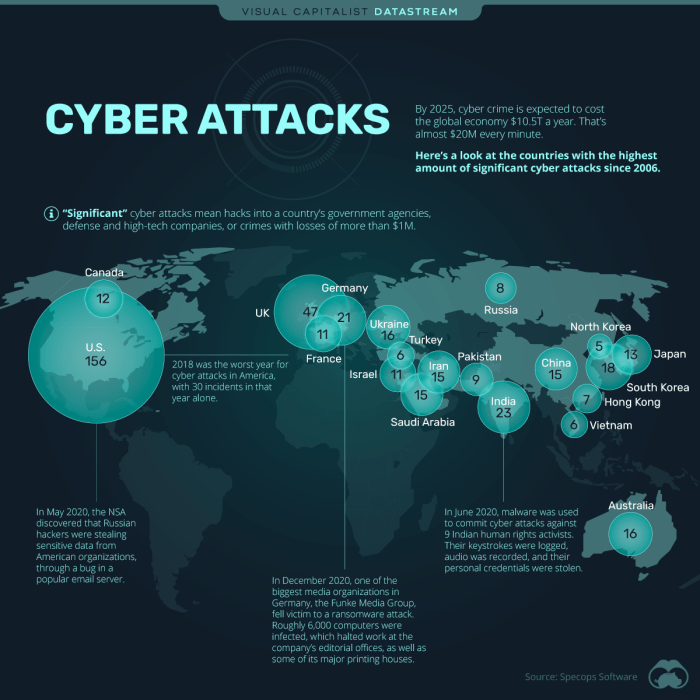
The frequency of cyberattacks has been steadily increasing. According to a recent report by [insert reputable source], the number of global cyberattacks doubled in [year] compared to [previous year]. This surge in attacks has had a profound impact on various sectors, resulting in significant financial losses, data breaches, and operational disruptions.
- Financial Loss:Cyberattacks can lead to substantial financial losses for individuals and organizations. These losses can arise from stolen funds, ransom demands, data recovery costs, and business disruptions. For instance, the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017 caused billions of dollars in damage to businesses worldwide.
- Data Breaches:Cyberattacks often involve the theft of sensitive data, including personal information, financial records, and intellectual property. These breaches can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations, leading to identity theft, fraud, and reputational damage. The Equifax data breach in 2017 compromised the personal information of millions of individuals, highlighting the potential impact of data breaches.
The news about global cyber attacks doubling QBE is definitely concerning, especially considering the growing reliance on digital infrastructure. It’s a reminder that even seemingly simple tasks, like how to hardwire a light fixture , can have cybersecurity implications.
Whether it’s securing your home network or understanding the risks associated with connected devices, staying informed about cybersecurity is crucial in today’s interconnected world.
- Operational Disruptions:Cyberattacks can disrupt critical operations, leading to service outages, system downtime, and production delays. This can have a significant impact on businesses, governments, and critical infrastructure, causing financial losses and impacting public safety.
Motives Behind Cyber Attacks
Cyberattacks are driven by a variety of motives, including financial gain, espionage, and disruption. Understanding these motives is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies.
- Financial Gain:Many cyberattacks are motivated by financial gain. Hackers often target financial institutions, businesses, and individuals to steal money, credit card information, and other valuable assets. For example, the recent rise of ransomware attacks, where hackers encrypt data and demand payment for its decryption, highlights the financial motivation behind these attacks.
- Espionage:Cyberattacks can be used for espionage, where hackers aim to steal sensitive information, such as trade secrets, military intelligence, and government data. Nation-state actors are often involved in these attacks, seeking to gain a strategic advantage over their adversaries. For example, the SolarWinds hack in 2020, which targeted government agencies and businesses, is believed to have been conducted by Russian intelligence.
- Disruption:Some cyberattacks are motivated by disruption, aiming to cause chaos and damage to critical infrastructure or systems. These attacks can target power grids, transportation networks, and communication systems, potentially impacting public safety and economic stability. The Stuxnet worm, which targeted Iranian nuclear facilities in 2010, is a notable example of a cyberattack aimed at disruption.
The Role of QBE in Cyber Security
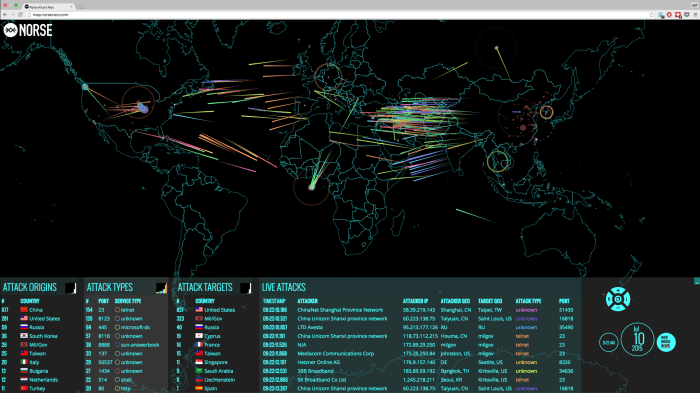
Query by Example (QBE) is a powerful technique that has gained significant traction in the realm of cyber security. It offers a unique approach to threat detection and analysis, enabling security professionals to identify and understand malicious patterns within vast datasets.
This section delves into the fundamental principles of QBE and explores its application in safeguarding against cyber threats.
QBE: A Paradigm Shift in Cyber Security, Global cyber attacks double qbe
QBE empowers analysts to identify malicious patterns by providing examples of known threats. The system then uses these examples to automatically generate queries that can be used to search for similar patterns in the data. This approach contrasts with traditional methods that rely on predefined rules or signatures, which can be easily bypassed by sophisticated attackers.
The Mechanics of QBE in Threat Detection
QBE operates by leveraging the power of machine learning algorithms. The core principle is to train a model on a set of known malicious activities, allowing it to learn the characteristics of these threats. Once trained, the model can be used to identify new instances of similar attacks by comparing them to the learned patterns.
This process involves several key steps:
- Data Collection:Gathering data from various sources, such as network logs, security alerts, and user activity records.
- Example Selection:Identifying and labeling examples of known malicious activities. This could involve analyzing past attacks, known malware signatures, or common attack vectors.
- Model Training:Using machine learning algorithms to train a model on the selected examples. The model learns the patterns and characteristics associated with malicious activities.
- Query Generation:Based on the trained model, QBE generates queries that can be used to search for similar patterns in the data.
- Threat Detection:The queries are executed against the collected data, identifying potential threats that match the learned patterns.
QBE vs. Traditional Threat Detection Methods
QBE offers several advantages over traditional methods, including:
- Adaptability:QBE can adapt to evolving threats by continuously learning from new examples. This allows it to stay ahead of attackers who constantly modify their tactics.
- Efficiency:QBE automates the process of threat detection, reducing the manual effort required by security analysts. This allows them to focus on more complex tasks and respond to threats more effectively.
- Accuracy:By learning from real-world examples, QBE can achieve higher accuracy in identifying threats compared to rule-based systems that rely on predefined signatures.
“QBE offers a powerful approach to cyber security, enabling organizations to identify and respond to evolving threats more effectively.”
Impact of Cyber Attacks on Businesses and Individuals
Cyber attacks are a growing threat to businesses and individuals alike. They can disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, and damage reputations. The consequences of cyber attacks can be severe, leading to financial losses, legal liabilities, and even reputational damage.
Industries Most Vulnerable to Cyber Attacks
The impact of cyber attacks can vary significantly depending on the industry. Some industries are more vulnerable than others due to the nature of their operations, the sensitivity of their data, and the criticality of their infrastructure.
- Financial institutionsare highly vulnerable to cyber attacks due to the large amounts of sensitive financial data they hold. Cybercriminals often target banks, credit card companies, and other financial institutions to steal money, credit card information, and other valuable data.
- Healthcare organizationsare also vulnerable to cyber attacks, as they store a large amount of sensitive patient data. Hackers can use this data for identity theft, medical fraud, and other malicious purposes. In addition, the criticality of healthcare systems makes them a tempting target for ransomware attacks.
- Energy and utilities companiesare critical infrastructure providers, making them prime targets for cyber attacks. These attacks can disrupt power grids, water treatment plants, and other essential services, causing widespread damage and disruption.
- Government agenciesare increasingly targeted by cyber attacks, both from foreign governments and criminal organizations. These attacks can steal classified information, disrupt government operations, and even influence elections.
- Retailersare vulnerable to cyber attacks due to the large amount of customer data they collect. Hackers can use this data to steal credit card information, personal details, and other sensitive information. Additionally, retailers can be targeted by ransomware attacks, which can disrupt their operations and cause significant financial losses.
The news of global cyber attacks doubling QBE’s losses is definitely concerning, but it’s also a reminder that technology is constantly evolving. It’s interesting to see that Apple is still working on AR smart glasses, and two recent patents show some impressive innovations better thermal ergonomics and eyewear stabilization.
Perhaps this type of technology could help us better defend against future cyber threats, or even help us navigate the complex world of data security in a more intuitive way. It’s definitely something to keep an eye on as the tech landscape continues to shift.
Financial and Reputational Damage Caused by Cyber Attacks
Cyber attacks can cause significant financial and reputational damage to businesses and individuals.
- Financial lossescan include the cost of recovering from an attack, lost revenue, and legal expenses. For example, the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017 caused billions of dollars in damage to businesses worldwide.
- Reputational damagecan result from the loss of customer trust, damage to brand image, and negative media coverage. For example, the Equifax data breach in 2017 affected over 147 million people and resulted in significant reputational damage for the company.
Examples of High-Profile Cyber Attacks and Their Consequences
- The WannaCry ransomware attackin 2017 infected over 200,000 computers in 150 countries, disrupting businesses and government agencies worldwide. The attack caused billions of dollars in damage and highlighted the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to cyber attacks.
- The Equifax data breachin 2017 exposed the personal information of over 147 million people, including Social Security numbers, birth dates, and addresses. The breach caused significant reputational damage to Equifax and led to a class-action lawsuit.
- The SolarWinds hackin 2020 involved the compromise of software from SolarWinds, a company that provides IT management software to government agencies and businesses. The attack allowed hackers to gain access to the networks of numerous organizations, including government agencies and private companies.
It’s a wild world out there, with global cyberattacks doubling QBE. It’s a reminder that we need to be vigilant about our online security, especially as platforms like SoundCloud launches on Xbox One , expanding the potential for cyber threats.
But it’s not all doom and gloom; with a little caution, we can navigate this digital landscape safely, enjoying the benefits of these exciting new developments.
Defensive Measures Against Cyber Attacks
In the face of escalating cyber threats, proactive security measures are crucial for organizations and individuals alike. Implementing a robust defense strategy is essential to mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive data. This involves a multi-layered approach that encompasses network security, endpoint protection, data encryption, and user awareness training.
Network Security
Network security forms the foundation of a comprehensive defense strategy. It involves measures to protect the network infrastructure and data flowing through it.
- Firewalls:Firewalls act as a barrier between the internal network and the external world, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. They block unauthorized access and prevent malicious software from entering the network.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS):These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and alert administrators to potential threats. IDS systems detect and report suspicious activity, while IPS systems take proactive measures to block or mitigate threats.
- Network Segmentation:Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments reduces the impact of a successful attack. This limits the attacker’s ability to move laterally within the network and access sensitive data.
Endpoint Protection
Endpoints, such as computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are vulnerable entry points for cyberattacks. Endpoint protection solutions are designed to safeguard these devices and the data they contain.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software:These programs scan devices for known malware and protect against infections. They detect and remove viruses, worms, Trojans, and other malicious software.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities. They monitor endpoint activity, detect suspicious behavior, and enable rapid incident response.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):DLP solutions prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. They monitor data transfers, identify confidential information, and block unauthorized attempts to export data.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a critical security measure that transforms data into an unreadable format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals.
- Encryption at Rest:This involves encrypting data while it is stored on hard drives, servers, or other storage devices. Encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are commonly used to secure data at rest.
- Encryption in Transit:Data is encrypted while it is being transmitted over networks, such as the internet. This protects data from eavesdropping and interception during transmission.
- Key Management:Securely managing encryption keys is essential for effective data protection. Key management systems ensure the integrity and confidentiality of encryption keys.
User Awareness and Training
Human error is often a key factor in cyberattacks. User awareness and training programs play a vital role in reducing the risk of human-related security breaches.
- Phishing Awareness:Phishing attacks use deceptive emails or websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Training programs educate users about common phishing techniques and how to identify and avoid such attacks.
- Password Security:Strong passwords are essential for protecting accounts and data. Users should be trained on creating and managing strong passwords, avoiding common password patterns, and using multi-factor authentication.
- Social Engineering Awareness:Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology to gain access to systems or information. Training programs teach users about common social engineering tactics and how to resist manipulation attempts.
The Future of Cyber Security
The landscape of cyber security is constantly evolving, driven by the rapid advancements in technology and the ever-increasing sophistication of cybercriminals. Predicting the future of cyber security requires a careful analysis of current trends and a deep understanding of the motivations and capabilities of those who seek to exploit vulnerabilities in our digital world.
Emerging Trends in Cyber Attacks
The future of cyber attacks will be characterized by an increased focus on automation, artificial intelligence, and the exploitation of emerging technologies. These trends will significantly impact the nature of cyber threats, making them more difficult to detect and defend against.
- AI-Powered Attacks:The use of AI and machine learning in cyber attacks will enable attackers to automate their activities, making them more efficient and effective. AI can be used to identify and exploit vulnerabilities, create custom malware, and launch highly targeted attacks.
For example, AI-powered phishing campaigns can personalize emails and tailor them to specific individuals, making them more convincing and increasing the likelihood of success.
- IoT and Edge Computing Attacks:The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the rise of edge computing will create new attack vectors for cybercriminals. These devices are often poorly secured, making them easy targets for attackers who can use them to launch attacks on other systems or steal sensitive data.
For instance, hackers could compromise a network of smart home devices to launch a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack against a critical infrastructure target.
- Cybercrime-as-a-Service:The emergence of cybercrime-as-a-service (CaaS) platforms will make it easier for individuals with limited technical skills to carry out sophisticated cyber attacks. These platforms provide access to malware, tools, and expertise, allowing anyone to launch attacks without having to develop their own capabilities.
This trend will democratize cybercrime, making it more accessible to a wider range of individuals and organizations.
Hypothetical Future Cyber Attack Scenario
Imagine a scenario where a highly sophisticated AI-powered ransomware attack targets a major global financial institution. The attack leverages vulnerabilities in the bank’s cloud infrastructure and uses social engineering tactics to gain access to critical systems. The attackers then encrypt sensitive data, including customer information, financial records, and trading data, demanding a large ransom for its release.
The attack disrupts the bank’s operations, causing significant financial losses and reputational damage. Furthermore, the stolen data could be used for identity theft and other malicious purposes.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning for Cyber Defense
While AI poses significant threats to cyber security, it can also be a powerful tool for defense. AI and machine learning can be used to:
- Detect and Respond to Threats:AI-powered security systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify suspicious activity and patterns that indicate potential attacks. They can also automate responses to threats, such as blocking malicious traffic or isolating infected systems.
- Predict and Prevent Attacks:AI can be used to analyze historical data and identify trends that could indicate future attacks. This information can be used to develop proactive security measures and strengthen defenses against emerging threats.
- Improve Security Awareness:AI can be used to train employees on cybersecurity best practices and to develop personalized security awareness programs. This can help to reduce the risk of human error and improve overall security posture.