On-Premise vs. Cloud Security: Which Is Right for You?
On premise vs cloud security – On-premise vs. cloud security – it’s a debate that’s been raging for years. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud computing, the question of how to best secure their data and applications has become more complex. The traditional approach of on-premise security, with its physical controls and dedicated security teams, is being challenged by the agility and scalability of cloud security solutions.
This article dives into the pros and cons of each approach, exploring the unique challenges and opportunities presented by each model.
From firewalls and intrusion detection systems to cloud access security brokers and cloud workload protection platforms, the security landscape is rapidly evolving. Understanding the differences between on-premise and cloud security is crucial for any organization looking to protect its sensitive data and systems.
Understanding the Landscape
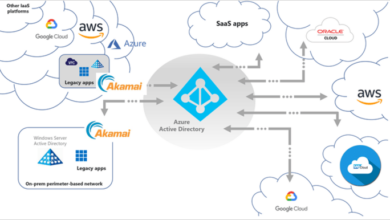
The security landscape is constantly evolving, and the rise of cloud computing has introduced a new set of challenges and opportunities for organizations. Understanding the fundamental differences between on-premise and cloud security is crucial for making informed decisions about your security strategy.On-premise security refers to the traditional approach where organizations own and manage their own physical infrastructure and security systems.
This includes hardware, software, and network devices located within their own data centers. In contrast, cloud security involves relying on third-party cloud providers to manage and secure the infrastructure and services that organizations use.
On-Premise vs. Cloud Security: A Comparative Overview
The primary difference between on-premise and cloud security lies in the responsibility and control over security measures.
- On-premise security typically involves organizations taking full responsibility for managing all aspects of security, including physical security, network security, and data security. They control the hardware, software, and configurations of their security systems.
- In cloud security, the responsibility is shared between the cloud provider and the organization. Cloud providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure and services, while organizations are responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud environment.
The Evolving Security Landscape
The adoption of cloud computing has significantly impacted the security landscape.
- Increased attack surface: Cloud adoption has expanded the attack surface, as organizations now have to secure data and applications across multiple cloud providers and platforms. This presents new challenges for security teams.
- Shifting security responsibilities: Cloud providers offer a range of security services, but organizations still need to manage their own security responsibilities, such as data encryption, access control, and vulnerability management.
- Emergence of new threats: The cloud environment has also seen the emergence of new threats, such as cloud-specific malware, account hijacking, and API vulnerabilities.
Impact of Cloud Adoption on Security
The adoption of cloud computing has both positive and negative impacts on security.
- Enhanced security capabilities: Cloud providers offer advanced security features, such as intrusion detection and prevention systems, data loss prevention, and threat intelligence, which can help organizations improve their security posture.
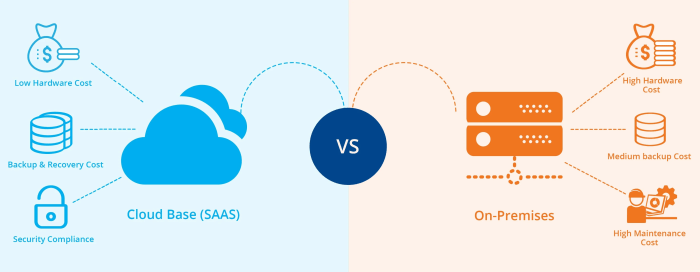
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud security services can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premise solutions, as organizations can pay for only the resources they need and avoid the upfront costs of hardware and software.
- Increased agility: Cloud security solutions are highly scalable and flexible, allowing organizations to adapt quickly to changing security threats and requirements.
On-Premise Security
On-premise security refers to the traditional approach of securing data and applications within an organization’s own physical infrastructure. This involves implementing a range of security measures directly on the organization’s servers, networks, and devices.
Traditional Security Measures
Traditional security measures in on-premise environments aim to protect data and systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These measures include:
- Firewalls:Act as a barrier between an organization’s internal network and the external world, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. They block unauthorized access and prevent malicious traffic from entering the network.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS):Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential threats. They identify patterns that may indicate an attack and provide real-time threat detection.
- Antivirus Software:Scans for and removes malware from computers and networks. It protects against viruses, worms, Trojans, and other malicious software that can compromise system security.
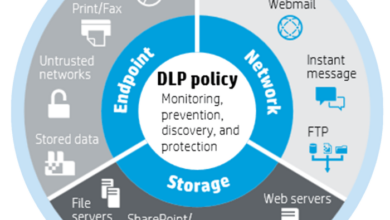
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):Prevents sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network. It monitors data transfers, identifies sensitive information, and blocks unauthorized attempts to export or share it.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs):Define specific permissions for users and devices, restricting access to certain resources based on their roles and responsibilities. They help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems.
- Physical Security:Includes measures like security guards, surveillance systems, and restricted access to data centers. It aims to prevent physical access to servers and network equipment, protecting them from theft or damage.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Control:Organizations have complete control over their security infrastructure and can customize security measures to meet their specific needs. They have full visibility into their systems and data, allowing them to manage security risks effectively.
- Physical Security:On-premise environments allow for strong physical security measures, such as secure data centers and restricted access to equipment. This helps protect against physical threats like theft or vandalism.
- Compliance:Some industries require strict compliance with regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare or PCI DSS for payment card processing. On-premise security can provide greater control over data and systems, making it easier to meet these compliance requirements.
Disadvantages
- Cost:Setting up and maintaining an on-premise security infrastructure can be expensive. This includes hardware costs, software licenses, personnel for security management, and ongoing maintenance.
- Scalability:On-premise security can be challenging to scale as an organization grows. Expanding infrastructure and adding new security measures can require significant investments and time.
- Expertise:Managing on-premise security requires specialized expertise and resources. Organizations need skilled security professionals to implement, monitor, and maintain security measures.
Common On-Premise Security Solutions
| Solution | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firewalls | Act as a barrier between an organization’s internal network and the external world, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. | Prevent unauthorized access, block malicious traffic, and provide network segmentation. | Can be complex to configure and manage, may require specialized expertise. |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators to potential threats. | Identify patterns that may indicate an attack, provide real-time threat detection, and improve security posture. | May generate false positives, require regular tuning and maintenance. |
| Antivirus Software | Scans for and removes malware from computers and networks. | Protect against viruses, worms, Trojans, and other malicious software, enhance system security. | May miss new threats, require regular updates, and can impact system performance. |
Cloud Security: On Premise Vs Cloud Security
The cloud has revolutionized how businesses operate, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, this shift brings unique security challenges that require a different approach to safeguarding data and applications. Cloud security encompasses the measures taken to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud environments.
It involves a range of security controls and practices, including access management, encryption, threat detection, and incident response.
Cloud Security Challenges
Cloud computing presents a distinct set of security challenges that require a different approach compared to on-premise security.
- Shared Responsibility Model:Cloud providers typically share security responsibility with their customers, making it crucial to understand who is accountable for what. This shared responsibility model can lead to confusion and potential security gaps if not clearly defined and implemented.
- Data Security and Privacy:Data stored in the cloud can be vulnerable to breaches, especially if proper encryption and access controls are not in place. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, becomes a significant concern.
- Network Security:Cloud environments are interconnected networks, making them susceptible to attacks targeting network vulnerabilities. Securing the cloud network is essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Cloud Service Misconfigurations:Improperly configured cloud services can create security loopholes, making it easier for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities. This includes misconfigured firewalls, access control lists, and other security settings.
- Cloud-Native Threats:Cloud environments are subject to new threats, such as serverless attacks, container vulnerabilities, and API security breaches. These require specialized security solutions and expertise.
Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model is a fundamental concept in cloud security, where both the cloud provider and the customer share responsibility for security.
The cloud provider is responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure, such as the physical data centers, network, and operating systems. The customer is responsible for securing their applications, data, and user accounts.
Understanding the shared responsibility model is critical for implementing effective cloud security measures. Customers need to clearly define their security responsibilities and work with the cloud provider to ensure appropriate security controls are in place.
Best Practices for Securing Cloud Environments, On premise vs cloud security
Securing cloud environments requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various best practices:
- Data Encryption:Encrypting data at rest and in transit is essential to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. This includes encrypting data stored in databases, storage services, and during data transfers.
- Access Control:Implement robust access control mechanisms to restrict access to cloud resources based on user roles and permissions. This ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and applications.
- Vulnerability Management:Regularly scan cloud environments for vulnerabilities and patch them promptly to prevent exploitation by attackers. This includes identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in cloud services, applications, and infrastructure.
- Security Monitoring and Logging:Continuously monitor cloud environments for suspicious activities and security events. Implement security information and event management (SIEM) systems to collect, analyze, and correlate security logs to detect threats.
- Incident Response:Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to address security breaches and data leaks. This includes steps for containment, investigation, remediation, and recovery.
Common Cloud Security Services
Several cloud security services can help organizations enhance their cloud security posture.
| Service | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) | CASBs act as a security gateway between users and cloud applications, providing visibility and control over cloud traffic. They enforce security policies, detect threats, and prevent data leaks. | Improved cloud security posture, data loss prevention, and compliance with regulations. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | SIEM solutions collect, analyze, and correlate security logs from various sources, providing real-time threat detection and incident response capabilities. | Enhanced threat detection, improved incident response, and centralized security monitoring. |
| Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs) | CWPPs provide comprehensive security for cloud workloads, including container security, serverless security, and microservices security. | Improved workload security, enhanced threat detection, and reduced attack surface. |
Comparing Security Models
Choosing between on-premise and cloud security is a crucial decision for any organization. Each approach has its own set of strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on factors like your specific security requirements, budget, and technical expertise.
Security Strengths and Weaknesses
It’s important to understand the security strengths and weaknesses of both on-premise and cloud environments to make an informed decision.
- On-Premise Security:
- Strengths:
- Greater control over your data and infrastructure. You have complete ownership and visibility into your systems and can customize security measures to meet your specific needs.
- Improved physical security. On-premise data centers can be secured with physical barriers like fences, security guards, and surveillance systems, offering a higher level of physical protection.
- Reduced latency for applications and data access. On-premise environments are typically located closer to users, minimizing latency and improving application performance.
- Weaknesses:
- Higher upfront costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure maintenance.
- More complex to manage and maintain. On-premise security requires dedicated IT staff and expertise to manage security updates, patches, and incident response.
- Increased risk of security breaches due to human error or internal threats.
- Cloud Security:
- Strengths:
- Scalability and flexibility. Cloud services can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing needs, reducing the need for significant upfront investments.
- Improved security posture through shared responsibility. Cloud providers invest heavily in security and offer a range of security features and services, including data encryption, access control, and threat monitoring.
- Reduced operational costs. Cloud services eliminate the need for expensive hardware and software licenses, and cloud providers handle infrastructure maintenance and security updates.
- Weaknesses:
- Potential for data breaches due to cloud provider vulnerabilities or misconfigurations.
- Limited control over data and infrastructure. You rely on the cloud provider’s security measures and policies, and may have limited access to underlying infrastructure.
- Data sovereignty and compliance concerns. Data stored in the cloud may be subject to different legal and regulatory requirements, depending on the cloud provider’s location and data storage practices.
Key Security Considerations
When choosing between on-premise and cloud deployments, it’s important to consider the following security factors:
- Data Sensitivity:If you handle highly sensitive data, such as financial information or personal health records, you may need to consider the security controls and compliance requirements of both on-premise and cloud environments to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Compliance Requirements:Different industries and regulations have specific compliance requirements, such as HIPAA for healthcare or PCI DSS for payment card processing. Ensure that the chosen security model meets the required compliance standards.
- Budget and Resources:On-premise deployments typically require higher upfront costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure maintenance, while cloud services offer a pay-as-you-go model with potentially lower operational costs. Consider your budget and available resources when making your decision.
- Technical Expertise:On-premise security requires dedicated IT staff and expertise to manage security updates, patches, and incident response. Cloud services offer managed security services that can reduce the need for in-house expertise.
- Security Features and Services:Both on-premise and cloud environments offer various security features and services. Evaluate the security controls and capabilities of each option to ensure they meet your specific security requirements.
Security Model Comparison
The following table highlights key differences in security controls, compliance requirements, and risk management strategies between on-premise and cloud environments: